前言
距离上一篇博文的更新时间已经过了一个月,一则是除了开发自己的项目之外,还临时接手了其他同事的开发任务,大家都懂得。二则是写这篇博文需要准备的东西着实不少,调试、画图、总结、整理笔记,需要花不少时间和精力。当然本着撸穿源码的目标,还是坚持整理完成,就先个自己打个call吧,O(∩_∩)O哈哈~。
1. 初始化流程概述图、代码流程图
1.1 初始化流程概述
通过debug的方式(如何准备源码调试环境,大家可以参考我之前写的 这篇文章)总结了Vue从初始化到递归创建元素的大致流程:定义Vue构造函数/全局API/实例的属性方法 -> new Vue() -> init() -> mountComponent -> render -> patch -> createElm-> createComponent -> createChildren -> insert,整理的流程概述图如下。

1.2 初始化代码执行流程图
下图代码的执行逻辑,表示Vue从初始化到DOM渲染的一个流程。之前看源码的时候,主要是用到什么API,再去看与这个API相关的逻辑。但是这样看代码缺少系统性,不利于总结和复习。所以就一边写demo,一边断点,画出大概的代码执行流程,虽然不是很完善,但至少能有个总线。等到要看其他功能代码的时候,可以在此基础上进行扩展,同时也便于代码定位和逻辑的梳理。
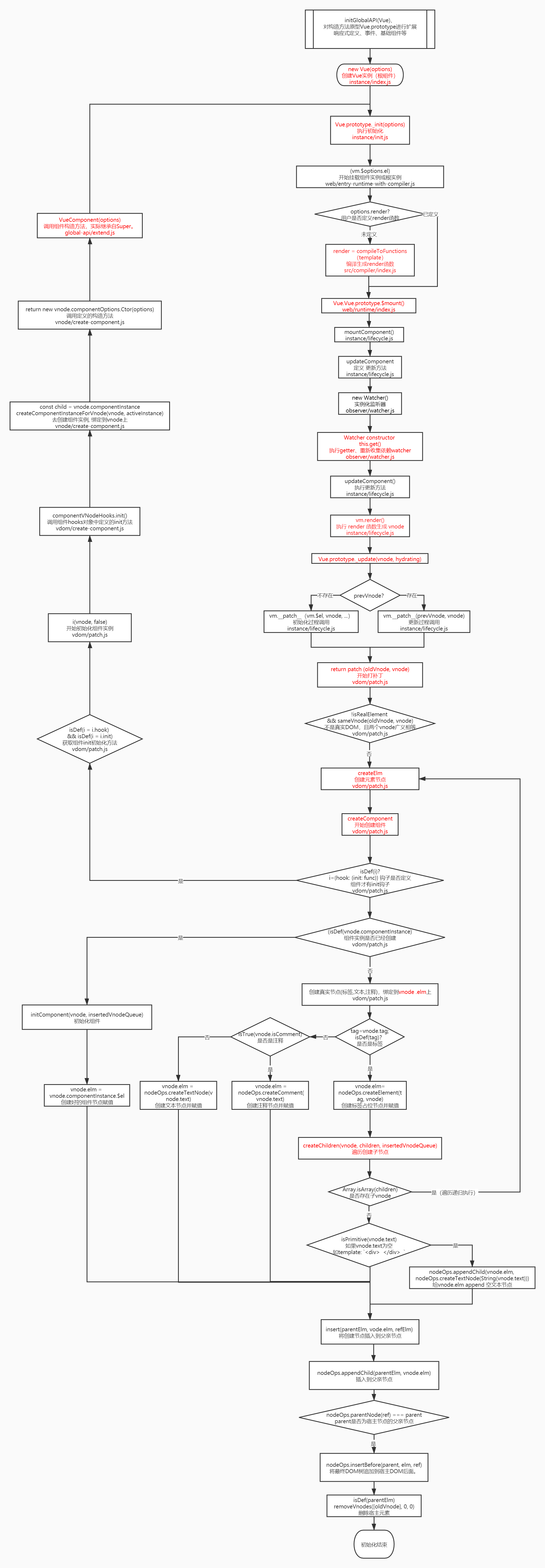
2. 初始化相关代码分析
2.1 initGlobalAPI(Vue) 初始化Vue的全局静态API
平时开发通过 new Vue({...}) 去创建了根实例,当然在此之前,Vue已经做了一些前期的准备工作。Vue 的核心代码都在 src/core 目录中,我们先来看看 core/index.js 这个入口文件,这部分代码逻辑很简单。
import Vue from './instance/index'
import { initGlobalAPI } from './global-api/index'
import { isServerRendering } from 'core/util/env'
import { FunctionalRenderContext } from 'core/vdom/create-functional-component'
// 初始化全局API
initGlobalAPI(Vue)
// 下面代码是服务端ssr渲染使用,web端可以忽略
Object.defineProperty(Vue.prototype, '$isServer', {
get: isServerRendering
})
Object.defineProperty(Vue.prototype, '$ssrContext', {
get () {
/* istanbul ignore next */
return this.$vnode && this.$vnode.ssrContext
}
})
// expose FunctionalRenderContext for ssr runtime helper installation
Object.defineProperty(Vue, 'FunctionalRenderContext', {
value: FunctionalRenderContext
})
// 添加 vue 版本号这个静态变量
Vue.version = '__VERSION__'
export default Vue
我们主要关注的 initGlobalAPI(Vue) 这个函数,它定义在 core/global-api/index.js 文件中,主要给构造函数,添加诸如 Vue.set/delete/use/mixin/extend/component/directive/filter 这些静态方法。
/* @flow */
import config from '../config'
import { initUse } from './use'
import { initMixin } from './mixin'
import { initExtend } from './extend'
import { initAssetRegisters } from './assets'
import { set, del } from '../observer/index'
import { ASSET_TYPES } from 'shared/constants'
import builtInComponents from '../components/index'
import { observe } from 'core/observer/index'
import {
warn,
extend,
nextTick,
mergeOptions,
defineReactive
} from '../util/index'
export function initGlobalAPI (Vue: GlobalAPI) {
// config
// 这个是给 Vue 设置的 config 属性,不要手动的去替换这个对象,
// 如果替换,vue 会给 warn 提示
const configDef = {}
configDef.get = () => config
if (process.env.NODE_ENV !== 'production') {
configDef.set = () => {
warn(
'Do not replace the Vue.config object, set individual fields instead.'
