一、Bean的Scope
Scope描述的是Spring容器如何新建Bean实例的。Spring的Scope有以下几种,通过@Scope注解来实现。
(1)Singleton:一个Spring容器中只有一个Bean的实例,此为Spring的默认配置,全容器共享一个实例。
(2)Prototype:每次调用新建一个Bean实例。
(3)Request:Web项目中,给每一个 http request 新建一个Bean实例。
(4)Session:Web项目中,给每一个 http session 新建一个Bean实例。
(5)GlobalSession:这个只在portal应用中有用,给每一个 global http session 新建一个Bean实例。
另外,在Spring Batch中还有一个Scope是使用@StepScope,我们将在批处理介绍这个Scope。
接下来简单演示默认的 Singleton 和 Prototype,分别从Spring容器中获取两次Bean,判断Bean的实例是否相等。
1.编写Singleton的Bean。
package com.ecworking.scope; import org.springframework.stereotype.Service; @Service //默认为Singleton,相当于@Scope("singleton")。 public class DemoSingletonService { }
2.编写Prototype的Bean。
package com.ecworking.scope; import org.springframework.context.annotation.Scope; import org.springframework.stereotype.Service; @Service @Scope("prototype") //声明Scopew为Prototype。 public class DemoPrototypeService { }
3.配置类。
package com.ecworking.scope; import org.springframework.context.annotation.ComponentScan; import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration; @Configuration @ComponentScan("com.ecworking.scope") public class ScopeConfig { }
4.运行。
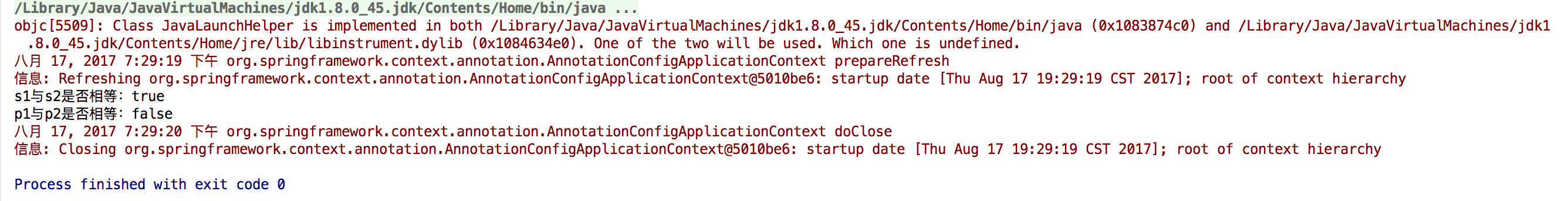
package com.ecworking.scope; import org.springframework.context.annotation.AnnotationConfigApplicationContext; public class Main { public static void main(String[] args) { AnnotationConfigApplicationContext context = new AnnotationConfigApplicationContext(ScopeConfig.class); DemoSingletonService s1 = context.getBean(DemoSingletonService.class); DemoSingletonService s2 = context.getBean(DemoSingletonService.class); DemoPrototypeService p1 = context.getBean(DemoPrototypeService.class); DemoPrototypeService p2 = context.getBean(DemoPrototypeService.class); System.out.println("s1与s2是否相等:" + s1.equals(s2)); System.out.println("p1与p2是否相等:" + p1.equals(p2)); context.close(); } }
运行结果:
二、Spring EL和资源调用
Spring EL-Spring表达式语言,支持在xml和注解中使用表达式,类似于JSP的EL表达式语言。
Spring 开发中经常涉及调用各种资源的情况,包含普通文件、网址、配置文件、系统环境变量等,我们可以使用Spring表达式语言实现资源的注入。
Spring 主要在注解@Value的参数中使用表达式。
本节演示实现以下几种情况:
(1)注入普通字符;
(2)注入操作系统属性;
(3)注入表达式运算结果;
(4)注入其他Bean的属性;
(5)注入文件内容;
(6)注入网址内容;
(7)注入属性文件;
1. 准备,增加commons-io可简化文件相关操作。
本例中使用commons-io将file转换成字符串:
<dependency>
<groupId>commons-io</groupId>
<artifactId>commons-io</artifactId>
<version>2.3</version>
</dependency>
在com.ecworking.el.source包下新建test.txt,内容随意。
在com.ecworking.el.source包下新建test.propertise,内容如下:
book.author = dongyp
book.name = spring boot
2. 需要被注入的Bean。
package com.ecworking.el; import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Value; import org.springframework.stereotype.Service; @Service public class DemoService { @Value("其他类的属性") //此处为注入普通字符串 private String another; public String getAnother() { return another; } public void setAnother(String another) { this.another = another; } }
3. 演示类Bean。
package com.ecworking.el; import org.apache.commons.io.IOUtils; import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired; import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Value; import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean; import org.springframework.context.annotation.PropertySource; import org.springframework.context.support.PropertySourcesPlaceholderConfigurer; import org.springframework.core.env.Environment; import org.springframework.core.io.Resource; import org.springframework.stereotype.Service; import java.io.IOException; @Service @PropertySource("classpath:test.properties") //注入配置文件需使用@PropertySource指定文件地址,若使用@Value注入,则要配置一个PropertySourcesPlaceholderConfigurer的Bean。注意@Value("${book.name}"),使用的是$而不是#。 //注入 Properties 还可以从 Environment 中获得。 public class DemoElService { @Value("I LOVE YOU!") //注入普通字符串 private String normal; @Value("#{systemProperties['os.name']}") //注入操作系统属性 private String osName; @Value("#{T(java.lang.Math).random() * 100.0}") //注入表达式结果 private String randomNumber; @Value("#{demoService.another}") //注入其他Bean属性 private String fromAnother; @Value("classpath:/test.txt") //注入文件资源 private Resource testFile; @Value("http://www.baidu.com") //注入网址资源 private Resource testUrl; @Value("${book.name}") // 注入配置文件 private String bookName; @Autowired // 注入配置文件 private Environment environment; @Bean // 注入配置文件 public static PropertySourcesPlaceholderConfigurer propertyConfigurer(){ return new PropertySourcesPlaceholderConfigurer(); } public void outputResource(){ try { System.out.println(normal); System.out.println(osName); System.out.println(randomNumber); System.out.println(fromAnother); System.out.println(IOUtils.toString(testFile.getInputStream())); System.out.println(IOUtils.toString(testUrl.getInputStream())); System.out.println(bookName); System.out.println(environment.getProperty("book.author")); } catch (IOException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } }
4.配置类。
package com.ecworking.el; import org.springframework.context.annotation.ComponentScan; import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration; @Configuration @ComponentScan("com.ecworking.el") public class ElConfig { }
5.运行。
package com.ecworking.el; import org.springframework.context.annotation.AnnotationConfigApplicationContext; public class Main { public static void main(String[] args) { AnnotationConfigApplicationContext context = new AnnotationConfigApplicationContext(ElConfig.class); DemoElService demoElService = context.getBean(DemoElService.class); demoElService.outputResource(); context.close(); } }
运行结果:
