Shorten Diameter
Time limit : 2sec / Stack limit : 256MB / Memory limit : 256MB
Score : 600 points
Problem Statement
Given an undirected tree, let the distance between vertices u and v be the number of edges on the simple path from u to v. The diameter of a tree is the maximum among the distances between any two vertices. We will call a tree good if and only if its diameter is at most K.
You are given an undirected tree with N vertices numbered 1 through N. For each i(1≦i≦N−1), there is an edge connecting vertices Ai and Bi.
You want to remove zero or more vertices from the tree, so that the resulting tree is good. When a vertex is removed, all incident edges will also be removed. The resulting graph must be connected.
Find the minimum number of vertices that you need to remove in order to produce a good tree.
Constraints
- 2≦N≦2000
- 1≦K≦N−1
- 1≦Ai≦N,1≦Bi≦N
- The graph defined by Ai and Bi is a tree.
Input
The input is given from Standard Input in the following format:
N K A1 B1 A2 B2 : AN−1 BN−1
Output
Print the minimum number of vertices that you need to remove in order to produce a good tree.
Sample Input 1
6 2 1 2 3 2 4 2 1 6 5 6
Sample Output 1
2
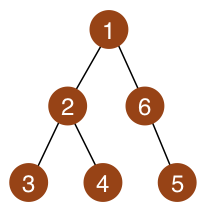
The tree is shown below. Removing vertices 5 and 6 will result in a good tree with the diameter of 2.
Sample Input 2
6 5 1 2 3 2 4 2 1 6 5 6
Sample Output 2
0
Since the given tree is already good, you do not need to remove any vertex.
分析:虽然没做出来,不过看了陈高远大牛的代码还是可以yy一下的。
可以先求出任意两点间的距离(dfs),然后考虑最优情况是左右子树平衡的时候(有2种情况),遍历至最优情况即可
代码:
#include <iostream> #include <cstdio> #include <cstdlib> #include <cmath> #include <algorithm> #include <climits> #include <cstring> #include <string> #include <set> #include <map> #include <queue> #include <stack> #include <vector> #include <list> #include <ext/rope> #define rep(i,m,n) for(i=m;i<=n;i++) #define rsp(it,s) for(set<int>::iterator it=s.begin();it!=s.end();it++) #define vi vector<int> #define pii pair<int,int> #define mod 1000000007 #define inf 0x3f3f3f3f #define pb push_back #define mp make_pair #define fi first #define se second #define ll long long #define pi acos(-1.0) const int maxn=2e3+10; const int dis[4][2]={{0,1},{-1,0},{0,-1},{1,0}}; using namespace std; using namespace __gnu_cxx; ll gcd(ll p,ll q){return q==0?p:gcd(q,p%q);} ll qpow(ll p,ll q){ll f=1;while(q){if(q&1)f=f*p;p=p*p;q>>=1;}return f;} int n,m,a[maxn][maxn],mi,cnt; vi p[maxn]; pii q[maxn]; void dfs(int root,int pre,int now,int s) { a[root][now]=s; for(int x:p[now]) { if(x!=pre)dfs(root,now,x,s+1); } } int main() { int i,j,k,t; mi=inf; scanf("%d%d",&n,&k); rep(i,1,n-1){ scanf("%d%d",&j,&t); p[j].pb(t),p[t].pb(j); q[i].fi=j,q[i].se=t; } rep(i,1,n)dfs(i,-1,i,0); rep(i,1,n) { cnt=0; rep(j,1,n) if(2*a[i][j]>k)cnt++; mi=min(mi,cnt); } rep(i,1,n-1) { cnt=0; rep(j,1,n) if(2*min(a[j][q[i].fi],a[j][q[i].se])+1>k) cnt++; mi=min(mi,cnt); } printf("%d ",mi); //system ("pause"); return 0; }