rpc服务框架目前主要有 thrift, grpc, dubbo, HSF等
这里主要介绍thrift框架
git地址 :https://github.com/apache/thrift/tree/0.9.1
1. 接口定义 tutorial.thrift
include "shared.thrift"
/**
* Thrift files can namespace, package, or prefix their output in various
* target languages.
*/
namespace cl tutorial
namespace cpp tutorial
namespace d tutorial
namespace dart tutorial
namespace java tutorial
namespace php tutorial
namespace perl tutorial
namespace haxe tutorial
namespace netcore tutorial
namespace netstd tutorial
/**
* Thrift lets you do typedefs to get pretty names for your types. Standard
* C style here.
*/
typedef i32 MyInteger
/**
* Thrift also lets you define constants for use across languages. Complex
* types and structs are specified using JSON notation.
*/
const i32 INT32CONSTANT = 9853
const map<string,string> MAPCONSTANT = {'hello':'world', 'goodnight':'moon'}
/**
* You can define enums, which are just 32 bit integers. Values are optional
* and start at 1 if not supplied, C style again.
*/
enum Operation {
ADD = 1,
SUBTRACT = 2,
MULTIPLY = 3,
DIVIDE = 4
}
/**
* Structs are the basic complex data structures. They are comprised of fields
* which each have an integer identifier, a type, a symbolic name, and an
* optional default value.
*
* Fields can be declared "optional", which ensures they will not be included
* in the serialized output if they aren't set. Note that this requires some
* manual management in some languages.
*/
struct Work {
1: i32 num1 = 0,
2: i32 num2,
3: Operation op,
4: optional string comment,
}
/**
* Structs can also be exceptions, if they are nasty.
*/
exception InvalidOperation {
1: i32 whatOp,
2: string why
}
/**
* Ahh, now onto the cool part, defining a service. Services just need a name
* and can optionally inherit from another service using the extends keyword.
*/
service Calculator extends shared.SharedService {
/**
* A method definition looks like C code. It has a return type, arguments,
* and optionally a list of exceptions that it may throw. Note that argument
* lists and exception lists are specified using the exact same syntax as
* field lists in struct or exception definitions.
*/
void ping(),
i32 add(1:i32 num1, 2:i32 num2),
i32 calculate(1:i32 logid, 2:Work w) throws (1:InvalidOperation ouch),
/**
* This method has a oneway modifier. That means the client only makes
* a request and does not listen for any response at all. Oneway methods
* must be void.
*/
oneway void zip()
}
2. 根据接口定义文件生成相应的服务接口
thrift -r --gen py tutorial.thrift 根据thrift接口定义生成服务接口
执行完后会在当前目录生成 gen-py文件夹, 下面包含 tutorial shared两个子文件夹
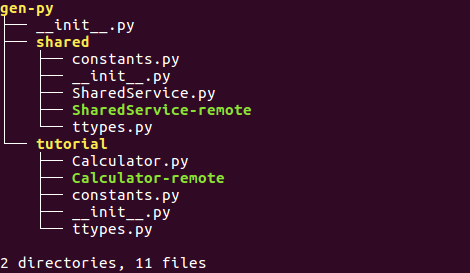
主要文件就是Calulator.py 定义了相应语言的接口协议
3. 根据接口,实现接口功能,提供服务
这步是最重要的,开始实现接口功能, 上面由接口定义文件service可知, 定义了4个功能: ping add caculate zip
这里用python实现上述接口, PythonServer.py
import glob
import sys
sys.path.append('gen-py')
sys.path.insert(0, glob.glob('../../lib/py/build/lib*')[0])
from tutorial import Calculator
