教材
-
并发
- 概念:只要逻辑控制流在时间上重叠,那么就可以称为并发。
- 意义:访问慢速设备(如I/O设备)
- 与人交互:每次用户进行某种操作的请求的时候,一个独立的逻辑并发流被用来处理这个程序。
通过推迟工作来降低延迟服务多个网络客户端 - 进程:每个逻辑控制流都是一个进程,由内核进行调度和维护。进程间的通信也必须有显式的通信机制。
- I/O多路复用:在并发编程中,一个程序在上下文中调用它们自己的逻辑流。因为程序是一个单独的进程,所以所有的流共享一个地址空间。
- 线程:像进程一样由内核调用,像I/O多路复用一样共享同样的虚拟地址空间
-
构造并发服务器过程
- (假设是一个服务器端两个客户端,服务器端始终监听)服务器正在监听一个描述符3,客户端1向服务器端提出申请,服务器端返回一个已经建立连接描述符4;服务器派生一个子进程处理该连接。子进程拥有从父进程服务器描述符列表中完整的拷贝。此时,父进程与子进程需要各自切断连接:父进程切断它的描述符列表中的连接描述符4,子进程切断它拷贝的监听描述符3;服务器接收新的客户端2的连接请求,同样返回连接描述符5,派生一个子进程;服务器端继续等待请求,两个子进程并发地处理客户端连接。【直到父子进程都关闭,到客户端的连接才会终止】
-
基于I/O多路复用的并发编程
- 说明:如果服务器要既能相应客户端的连接请求,又能响应用户的键盘输入,那么会产生等待谁的冲突。使用select函数,要求内核挂起进程,只有在一个或多个I/O事件发生之后,才将控制返回给进程。
- select函数原型:int select(int n,fd_set *fdset,UNLL,NULL,NULL);返回已经准备好的描述符的非零的个数,若出错则为-1
- 说明:select函数有两个输入,一个称为读集合的描述符集合和该集合的基数。select函数会一直阻塞直到该集合中有一个或者多个描述符准备好可以读了。当且仅当一个从该描述符读取字节的请求不会被拒绝的时候,该描述符才是准备好可以读的。另外,每次调用select函数的时候都要更新读集合。
-
基于I/O多路复用的并发echo服务器
- 综述:服务器借助select函数检测输入事件的发生。当每个已经连接的描述符准备好可读的时候,服务器就为相应的状态机执行转移(即,从描述符读和写回一个文本行)。【什么是写回?可以参考下方的代码中的check_client函数的解释】
- 分步解释:活动客户端的集合【注:这里的意思应该就是可能并且可以发送连接请求进行文本行读取的客户端在进行输入的时候需要用到的数据】维护在一个pool结构里。调用init函数初始化池,然后无限循环。在循环的每次迭代中,服务器端调用select函数来检测两种不同类型的输入事件:来自一个新客户的连接请求到达【先打开连接,然后调用add_client函数将其添加到池里】;一个已经存在的客户的已连接描述符准备好可以读了。【因为是无限循环,所以每次循环开始的时候服务器都会把现在active的客户端描述符赋值给表示已准备好的描述符中去,然后检测有没有“新来的”客户端(如果有就放入池中),最后是统一把已经准备好的描述符的文本行写回】。
-
状态机
- I/O多路复用可以作为并发事件驱动程序的基础;在并发事件中,流是因为某种事件而前进的。一般是将逻辑流模型化为状态机。一个状态机可以简化为一组 状态、输入事件和转移(将前两者映射到状态) 。(自循环是同一输入和输出状态之间的转移)
- 通常把状态机画成有向图,其中节点表示状态,有向弧表示转移,弧上的标号表示输入事件。对于每一个新的客户端k,基于I/O多路复用的并发服务器会创建一个新的状态机sk,并将它和已连接描述符dk连接起来。
-
基于线程的并发编程
- 线程,就是运行在进程上下文中的逻辑流,由内核自动调度。每个线程都有它自己的线程上下文,包括唯一的一个整数线程ID、栈、栈指针等。所有运行在一个进程里的线程共享该进程的地址空间。
- 线程执行模型:每个进程开始生命周期的时候都是单一线程,这个线程称为主线程;在某一时刻,主线程创建一个对等线程,从这个时间点开始,两个线程并发地运行。
- 与进程的区别:线程的上下文比进程上下文小得多,而且上下文切换比进程快得多;线程不像进程那样有着严格的父子层次,主线程和其他线程的区别在于前者是进程中第一个运行的线程(仅此而已)————很重要的影响是,线程可以杀死它的任何对等线程。
-
Posix线程
- Posix线程(Pthreads)是在C程序中处理线程的一个标准接口,在大多数unix系统中都可以调用。它定义了约60个函数,允许程序创建、杀死和回收线程,与对等线程安全地共享数据等。
- 主线程创建一个对等线程,然后等待它的终止。对等线程输出“Hello,world! ”并终止。当主线程检测到对等线程终止以后,它就通过调用exit终止该进程。
