异步编程的最高境界就是不关心它是否是异步。async、await很好的解决了这一点,将异步强行转换为同步处理。
async/await与promise不存在谁代替谁的说法,因为async/await是寄生于Promise,是Generater的语法糖。
温馨提示:如果你已经知道了关于async await的基本用法,请直接看分割线以下内容
Generator
function* helloWorld () {
yield 'hello'
yield 'world'
return 'ending'
}
var hw = helloWorld()
console.log(hw) // helloWorld {<suspended>}
console.log(hw.next()) // {value: "hello", done: false}
console.log(hw.next()) // {value: "world", done: false}
console.log(hw.next()) // {value: "ending", done: false}
console.log(hw.next()) // {value: undefined, done: true}
async function fn() {
await console.log(1111111)
await console.log(2222222)
await console.log(3333333)
}
fn()
// 1111111
// 2222222
// 3333333
async function fn () {
await 100
await 200
return 300
}
fn().then(res => {
console.log(res) // 300
})
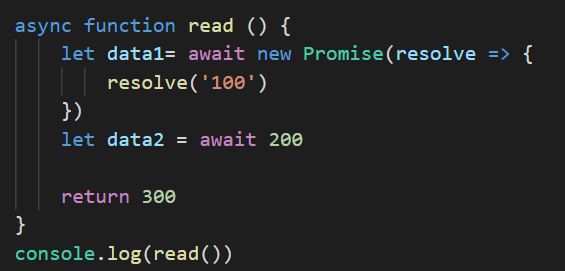
打印结果如下:(返回的是promise对象)

如果在async函数中抛出了错误,则终止错误结果,不会继续向下执行:

async function f() {
try {
await Promise.reject('出错了');
} catch(e) {
}
return await Promise.resolve('hello world');
}
f()
.then(v => console.log(v)) // hello world
// catch
async function f() {
await Promise.reject('出错了')
.catch(e => console.log(e)); // 出错了
return await Promise.resolve('hello world');
}
f()
.then(v => console.log(v)) // hello world
================================ 分割线 ==================================
面试题
【例1】
async function async1() {
console.log("async1 start");
await async2();
console.log("async1 end");
return 'async return';
}
async function async2() {
console.log("async2");
}
console.log("script start");
setTimeout(function() {
console.log("setTimeout");
}, 0);
async1().then(function (message) { console.log(message) });
new Promise(function(resolve) {
console.log("promise1");
resolve();
}).then(function() {
console.log("promise2");
});
console.log("script end");
输出顺序如下:
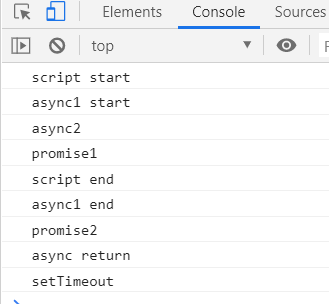
这道题目考查的是我们对 事件循环 任务队列 的理解:
事件循环(Event Loop): 1. JS会首先判断代码是同步还是异步,同步进入主线程,异步进入任务队列; 2. 同步任务进入主线程后一直执行,直到主线程空闲后,才会去任务队列中查看是否有可执行的异步任务,如果有就推入主线程中执行; 3. 事件循环是一个先进先出(FIFO)队列,这说明回调是按照它们被加入队列的顺序执行的。
[ 分析 ]:
1. 在单线程的js中,异步代码会被放入一个事件队列,等到所有其他代码执行后再执行,而不会阻塞线程。我们从上到下看,首先打印:script start;
2. setTimeout / setInterval 要放到任务队列的末尾,等待后续执行。继续往下走;
此时的任务队列: setTimeout
3. async1 开始执行,当函数里遇到await时,暂停执行(await所在行放在本次执行完),而 async1 函数 未完成部分被添加到任务队列;
此时的任务队列: async1 setTimeout
4. new Promise() 实例对象被new出来后,它里面的promise1会立刻打印,然后又遇到 then, 此时 promise 实例 被添加到任务队列;
此时的任务队列: async1 promise实例 setTimeout
5. 接着打印:script end。至此,同步代码已执行完毕。
而我们的任务队列中还存在着 async1, promise对象, setTimeout异步回调;
6. 由于异步代码第一次执行时,async1 函数 要早于 promise对象,所以紧接着 async1 函数继续执行没有执行完成的部分,执行完毕后,退出任务队列,打印:async1 end。然后把它的 then 逻辑添加到任务 队列中;
此时的任务队列: promise实例 async1的then逻辑部分 setTimeout
7. promise 实例 继续执行它的 then 的逻辑,打印:promise2。执行完毕后,退出任务队列;
此时的任务队列: async1的then逻辑部分 setTimeout
8. async 函数执行 then 逻辑;
此时的任务队列: setTimeout
9. setTimeout是宏任务会在最后执行。
【 补充说明 】:
1. 因为在 async1 函数内部被一个 await 分为两部分,需要分两步才可执行完。3的时候执行完第一步后暂停,而将剩余部分放到任务队列等待执行;
2. 在5的时候同步代码已执行完毕,所以 js 回过头来去任务队列上找未完成的异步任务,这个时候首先去执行 async1(在6时候), 因为它最先被放到任务队列;
3. 在6时候,async1 函数并没有紧接着执行 then 的逻辑,而是继续执行没有执行完成的部分,而这次当 async1 执行完毕之后,会把 then 放到任务队列当中,且排在promise对象之后。7的时候promise 实例继续执行下一步异步代码,执行完毕之后,任务队列此时只剩下 async1 的 then 逻辑,这时执行栈会执行 async1 的 then 逻辑。
【例2】:
var p = new Promise((res,rej) => {
res('hello one')
console.log('good morning')
})
function hello() {
console.log('hello begins')
return p
}
hello().then(res => {
console.log(res)
console.log('hello1111111111')
return 'hello two'
}).then(res => {
console.log(res)
console.log('hello22222222222')
return 'hello three'
}).then(res => {
console.log(res)
console.log('hello33333333333')
})
function test1 () {
console.log('test1')
}
async function asy () {
console.log('asy begins')
await console.log('asy---111111')
console.log('async1')
await console.log('asy---222222')
console.log('asy ends')
}
asy()
test1()
function* gnrt () {
console.log(1)
yield console.log(11111111)
console.log(2)
yield console.log(22222222)
console.log(3)
yield console.log(33333333)
}
var result = gnrt()
result.next()
result.next()
result.next()
输出顺序如下:
