sum_weights 可以通过参数设置。 如果不设置,那么值就是样本的个数。 指定每个样本的权重。
我突然想到基金预测,可以设置样本的权重。 真实涨幅越高,权重越小。 反之,权重越高。 因为如果预测偏低,那么loss 损失越大。
"rmse":
sum_loss = 和 (score - label)*(score - label)
loss = std::sqrt(sum_loss / sum_weights);
"l2": 误差的平方:
sum_loss = 和 (score - label)*(score - label)
loss = sum_loss / sum_weights
"l1": 误差的绝对值:
sum_loss = 和 fabs(score - label)
loss = sum_loss / sum_weights
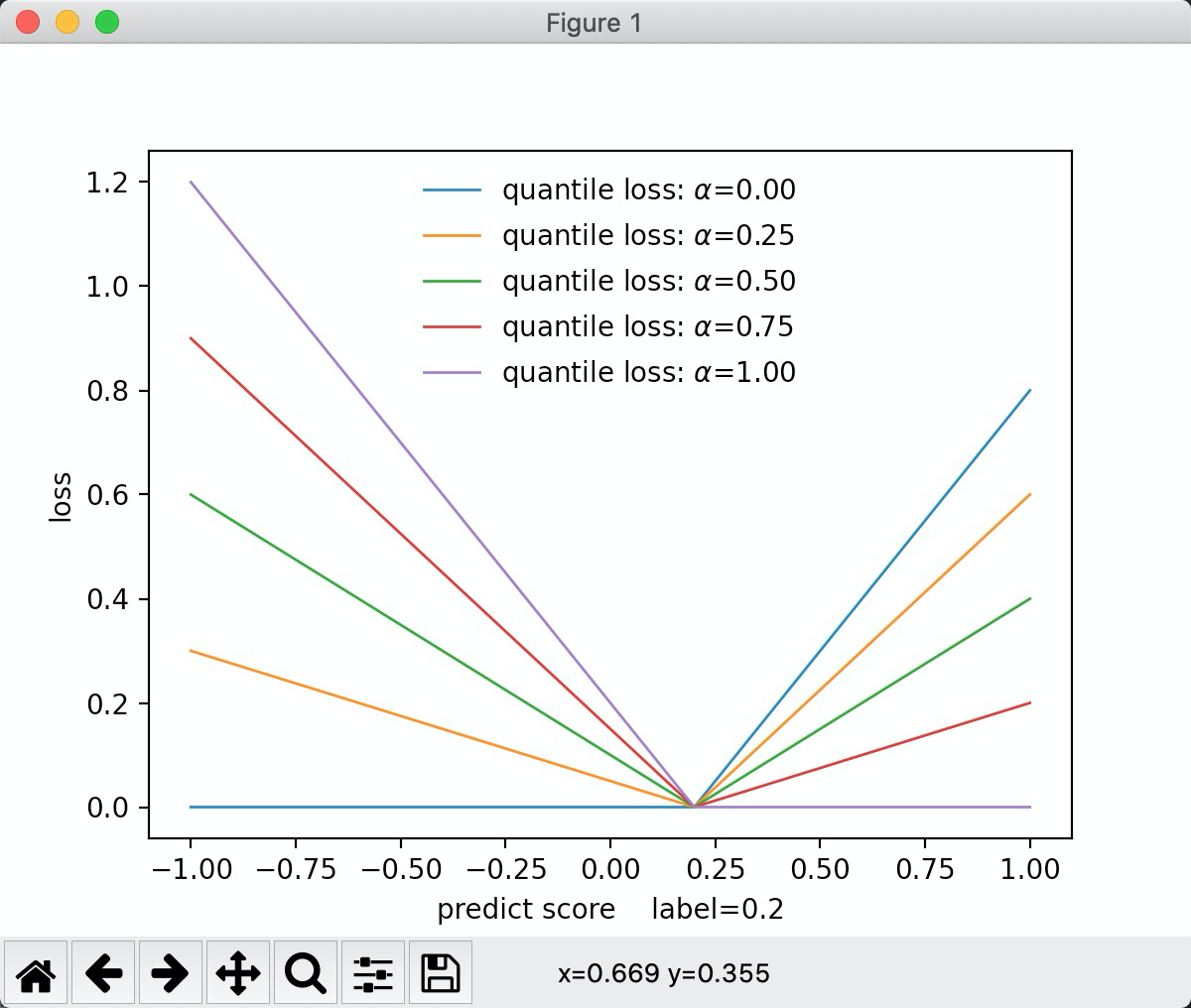
"quantile": 分位数损失
inline static double LossOnPoint(label_t label, double score, const Config& config) {
double delta = label - score;
if (delta < 0) {
return (config.alpha - 1.0f) * delta;
} else {
return config.alpha * delta;
}
}
从c++ 代码可以看到, 如果alpha为0.5, 那么就是误差的绝对值* 0.5. 如果为0.2。 那么就是负误差越小,损失越大。 从图中可以看出,alpha值越大,正误差损失斜率越低。 为0.5时正负斜率相等
sum_loss = 和 LossOnPoint(label, score)
loss = sum_loss / sum_weights
"huber":
inline static double LossOnPoint(label_t label, double score, const Config& config) {
const double diff = score - label;
if (std::abs(diff) <= config.alpha) {
return 0.5f * diff * diff;
} else {
return config.alpha * (std::abs(diff) - 0.5f * config.alpha);
}
}
预测的分数离标签值越近,越趋近0. 从图中可以看出, 就是平方损失函数的压缩版。 huber损失值相对平方损失压小了。 alpha越小, Huber损失值压的越狠。

"fair":公允价值变动损失
inline static double LossOnPoint(label_t label, double score, const Config& config) { const double x = std::fabs(score - label); const double c = config.fair_c; return c * x - c * c * std::log(1.0f + x / c); }
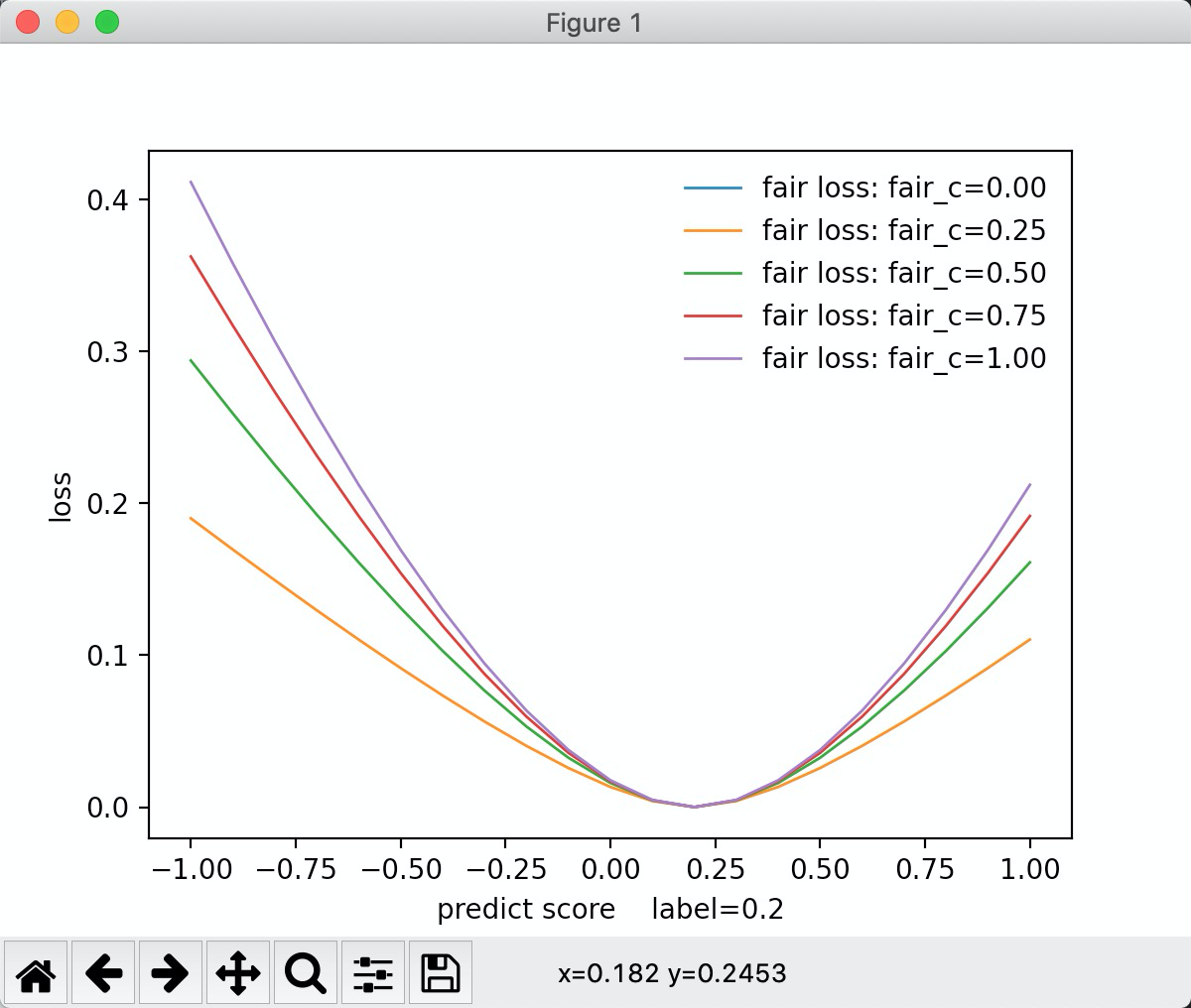
从图中可以看出, fair_c 越小, 损失越小。 fair_c 越大损失越大
"poisson": 柏松回归
inline static double LossOnPoint(label_t label, double score, const Config&) {
const double eps = 1e-10f;
if (score < eps) {
score = eps;
}
return score - label * std::log(score);
}

如果出现负误差, 那么损失值非常大。
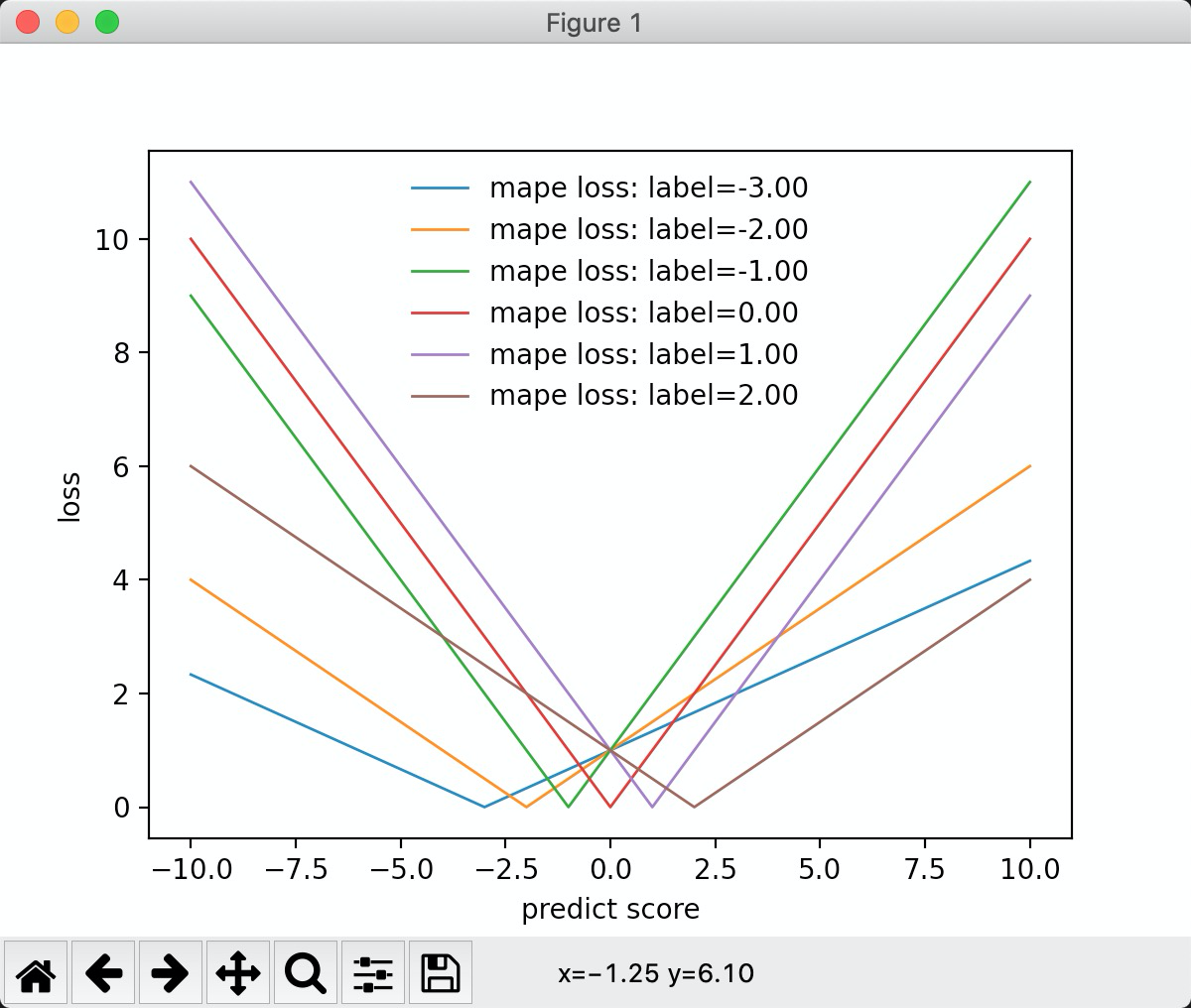
mape:
inline static double LossOnPoint(label_t label, double score, const Config&) {