from tutorial.ttypes import InvalidOperation, Operation
from shared.ttypes import SharedStruct
from thrift.transport import TSocket
from thrift.transport import TTransport
from thrift.protocol import TBinaryProtocol
from thrift.server import TServer
class CalculatorHandler:
def __init__(self):
self.log = {}
def ping(self):
print('ping()')
def add(self, n1, n2):
print('add(%d,%d)' % (n1, n2))
return n1 + n2
def calculate(self, logid, work):
print('calculate(%d, %r)' % (logid, work))
if work.op == Operation.ADD:
val = work.num1 + work.num2
elif work.op == Operation.SUBTRACT:
val = work.num1 - work.num2
elif work.op == Operation.MULTIPLY:
val = work.num1 * work.num2
elif work.op == Operation.DIVIDE:
if work.num2 == 0:
x = InvalidOperation()
x.whatOp = work.op
x.why = 'Cannot divide by 0'
raise x
val = work.num1 / work.num2
else:
x = InvalidOperation()
x.whatOp = work.op
x.why = 'Invalid operation'
raise x
log = SharedStruct()
log.key = logid
log.value = '%d' % (val)
self.log[logid] = log
return val
def getStruct(self, key):
print('getStruct(%d)' % (key))
return self.log[key]
def zip(self):
print('zip()')
if __name__ == '__main__':
handler = CalculatorHandler()
processor = Calculator.Processor(handler)
transport = TSocket.TServerSocket(host='127.0.0.1', port=9090)
tfactory = TTransport.TBufferedTransportFactory()
pfactory = TBinaryProtocol.TBinaryProtocolFactory()
server = TServer.TSimpleServer(processor, transport, tfactory, pfactory)
python PythonServer.py 然后可以看到rpc对外开始提供服务, 这里注意host, port
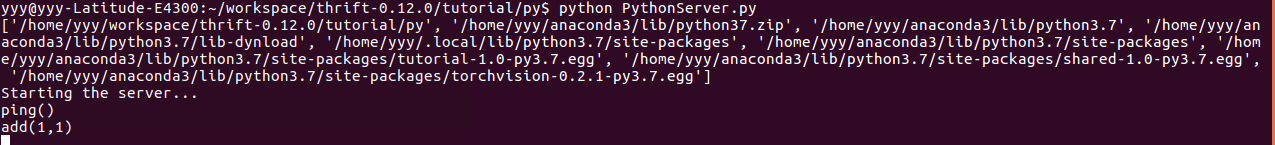
4.实现客户端,连接rpc服务接口
PythonClient.py
import sys
import glob
sys.path.append('gen-py')
sys.path.insert(0, glob.glob('../../lib/py/build/lib*')[0])
from tutorial import Calculator
from tutorial.ttypes import InvalidOperation, Operation, Work
from thrift import Thrift
from thrift.transport import TSocket
from thrift.transport import TTransport
from thrift.protocol import TBinaryProtocol
def main():
# Make socket
transport = TSocket.TSocket('localhost', 9090)
# Buffering is critical. Raw sockets are very slow
transport = TTransport.TBufferedTransport(transport)
# Wrap in a protocol
protocol = TBinaryProtocol.TBinaryProtocol(transport)
# Create a client to use the protocol encoder
client = Calculator.Client(protocol)
# Connect!
transport.open()
client.ping()
print('ping()')
sum_ = client.add(1, 1)
print('1+1=%d' % sum_)
work = Work()
work.op = Operation.DIVIDE
work.num1 = 1
work.num2 = 0
try:
quotient = client.calculate(1, work)
print('Whoa? You know how to divide by zero?')
print('FYI the answer is %d' % quotient)
except InvalidOperation as e:
print('InvalidOperation: %r' % e)
work.op = Operation.SUBTRACT
work.num1 = 15
work.num2 = 10
diff = client.calculate(1, work)
print('15-10=%d' % diff)
log = client.getStruct(1)
print('Check log: %s' % log.value)
# Close!
transport.close()
启动客户端,连接rpc服务

可以看到,已经能get到结果了,通过rpc,可以实现,接口实现与使用的分离, 使用不同语言,而且效率远比restful接口高效