1.读取
1 def read_dataset():
2 file_path = r'SHSSpamCollection'
3 sms = open(file_path,encoding='utf-8')
4 sms_data = []
5 sms_label = []
6 csv_reader = csv.reader(sms,delimiter=' ')
7 for line in csv_reader:
8 sms_label.append(line[0])
9 sms_data.append(preprocessing(line[1]))
10 sms.close()
11 return sms_data,sms_label
2.数据预处理
1 def preprocess(text):
2 tokens = [word for sent in nltk.sent_tokenize(text) for word in nltk.word_tokenize(sent)] # 分词
3 stops = stopwords.words('english') # 使用英文的停用词表
4 tokens = [token for token in tokens if token not in stops] # 去除停用词
5 tokens = [token.lower() for token in tokens if len(token) >= 3] # 大小写,短词
6 wnl = WordNetLemmatizer()
7 tag = nltk.pos_tag(tokens) # 词性
8 tokens = [wnl.lemmatize(token, pos=get_wordnet_pos(tag[i][1])) for i, token in enumerate(tokens)] # 词性还原
9 preprocessed_text = ' '.join(tokens)
10 return preprocessed_text
3.数据划分—训练集和测试集数据划分
from sklearn.model_selection import train_test_split
x_train,x_test, y_train, y_test = train_test_split(data, target, test_size=0.2, random_state=0, stratify=y_train)
1 def split_dataset(data, label):
2 x_train, x_test, y_train, y_test = train_test_split(data, label, test_size=0.2, random_state=0, stratify=label)
3 return x_train, x_test, y_train, y_tes
4.文本特征提取
sklearn.feature_extraction.text.CountVectorizer
sklearn.feature_extraction.text.TfidfVectorizer
from sklearn.feature_extraction.text import TfidfVectorizer
tfidf2 = TfidfVectorizer()
观察邮件与向量的关系
向量还原为邮件
1 # 文本转化为tf-idf的特征矩阵
2 def tfidf_dataset(x_train, x_test):
3 tfidf = TfidfVectorizer()
4 X_train = tfidf.fit_transform(x_train)
5 X_test = tfidf.transform(x_test)
6 return X_train, X_test, tfidf
7
8 # 向量还原成邮件
9 def revert_mail(x_train, X_train, model):
10 s = X_train.toarray()[0]
11 print("第一封邮件向量表示为:", s)
12 a = np.flatnonzero(X_train.toarray()[0]) # 非零元素的位置(index)
13 print("非零元素的位置:", a)
14 print("向量的非零元素的值:", s[a])
15 b = model.vocabulary_ # 词汇表
16 key_list = []
17 for key, value in b.items():
18 if value in a:
19 key_list.append(key) # key非0元素对应的单词
20 print("向量非零元素对应单词:", key_list)
21 print("向量化之前的邮件:", x_train[0])
4.模型选择
from sklearn.naive_bayes import GaussianNB
from sklearn.naive_bayes import MultinomialNB
说明为什么选择这个模型?
源码如下:
1 def mnb_model(x_train, x_test, y_train, y_test):
2 mnb = MultinomialNB()
3 mnb.fit(x_train, y_train)
4 predict = mnb.predict(x_test)
5 print("总数:", len(y_test))
6 print("预测正确数:", (predict == y_test).sum())
7 print("预测准确率:",sum(predict == y_test) / len(y_test))
8 return predict
因为它并不符合正态分布的特征,因此要选择多项式分布类型。
5.模型评价:混淆矩阵,分类报告
from sklearn.metrics import confusion_matrix
confusion_matrix = confusion_matrix(y_test, y_predict)
说明混淆矩阵的含义
from sklearn.metrics import classification_report
说明准确率、精确率、召回率、F值分别代表的意义
1 def class_report(ypre_mnb, y_test):
2 conf_matrix = confusion_matrix(y_test, ypre_mnb)
3 print("=======================================")
4 print("混淆矩阵:
", conf_matrix)
5 c = classification_report(y_test, ypre_mnb)
6 print("=======================================")
7 print("分类报告:
", c)
8 print("模型准确率:", (conf_matrix[0][0] + conf_matrix[1][1]) / np.sum(conf_matrix))
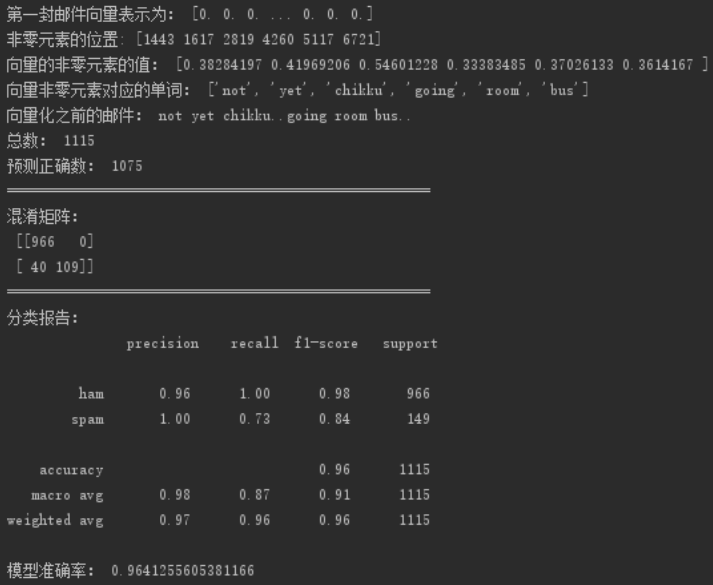
混淆矩阵 confusion-matrix:
TP(True Positive):真实为0,预测为0
TN(True Negative):真实为1,预测为1
FP(False Positive):真实为1,预测为0
FN(False Negative):真实为0,预测为1
分类确率:所有样本中被预测正确的样本的比率。
精确率:在被所有预测为正的样本中实际为正样本的概率。
召回率 :指在实际为正的样本中被预测为正样本的概率。
F1值:准确率和召回率的加权调和平均。
6.比较与总结
如果用CountVectorizer进行文本特征生成,与TfidfVectorizer相比,效果如何?
答:CountVectorizer只考虑每种词汇在该训练文本中出现的频率,而TfidfVectorizer除了考量某一词汇在当前训练文本中出现的频率之外,同时关注包含这个词汇的其它训练文本数目的倒数。相比之下,训练文本的数量越多,TfidfVectorizer这种特征量化方式就更有优势