opengl 学习 之 03 lesson
简介
使用MVP变换来观察生成的三角形
link
http://www.opengl-tutorial.org/uncategorized/2017/06/07/website-update/
向量介绍
We will now have (x,y,z,w) vectors.
If w == 1, then the vector (x,y,z,1) is a position in space.
If w == 0, then the vector (x,y,z,0) is a direction.
变换矩阵(Translation matrices)
In 3D graphics we will mostly use 4x4 matrices. They will allow us to transform our (x,y,z,w) vertices. This is done by multiplying the vertex with the matrix :
Example
So if we want to translate the vector (10,10,10,1) of 10 units in the X direction, we get :
Let’s now see what happens to a vector that represents a direction towards the -z axis : (0,0,-1,0)
单位阵(Identity matrix)
单位阵啥也不干
缩放矩阵(Scaling matrices)
So if you want to scale a vector (position or direction, it doesn’t matter) by 2.0 in all directions :
合并作用
作用顺序是,首先缩放,在旋转,在移动。
The Model Matrix (模型矩阵)
You apply this matrix to all your vertices at each frame (in GLSL, not in C++!) and everything moves. Something that doesn’t move will be at the center of the world.
应该就是 上面的 缩放、移动和旋转的集合就是模型矩阵。
模型的坐标通过模型矩阵变化到世界坐标系
The View matrix(视图矩阵)
功能类似于摄像机。
世界坐标系通过视图举证变换到摄像机坐标。
glm::mat4 CameraMatrix = glm::lookAt(
cameraPosition, // the position of your camera, in world space
cameraTarget, // where you want to look at, in world space
upVector // probably glm::vec3(0,1,0), but (0,-1,0) would make you looking upside-down, which
can be great too
);
The Projection matrix(投影矩阵)
如何放在电脑屏幕上显示,通过一个梯形体,类似于埃及金字塔削去了顶部一个四面体。
// Generates a really hard-to-read matrix, but a normal, standard 4x4 matrix nonetheless
glm::mat4 projectionMatrix = glm::perspective(
FoV, // The horizontal Field of View, in degrees : the amount of "zoom". Think "camera lens".
Usually between 90° (extra wide) and 30° (quite zoomed in)
4.0f / 3.0f, // Aspect Ratio. Depends on the size of your window. Notice that 4/3 == 800/600 ==
1280/960, sounds familiar ?
0.1f, // Near clipping plane. Keep as big as possible, or you'll get precision issues.
100.0f // Far clipping plane. Keep as little as possible.
);
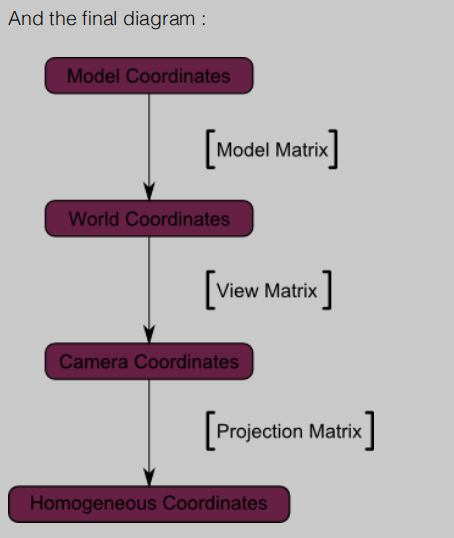
上图即为流程图。
累计变换:MVP(ModelViewProjection)
// C++ : compute the matrix
glm::mat4 MVPmatrix = projection * view * model; // Remember : inverted !
image

code
// Include standard headers
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
// Include GLEW
#include <GL/glew.h>
// Include GLFW
#include <GLFW/glfw3.h>
GLFWwindow* window;
// Include GLM
#include <glm/glm.hpp>
#include <glm/gtc/matrix_transform.hpp>
using namespace glm;
#include <common/shader.hpp>
int main( void )
{
// Initialise GLFW
if( !glfwInit() )
{
fprintf( stderr, "Failed to initialize GLFW
" );
getchar();
return -1;
}
glfwWindowHint(GLFW_SAMPLES, 4);
glfwWindowHint(GLFW_CONTEXT_VERSION_MAJOR, 3);
glfwWindowHint(GLFW_CONTEXT_VERSION_MINOR, 3);
glfwWindowHint(GLFW_OPENGL_FORWARD_COMPAT, GL_TRUE); // To make MacOS happy; should not be needed
glfwWindowHint(GLFW_OPENGL_PROFILE, GLFW_OPENGL_CORE_PROFILE); //We don't want the old OpenGL
// Open a window and create its OpenGL context
window = glfwCreateWindow( 1024, 768, "Tutorial 03 - Matrices", NULL, NULL);
if( window == NULL ){
fprintf( stderr, "Failed to open GLFW window. If you have an Intel GPU, they are not 3.3 compatible. Try the 2.1 version of the tutorials.