)
}
}
Object.defineProperty(Vue, 'config', configDef)
// exposed util methods.
// NOTE: these are not considered part of the public API - avoid relying on
// them unless you are aware of the risk.
Vue.util = {
warn,
extend,
mergeOptions,
defineReactive
}
// Vue的静态方法: Vue.set/delete/nextTick
Vue.set = set
Vue.delete = del
Vue.nextTick = nextTick
// 2.6 explicit observable API
Vue.observable = <T>(obj: T): T => {
observe(obj)
return obj
}
Vue.options = Object.create(null)
ASSET_TYPES.forEach(type => {
Vue.options[type + 's'] = Object.create(null)
})
// 用于标识 Weex 多实例场景中,通过“base”标识普通对象组件的构造函数。
// this is used to identify the "base" constructor to extend all plain-object
// components with in Weex's multi-instance scenarios.
Vue.options._base = Vue
extend(Vue.options.components, builtInComponents)
// Vue的静态方法: Vue.use/mixin/extend
initUse(Vue)
initMixin(Vue)
initExtend(Vue)
// Vue的静态属性方法:Vue.component/directive/filter
initAssetRegisters(Vue)
}
其中 initAssetRegisters(Vue),通过静态变量数组 [ 'component', 'directive','filter'] 遍历创建了Vue.component/directive/filter 这三个静态属性方法。 静态变量配置在 src/shared/constants.js 文件中,方法定义在 core/global-api/assets.js 文件中。
export const SSR_ATTR = 'data-server-rendered'
// 注册全局API时候使用
export const ASSET_TYPES = [
'component',
'directive',
'filter'
]
// 生命周期函数使用
export const LIFECYCLE_HOOKS = [
'beforeCreate',
'created',
'beforeMount',
'mounted',
'beforeUpdate',
'updated',
'beforeDestroy',
'destroyed',
'activated',
'deactivated',
'errorCaptured',
'serverPrefetch'
]
/* @flow */
import { ASSET_TYPES } from 'shared/constants'
import { isPlainObject, validateComponentName } from '../util/index'
export function initAssetRegisters (Vue: GlobalAPI) {
/**
* Create asset registration methods.
*/
ASSET_TYPES.forEach(type => {
// Vue.comoponent/directive/filter 静态方法的绑定
Vue[type] = function (
id: string,
definition: Function | Object
): Function | Object | void {
if (!definition) {
return this.options[type + 's'][id]
} else {
/* istanbul ignore if */
if (process.env.NODE_ENV !== 'production' && type === 'component') {
validateComponentName(id)
}
if (type === 'component' && isPlainObject(definition)) {
definition.name = definition.name || id
definition = this.options._base.extend(definition)
}
if (type === 'directive' && typeof definition === 'function') {
definition = { bind: definition, update: definition }
}
this.options[type + 's'][id] = definition
return definition
}
}
})
}

