(1)style.left是带单位"px"的,而offsetLeft没有单位,另外,style.left必须是内联样式,或者在JS中通过style.left赋值,否则取得的将为空字符串(在内部样式和外部样式中指定left是无效的)
(2)如果没有已经定位的父元素,那么offsetLeft指向的是文档(document)的左边缘
<!DOCTYPE html> <html lang="en"> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <title>OFFSET</title> <style> #div1{ height: 500px; 500px; border: 1px solid red; } #div2{ 100px; height: 100px; background: blue; margin-left: 100px; } </style> </head> <body> <div id="div1"> <div id="div2"></div> </div> <button onclick="handle()">click</button> <script> function handle(){ var d2 = document.getElementById("div2"); alert(d2.offsetLeft); //109 console.log(d2.style.left) //打印空白 } </script> </body> </html>
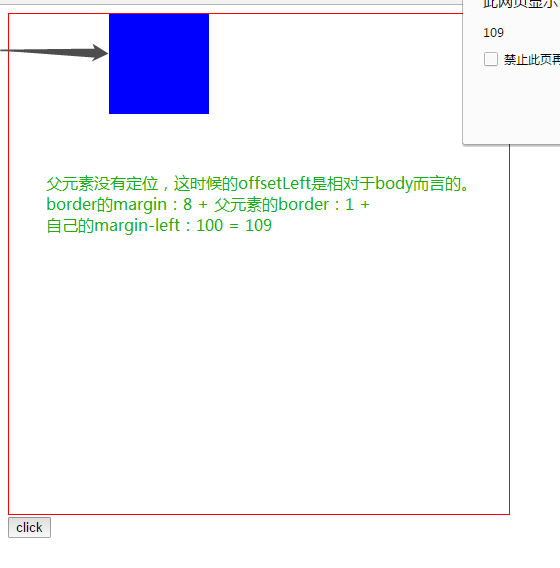
(3)父元素相对定位(代码结构如上,就是父元素增加position:relative)子元素的offsetLeft是相对于父元素
#div1{
height: 500px;
500px;
border: 1px solid red;
position: relative;
}

子元素增加了position:absolute和left:10px; offsetLeft依然是相对于父
(4)获取offsetLeft、offsetTop、offsetWidth、offsetHeight
<!DOCTYPE html> <html lang="en"> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <title>OFFSET</title> <style> #div1{ height: 500px; 500px; border: 1px solid red; position: relative; } #div2{ 100px; height: 100px; background: blue; margin-left: 100px; position: absolute; } </style> </head> <body> <div id="div1"> <div id="div2"></div> </div> <button onclick="handle()">click</button> <script> function handle(){ var d2 = document.getElementById("div2"); console.log(offset(d2)); } function offset(elem){ var obj={ left:elem.offsetLeft, top:elem.offsetTop, elem.offsetWidth, height:elem.offsetHeight } return obj; } </script> </body> </html>
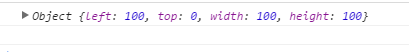
(5)offsetParent的作用
<!DOCTYPE html> <html lang="en"> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <title>OFFSET</title> <style> #div1{ height: 500px; 500px; border: 1px solid red; position: relative; } #div2{ 100px; height: 100px; background: blue; margin-left: 100px; position: absolute; } </style> </head> <body> <div id="div1"> <div id="div2"></div> </div> <button onclick="handle()">click</button> <script> function handle(){ var d2 = document.getElementById("div2"); console.log(offset(d2)); } function offset(elem){ var obj={ left:elem.offsetLeft, top:elem.offsetTop, elem.offsetWidth, height:elem.offsetHeight } while(elem != document.body){ elem = elem.offsetParent ; console.log(elem); obj.left += elem.offsetLeft ; //得到是元素距离视口的左边距和上边距(不包括border) obj.top += elem.offsetTop ; } return obj; } </script> </body> </html>
解释:
偏移量(offset dimension)是javascript中的一个重要的概念。涉及到偏移量的主要是offsetLeft、offsetTop、offsetHeight、offsetWidth这四个属性。当然,还有一个偏移参照——定位父级offsetParent。本文将详细介绍该部分内容

定位父级
在理解偏移大小之前,首先要理解offsetParent。人们并没有把offsetParent翻译为偏移父级,而是翻译成定位父级,很大原因是offsetParent与定位有关
定位父级offsetParent的定义是:与当前元素最近的经过定位(position不等于static)的父级元素,主要分为下列几种情况
【1】元素自身有fixed定位,offsetParent的结果为null
当元素自身有fixed固定定位时,我们知道固定定位的元素相对于视口进行定位,此时没有定位父级,offsetParent的结果为null
[注意]firefox浏览器有兼容性问题
<div id="test" style="position:fixed"></div> <script> //firefox并没有考虑固定定位的问题,返回<body>,其他浏览器都返回null console.log(test.offsetParent); </script>
【2】元素自身无fixed定位,且父级元素都未经过定位,offsetParent的结果为<body>
<div id="test"></div> <script> console.log(test.offsetParent);//<body> </script>
【3】元素自身无fixed定位,且父级元素存在经过定位的元素,offsetParent的结果为离自身元素最近的经过定位的父级元素
<div id="div0" style="position:absolute;">
<div id="div1" style="position:absolute;">
<div id='test'></div>
</div>
</div>
<script>
console.log(test.offsetParent); //<div id="div1">
</script>
【4】<body>元素的parentNode是null
console.log(document.body.offsetParent);//null
IE7-浏览器Bug
对于定位父级offsetParent来说,IE7-浏览器存在以下bug
【bug1】当元素本身经过绝对定位或相对定位,且父级元素无经过定位的元素时,IE7-浏览器下,offsetParent是<html>
<div id="test" style="position:absolute;"></div> <script> //IE7-浏览器返回<html>,其他浏览器返回<body> console.log(test.offsetParent); </script>
<div id="test" style="position:relative;"></div> <script> //IE7-浏览器返回<html>,其他浏览器返回<body> console.log(test.offsetParent); </script>
<div id="test" style="position:fixed;"></div> <script> //firefox并没有考虑固定定位的问题,返回<body>,其他浏览器都返回null console.log(test.offsetParent); </script>
【bug2】如果父级元素存在触发haslayout的元素或经过定位的元素,且offsetParent的结果为离自身元素最近的经过定位或触发haslayout的父级元素
[注意]关于haslayout的详细信息移步至此
<div id="div0" style="display:inline-block;">
<div id='test'></div>
</div>
<script>
//IE7-浏览器返回<div id="div0">,其他浏览器返回<body>
console.log(test.offsetParent);
</script>
<div id="div0" style="position:absolute;">
<div id="div1" style="display:inline-block;">
<div id='test'></div>
</div>
</div>
<script>
//IE7-浏览器返回<div id="div1">,其他浏览器返回<div id="div0">
console.log(test.offsetParent);
</script>
<div id="div0" style="display:inline-block;">
<div id="div1" style="position:absolute;">
<div id='test'></div>
</div>
</div>
<script>
//所有浏览器都返回<div id="div1">
console.log(test.offsetParent);
</script>
偏移量
偏移量共包括offsetHeight、offsetWidth、offsetLeft、offsetTop这四个属性
offsetWidth
offsetWidth表示元素在水平方向上占用的空间大小,无单位(以像素px计)
offsetWidth = border-left-width + padding-left + width + padding-right + border-right-width;
offsetHeight
offsetHeight表示元素在垂直方向上占用的空间大小,无单位(以像素px计)
offsetHeight = border-top-width + padding-top + height + padding-bottom + border-bottom-width
<div id="test" style="100px; height:100px; padding:10px; margin:10px; border:1px solid black;"></div> <script> //122=1+10+100+10+1 console.log(test.offsetWidth); console.log(test.offsetHeight); </script>
[注意]如果存在垂直滚动条,offsetWidth也包括垂直滚动条的宽度;如果存在水平滚动条,offsetHeight也包括水平滚动条的高度
<div id="test" style="100px; height:100px; padding:10px; margin:10px; border:1px solid black; overflow: scroll;"></div>
<script>
//IE8-浏览器将垂直滚动条的宽度计算在width宽度和height高度中,width和height的值仍然是100px;
//而其他浏览器则把垂直滚动条的宽度从width宽度中移出,把水平滚动条的高度从height高度中移出,则滚动条宽度为17px,width宽度和height高度为剩下的83px
if(window.getComputedStyle){
console.log(getComputedStyle(test).width,getComputedStyle(test).height)//83px
}else{
console.log(test.currentStyle.width,test.currentStyle.height);//100px
}
//122=1+10+100+10+1
console.log(test.offsetWidth,test.offsetHeight);
</script>
offsetTop
offsetTop表示元素的上外边框至offsetParent元素的上内边框之间的像素距离
offsetLeft
offsetLeft表示元素的左外边框至offsetParent元素的左内边框之间的像素距离
<div id="out" style="padding: 5px;position: relative;margin: 6px;border:1px solid black">
<div id="test" style="100px; height:100px; margin:10px;"></div>
</div>
<script>
//15=test.marginTop(10) + out.paddingTop(5)
alert(test.offsetTop);
//15=test.marginLeft(10) + out.paddingLeft(5)
alert(test.offsetLeft);
</script>
IE7-Bug
IE7-浏览器在offsetTop属性的处理上存在bug
【1】若父级设置position: relative,则在IE7-浏览器下,offsetTop值为offsetParent元素的paddingBottom值
<div id="out" style="padding: 5px;position: relative;">
<div id="test" style="100px; height:100px; margin:10px;"></div>
</div>
<script>
//其他浏览器返回15(5+10),而IE7-浏览器返回5
console.log(test.offsetTop);
</script>
【2】若父级设置position: aboslute(或其他触发haslayout的条件),offsetTop值为offsetParent元素的paddingBottom值和当前元素的marginTop值的较大值
<div id="out" style="padding: 5px;position:absolute;">
<div id="test" style="100px; height:100px; margin:10px;"></div>
</div>
<script>
//其他浏览器返回15(5+10),而IE7-浏览器返回10(10和5的较大值)
console.log(test.offsetTop);
</script>
页面偏移
要知道某个元素在页面上的偏移量,将这个元素的offsetLeft和offsetTop与其offsetParent的相同属性相加,并加上offsetParent的相应方向的边框,如此循环直到根元素,就可以得到元素到页面的偏移量
[注意]在默认情况下,IE8-浏览器下如果使用currentStyle()方法获取<html>和<body>(甚至普通div元素)的边框宽度都是medium,而如果使用clientLeft(或clientTop)获取边框宽度,则是实际的数值
html,body{border: 0;}
body{margin:0;}
function getElementLeft(element){
var actualLeft = element.offsetLeft;
var current = element.offsetParent;
while(current != null){
actualLeft += current.offsetLeft + current.clientLeft;
current = current.offsetParent;
}
return actualLeft + 'px';
}
function getElementTop(element){
var actualTop = element.offsetTop;
var current = element.offsetParent;
while(current != null){
actualTop += current.offsetTop + current.clientTop;
current = current.offsetParent;
}
return actualTop + 'px';
}
<div style="padding: 20px;border:1px solid black;position:absolute;">
<div id="test" style="100px; height:100px; margin:10px;"></div>
</div>
<script>
//其他浏览器返回31(10+20+1),而IE7-浏览器返回21((20和10的较大值)+1)
console.log(getElementTop(test));
//所有浏览器返回31(10+20+1)
console.log(getElementLeft(test));
</script>
注意事项
【1】所有偏移量属性都是只读的
<div id="test" style="100px; height:100px; margin:10px;"></div> <script> console.log(test.offsetWidth);//100 //IE8-浏览器会报错,其他浏览器则静默失败 test.offsetWidth = 10; console.log(test.offsetWidth);//100 </script>
【2】如果给元素设置了display:none,则它的偏移量属性都为0
<div id="test" style="100px; height:100px; margin:10px;display:none"></div> <script> console.log(test.offsetWidth);//0 console.log(test.offsetTop);//0 </script>
【3】每次访问偏移量属性都需要重新计算
<div id="test" style="100px; height:100px; margin:10px;"></div>
<script>
console.time("time");
for(var i = 0; i < 100000; i++){
var a = test.offsetWidth;
}
console.timeEnd('time');//65.129ms
</script>
<div id="test" style="100px; height:100px; margin:10px;"></div>
<script>
console.time("time");
var a = test.offsetWidth;
for(var i = 0; i < 100000; i++){
var b = a;
}
console.timeEnd('time');//1.428ms
</script>
由上面代码对比可知,重复访问偏移量属性需要耗费大量的性能,所以要尽量避免重复访问这些属性。如果需要重复访问,则把它们的值保存在变量中,以提高性能