- 分析:线程的代码和本地数据被封装在一个线程示例(thread routine)中。代码第2行,每个线程都用一个通用指针为输入,并返回一个通用指针;代码第7行,主线程创建对等线程,在pthread_create函数返回之后,主线程和对等线程才同时运行。
-
进度图
- 概念:将n个并发线程的执行模型化为一条n维笛卡儿空间中的轨迹线。每条轴k对应于线程k的进度。每个点(I1,I2,I3……,In)代表线程k已经完成了指令IK这一状态。进度图将指令执行模型化为从一种状态到另一种状态的转换。转换被表示为从一点到相邻点的有向边。
-
互斥
- 我们要确保每个线程在执行它的临界区中的指令的时候,拥有对共享变量的互斥的访问。通常这种现象称为互斥。在进度图中,两个临界区的交集形成的状态空间区域称为不安全区(不包括毗邻不安全区的那些点)。
-
信号量
- 概念:信号量s是具有非负整数值的全局变量,只能由两种特殊的操作来处理
- 操作:P(s):如果s为0,那么P将s减1,并且立即返回。如果s为零,那么就挂起这个线程,直到s为非零;而V操作会重启这个线程。在重启之后,P操作将s减一,并将控制返回给调用者V(s):V操作将s加一;如果有任何线程阻塞在P操作等待s变成非0,那么V操作会重启这些线程中的一个,然后该线程将s减1,完成它的P操作。
- 【注意:P中的测试和减1操作是不可分割的;V中的重启和加1操作也是不可分割的。此外,V的定义中没有说明等待线程被重启的顺序,也就是说,当多个线程在等待同一个信号量的时候,你不能预测V操作要重启哪个线程】
11.用信号量实现互斥的代码
volitale int cnt = 0;
sem_t mutex;
Sem_init(&mutex,0,1);//mutex = 1;
for(int i =0;i<niters;i++)
{
P(&mutex);
cnt++;
V(&mutex);
}
- 利用互斥信号量来调度共享资源——读者&写者问题
- 概述:一组并发的线程要访问一个共享对象。有些线程只读对象,其他线程只修改对象。前者叫做读者,后者叫做写者。写者必须拥有对对象的独占的访问,而读者可以和无限多的其他的读者共享对象。
- 解决方案:信号量w控制对访问共享对象的临界区的访问。信号量mutex保护对共享变量readcnt的访问,readcnt统计当前在临界区中的读者的数量。每当一个写者进入临界区的时候,它对w加锁,离开的时候对w解锁。这就保证了任意一个时刻缓冲区中最多有一个写者。另一方面,只有第一个进入临界区的读者会对w加锁,最后一个离开临界区的读者对w解锁。这就意味着,读者可以没有障碍地进入临界区。
代码
- condvar
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <pthread.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
typedef struct _msg{
struct _msg * next;
int num;
} msg;
msg *head;
pthread_cond_t has_product = PTHREAD_COND_INITIALIZER;
pthread_mutex_t lock = PTHREAD_MUTEX_INITIALIZER;
void *consumer ( void * p )
{
msg * mp;
for( ;; ) {
pthread_mutex_lock( &lock );
while ( head == NULL )
pthread_cond_wait( &has_product, &lock );
mp = head;
head = mp->next;
pthread_mutex_unlock ( &lock );
printf( "Consume %d tid: %d
", mp->num, pthread_self());
free( mp );
sleep( rand() % 5 );
}
}
void *producer ( void * p )
{
msg * mp;
for ( ;; ) {
mp = malloc( sizeof(msg) );
pthread_mutex_lock( &lock );
mp->next = head;
mp->num = rand() % 1000;
head = mp;
printf( "Produce %d tid: %d
", mp->num, pthread_self());
pthread_mutex_unlock( &lock );
pthread_cond_signal( &has_product );
sleep ( rand() % 5);
}
}
int main(int argc, char *argv[] )
{
pthread_t pid1, cid1;
pthread_t pid2, cid2;
srand(time(NULL));