2.2 定义Vue构造函数、实例方法
Vue 这个构造函数,定义在 core/instance/index.js 文件中。从代码中可以看到,用工厂模式,执行不同的混入函数,对 Vue.prototype 原型进行加工,给实例添加对应的属性方法。
import { initMixin } from './init'
import { stateMixin } from './state'
import { renderMixin } from './render'
import { eventsMixin } from './events'
import { lifecycleMixin } from './lifecycle'
import { warn } from '../util/index'
function Vue (options) {
if (process.env.NODE_ENV !== 'production' &&
!(this instanceof Vue)
) {
warn('Vue is a constructor and should be called with the `new` keyword')
}
// 构造函数中执行 Vue.prototype._init 方法
this._init(options)
}
// 实例初始化方法: Vue.prototype._init
initMixin(Vue)
// 实例数据状态相关方法: Vue.prototype.$data/$props/$set/$delete,$watch
stateMixin(Vue)
// 实例事件相关方法: Vue.prototype.$on/$once/$off/$emit
eventsMixin(Vue)
// 实例生命周期相关方法:Vue.prototype._update/$forceUpdate/$destory
lifecycleMixin(Vue)
// 实例渲染相关方法:Vue.prototype.$nextTick/_render
renderMixin(Vue)
export default Vue
2.3 new Vue(options)
执行 new Vue() 创建组件实例,同时 this._init(options) 初始化方法被执行,合并用户配置、初始化周期、事件、数据、属性等。
new Vue({
data: {...},
props: {...},
methods: {...},
computed: {...}
...
})
这部分处理逻辑在 core/instance/indexjs 文件中,与 _init() 相关的主要看 initMixin 这个函数。
/* @flow */
import config from '../config'
import { initProxy } from './proxy'
import { initState } from './state'
import { initRender } from './render'
import { initEvents } from './events'
import { mark, measure } from '../util/perf'
import { initLifecycle, callHook } from './lifecycle'
import { initProvide, initInjections } from './inject'
import { extend, mergeOptions, formatComponentName } from '../util/index'
let uid = 0
export function initMixin (Vue: Class<Component>) {
Vue.prototype._init = function (options?: Object) {
const vm: Component = this
// a uid
vm._uid = uid++
let startTag, endTag
/* istanbul ignore if */
if (process.env.NODE_ENV !== 'production' && config.performance && mark) {
startTag = `vue-perf-start:${vm._uid}`
endTag = `vue-perf-end:${vm._uid}`
mark(startTag)
}
// a flag to avoid this being observed
vm._isVue = true
// merge options // 合并用户配置
if (options && options._isComponent) {
// optimize internal component instantiation
// since dynamic options merging is pretty slow, and none of the
// internal component options needs special treatment.
initInternalComponent(vm, options)
} else {
vm.$options = mergeOptions(
resolveConstructorOptions(vm.constructor),
options || {},
vm
)
}
/* istanbul ignore else */
if (process.env.NODE_ENV !== 'production') {
initProxy(vm)
} else {
vm._renderProxy = vm
}
// expose real self // 抛出vue实例本身
vm._self = vm
// 初始化属性:vm.$parent/$root/$children/$refs
initLifecycle(vm)
// 初始化父组件传入的 _parentListeners 事件。
initEvents(vm)
// 初始化render相关:vm.$slot/scopedSlots/_c/$createElement
initRender(vm)
// 调用生命钩子 beforeCreate
callHook(vm, 'beforeCreate')
// 在data/props之前解析注入
initInjections(vm) // resolve injections before data/props
// 初始化相关用户配置的数据响应式:vm._props/_data, 以及computed、watch、methods
initState(vm)
// 在 data/props 之后提供数据
initProvide(vm) // resolve provide after data/props
// 调用生命钩子 created
callHook(vm, 'created')
/* istanbul ignore if */
if (process.env.NODE_ENV !== 'production' && config.performance && mark) {
vm._name = formatComponentName(vm, false)
mark(endTag)
measure(`vue ${vm._name} init`, startTag, endTag)
}
if (vm.$options.el) {
vm.$mount(vm.$options.el)
}
}
}
......
2.4 执行 $mount 进行挂载
执行 $mount 挂载,目录是为了生成 vnode,进而转换为真实DOM执行更新。 $mount 方法在 web 端相关两个 src/platform/web/entry-runtime-with-compiler.js、src/platform/web/runtime/index.js 构建文件中都有定义。我们这里分析 entry-runtime-with-compiler.js 带 compiler 版本的入口文件。关于 Vue scripts 脚本构建相关的内容,大家可以参考我之前写的 这篇文章 的第2章节。
entry-runtime-with-compiler.js 版本,是在 src/platform/web/runtime/index.js 版本的基础上,加 compiler 相关的功能逻辑。它首先保存 runtime 版本的 mount = Vue.prototype.$mount 方法。再重写 Vue.prototype.$mount 方法。如果用户传入 template 模板,就通过编译,转换成 render 函数。最后通过先前保存的 mount 方法进行挂载。下面我们在再来复习一下这个 $mount 实现逻辑。
......
// 1. 保存 runtime 版本 Vue.prototype 上的 $mount 方法
const mount = Vue.prototype.$mount
// 2. 重写 Vue.prototype 上的 $mount(加上 compiler 相关功能逻辑)
Vue.prototype.$mount = function (
el?: string | Element,
hydrating?: boolean
): Component {
el = el && query(el)
/* istanbul ignore if */
if (el === document.body || el === document.documentElement) {
process.env.NODE_ENV !== 'production' && warn(
`Do not mount Vue to <html> or <body> - mount to normal elements instead.`
)
return this
}
// 处理 options 配置
const options = this.$options
// resolve template/el and convert to render function
if (!options.render) {
let template = options.template
if (template) {
if (typeof template === 'string') {
if (template.charAt(0) === '#') {
template = idToTemplate(template)
/* istanbul ignore if */
if (process.env.NODE_ENV !== 'production' && !template) {
warn(
`Template element not found or is empty: ${options.template}`,