" );
getchar();
glfwTerminate();
return -1;
}
glfwMakeContextCurrent(window);
// Initialize GLEW
glewExperimental = true; // Needed for core profile
if (glewInit() != GLEW_OK) {
fprintf(stderr, "Failed to initialize GLEW
");
getchar();
glfwTerminate();
return -1;
}
// Ensure we can capture the escape key being pressed below
glfwSetInputMode(window, GLFW_STICKY_KEYS, GL_TRUE);
// Dark blue background
glClearColor(0.0f, 0.0f, 0.4f, 0.0f);
GLuint VertexArrayID;
glGenVertexArrays(1, &VertexArrayID);
glBindVertexArray(VertexArrayID);
// Create and compile our GLSL program from the shaders
GLuint programID = LoadShaders( "SimpleTransform.vertexshader", "SingleColor.fragmentshader" );
// Get a handle for our "MVP" uniform
GLuint MatrixID = glGetUniformLocation(programID, "MVP");
// Projection matrix : 45� Field of View, 4:3 ratio, display range : 0.1 unit <-> 100 units
glm::mat4 Projection = glm::perspective(glm::radians(45.0f), 4.0f / 3.0f, 0.1f, 100.0f);
// Or, for an ortho camera :
//glm::mat4 Projection = glm::ortho(-10.0f,10.0f,-10.0f,10.0f,0.0f,100.0f); // In world coordinates
// Camera matrix
glm::mat4 View = glm::lookAt(
glm::vec3(4,3,3), // Camera is at (4,3,3), in World Space
glm::vec3(0,0,0), // and looks at the origin
glm::vec3(0,1,0) // Head is up (set to 0,-1,0 to look upside-down)
);
// Model matrix : an identity matrix (model will be at the origin)
glm::mat4 Model = glm::mat4(1.0f);
// Our ModelViewProjection : multiplication of our 3 matrices
glm::mat4 MVP = Projection * View * Model; // Remember, matrix multiplication is the other way around
static const GLfloat g_vertex_buffer_data[] = {
-1.0f, -1.0f, 0.0f,
1.0f, -1.0f, 0.0f,
0.0f, 1.0f, 0.0f,
};
GLuint vertexbuffer;
glGenBuffers(1, &vertexbuffer);
glBindBuffer(GL_ARRAY_BUFFER, vertexbuffer);
glBufferData(GL_ARRAY_BUFFER, sizeof(g_vertex_buffer_data), g_vertex_buffer_data, GL_STATIC_DRAW);
do{
// Clear the screen
glClear( GL_COLOR_BUFFER_BIT );
// Use our shader
glUseProgram(programID);
// Send our transformation to the currently bound shader,
// in the "MVP" uniform
glUniformMatrix4fv(MatrixID, 1, GL_FALSE, &MVP[0][0]);
// 1rst attribute buffer : vertices
glEnableVertexAttribArray(0);
glBindBuffer(GL_ARRAY_BUFFER, vertexbuffer);
glVertexAttribPointer(
0, // attribute. No particular reason for 0, but must match the layout in the shader.
3, // size
GL_FLOAT, // type
GL_FALSE, // normalized?
0, // stride
(void*)0 // array buffer offset
);
// Draw the triangle !
glDrawArrays(GL_TRIANGLES, 0, 3); // 3 indices starting at 0 -> 1 triangle
glDisableVertexAttribArray(0);
// Swap buffers
glfwSwapBuffers(window);
glfwPollEvents();
} // Check if the ESC key was pressed or the window was closed
while( glfwGetKey(window, GLFW_KEY_ESCAPE ) != GLFW_PRESS &&
glfwWindowShouldClose(window) == 0 );
// Cleanup VBO and shader
glDeleteBuffers(1, &vertexbuffer);
glDeleteProgram(programID);
glDeleteVertexArrays(1, &VertexArrayID);
// Close OpenGL window and terminate GLFW
glfwTerminate();
return 0;
}
#version 330 core
// Output data
out vec3 color;
void main()
{
// Output color = red
color = vec3(1,0,0);
}
#version 330 core
// Output data
out vec3 color;
void main()
{
// Output color = red
color = vec3(1,0,0);
}
#version 330 core
// Input vertex data, different for all executions of this shader.
layout(location = 0) in vec3 vertexPosition_modelspace;
// Values that stay constant for the whole mesh.
uniform mat4 MVP;
void main(){
// Output position of the vertex, in clip space : MVP * position
gl_Position = MVP * vec4(vertexPosition_modelspace,1);
}
shader 加载函数
#include <stdio.h>
#include <string>
#include <vector>
#include <iostream>
#include <fstream>
#include <algorithm>
#include <sstream>
using namespace std;
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <GL/glew.h>
#include "shader.hpp"
GLuint LoadShaders(const char * vertex_file_path,const char * fragment_file_path){
// Create the shaders
GLuint VertexShaderID = glCreateShader(GL_VERTEX_SHADER);
GLuint FragmentShaderID = glCreateShader(GL_FRAGMENT_SHADER);
// Read the Vertex Shader code from the file
std::string VertexShaderCode;
std::ifstream VertexShaderStream(vertex_file_path, std::ios::in);
if(VertexShaderStream.is_open()){
std::stringstream sstr;
sstr << VertexShaderStream.rdbuf();
VertexShaderCode = sstr.str();
VertexShaderStream.close();
}else{
printf("Impossible to open %s. Are you in the right directory ? Don't forget to read the FAQ !
", vertex_file_path);
getchar();
return 0;
}
// Read the Fragment Shader code from the file
std::string FragmentShaderCode;
std::ifstream FragmentShaderStream(fragment_file_path, std::ios::in);
if(FragmentShaderStream.is_open()){
std::stringstream sstr;
sstr << FragmentShaderStream.rdbuf();
FragmentShaderCode = sstr.str();
FragmentShaderStream.close();
}
GLint Result = GL_FALSE;
int InfoLogLength;
// Compile Vertex Shader
printf("Compiling shader : %s
", vertex_file_path);
char const * VertexSourcePointer = VertexShaderCode.c_str();
glShaderSource(VertexShaderID, 1, &VertexSourcePointer , NULL);
glCompileShader(VertexShaderID);
// Check Vertex Shader
glGetShaderiv(VertexShaderID, GL_COMPILE_STATUS, &Result);
glGetShaderiv(VertexShaderID, GL_INFO_LOG_LENGTH, &InfoLogLength);
if ( InfoLogLength > 0 ){
std::vector<char> VertexShaderErrorMessage(InfoLogLength+1);
glGetShaderInfoLog(VertexShaderID, InfoLogLength, NULL, &VertexShaderErrorMessage[0]);
printf("%s
", &VertexShaderErrorMessage[0]);
}
// Compile Fragment Shader
printf("Compiling shader : %s
", fragment_file_path);
char const * FragmentSourcePointer = FragmentShaderCode.c_str();
glShaderSource(FragmentShaderID, 1, &FragmentSourcePointer , NULL);
glCompileShader(FragmentShaderID);
// Check Fragment Shader
glGetShaderiv(FragmentShaderID, GL_COMPILE_STATUS, &Result);
glGetShaderiv(FragmentShaderID, GL_INFO_LOG_LENGTH, &InfoLogLength);
if ( InfoLogLength > 0 ){
std::vector<char> FragmentShaderErrorMessage(InfoLogLength+1);
glGetShaderInfoLog(FragmentShaderID, InfoLogLength, NULL, &FragmentShaderErrorMessage[0]);
printf("%s
", &FragmentShaderErrorMessage[0]);
}
// Link the program
printf("Linking program
");
GLuint ProgramID = glCreateProgram();
glAttachShader(ProgramID, VertexShaderID);
glAttachShader(ProgramID, FragmentShaderID);
glLinkProgram(ProgramID);
// Check the program
glGetProgramiv(ProgramID, GL_LINK_STATUS, &Result);
glGetProgramiv(ProgramID, GL_INFO_LOG_LENGTH, &InfoLogLength);
if ( InfoLogLength > 0 ){
std::vector<char> ProgramErrorMessage(InfoLogLength+1);
glGetProgramInfoLog(ProgramID, InfoLogLength, NULL, &ProgramErrorMessage[0]);
printf("%s
", &ProgramErrorMessage[0]);
}
glDetachShader(ProgramID, VertexShaderID);
glDetachShader(ProgramID, FragmentShaderID);
glDeleteShader(VertexShaderID);
glDeleteShader(FragmentShaderID);
return ProgramID;
}
#ifndef SHADER_HPP
#define SHADER_HPP
GLuint LoadShaders(const char * vertex_file_path,const char * fragment_file_path);
#endif