pthread_create( &pid1, NULL, producer, NULL);
pthread_create( &pid2, NULL, producer, NULL);
pthread_create( &cid1, NULL, consumer, NULL);
pthread_create( &cid2, NULL, consumer, NULL);
pthread_join( pid1, NULL );
pthread_join( pid2, NULL );
pthread_join( cid1, NULL );
pthread_join( cid2, NULL );
return 0;
}
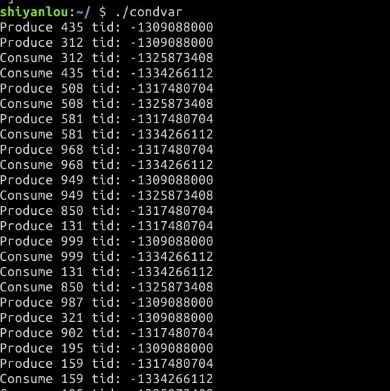
消费者等待生产者产出产品后才打印,否则消费者阻塞等待生产者生产。
- count
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <pthread.h>
#define NLOOP 5000
int counter;
void *doit( void * );
int main(int argc, char **argv)
{
pthread_t tidA, tidB;
pthread_create( &tidA ,NULL, &doit, NULL );
pthread_create( &tidB ,NULL, &doit, NULL );
pthread_join( tidA, NULL );
pthread_join( tidB, NULL );
return 0;
}
void * doit( void * vptr)
{
int i, val;
for ( i=0; i<NLOOP; i++ ) {
val = counter++;
printf("%x: %d
", (unsigned int) pthread_self(), val + 1);
counter = val + 1;
}
}
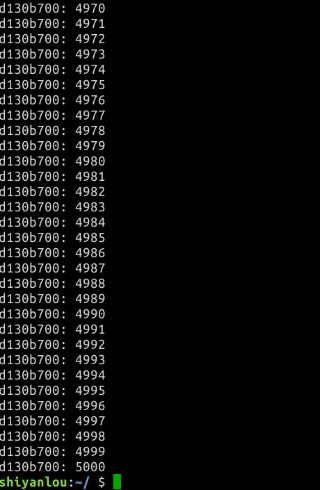
不加锁的创建两个线程共享同一变量都实现加一操作
- countwithmutex
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <pthread.h>
#define NLOOP 5000
int counter;
pthread_mutex_t counter_mutex = PTHREAD_MUTEX_INITIALIZER;
void *doit( void * );
int main(int argc, char **argv)
{
pthread_t tidA, tidB;
pthread_create( &tidA ,NULL, &doit, NULL );
pthread_create( &tidB ,NULL, &doit, NULL );
pthread_join( tidA, NULL );
pthread_join( tidB, NULL );
return 0;
}
void * doit( void * vptr)
{
int i, val;
for ( i=0; i<NLOOP; i++ ) {
pthread_mutex_lock( &counter_mutex );
val = counter++;
printf("%x: %d
", (unsigned int) pthread_self(), val + 1);
counter = val + 1;
pthread_mutex_unlock( &counter_mutex );
}
return NULL;
}
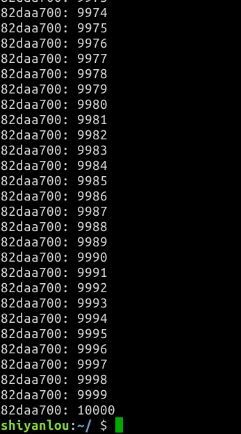
引入互斥锁
- cp_t
#include <stdio.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <fcntl.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <sys/mman.h>
#include <pthread.h>
typedef struct {
char *src_address;
char *dest_address;
int len;
} arg_t;
static void err_sys(const char *s);
static int get_file_length(int fd);
static int extend(int fd, int len);
arg_t map_src_dest(const char *src, const char *dest);
static void *cpy(void *arg);
void divide_thread(int pnum, arg_t arg_file);
int main(int argc, char *argv[])
{
arg_t arg_file;
if (argc != 4) {
fprintf(stderr, "Usage:%s file1 file2 thread_num", argv[0]);
exit(1);
}
arg_file = map_src_dest(argv[1], argv[2]);
divide_thread(atoi(argv[3]), arg_file);
munmap(arg_file.src_address, arg_file.len);
munmap(arg_file.dest_address, arg_file.len);
return 0;
}
static void err_sys(const char *s)
{
perror(s);
exit(1);
}
static int get_file_length(int fd)
{
int position = lseek(fd, 0, SEEK_CUR);
int length = lseek(fd, 0, SEEK_END);
lseek(fd, position, SEEK_SET);
return length;
}
static int extend(int fd, int len)
{
int file_len = get_file_length(fd);
if (file_len >= len) {
return -1;
}
lseek(fd, len - file_len - 1, SEEK_END);
write(fd, "", 1);
return 0;
}
arg_t map_src_dest(const char *src, const char *dest)
{
int fd_src, fd_dest, len;
char *src_address, *dest_address;
arg_t arg_file;
fd_src = open(src, O_RDONLY);
if (fd_src < 0) {
err_sys("open src");
}
len = get_file_length(fd_src);
src_address = mmap(NULL, len, PROT_READ, MAP_SHARED, fd_src, 0);
if (src_address == MAP_FAILED) {
err_sys("mmap src");
}
close(fd_src);
fd_dest = open(dest, O_RDWR | O_CREAT | O_TRUNC, 0644);
if (fd_dest < 0) {
err_sys("open dest");
}
extend(fd_dest, len);
dest_address = mmap(NULL, len, PROT_WRITE, MAP_SHARED, fd_dest, 0);
if (dest_address == MAP_FAILED) {
err_sys("mmap dest");
}
close(fd_dest);
arg_file.len = len;
arg_file.src_address = src_address;
arg_file.dest_address = dest_address;
return arg_file;
}
static void *cpy(void *arg)
{
char *src_address, *dest_address;
int len;
src_address = ((arg_t *) arg)->src_address;
dest_address = ((arg_t *) arg)->dest_address;
len = ((arg_t *) arg)->len;
memcpy(dest_address, src_address, len);
return NULL;
}
void divide_thread(int pnum, arg_t arg_file)
{
int i, len;
char *src_address, *dest_address;
pthread_t *pid;
arg_t arg[pnum];
len = arg_file.len;
src_address = arg_file.src_address;
dest_address = arg_file.dest_address;
pid = malloc(pnum * sizeof(pid));
if (pnum > len) {
fprintf(stderr,
"too many threads, even larger than length, are you crazy?!
");
exit(1);
}
for (i = 0; i < pnum; i++) {
arg[i].src_address = src_address + len / pnum * i;
arg[i].dest_address = dest_address + len / pnum * i;
if (i != pnum - 1) {
arg[i].len = len / pnum;
} else {
arg[i].len = len - len / pnum * i;
}
pthread_create(&pid[i], NULL, cpy, &arg[i]);
}
for (i = 0; i < pnum; i++) {
pthread_join(pid[i], NULL);
}
free(pid);
}
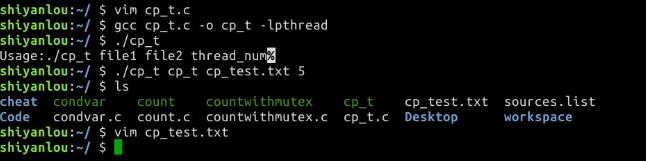
用法:./cp_t [源文件名] [目的文件名] [创建线程数]
- createthread
#include <stdio.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <pthread.h>
#include <unistd.h>
pthread_t ntid;
void printids( const char *s )
{
pid_t pid;
pthread_t tid;
pid = getpid();
tid = pthread_self();
printf("%s pid %u tid %u (0x%x)
", s , ( unsigned int ) pid,
( unsigned int ) tid, (unsigned int ) tid);
}
void *thr_fn( void * arg )
{
printids( arg );
return NULL;
}
int main( void )
{
int err;
err = pthread_create( &ntid, NULL, thr_fn, "new thread: " );
if ( err != 0 ){
fprintf( stderr, "can't create thread: %s
", strerror( err ) );
exit( 1 );
}
printids( "main threads: " );
sleep(1);
return 0;
}
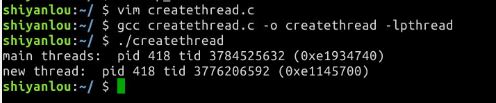
打印进程和线程ID
- semphore
#include <stdio.h>
#include <pthread.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <semaphore.h>
#define NUM 5
int queue[NUM];
sem_t blank_number, product_number;
void *producer ( void * arg )
{
static int p = 0;
for ( ;; ) {
sem_wait( &blank_number );
queue[p] = rand() % 1000;
printf("Product %d
", queue[p]);
p = (p+1) % NUM;
sleep ( rand() % 5);
sem_post( &product_number );
}
}
void *consumer ( void * arg )
{
static int c = 0;
for( ;; ) {
sem_wait( &product_number );
printf("Consume %d
", queue[c]);
c = (c+1) % NUM;
sleep( rand() % 5 );
sem_post( &blank_number );
}
}
int main(int argc, char *argv[] )
{
pthread_t pid, cid;
sem_init( &blank_number, 0, NUM );
sem_init( &product_number, 0, 0);
pthread_create( &pid, NULL, producer, NULL);
pthread_create( &cid, NULL, consumer, NULL);
pthread_join( pid, NULL );
pthread_join( cid, NULL );
sem_destroy( &blank_number );
sem_destroy( &product_number );
return 0;
}
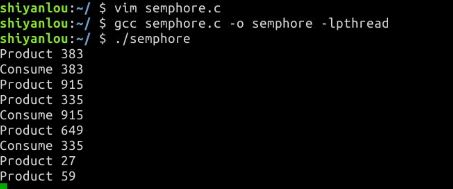
- share
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <pthread.h>
#include <unistd.h>
char buf[BUFSIZ];
void *thr_fn1( void *arg )
{
printf("thread 1 returning %d
", getpid());
printf("pwd:%s
", getcwd(buf, BUFSIZ));
*(int *)arg = 11;
return (void *) 1;
}
void *thr_fn2( void *arg )
{
printf("thread 2 returning %d
", getpid());
printf("pwd:%s
", getcwd(buf, BUFSIZ));
pthread_exit( (void *) 2 );
}
void *thr_fn3( void *arg )
{
while( 1 ){
printf("thread 3 writing %d
", getpid());
printf("pwd:%s
", getcwd(buf, BUFSIZ));
sleep( 1 );
}
}
int n = 0;
int main( void )
{
pthread_t tid;
void *tret;
pthread_create( &tid, NULL, thr_fn1, &n);
pthread_join( tid, &tret );
printf("n= %d
", n );
printf("thread 1 exit code %d
", (int) tret );
pthread_create( &tid, NULL, thr_fn2, NULL);
pthread_join( tid, &tret );
printf("thread 2 exit code %d
", (int) tret );
pthread_create( &tid, NULL, thr_fn3, NULL);
sleep( 3 );
pthread_cancel(tid);
pthread_join( tid, &tret );
printf("thread 3 exit code %d
", (int) tret );
}

获得线程的终止状态
- threadexit
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <pthread.h>
#include <unistd.h>
void *thr_fn1( void *arg )
{
printf("thread 1 returning %d
", getpid());
*(int *)arg = 11;
return (void *) 1;
}
void *thr_fn2( void *arg )
{
printf("thread 2 returning %d
", getpid());
pthread_exit( (void *) 2 );
}
void *thr_fn3( void *arg )
{
while( 1 ){
printf("thread 3 writing %d
", getpid());
sleep( 1 );
}
}
int n = 0;
int main( void )
{
pthread_t tid;
void *tret;
pthread_create( &tid, NULL, thr_fn1, &n);
pthread_join( tid, &tret );
printf("n= %d
", n );
printf("thread 1 exit code %d
", (int) tret );
pthread_create( &tid, NULL, thr_fn2, NULL);
pthread_join( tid, &tret );
printf("thread 2 exit code %d
", (int) tret );
pthread_create( &tid, NULL, thr_fn3, NULL);
sleep( 3 );
pthread_cancel(tid);
pthread_join( tid, &tret );
printf("thread 3 exit code %d
", (int) tret );
}
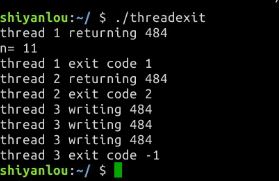
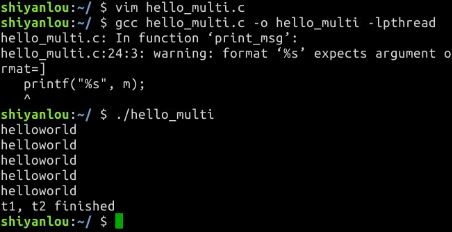
- hello_multi
#include <stdio.h>
#include <pthread.h>
#define NUM 5
void *print_msg(void *);
int main()
{
pthread_t t1, t2; /* two threads */
//print_msg("hello");
pthread_create(&t1, NULL, print_msg, (void *)"hello");
//print_msg("world
");
pthread_create(&t2, NULL, print_msg, (void *)"world
");
pthread_join(t1, NULL);
pthread_join(t2, NULL);
printf("t1, t2 finished
");
return 0;
}
void *print_msg(void *m)
{
char *cp = (char *) m;
int i;
for(i=0 ; i<NUM ; i++){
printf("%s", m);
fflush(stdout);
sleep(1);
}
return NULL;
}
- hello_multi1
#include <stdio.h>
#include <pthread.h>
#define NUM 5
void *print_msg(void *);
int main()
{
pthread_t t[100]; /* two threads */
char arg[30];
int i;
for(i=0; i<100; i++){
sprintf(arg, "hello%d
", i);
pthread_create(&t[i], NULL, print_msg, (void *)arg);
}
for(i=0; i<100; i++)
pthread_join(t[i], NULL);
return 0;
}
void *print_msg(void *m)
{
char *cp = (char *) m;
int i;
for(i=0 ; i<NUM ; i++){
printf("%s", m);
fflush(stdout);
sleep(1);
}
return NULL;
}
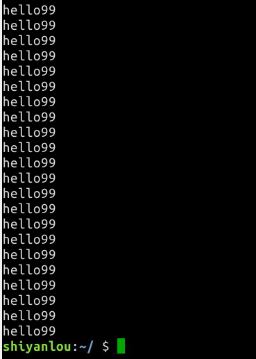
- hello_single
#include <stdio.h>
#define NUM 5
void print_msg(char *);
int main()
{
print_msg("hello");
print_msg("world
");
}
void print_msg(char *m)
{
int i;
for(i=0 ; i<NUM ; i++){
printf("%s", m);
fflush(stdout);
sleep(1);
}
}

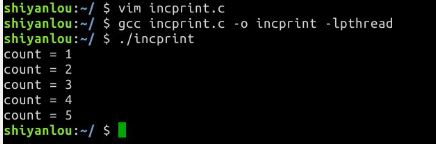
- incprint
#include <stdio.h>
#include <pthread.h>
#define NUM 5
int counter = 0;
int main()
{
pthread_t t1; /* one thread */
void *print_count(void *); /* its function */
int i;
pthread_create(&t1, NULL, print_count, NULL);
for( i = 0 ; i<NUM ; i++ ){
counter++;
sleep(1);
}
pthread_join(t1, NULL);
}
void *print_count(void *m)
{
int i;
for(i=0 ; i<NUM ; i++){
printf("count = %d
", counter);
sleep(1);
}
return NULL;
}
- twordcount1
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <pthread.h>
#include <ctype.h>
int total_words ;
void *count_words(void *);
int main(int argc, char *argv[])
{
pthread_t t1, t2;
if ( argc != 3 ){
printf("usage: %s file1 file2
", argv[0]);
exit(1);
}
total_words = 0;
pthread_create(&t1, NULL, count_words, (void *) argv[1]);
pthread_create(&t2, NULL, count_words, (void *) argv[2]);
pthread_join(t1, NULL);
pthread_join(t2, NULL);
printf("%5d: total words
", total_words);
}
void *count_words(void *f)
{
char *filename = (char *) f;
FILE *fp;
int c, prevc = '�';
if ( (fp = fopen(filename, "r")) != NULL ){
while( ( c = getc(fp)) != EOF ){
if ( !isalnum(c) && isalnum(prevc) )
total_words++;
prevc = c;
}
fclose(fp);
} else
perror(filename);
return NULL;
}
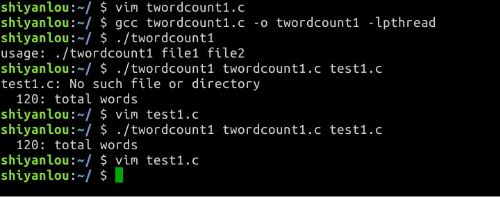
统计文件1及文件2两个文件的总字数
- twordcount2
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <pthread.h>
#include <ctype.h>
void *count_words(void *);
int total_words ;
pthread_mutex_t counter_lock = PTHREAD_MUTEX_INITIALIZER;
int main(int argc, char *argv[])
{
pthread_t t1, t2;
if ( argc != 3 ){
printf("usage: %s file1 file2
", argv[0]);
exit(1);
}
total_words = 0;
pthread_create(&t1, NULL, count_words, (void *) argv[1]);
pthread_create(&t2, NULL, count_words, (void *) argv[2]);
pthread_join(t1, NULL);
pthread_join(t2, NULL);
printf("%5d: total words
", total_words);
}
void *count_words(void *f)
{
char *filename = (char *) f;
FILE *fp;
int c, prevc = '�';
if ( (fp = fopen(filename, "r")) != NULL ){
while( ( c = getc(fp)) != EOF ){
if ( !isalnum(c) && isalnum(prevc) ){
pthread_mutex_lock(&counter_lock);
total_words++;
pthread_mutex_unlock(&counter_lock);
}
prevc = c;
}
fclose(fp);
} else
perror(filename);
return NULL;
}
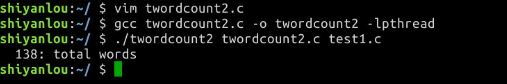
- twordcount3
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <pthread.h>
#include <ctype.h>
struct arg_set {
char *fname;
int count;
};
void *count_words(void *);
int main(int argc, char *argv[])
{
pthread_t t1, t2;
struct arg_set args1, args2; /* two argsets */
if ( argc != 3 ){
printf("usage: %s file1 file2
", argv[0]);
exit(1);
}
args1.fname = argv[1];
args1.count = 0;
pthread_create(&t1, NULL, count_words, (void *) &args1);
args2.fname = argv[2];
args2.count = 0;
pthread_create(&t2, NULL, count_words, (void *) &args2);
pthread_join(t1, NULL);
pthread_join(t2, NULL);
printf("%5d: %s
", args1.count, argv[1]);
printf("%5d: %s
", args2.count, argv[2]);
printf("%5d: total words
", args1.count+args2.count);
}
void *count_words(void *a)
{
struct arg_set *args = a;
FILE *fp;
int c, prevc = '�';
if ( (fp = fopen(args->fname, "r")) != NULL ){
while( ( c = getc(fp)) != EOF ){
if ( !isalnum(c) && isalnum(prevc) )
args->count++;
prevc = c;
}
fclose(fp);
} else
perror(args->fname);
return NULL;
}

分别对文件1、文件2两个文件进行字数统计,并把两个文件的字数加起来统计两个文件的总字数
- twordcount4
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <pthread.h>
#include <ctype.h>
struct arg_set {
char *fname;
int count;
};
struct arg_set *mailbox = NULL;
pthread_mutex_t lock = PTHREAD_MUTEX_INITIALIZER;
pthread_cond_t flag = PTHREAD_COND_INITIALIZER;
void *count_words(void *);
int main(int argc, char *argv[])
{
pthread_t t1, t2;
struct arg_set args1, args2;
int reports_in = 0;
int total_words = 0;
if ( argc != 3 ){
printf("usage: %s file1 file2
", argv[0]);
exit(1);
}
args1.fname = argv[1];
args1.count = 0;
pthread_create(&t1, NULL, count_words, (void *) &args1);
args2.fname = argv[2];
args2.count = 0;
pthread_create(&t2, NULL, count_words, (void *) &args2);
pthread_mutex_lock(&lock);
while( reports_in < 2 ){
printf("MAIN: waiting for flag to go up
");
pthread_cond_wait(&flag, &lock);
printf("MAIN: Wow! flag was raised, I have the lock
");
printf("%7d: %s
", mailbox->count, mailbox->fname);
total_words += mailbox->count;
if ( mailbox == &args1)
pthread_join(t1,NULL);
if ( mailbox == &args2)
pthread_join(t2,NULL);
mailbox = NULL;
pthread_cond_signal(&flag);
reports_in++;
}
pthread_mutex_unlock(&lock);
printf("%7d: total words
", total_words);
}
void *count_words(void *a)
{
struct arg_set *args = a;
FILE *fp;
int c, prevc = '�';
if ( (fp = fopen(args->fname, "r")) != NULL ){
while( ( c = getc(fp)) != EOF ){
if ( !isalnum(c) && isalnum(prevc) )
args->count++;
prevc = c;
}
fclose(fp);
} else
perror(args->fname);
printf("COUNT: waiting to get lock
");
pthread_mutex_lock(&lock);
printf("COUNT: have lock, storing data
");
if ( mailbox != NULL ){
printf("COUNT: oops..mailbox not empty. wait for signal
");
pthread_cond_wait(&flag,&lock);
}
mailbox = args;
printf("COUNT: raising flag
");
pthread_cond_signal(&flag);
printf("COUNT: unlocking box
");
pthread_mutex_unlock(&lock);
return NULL;
}
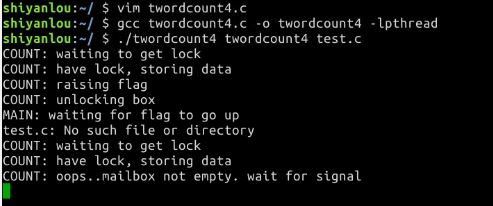
分别运行代码,根据锁的情况分别统计字数,再把两个文件的字数加起来统计两个文件的总字数
代码托管
链接:http://git.oschina.net/entropy_z/Linux
学习进度条
| 代码行数(新增/累积) | 博客量(新增/累积) | 学习时间(新增/累积) | 重要成长 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 目标 | 5000行 | 30篇 | 400小时 | |
| 第一周 | 200/200 | 1/1 | 20/20 | |
| 第二周 | 300/500 | 1/2 | 18/38 | |
| 第三周 | 500/1000 | 1/3 | 22/60 | |
| 第四周 | 150/1150 | 1/4 | 30/90 | |
| 第五周 | 150/1300 | 1/5 | 30/120 | |
| 第六周 | 50/1350 | 1/6 | 30/150 | |
| 第七周 | 50/1400 | 1/7 | 20/170 | |
| 第八周 | 50/1450 | 1/8 | 20/190 | |
| 第九周 | 50/1500 | 1/9 | 20/210 | |
| 第十周 | 300/1800 | 1/10 | 20/230 | |
| 第十一周 | 300/2100 | 1/11 | 20/250 | |
| 第十三周 | 300/2400 | 1/18 | 20/280 |