this
)
}
}
} else if (template.nodeType) {
template = template.innerHTML
} else {
if (process.env.NODE_ENV !== 'production') {
warn('invalid template option:' + template, this)
}
return this
}
} else if (el) {
template = getOuterHTML(el)
}
// 3. 存在 template 选项内容,就进行编译。
if (template) {
/* istanbul ignore if */
if (process.env.NODE_ENV !== 'production' && config.performance && mark) {
mark('compile')
}
// 编译获取 render 函数
const { render, staticRenderFns } = compileToFunctions(template, {
outputSourceRange: process.env.NODE_ENV !== 'production',
shouldDecodeNewlines,
shouldDecodeNewlinesForHref,
delimiters: options.delimiters,
comments: options.comments
}, this)
options.render = render
options.staticRenderFns = staticRenderFns
/* istanbul ignore if */
if (process.env.NODE_ENV !== 'production' && config.performance && mark) {
mark('compile end')
measure(`vue ${this._name} compile`, 'compile', 'compile end')
}
}
}
// 4. 编译结束,调用 runtime 版本的 $mount 方法进行挂载
return mount.call(this, el, hydrating)
}
......
最后,代码执行 mount.call(this, el, hydrating)。实际上复用了 runtime/index.js 中的定义的 $mount 公共方法,代码注释如下。
/* @flow */
import Vue from 'core/index'
import config from 'core/config'
import { extend, noop } from 'shared/util'
import { mountComponent } from 'core/instance/lifecycle'
import { devtools, inBrowser } from 'core/util/index'
import {
query,
mustUseProp,
isReservedTag,
isReservedAttr,
getTagNamespace,
isUnknownElement
} from 'web/util/index'
import { patch } from './patch'
import platformDirectives from './directives/index'
import platformComponents from './components/index'
// install platform specific utils
Vue.config.mustUseProp = mustUseProp
Vue.config.isReservedTag = isReservedTag
Vue.config.isReservedAttr = isReservedAttr
Vue.config.getTagNamespace = getTagNamespace
Vue.config.isUnknownElement = isUnknownElement
// install platform runtime directives & components
extend(Vue.options.directives, platformDirectives)
extend(Vue.options.components, platformComponents)
// install platform patch function
Vue.prototype.__patch__ = inBrowser ? patch : noop
// 定义了公共的 $mount 方法
// public mount method
Vue.prototype.$mount = function (
el?: string | Element,
hydrating?: boolean
): Component {
el = el && inBrowser ? query(el) : undefined
return mountComponent(this, el, hydrating)
}
// devtools global hook
/* istanbul ignore next */
....
export default Vue
公共 $mount 方法实际上调用了 mountComponent 函数,它 core/instance/lifecycle.js 文件中定义,在mountComponent 函数中,实例化一个渲染Watcher,此时 Watcher 内部逻辑中调用定义的 updateComponent 函数。updateComponent 被调用, vm._render 执行生成 vnode,最终调用 _update 将 vnode 更新成 DOM,代码注释如下。
...
export function mountComponent (
vm: Component,
el: ?Element,
hydrating?: boolean
): Component {
vm.$el = el
if (!vm.$options.render) {
vm.$options.render = createEmptyVNode
if (process.env.NODE_ENV !== 'production') {
/* istanbul ignore if */
if ((vm.$options.template && vm.$options.template.charAt(0) !== '#') ||
vm.$options.el || el) {
warn(
'You are using the runtime-only build of Vue where the template ' +
'compiler is not available. Either pre-compile the templates into ' +
'render functions, or use the compiler-included build.',
vm
)
} else {
warn(
'Failed to mount component: template or render function not defined.',
vm
)
}
}
}
// 调用 beforeMount 钩子
callHook(vm, 'beforeMount')
let updateComponent
/* istanbul ignore if */ // web端可以忽略
if (process.env.NODE_ENV !== 'production' && config.performance && mark) {
updateComponent = () => {
const name = vm._name
const id = vm._uid
const startTag = `vue-perf-start:${id}`
const endTag = `vue-perf-end:${id}`
mark(startTag)
const vnode = vm._render()
mark(endTag)
measure(`vue ${name} render`, startTag, endTag)
mark(startTag)
vm._update(vnode, hydrating)
mark(endTag)
measure(`vue ${name} patch`, startTag, endTag)
}
} else {
// 定义updateComponent方法,渲染 watcher 内部会调用。
// 如果 updateComponent 被调用,render 方法先执行,生成 vnode。
// 最后执行 _update 方法,进行DOM更新,new Vue() 走的是创建DOM逻辑。
updateComponent = () => {
vm._update(vm._render(), hydrating)
}
}
// 初始化渲染 watcher,内部逻辑会调用 updateComponent。
// we set this to vm._watcher inside the watcher's constructor
// since the watcher's initial patch may call $forceUpdate (e.g. inside child
// component's mounted hook), which relies on vm._watcher being already defined
new Watcher(vm, updateComponent, noop, {
before () {
if (vm._isMounted && !vm._isDestroyed) {
callHook(vm, 'beforeUpdate')
}
}
}, true /* isRenderWatcher */)
hydrating = false
// 如果 vm.$vnode === null 当前 vm 的父 vnode 为null。
// 即判断 vm 当前实例为 Vue 的根实例.
// manually mounted instance, call mounted on self
// mounted is called for render-created child components in its inserted hook
if (vm.$vnode == null) {
vm._isMounted = true // 标记该Vue根实例挂载结束
callHook(vm, 'mounted') // 执行钩子 mounted。
}
return vm
}
...

2.5 执行 _render 生成 vnode
vm._render 方法在之前的内容中有提到,它定义 instance/index.js 文件中,它是在 Vue 构造函数定义的时候,给Vue添加的实例方法。

具体逻辑在 src/core/instance/render.js 文件中。其他代码逻辑可以先不关注,主要关注,vnode = render.call(vm._renderProxy, vm.$createElement) 这部分调用。
export function renderMixin (Vue: Class<Component>) {
// install runtime convenience helpers
installRenderHelpers(Vue.prototype)
Vue.prototype.$nextTick = function (fn: Function) {
return nextTick(fn, this)
}
// 给实例初始化render方法
Vue.prototype._render = function (): VNode {
...
try {
// There's no need to maintain a stack because all render fns are called
// separately from one another. Nested component's render fns are called
// when parent component is patched.
currentRenderingInstance = vm
// 调用 render 函数生成 vnode。
// 其中只有当用户自定义render函数时, vm.$createElement 作为回调函数被执行。
vnode = render.call(vm._renderProxy, vm.$createElement)
}
...
return vnode
}
}
render.call 执行,传入了 vm.$createElement,这里就是用户可以通过手写 render 函数,用来生成 vnode 的实现。示例如下,其中 h 就是 vm.$createElement。
<div id="app">
{{title}}
</div>
<script>
window.app = new Vue({
data: {
title: 'vue render'
},
// 手写 render 函数,h === vm.$createElement
render(h) {
return h(
'div',
{
attrs: {
id: 'demo'
}
},
this.title
);
}
}).$mount('#app');
</script>
vm.$createElement 方法会在实例 _init() 初始化阶段,通过执行 initRender 函数添加。

initRender 方法定义在 src/core/instance/render.js 文件中,可以看到 vm._c 和 vm.$createElement 方法最终都是执行 createElement 来生成 vnode。vm._c 是 实例内部方法来创建 vnode,vm.$createElement 是用户手写 render 函数来创建 vnode,代码注释如下。
export function initRender (vm: Component) {
...
// 内部版本,由模板编译的 render 函数使用
// 它就是 template 编译生成 render 函数中使用的 vm._c
vm._c = (a, b, c, d) => createElement(vm, a, b, c, d, false)
// normalization is always applied for the public version, used in
// user-written render functions.
// 用户手写的 render 函数调用(上面例子中的 h 函数会被执行)
vm.$createElement = (a, b, c, d) => createElement(vm, a, b, c, d, true)
...
}
2.5 执行update将vnode转化为真实DOM
上节内容中介绍了 Vue 在 $mount 方法执行挂载的时候,vm._update 方法中的 vm.render() 执行生成 vnode,下面继续分析这个 vm._update 方法。

vm._update 这个方法也定义在 src/core/instance/lifecycle.js 文件中,内部通过 prevVnode 这个条件判断,执行不同参数的 patch 方法,来选择是初始化操作或还是更新操作。本章内容是执行初始化,所以 vm.$el = vm.__patch__(vm.$el, vnode, hydrating, false /* removeOnly */) 这个方法会被执行,创建DOM。
export function lifecycleMixin (Vue: Class<Component>) {
Vue.prototype._update = function (vnode: VNode, hydrating?: boolean) {
const vm: Component = this
const prevEl = vm.$el
const prevVnode = vm._vnode
const restoreActiveInstance = setActiveInstance(vm)
vm._vnode = vnode
// Vue.prototype.__patch__ is injected in entry points
// based on the rendering backend used.
if (!prevVnode) {
// initial render // 初始化调用。
vm.$el = vm.__patch__(vm.$el, vnode, hydrating, false /* removeOnly */)
} else {
// updates // 更新调用
vm.$el = vm.__patch__(prevVnode, vnode)
}
restoreActiveInstance()
// update __vue__ reference
if (prevEl) {
prevEl.__vue__ = null
}
if (vm.$el) {
vm.$el.__vue__ = vm
}
// if parent is an HOC, update its $el as well
if (vm.$vnode && vm.$parent && vm.$vnode === vm.$parent._vnode) {
vm.$parent.$el = vm.$el
}
// updated hook is called by the scheduler to ensure that children are
// updated in a parent's updated hook.
}
...
}
关于 update 后面的流程,简单来说,就是通过遍历子vnode,递归创建DOM子节点,再插入到父节点的逻辑,它实现方式也蛮有意思的,我会在下一篇博文中对这部分代码做分析。
3. 代码调试
demo示例
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8" />
<meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="IE=edge" />
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0" />
<title>init</title>
<script src="../dist/vue.js"></script>
</head>
<body>
<div id="app">
<div>{{title}}</div>
文本
</div>
<script>
window.app = new Vue({
// el: "#app",
data: {
title: '初始化'
}
})
.$mount('#app');
</script>
</body>
</html>
debug:找到断点入口
当vue.js 被加载。dev 环境下,通过 --sourcemap 配置,生成vue.js.map 文件对源码进行定位,通过入口文件entry-runtime-with-compiler.js,知道不同 index.js 入口文件的引用关系如下。entry-runtime-with-compiler.js
⬆
web/runtime/index.js
⬆
src/core/index.js
⬆
core/instance/index.js。 // 该文件较上面三个文件,被最先解析执行
确定断点位置如下。

debug:添加实例属性、方法。
在 core/instance/index.js 文件中断点如下,在 initMixin(Vue) 之前,Vue 只是一个单纯的构造函数。

继续断点执行,可以看到Vue.prototype 上添加了相应的实例方法。

debug:添加全局静态属性方法
断点 core/index.js 文件执行,可以看到给Vue添加的全局静态属性方法。

debug:new Vue()、_init 初始化
断点到demo文件,开始实例化。

step into 进入调用的构造函数。断点 this._init(options) 处。

step into 进入,可以看到此时 vm 实例上还没有相应的属性。

执行断点如下,可以看vm实例上,已经初始化 (parent、)slots、_c 等属性方法。

step over 一直单步执行,直到断点 $mout 处进行挂载。

debug:$mount 执行挂载
断点至 entry-runtime-with-compiler.js 文件的如下位置。此时需要关注 render 函数。通过 compileToFunctions 已经将 template 模板,编译成了 render 函数,赋值给 this.$options 。 并且通过 return mount.call(this, el, hydrating),将当前实例的 this 引用,通过参数的方式进行传递。

生成的 render 函数,可以点击 [[FunctionLocation]] 进行查看,截图如下。

单步执行,进入 调用 mountComponent。

step into 进入函数调用,并且打上断点。

继续单步执行可以看到定义了 updateComponent 这个方法。

继续单步执行到 new Watcher,断点进入。
debug:实例化渲染watcher
断点到 this.get() 处,watcher 的依赖收集等其他代码逻辑这里先不关注,主要关注这个this.get() 执行,内部调用 this.getter.call(vm, vm),进而执行先前定义的 updateComponent 方法。

step into 进入 updateComponent,打上断点标记。

debug:render执行生成vnode
如何生成 render 函数的编译逻辑这里先不关注,之后的博文中会对compiler内容进行代码分析。step over 单步执行一下,让 vm._render() 执行结束,返回 vnode 作为参数传递给 vm._update。

debug:update 执行生成真实DOM
step into 进入 vm._update(vm._render(), hydrating) 方法,它将传入的 vnode 作为当前实例的_vnode 私有属性。

step over 单步往下走,执行完 update 之后,可以看到界面中的DOM已经替换完成。

总结
- Vue 在实例化之前,给原型对象 Vue.prototype 扩展了实例的属性和方法,同时给 Vue 构造函数,扩展全局静态属性和方法。
- 当执行 new Vue() 创建实例,构造函数内部执行 _init 初始化逻辑,给当前实例添加诸如 (parent、)slots、_c 等属性方法。
- 初始化结束之后,执行 $mount 进行挂载,最终是通过 mountComponent 方法来实现的。
- mountComponent 重点是给当前实例创建一个渲染Watcher,在 Watcher 的 this.get() 逻辑中会调用先前定义的 updateComponent 方法,开始更新。
- updateComponent 先执行 vm._render 方法生成 vnode,最终调用 vm._update 将 vnode 转化成真实DOM更新视图。