A new airplane SuperPuperJet has an infinite number of rows, numbered with positive integers starting with 1 from cockpit to tail. There are six seats in each row, denoted with letters from 'a' to 'f'. Seats 'a', 'b' and 'c' are located to the left of an aisle (if one looks in the direction of the cockpit), while seats 'd', 'e' and 'f' are located to the right. Seats 'a' and 'f' are located near the windows, while seats 'c' and 'd' are located near the aisle.
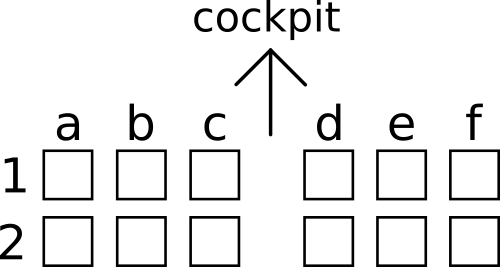
It's lunch time and two flight attendants have just started to serve food. They move from the first rows to the tail, always maintaining a distance of two rows from each other because of the food trolley. Thus, at the beginning the first attendant serves row 1 while the second attendant serves row 3. When both rows are done they move one row forward: the first attendant serves row 2 while the second attendant serves row 4. Then they move three rows forward and the first attendant serves row 5 while the second attendant serves row7. Then they move one row forward again and so on.
Flight attendants work with the same speed: it takes exactly 1 second to serve one passenger and 1 second to move one row forward. Each attendant first serves the passengers on the seats to the right of the aisle and then serves passengers on the seats to the left of the aisle (if one looks in the direction of the cockpit). Moreover, they always serve passengers in order from the window to the aisle. Thus, the first passenger to receive food in each row is located in seat 'f', and the last one — in seat 'c'. Assume that all seats are occupied.
Vasya has seat s in row n and wants to know how many seconds will pass before he gets his lunch.
The only line of input contains a description of Vasya's seat in the format ns, where n (1 ≤ n ≤ 1018) is the index of the row and s is the seat in this row, denoted as letter from 'a' to 'f'. The index of the row and the seat are not separated by a space.
Print one integer — the number of seconds Vasya has to wait until he gets his lunch.
1f
1
2d
10
4a
11
5e
18
In the first sample, the first flight attendant serves Vasya first, so Vasya gets his lunch after 1 second.
In the second sample, the flight attendants will spend 6 seconds to serve everyone in the rows 1 and 3, then they will move one row forward in 1 second. As they first serve seats located to the right of the aisle in order from window to aisle, Vasya has to wait 3 more seconds. The total is 6 + 1 + 3 = 10.
分析:模拟即可;
代码:
#include <iostream> #include <cstdio> #include <cstdlib> #include <cmath> #include <algorithm> #include <climits> #include <cstring> #include <string> #include <set> #include <map> #include <unordered_map> #include <queue> #include <stack> #include <vector> #include <list> #define rep(i,m,n) for(i=m;i<=n;i++) #define rsp(it,s) for(set<int>::iterator it=s.begin();it!=s.end();it++) #define mod 1000000007 #define inf 0x3f3f3f3f #define vi vector<int> #define pb push_back #define mp make_pair #define fi first #define se second #define ll long long #define pi acos(-1.0) #define pii pair<int,int> #define Lson L, mid, ls[rt] #define Rson mid+1, R, rs[rt] #define sys system("pause") const int maxn=2e5+10; using namespace std; ll gcd(ll p,ll q){return q==0?p:gcd(q,p%q);} ll qpow(ll p,ll q){ll f=1;while(q){if(q&1)f=f*p;p=p*p;q>>=1;}return f;} inline ll read() { ll x=0;int f=1;char ch=getchar(); while(ch<'0'||ch>'9'){if(ch=='-')f=-1;ch=getchar();} while(ch>='0'&&ch<='9'){x=x*10+ch-'0';ch=getchar();} return x*f; } int n,m,k,t; char a[20],x; ll num; string node="fedabc"; int main() { int i,j; scanf("%s",a); for(i=0;a[i]>='0'&&a[i]<='9';i++)num=num*10+a[i]-'0'; x=a[i]; ll b=(num-1)/4,c=num&1^1,ans=0; for(i=0;node[i]!=x;i++); ans+=i+1; ans+=b*16; if(c)ans+=7; cout<<ans<<endl; //system("Pause"); return 0; }