1. 简介
操作系统是管理硬件资源,为上层库与软件提供接口系统软件。
2. 基于Linux操作系统
| 序号 | 描述 | 链接 |
| 01 | 内核构建系统 | http://www.cnblogs.com/elewei/p/8244895.html |
| 02 | 进程 | http://www.cnblogs.com/elewei/p/4740512.html |
| 03 | 线程 | http://www.cnblogs.com/elewei/p/8151516.html |
| 04 | 进程间通信 | http://www.cnblogs.com/elewei/p/8157793.html |
| 05 | 内存管理 | |
| 06 | 文件系统 | http://www.cnblogs.com/elewei/p/7765716.html |
| 07 | 网络 | http://www.cnblogs.com/elewei/p/8079470.html |
| 08 | 字符驱动 | http://www.cnblogs.com/elewei/p/8214379.html |
| 09 | 内核调式技术 | http://www.cnblogs.com/elewei/p/8227903.html |
| 10 | 竞争与并发 | http://www.cnblogs.com/elewei/p/8228142.html |
| 11 | Linux服务器初始化配置 | http://www.cnblogs.com/elewei/p/5968846.html |
3. 基于Windows操作系统
| 序号 | 描述 | 链接 |
| 01 | Windows服务 | http://www.cnblogs.com/elewei/p/8677052.html |
4. 操作系统软件
操作系统设置
| 序号 | 描述 | 链接 |
| 01 | CentOS 初始化配置 | https://www.cnblogs.com/elewei/p/5968846.html |
| 序号 | 描述 | 链接 |
| 01 | CentOS 初始配置 | https://www.cnblogs.com/elewei/p/5968846.html |
| 02 | Ubuntu LAMP环境 | https://www.cnblogs.com/elewei/p/10036951.html |
一、参考资料
<Understanding the Linux Kernel> Daniel P.Bovet && Marco Cesati
<Linux Device Drivers> Jonathan Corbet
<Linux Kernel Development> Robert Love
<Advance Programming in the UNIX Environment> W. Richard Stevens
<深入理解Linux虚拟内存管理>
<深入理解Linux网络内幕>
BSD操作系统
https://cis.temple.edu/~ingargio/old/cis307s96/
经典网站:
https://www.infradead.org/~mchehab/kernel_docs/index.html
http://www.elinux.org/ Embeded Linux WiKi
http://kerneltrap.org/
https://www.linux.com/
https://kernelnewbies.org/Documents
https://lwn.net/Kernel/Index/
http://www.tldp.org/
http://www.kerneltravel.net/
http://www.daimabus.com/
Linux 邮件列表
http://fxr.watson.org/
http://elixir.free-electrons.com/linux/latest/source 内核源码
https://www.win.tue.nl/~aeb/linux/lk/lk.html#toc3
https://wiki.linuxfoundation.org/networking/start
https://kernelnewbies.org/KernelBuild 内核编译
http://derekmolloy.ie/writing-a-linux-kernel-module-part-1-introduction/
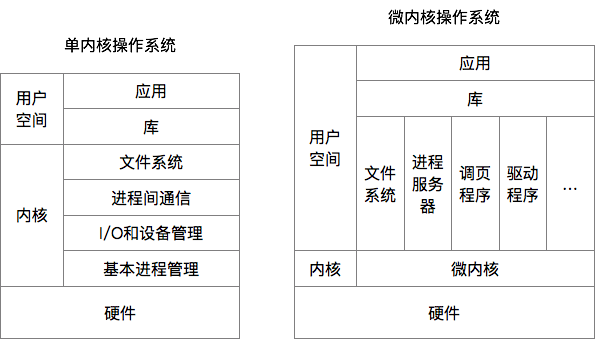
二、操作系统主要模块
内核区分与服务
三、Hello World
三类驱动
* 字符设备
* 块设备
* 网络接口
一个Hello World 模块
/** * @file hello.c * @author elewei * @date 2017/01/06 * @version 0.2 * @brief 一个Linux Hello World 模块! * 当调用insmod加载内核模块时,在/var/log/kern.log文件中显示消息 * 模块可以添加一个参数, Hello name * @see http://www.cnblogs.com/elewei/p/7688444.html 查看详细信息 */ #include <linux/init.h> // Macros used to mark up functions e.g., __init __exit #include <linux/module.h> // Core header for loading LKMs into the kernel #include <linux/kernel.h> // Contains types, macros, functions for the kernel MODULE_LICENSE("GPL"); // < The license type -- this affects runtime behavior MODULE_AUTHOR("Elewei"); // < The author -- visible when you use modinfo MODULE_DESCRIPTION("A simple Linux driver module example"); ///< The description -- see modinfo MODULE_VERSION("0.2"); ///< The version of the module static char *name = "world"; ///< An example LKM argument -- default value is "world" module_param(name, charp, S_IRUGO); ///< Param desc. charp = char ptr, S_IRUGO can be read/not changed MODULE_PARM_DESC(name, "The name to display in /var/log/kern.log"); ///< parameter description /** @brief The LKM initialization function * The static keyword restricts the visibility of the function to within this C file. The __init * macro means that for a built-in driver (not a LKM) the function is only used at initialization * time and that it can be discarded and its memory freed up after that point. * @return returns 0 if successful */ static int __init hello_init(void){ printk(KERN_INFO "EBB: Hello %s from the BBB LKM! ", name); return 0; } /** @brief The LKM cleanup function * Similar to the initialization function, it is static. The __exit macro notifies that if this * code is used for a built-in driver (not a LKM) that this function is not required. */ static void __exit hello_exit(void){ printk(KERN_INFO "EBB: Goodbye %s from the BBB LKM! ", name); } /** @brief A module must use the module_init() module_exit() macros from linux/init.h, which * identify the initialization function at insertion time and the cleanup function (as * listed above) */ module_init(hello_init); module_exit(hello_exit);
Makefile
// Makefile obj-m += hello.o all: make -C /lib/modules/$(shell uname -r)/build M=$(PWD) modules clean: make -C /lib/modules/$(shell uname -r)/build M=$(PWD) clean
上面的Makefile可以这样写
# 如果KERNELRELEASE已经定义, 可以从内核编译系统调用
ifneq ($(KERNELRELEASE),)
obj-m := hello.o
# 否则直接从命令行调用内核编译系统
KERNELDIR ?= /lib/modules/$(shell uname -r)/build
PWD := $(shell pwd)
default:
$(MAKE) -C $(KERNELDIR) M=$(PWD) modules
endif
第一步:编译内核
make
第二步:插入模块
insmod ./hello.ko
第三步:查看模块
lsmod
第四步:移除模块
rmmod hello
#include<stdio.h> #include<unistd.h> #include<stdlib.h> int main(void) { int pid; pid=fork(); if(pid==0) { printf("This is child process,pid=%d,bye! ",getpid()); exit(0); } sleep(1); printf("Press return to remove zombie process "); getchar(); wait(NULL); printf("Press return to exit "); getchar(); return 0; }