return std::fabs((label - score)) / std::max(1.0f, std::fabs(label));
}
gamma: 分布
inline static double LossOnPoint(label_t label, double score, const Config&) {
const double psi = 1.0;
const double theta = -1.0 / score;
const double a = psi;
const double b = -Common::SafeLog(-theta);
const double c = 1. / psi * Common::SafeLog(label / psi) - Common::SafeLog(label) - 0; // 0 = std::lgamma(1.0 / psi) = std::lgamma(1.0);
return -((label * theta - b) / a + c);
}
限制条件: label 必须大于0
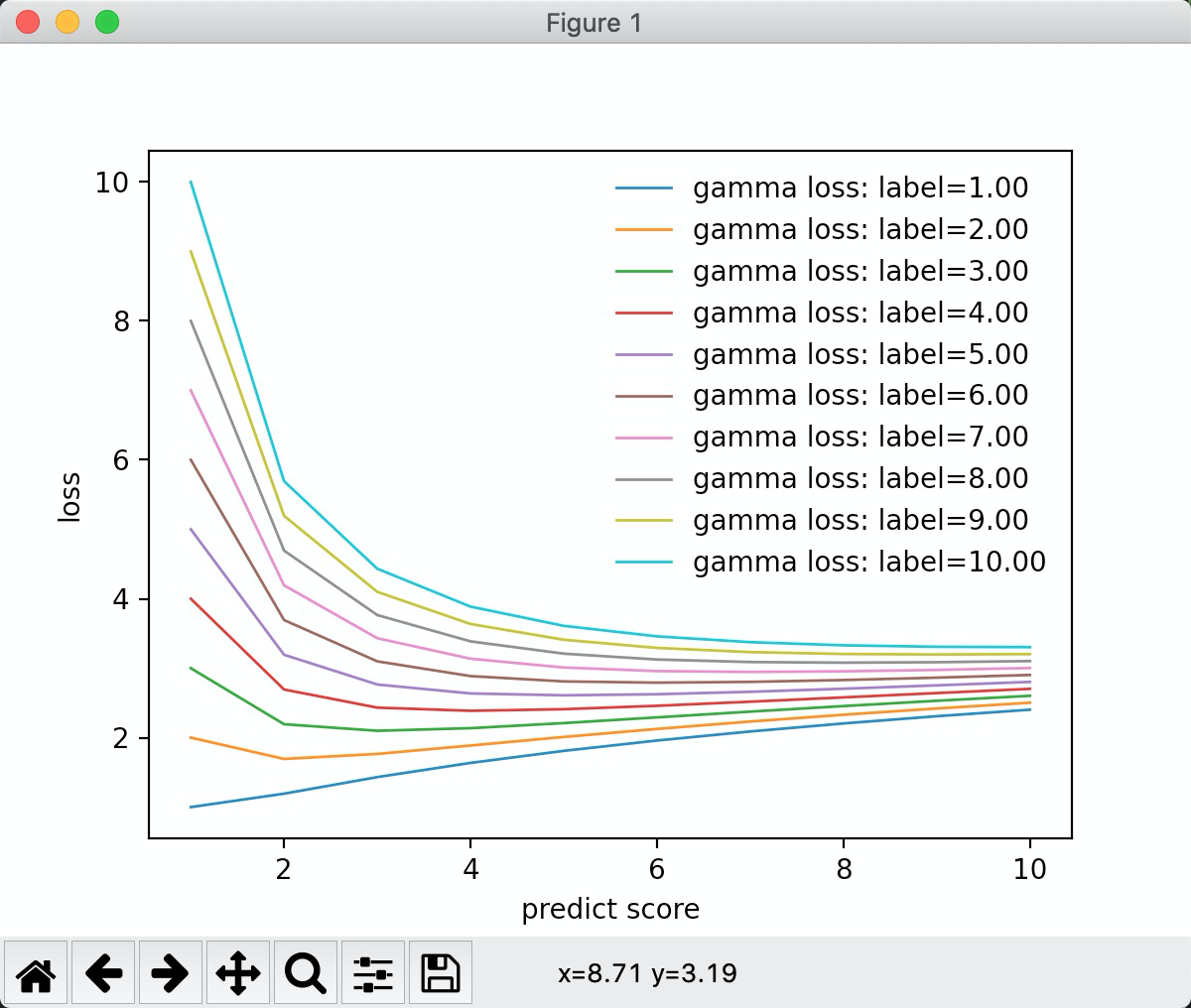
从图中可以看到, 标签值越大, 预测值离标签值越近,损失值越小。 在预测值在标签值附近的时候,损失值差别不大
"gamma_deviance":
inline static double LossOnPoint(label_t label, double score, const Config&) {
const double epsilon = 1.0e-9;
const double tmp = label / (score + epsilon);
return tmp - Common::SafeLog(tmp) - 1;
}
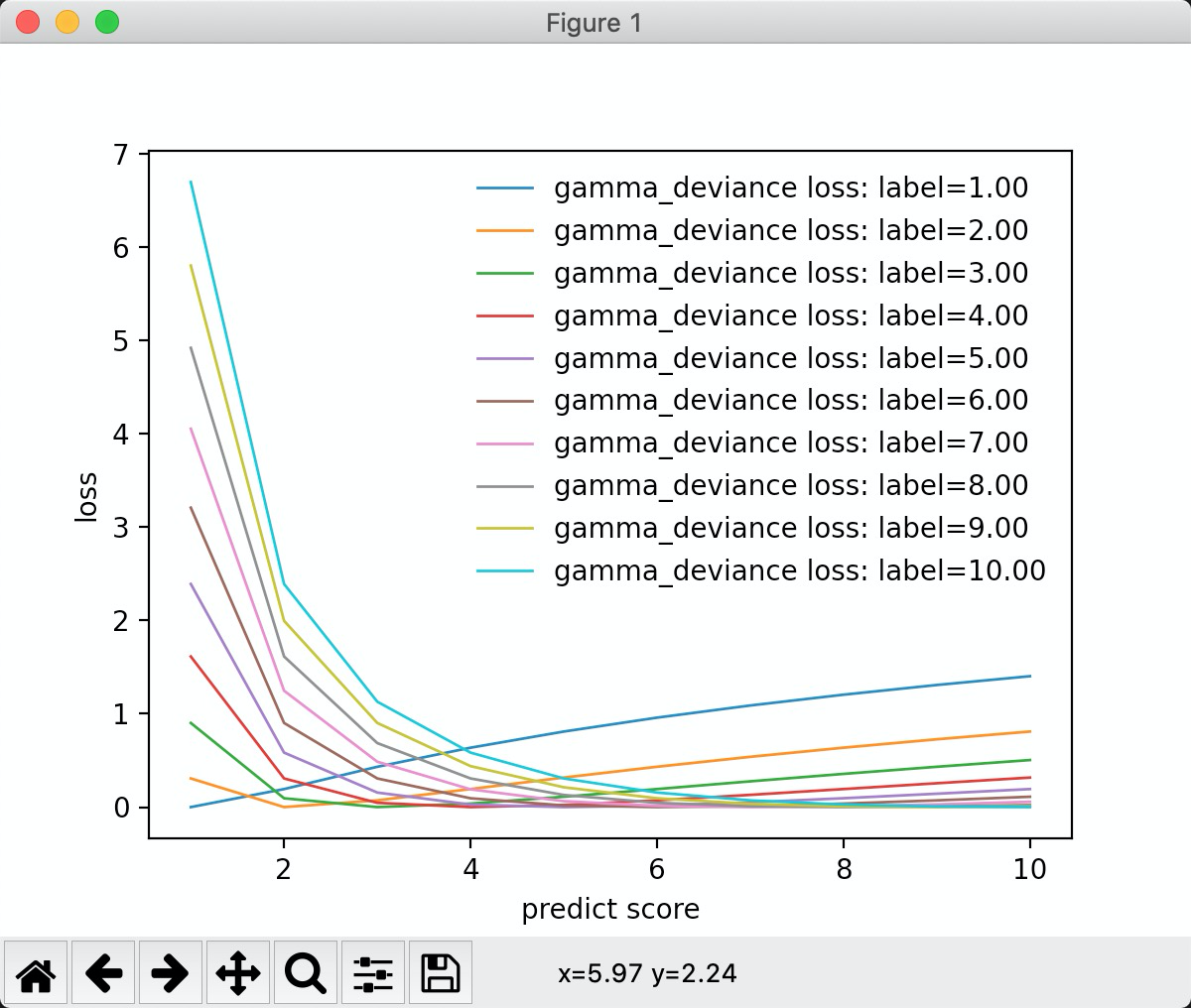
从图中可以看出, 当标签为1的时候,损失值是线性的, 标签值大于0的时候。 标签为2的时候,是分段线性的。 负误差的斜率和正误差的斜率要陡。
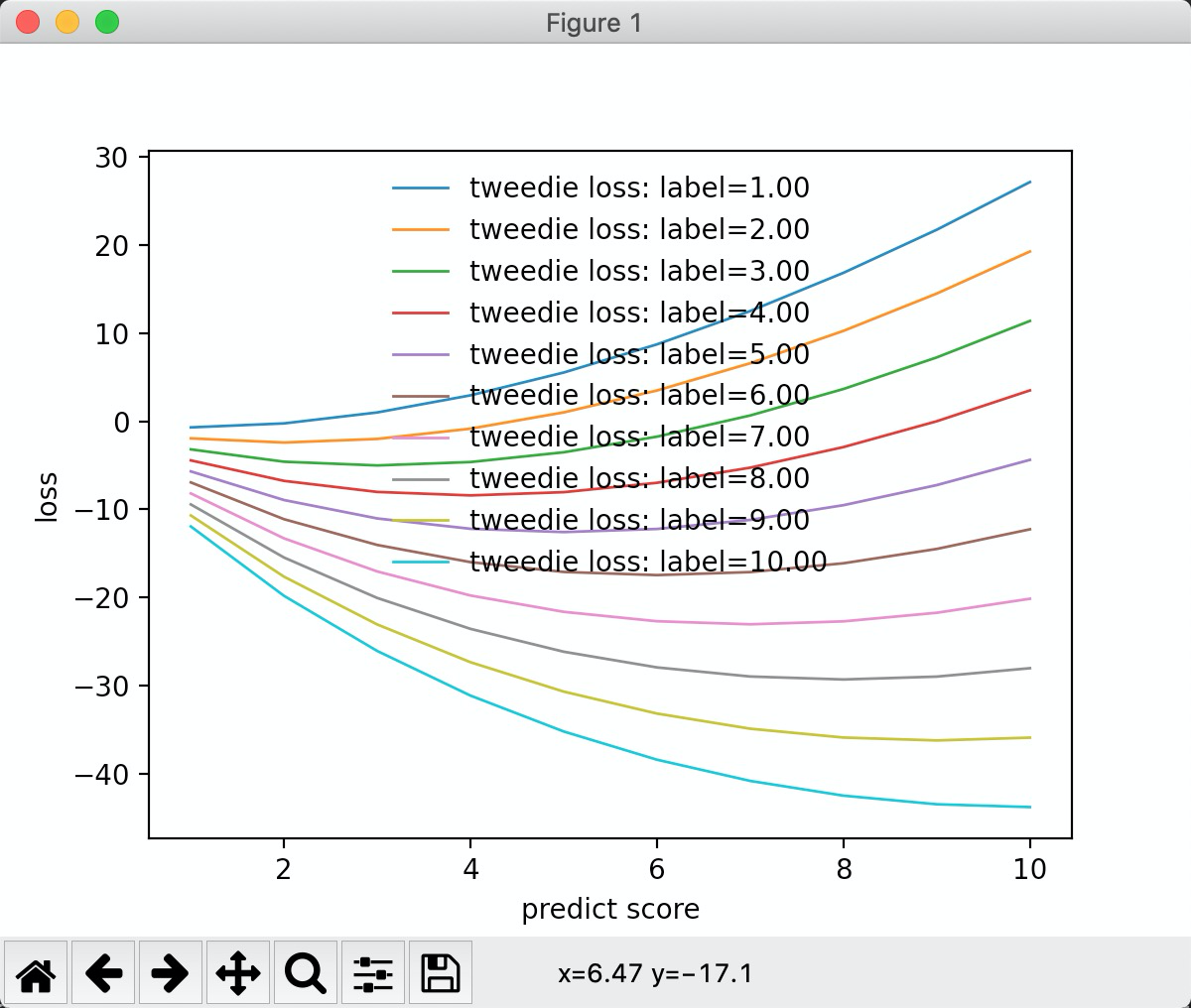
"tweedie" 类分布
inline static double LossOnPoint(label_t label, double score, const Config& config) {
const double rho = config.tweedie_variance_power;
const double eps = 1e-10f;
if (score < eps) {
score = eps;
}
const double a = label * std::exp((1 - rho) * std::log(score)) / (1 - rho);
const double b = std::exp((2 - rho) * std::log(score)) / (2 - rho);
return -a + b;
}
tweedie_variance_power = 0.2 时, 函数图形如下: