多线程是实现并发机制的一种有效手段。在 Java 中实现多线程有两种手段,一种是继承 Thread 类,另一种就是实现 Runnable/Callable 接口。
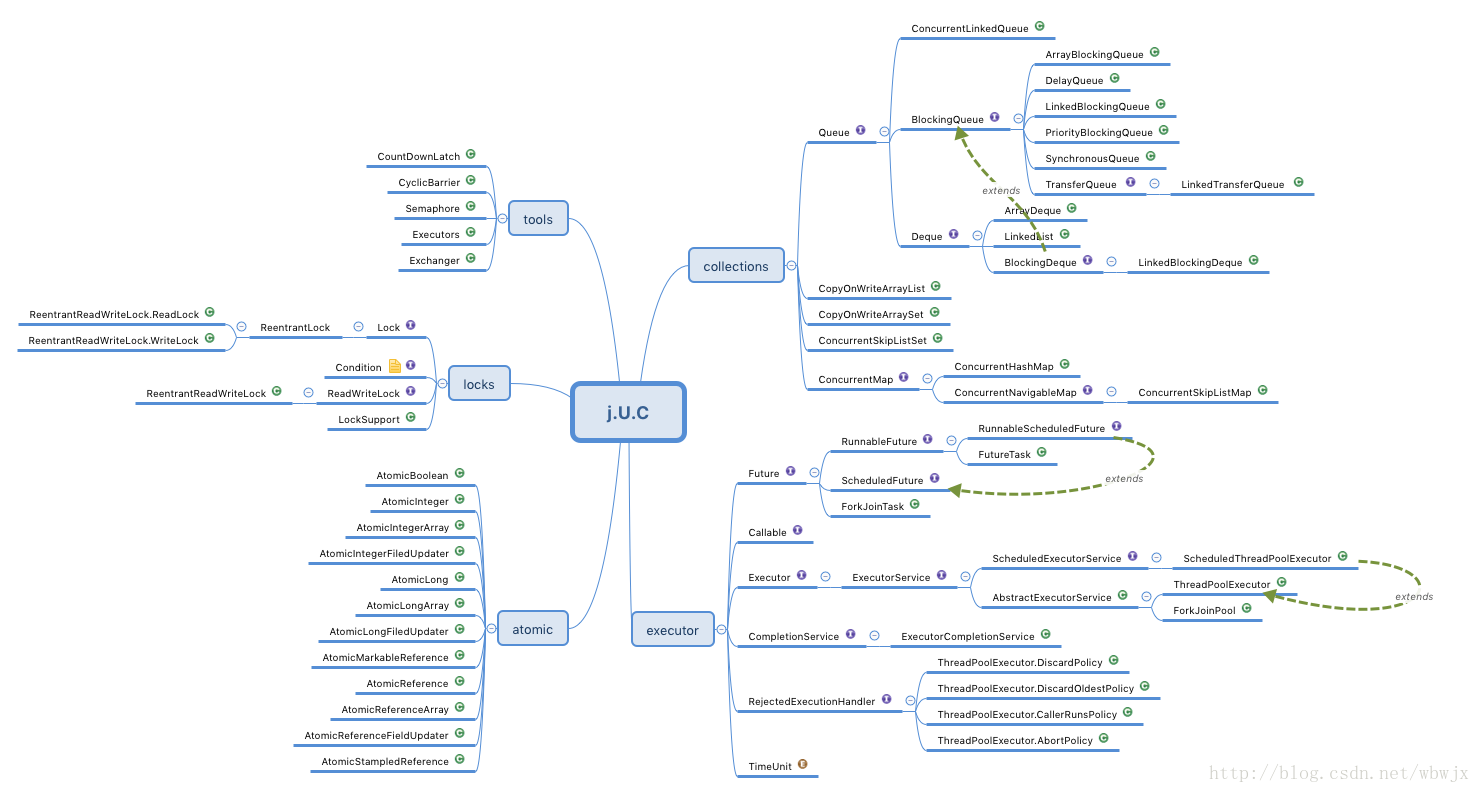
java.util.concurrent 包是专为 Java并发编程而设计的包。类图如下:
一、同步
1.1 synchronized 关键字,用来给对象和方法或者代码块加锁。
同步方法 synchronized T methodName(){} 同步方法锁定的是当前对象。当多线程通过同一个对象引用多次调用当前同步方法时,需同步执行。静态同步方法,锁的是当前类型的类对象。
同步方法只影响锁定同一个锁对象的同步方法。不影响其他线程调用非同步方法,或调用其他锁资源的同步方法。
锁可重入。 同一个线程,多次调用同步代码,锁定同一个锁对象,可重入。子类同步方法覆盖父类同步方法。可以指定调用父类的同步方法,相当于锁的重入。
当同步方法中发生异常的时候,自动释放锁资源。不会影响其他线程的执行。
同步代码块 T methodName(){ synchronized(object){} } 同步代码块在执行时,是锁定 object 对象。当多个线程调用同一个方法时,锁定对象不变的情况下,需同步执行。 同步代码块的同步粒度更加细致,效率更高。 T methodName(){ synchronized(this){} } 当锁定对象为 this 时,相当于同步方法。
同步代码一旦加锁后,那么会有一个临时的锁引用执行锁对象,和真实的引用无直接关联。在锁未释放之前,修改锁对象引用,不会影响同步代码的执行。
Java 虚拟机中的同步(Synchronization)基于进入和退出管程(Monitor)对象实现。同步方法 并不是由 monitor enter 和 monitor exit 指令来实现同步的,而是由方法调用指令读取运行时常量池中方法的 ACC_SYNCHRONIZED 标志来隐式实现的。在 Java 虚拟机(HotSpot)中,monitor 是由 ObjectMonitor 实现的。

1 /** 2 * synchronized关键字 3 * 锁对象。synchronized(this)和synchronized方法都是锁当前对象。 4 */ 5 package concurrent.t01; 6 7 import java.util.concurrent.TimeUnit; 8 9 public class Test_01 { 10 private int count = 0; 11 private Object o = new Object(); 12 13 public void testSync1(){ 14 synchronized(o){ 15 System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() 16 + " count = " + count++); 17 } 18 } 19 20 public void testSync2(){ 21 synchronized(this){ 22 System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() 23 + " count = " + count++); 24 } 25 } 26 27 public synchronized void testSync3(){ 28 System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() 29 + " count = " + count++); 30 try { 31 TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(3); 32 } catch (InterruptedException e) { 33 e.printStackTrace(); 34 } 35 } 36 37 public static void main(String[] args) { 38 final Test_01 t = new Test_01(); 39 new Thread(new Runnable() { 40 @Override 41 public void run() { 42 t.testSync3(); 43 } 44 }).start(); 45 new Thread(new Runnable() { 46 @Override 47 public void run() { 48 t.testSync3(); 49 } 50 }).start(); 51 } 52 53 }
1.2 volatile 关键字
变量的线程可见性。在 CPU 计算过程中,会将计算过程需要的数据加载到 CPU 计算缓存中,当 CPU 计算中断时,有可能刷新缓存,重新读取内存中的数据。在线程运行的过程中,如果某变量被其他线程修改,可能造成数据不一致的情况,从而导致结果错误。而 volatile修饰的变量是线程可见的,当 JVM 解释 volatile 修饰的变量时,会通知 CPU,在计算过程中,每次使用变量参与计算时,都会检查内存中的数据是否发生变化,而不是一直使用 CPU 缓存中的数据,可以保证计算结果的正确。volatile 只是通知底层计算时,CPU 检查内存数据,而不是让一个变量在多个线程中同步。

1 /** 2 * volatile关键字 3 * volatile的可见性 4 * 通知OS操作系统底层,在CPU计算过程中,都要检查内存中数据的有效性。保证最新的内存数据被使用。 5 * 6 */ 7 package concurrent.t01; 8 9 import java.util.concurrent.TimeUnit; 10 11 public class Test_09 { 12 13 volatile boolean b = true; 14 15 void m(){ 16 System.out.println("start"); 17 while(b){} 18 System.out.println("end"); 19 } 20 21 public static void main(String[] args) { 22 final Test_09 t = new Test_09(); 23 new Thread(new Runnable() { 24 @Override 25 public void run() { 26 t.m(); 27 } 28 }).start(); 29 30 try { 31 TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(1); 32 } catch (InterruptedException e) { 33 // TODO Auto-generated catch block 34 e.printStackTrace(); 35 } 36 37 t.b = false; 38 } 39 40 }

1 /** 2 * volatile关键字 3 * volatile的非原子性问题 4 * volatile, 只能保证可见性,不能保证原子性。 5 * 不是枷锁问题,只是内存数据可见。 6 */ 7 package concurrent.t01; 8 9 import java.util.ArrayList; 10 import java.util.List; 11 12 public class Test_10 { 13 14 volatile int count = 0; 15 /*synchronized*/ void m(){ 16 for(int i = 0; i < 10000; i++){ 17 count++; 18 } 19 } 20 21 public static void main(String[] args) { 22 final Test_10 t = new Test_10(); 23 List<Thread> threads = new ArrayList<>(); 24 for(int i = 0; i < 10; i++){ 25 threads.add(new Thread(new Runnable() { 26 @Override 27 public void run() { 28 t.m(); 29 } 30 })); 31 } 32 for(Thread thread : threads){ 33 thread.start(); 34 } 35 for(Thread thread : threads){ 36 try { 37 thread.join(); 38 } catch (InterruptedException e) { 39 // TODO Auto-generated catch block 40 e.printStackTrace(); 41 } 42 } 43 System.out.println(t.count); 44 } 45 }
1.3 wait¬ify
当线程执行wait()方法时候,会释放当前的锁,然后让出CPU,进入等待状态。只有当 notify/notifyAll() 被执行时候,才会唤醒一个或多个正处于等待状态的线程,然后继续往下执行,直到执行完synchronized 代码块的代码或是中途遇到wait() ,再次释放锁。
由于 wait()、notify/notifyAll() 在synchronized 代码块执行,说明当前线程一定是获取了锁的。wait()、notify/notifyAll() 方法是Object的本地final方法,无法被重写。

1 /** 2 * 生产者消费者 3 * wait¬ify 4 * wait/notify都是和while配合应用的。可以避免多线程并发判断逻辑失效问题。各位想想为什么不能用if 5 */ 6 package concurrent.t04; 7 8 import java.util.LinkedList; 9 import java.util.concurrent.TimeUnit; 10 11 public class TestContainer01<E> { 12 13 private final LinkedList<E> list = new LinkedList<>(); 14 private final int MAX = 10; 15 private int count = 0; 16 17 public synchronized int getCount(){ 18 return count; 19 } 20 21 public synchronized void put(E e){ 22 while(list.size() == MAX){ 23 try { 24 this.wait(); 25 } catch (InterruptedException e1) { 26 e1.printStackTrace(); 27 } 28 } 29 30 list.add(e); 31 count++; 32 this.notifyAll(); 33 } 34 35 public synchronized E get(){ 36 E e = null; 37 while(list.size() == 0){ 38 try{ 39 this.wait(); 40 } catch (InterruptedException e1) { 41 e1.printStackTrace(); 42 } 43 } 44 e = list.removeFirst(); 45 count--; 46 this.notifyAll(); 47 return e; 48 } 49 50 public static void main(String[] args) { 51 final TestContainer01<String> c = new TestContainer01<>(); 52 for(int i = 0; i < 10; i++){ 53 new Thread(new Runnable() { 54 @Override 55 public void run() { 56 for(int j = 0; j < 5; j++){ 57 System.out.println(c.get()); 58 } 59 } 60 }, "consumer"+i).start(); 61 } 62 try { 63 TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(2); 64 } catch (InterruptedException e) { 65 // TODO Auto-generated catch block 66 e.printStackTrace(); 67 } 68 for(int i = 0; i < 2; i++){ 69 new Thread(new Runnable() { 70 @Override 71 public void run() { 72 for(int j = 0; j < 25; j++){ 73 c.put("container value " + j); 74 } 75 } 76 }, "producer"+i).start(); 77 } 78 } 79 80 }
1.4 AtomicXxx 类型
原子类型。
在 concurrent.atomic 包中定义了若干原子类型,这些类型中的每个方法都是保证了原子操作的。多线程并发访问原子类型对象中的方法,不会出现数据错误。在多线程开发中,如果某数据需要多个线程同时操作,且要求计算原子性,可以考虑使用原子类型对象。
- AtomicBoolean,AtomicInteger,AtomicLong,AtomicReference
- AtomicIntegerArray,AtomicLongArray
- AtomicLongFieldUpdater,AtomicIntegerFieldUpdater,AtomicReferenceFieldUpdater
- AtomicMarkableReference,AtomicStampedReference,AtomicReferenceArray
注意:原子类型中的方法 是保证了原子操作,但多个方法之间是没有原子性的。即访问对2个或2个以上的atomic变量(或者对单个atomic变量进行2次或2次以上的操作),还是需要同步。

1 /** 2 * AtomicXxx 3 * 同步类型 4 * 原子操作类型。 其中的每个方法都是原子操作。可以保证线程安全。 5 */ 6 package concurrent.t01; 7 8 import java.util.ArrayList; 9 import java.util.List; 10 import java.util.concurrent.atomic.AtomicInteger; 11 12 public class Test_11 { 13 AtomicInteger count = new AtomicInteger(0); 14 void m(){ 15 for(int i = 0; i < 10000; i++){ 16 /*if(count.get() < 1000)*/ 17 count.incrementAndGet(); 18 } 19 } 20 21 public static void main(String[] args) { 22 final Test_11 t = new Test_11(); 23 List<Thread> threads = new ArrayList<>(); 24 for(int i = 0; i < 10; i++){ 25 threads.add(new Thread(new Runnable() { 26 @Override 27 public void run() { 28 t.m(); 29 } 30 })); 31 } 32 for(Thread thread : threads){ 33 thread.start(); 34 } 35 for(Thread thread : threads){ 36 try { 37 thread.join(); 38 } catch (InterruptedException e) { 39 // TODO Auto-generated catch block 40 e.printStackTrace(); 41 } 42 } 43 System.out.println(t.count.intValue()); 44 } 45 }
1.5 CountDownLatch 门闩
门闩是 concurrent 包中定义的一个类型,是用于多线程通讯的一个辅助类型。门闩相当于在一个门上加多个锁,当线程调用 await 方法时,会检查门闩数量,如果门闩数量大于 0,线程会阻塞等待。当线程调用 countDown 时,会递减门闩的数量,当门闩数量为 0 时,await 阻塞线程可执行。

1 /** 2 * 门闩 - CountDownLatch 3 * 可以和锁混合使用,或替代锁的功能。 4 * 在门闩未完全开放之前等待。当门闩完全开放后执行。 5 * 避免锁的效率低下问题。 6 */ 7 package concurrent.t01; 8 9 import java.util.concurrent.CountDownLatch; 10 import java.util.concurrent.TimeUnit; 11 12 public class Test_15 { 13 CountDownLatch latch = new CountDownLatch(5); 14 15 void m1(){ 16 try { 17 latch.await();// 等待门闩开放。 18 } catch (InterruptedException e) { 19 e.printStackTrace(); 20 } 21 System.out.println("m1() method"); 22 } 23 24 void m2(){ 25 for(int i = 0; i < 10; i++){ 26 if(latch.getCount() != 0){ 27 System.out.println("latch count : " + latch.getCount()); 28 latch.countDown(); // 减门闩上的锁。 29 } 30 try { 31 TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS.sleep(500); 32 } catch (InterruptedException e) { 33 // TODO Auto-generated catch block 34 e.printStackTrace(); 35 } 36 System.out.println("m2() method : " + i); 37 } 38 } 39 40 public static void main(String[] args) { 41 final Test_15 t = new Test_15(); 42 new Thread(new Runnable() { 43 @Override 44 public void run() { 45 t.m1(); 46 } 47 }).start(); 48 49 new Thread(new Runnable() { 50 @Override 51 public void run() { 52 t.m2(); 53 } 54 }).start(); 55 } 56 57 }
1.6 锁的重入
在 Java 中,同步锁是可以重入的。只有同一线程调用同步方法或执行同步代码块,对同一个对象加锁时才可重入。
当线程持有锁时,会在 monitor 的计数器中执行递增计算,若当前线程调用其他同步代码,且同步代码的锁对象相同时,monitor 中的计数器继续递增。每个同步代码执行结束,monitor 中的计数器都会递减,直至所有同步代码执行结束,monitor 中的计数器为 0 时,释放锁标记,_Owner 标记赋值为 null。

1 /** 2 * 锁可重入。 同一个线程,多次调用同步代码,锁定同一个锁对象,可重入。 3 */ 4 package concurrent.t01; 5 6 import java.util.concurrent.TimeUnit; 7 8 public class Test_06 { 9 10 synchronized void m1(){ // 锁this 11 System.out.println("m1 start"); 12 try { 13 TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(2); 14 } catch (InterruptedException e) { 15 e.printStackTrace(); 16 } 17 m2(); 18 System.out.println("m1 end"); 19 } 20 synchronized void m2(){ // 锁this 21 System.out.println("m2 start"); 22 try { 23 TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(1); 24 } catch (InterruptedException e) { 25 e.printStackTrace(); 26 } 27 System.out.println("m2 end"); 28 } 29 30 public static void main(String[] args) { 31 32 new Test_06().m1(); 33 34 } 35 36 }
1.7 ReentrantLock
重入锁,建议应用的同步方式。相对效率比 synchronized 高。量级较轻。使用重入锁, 必须手工释放锁标记。一般都是在 finally 代码块中定义释放锁标记的 unlock 方法。

1 /** 2 * ReentrantLock 3 * 重入锁 4 */ 5 package concurrent.t03; 6 7 import java.util.concurrent.TimeUnit; 8 import java.util.concurrent.locks.Lock; 9 import java.util.concurrent.locks.ReentrantLock; 10 11 public class Test_01 { 12 Lock lock = new ReentrantLock(); 13 14 void m1(){ 15 try{ 16 lock.lock(); // 加锁 17 for(int i = 0; i < 10; i++){ 18 TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(1); 19 System.out.println("m1() method " + i); 20 } 21 }catch(InterruptedException e){ 22 e.printStackTrace(); 23 }finally{ 24 lock.unlock(); // 解锁 25 } 26 } 27 28 void m2(){ 29 lock.lock(); 30 System.out.println("m2() method"); 31 lock.unlock(); 32 } 33 34 public static void main(String[] args) { 35 final Test_01 t = new Test_01(); 36 new Thread(new Runnable() { 37 @Override 38 public void run() { 39 t.m1(); 40 } 41 }).start(); 42 try { 43 TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(1); 44 } catch (InterruptedException e) { 45 e.printStackTrace(); 46 } 47 new Thread(new Runnable() { 48 @Override 49 public void run() { 50 t.m2(); 51 } 52 }).start(); 53 } 54 }

1 /** 2 * 尝试锁 3 */ 4 package concurrent.t03; 5 6 import java.util.concurrent.TimeUnit; 7 import java.util.concurrent.locks.Lock; 8 import java.util.concurrent.locks.ReentrantLock; 9 10 public class Test_02 { 11 Lock lock = new ReentrantLock(); 12 13 void m1(){ 14 try{ 15 lock.lock(); 16 for(int i = 0; i < 10; i++){ 17 TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(1); 18 System.out.println("m1() method " + i); 19 } 20 }catch(InterruptedException e){ 21 e.printStackTrace(); 22 }finally{ 23 lock.unlock(); 24 } 25 } 26 27 void m2(){ 28 boolean isLocked = false; 29 try{ 30 // 尝试锁, 如果有锁,无法获取锁标记,返回false。 31 // 如果获取锁标记,返回true 32 // isLocked = lock.tryLock(); 33 34 // 阻塞尝试锁,阻塞参数代表的时长,尝试获取锁标记。 35 // 如果超时,不等待。直接返回。 36 isLocked = lock.tryLock(5, TimeUnit.SECONDS); 37 38 if(isLocked){ 39 System.out.println("m2() method synchronized"); 40 }else{ 41 System.out.println("m2() method unsynchronized"); 42 } 43 }catch(Exception e){ 44 e.printStackTrace(); 45 }finally{ 46 if(isLocked){ 47 // 尝试锁在解除锁标记的时候,一定要判断是否获取到锁标记。 48 // 如果当前线程没有获取到锁标记,会抛出异常。 49 lock.unlock(); 50 } 51 } 52 } 53 54 public static void main(String[] args) { 55 final Test_02 t = new Test_02(); 56 new Thread(new Runnable() { 57 @Override 58 public void run() { 59 t.m1(); 60 } 61 }).start(); 62 try { 63 TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(1); 64 } catch (InterruptedException e) { 65 // TODO Auto-generated catch block 66 e.printStackTrace(); 67 } 68 new Thread(new Runnable() { 69 @Override 70 public void run() { 71 t.m2(); 72 } 73 }).start(); 74 } 75 }

1 /** 2 * 可打断 3 * 4 * 阻塞状态: 包括普通阻塞,等待队列,锁池队列。 5 * 普通阻塞: sleep(10000), 可以被打断。调用thread.interrupt()方法,可以打断阻塞状态,抛出异常。 6 * 等待队列: wait()方法被调用,也是一种阻塞状态,只能由notify唤醒。无法打断 7 * 锁池队列: 无法获取锁标记。不是所有的锁池队列都可被打断。 8 * 使用ReentrantLock的lock方法,获取锁标记的时候,如果需要阻塞等待锁标记,无法被打断。 9 * 使用ReentrantLock的lockInterruptibly方法,获取锁标记的时候,如果需要阻塞等待,可以被打断。 10 * 11 */ 12 package concurrent.t03; 13 14 import java.util.concurrent.TimeUnit; 15 import java.util.concurrent.locks.Lock; 16 import java.util.concurrent.locks.ReentrantLock; 17 18 public class Test_03 { 19 Lock lock = new ReentrantLock(); 20 21 void m1(){ 22 try{ 23 lock.lock(); 24 for(int i = 0; i < 5; i++){ 25 TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(1); 26 System.out.println("m1() method " + i); 27 } 28 }catch(InterruptedException e){ 29 e.printStackTrace(); 30 }finally{ 31 lock.unlock(); 32 } 33 } 34 35 void m2(){ 36 try{ 37 lock.lockInterruptibly(); // 可尝试打断,阻塞等待锁。可以被其他的线程打断阻塞状态 38 System.out.println("m2() method"); 39 }catch(InterruptedException e){ 40 System.out.println("m2() method interrupted"); 41 }finally{ 42 try{ 43 lock.unlock(); 44 }catch(Exception e){ 45 e.printStackTrace(); 46 } 47 } 48 } 49 50 public static void main(String[] args) { 51 final Test_03 t = new Test_03(); 52 new Thread(new Runnable() { 53 @Override 54 public void run() { 55 t.m1(); 56 } 57 }).start(); 58 try { 59 TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(1); 60 } catch (InterruptedException e) { 61 // TODO Auto-generated catch block 62 e.printStackTrace(); 63 } 64 Thread t2 = new Thread(new Runnable() { 65 @Override 66 public void run() { 67 t.m2(); 68 } 69 }); 70 t2.start(); 71 try { 72 TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(1); 73 } catch (InterruptedException e) { 74 // TODO Auto-generated catch block 75 e.printStackTrace(); 76 } 77 t2.interrupt();// 打断线程休眠。非正常结束阻塞状态的线程,都会抛出异常。 78 } 79 }

1 /** 2 * 公平锁 3 */ 4 package concurrent.t03; 5 6 import java.util.concurrent.locks.ReentrantLock; 7 8 public class Test_04 { 9 10 public static void main(String[] args) { 11 TestReentrantlock t = new TestReentrantlock(); 12 //TestSync t = new TestSync(); 13 Thread t1 = new Thread(t); 14 Thread t2 = new Thread(t); 15 t1.start(); 16 t2.start(); 17 } 18 } 19 20 class TestReentrantlock extends Thread{ 21 // 定义一个公平锁 22 private static ReentrantLock lock = new ReentrantLock(true); 23 public void run(){ 24 for(int i = 0; i < 5; i++){ 25 lock.lock(); 26 try{ 27 System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + " get lock"); 28 }finally{ 29 lock.unlock(); 30 } 31 } 32 } 33 34 } 35 36 class TestSync extends Thread{ 37 public void run(){ 38 for(int i = 0; i < 5; i++){ 39 synchronized (this) { 40 System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + " get lock in TestSync"); 41 } 42 } 43 } 44 }

1 /** 2 * 生产者消费者 3 * 重入锁&条件 4 * 条件 - Condition, 为Lock增加条件。当条件满足时,做什么事情,如加锁或解锁。如等待或唤醒 5 */ 6 package concurrent.t04; 7 8 import java.io.IOException; 9 import java.util.LinkedList; 10 import java.util.concurrent.TimeUnit; 11 import java.util.concurrent.locks.Condition; 12 import java.util.concurrent.locks.Lock; 13 import java.util.concurrent.locks.ReentrantLock; 14 15 public class TestContainer02<E> { 16 17 private final LinkedList<E> list = new LinkedList<>(); 18 private final int MAX = 10; 19 private int count = 0; 20 21 private Lock lock = new ReentrantLock(); 22 private Condition producer = lock.newCondition(); 23 private Condition consumer = lock.newCondition(); 24 25 public int getCount(){ 26 return count; 27 } 28 29 public void put(E e){ 30 lock.lock(); 31 try { 32 while(list.size() == MAX){ 33 System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + " 等待。。。"); 34 // 进入等待队列。释放锁标记。 35 // 借助条件,进入的等待队列。 36 producer.await(); 37 } 38 System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + " put 。。。"); 39 list.add(e); 40 count++; 41 // 借助条件,唤醒所有的消费者。 42 consumer.signalAll(); 43 } catch (InterruptedException e1) { 44 e1.printStackTrace(); 45 } finally { 46 lock.unlock(); 47 } 48 } 49 50 public E get(){ 51 E e = null; 52 53 lock.lock(); 54 try { 55 while(list.size() == 0){ 56 System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + " 等待。。。"); 57 // 借助条件,消费者进入等待队列 58 consumer.await(); 59 } 60 System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + " get 。。。"); 61 e = list.removeFirst(); 62 count--; 63 // 借助条件,唤醒所有的生产者 64 producer.signalAll(); 65 } catch (InterruptedException e1) { 66 e1.printStackTrace(); 67 } finally { 68 lock.unlock(); 69 } 70 71 return e; 72 } 73 74 public static void main(String[] args) { 75 final TestContainer02<String> c = new TestContainer02<>(); 76 for(int i = 0; i < 10; i++){ 77 new Thread(new Runnable() { 78 @Override 79 public void run() { 80 for(int j = 0; j < 5; j++){ 81 System.out.println(c.get()); 82 } 83 } 84 }, "consumer"+i).start(); 85 } 86 try { 87 TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(2); 88 } catch (InterruptedException e1) { 89 e1.printStackTrace(); 90 } 91 for(int i = 0; i < 2; i++){ 92 new Thread(new Runnable() { 93 @Override 94 public void run() { 95 for(int j = 0; j < 25; j++){ 96 c.put("container value " + j); 97 } 98 } 99 }, "producer"+i).start(); 100 } 101 } 102 103 }
1.8 ThreadLocal
ThreadLocal 提供了线程本地的实例。它与普通变量的区别在于,每个使用该变量的线程都会初始化一个完全独立的实例副本。ThreadLocal 变量通常被private static修饰。当一个线程结束时,它所使用的所有 ThreadLocal 相对的实例副本都可被回收。
ThreadLocal 适用于每个线程需要自己独立的实例且该实例需要在多个方法中被使用,也即变量在线程间隔离而在方法或类间共享的场景。每个 Thread 有自己的实例副本,且其它 Thread 不可访问,那就不存在多线程间共享的问题。

1 /** 2 * ThreadLocal 3 * 就是一个Map。key - 》 Thread.getCurrentThread(). value - 》 线程需要保存的变量。 4 * ThreadLocal.set(value) -> map.put(Thread.getCurrentThread(), value); 5 * ThreadLocal.get() -> map.get(Thread.getCurrentThread()); 6 * 内存问题 : 在并发量高的时候,可能有内存溢出。 7 * 使用ThreadLocal的时候,一定注意回收资源问题,每个线程结束之前,将当前线程保存的线程变量一定要删除 。 8 * ThreadLocal.remove(); 9 */ 10 package concurrent.t05; 11 12 import java.util.concurrent.TimeUnit; 13 14 public class Test_01 { 15 16 volatile static String name = "zhangsan"; 17 static ThreadLocal<String> tl = new ThreadLocal<>(); 18 19 public static void main(String[] args) { 20 new Thread(new Runnable() { 21 @Override 22 public void run() { 23 try { 24 TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(2); 25 } catch (InterruptedException e) { 26 e.printStackTrace(); 27 } 28 System.out.println(name); 29 System.out.println(tl.get()); 30 } 31 }).start(); 32 33 new Thread(new Runnable() { 34 @Override 35 public void run() { 36 try { 37 TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(1); 38 } catch (InterruptedException e) { 39 e.printStackTrace(); 40 } 41 name = "lisi"; 42 tl.set("wangwu"); 43 } 44 }).start(); 45 } 46 47 }
如果调用 ThreadLocal 的 set 方法将一个对象放入Thread中的成员变量threadLocals 中,那么这个对象是永远不会被回收的,因为这个对象永远都被Thread中的成员变量threadLocals引用着,可能会造成 OutOfMemoryError。需要调用 ThreadLocal 的 remove 方法 将对象从thread中的成员变量threadLocals中删除掉。
二、同步容器
线程安全的容器对象: Vector, Hashtable。线程安全容器对象,都是使用 synchronized方法实现的。
concurrent 包中的同步容器,大多数是使用系统底层技术实现的线程安全。类似 native。Java8 中使用 CAS。
2.1 Map/Set
- ConcurrentHashMap/ConcurrentHashSet
底层哈希实现的同步 Map(Set)。效率高,线程安全。使用系统底层技术实现线程安全。量级较 synchronized 低。key 和 value 不能为 null。
- ConcurrentSkipListMap/ConcurrentSkipListSet
底层跳表(SkipList)实现的同步 Map(Set)。有序,效率比 ConcurrentHashMap 稍低。

1 /** 2 * 并发容器 - ConcurrentMap 3 */ 4 package concurrent.t06; 5 6 import java.util.HashMap; 7 import java.util.Hashtable; 8 import java.util.Map; 9 import java.util.Random; 10 import java.util.concurrent.ConcurrentHashMap; 11 import java.util.concurrent.ConcurrentSkipListMap; 12 import java.util.concurrent.CountDownLatch; 13 14 public class Test_01_ConcurrentMap { 15 16 public static void main(String[] args) { 17 final Map<String, String> map = new Hashtable<>(); 18 // final Map<String, String> map = new ConcurrentHashMap<>(); 19 // final Map<String, String> map = new ConcurrentSkipListMap<>(); 20 final Random r = new Random(); 21 Thread[] array = new Thread[100]; 22 final CountDownLatch latch = new CountDownLatch(array.length); 23 24 long begin = System.currentTimeMillis(); 25 for(int i = 0; i < array.length; i++){ 26 array[i] = new Thread(new Runnable() { 27 @Override 28 public void run() { 29 for(int j = 0; j < 10000; j++){ 30 map.put("key"+r.nextInt(100000), "value"+r.nextInt(100000)); 31 } 32 latch.countDown(); 33 } 34 }); 35 } 36 for(Thread t : array){ 37 t.start(); 38 } 39 try { 40 latch.await(); 41 } catch (InterruptedException e) { 42 e.printStackTrace(); 43 } 44 long end = System.currentTimeMillis(); 45 System.out.println("执行时间为 : " + (end-begin) + "毫秒!"); 46 } 47 48 }
2.2 List
- CopyOnWriteArrayList

1 /** 2 * 并发容器 - CopyOnWriteList 3 * 写时复制集合。写入效率低,读取效率高。每次写入数据,都会创建一个新的底层数组。 4 */ 5 package concurrent.t06; 6 7 import java.util.ArrayList; 8 import java.util.List; 9 import java.util.Random; 10 import java.util.Vector; 11 import java.util.concurrent.CopyOnWriteArrayList; 12 import java.util.concurrent.CountDownLatch; 13 14 public class Test_02_CopyOnWriteList { 15 16 public static void main(String[] args) { 17 // final List<String> list = new ArrayList<>(); 18 // final List<String> list = new Vector<>(); 19 final List<String> list = new CopyOnWriteArrayList<>(); 20 final Random r = new Random(); 21 Thread[] array = new Thread[100]; 22 final CountDownLatch latch = new CountDownLatch(array.length); 23 24 long begin = System.currentTimeMillis(); 25 for(int i = 0; i < array.length; i++){ 26 array[i] = new Thread(new Runnable() { 27 @Override 28 public void run() { 29 for(int j = 0; j < 1000; j++){ 30 list.add("value" + r.nextInt(100000)); 31 } 32 latch.countDown(); 33 } 34 }); 35 } 36 for(Thread t : array){ 37 t.start(); 38 } 39 try { 40 latch.await(); 41 } catch (InterruptedException e) { 42 e.printStackTrace(); 43 } 44 long end = System.currentTimeMillis(); 45 System.out.println("执行时间为 : " + (end-begin) + "毫秒!"); 46 System.out.println("List.size() : " + list.size()); 47 } 48 49 }
2.3 Queue
- ConcurrentLinkedQueue 基础链表同步队列。

1 /** 2 * 并发容器 - ConcurrentLinkedQueue 3 * 队列 - 链表实现的。 4 */ 5 package concurrent.t06; 6 7 import java.util.Queue; 8 import java.util.concurrent.ConcurrentLinkedQueue; 9 10 public class Test_03_ConcurrentLinkedQueue { 11 12 public static void main(String[] args) { 13 Queue<String> queue = new ConcurrentLinkedQueue<>(); 14 for(int i = 0; i < 10; i++){ 15 queue.offer("value" + i); 16 } 17 18 System.out.println(queue); 19 System.out.println(queue.size()); 20 21 // peek() -> 查看queue中的首数据 22 System.out.println(queue.peek()); 23 System.out.println(queue.size()); 24 25 // poll() -> 获取queue中的首数据 26 System.out.println(queue.poll()); 27 System.out.println(queue.size()); 28 } 29 30 }
- LinkedBlockingQueue 阻塞队列,队列容量不足自动阻塞,队列容量为 0 自动阻塞。

1 /** 2 * 并发容器 - LinkedBlockingQueue 3 * 阻塞容器。 4 * put & take - 自动阻塞。 5 * put自动阻塞, 队列容量满后,自动阻塞 6 * take自动阻塞方法, 队列容量为0后,自动阻塞。 7 */ 8 package concurrent.t06; 9 10 import java.util.Random; 11 import java.util.concurrent.BlockingQueue; 12 import java.util.concurrent.LinkedBlockingQueue; 13 import java.util.concurrent.TimeUnit; 14 15 public class Test_04_LinkedBlockingQueue { 16 17 final BlockingQueue<String> queue = new LinkedBlockingQueue<>(); 18 final Random r = new Random(); 19 20 public static void main(String[] args) { 21 final Test_04_LinkedBlockingQueue t = new Test_04_LinkedBlockingQueue(); 22 23 new Thread(new Runnable() { 24 @Override 25 public void run() { 26 while(true){ 27 try { 28 t.queue.put("value"+t.r.nextInt(1000)); 29 TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(1); 30 } catch (InterruptedException e) { 31 e.printStackTrace(); 32 } 33 } 34 } 35 }, "producer").start(); 36 37 for(int i = 0; i < 3; i++){ 38 new Thread(new Runnable() { 39 @Override 40 public void run() { 41 while(true){ 42 try { 43 System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + 44 " - " + t.queue.take()); 45 } catch (InterruptedException e) { 46 e.printStackTrace(); 47 } 48 } 49 } 50 }, "consumer"+i).start(); 51 } 52 } 53 54 }
- ArrayBlockingQueue 底层数组实现的有界队列

1 /** 2 * 并发容器 - ArrayBlockingQueue 3 * 有界容器。 4 * 当容量不足的时候,有阻塞能力。 5 *add 方法在容量不足的时候,抛出异常。 6 *put 方法在容量不足的时候,阻塞等待。 7 *offer 方法, 8 *单参数 offer 方法,不阻塞。容量不足的时候,返回 false。当前新增数据操作放弃。 9 *三参数 offer 方法(offer(value,times,timeunit)),容量不足的时候,阻塞 times 时长(单 10 *位为 timeunit),如果在阻塞时长内,有容量空闲,新增数据返回 true。如果阻塞时长范围 11 *内,无容量空闲,放弃新增数据,返回 false。 12 */ 13 package concurrent.t06; 14 15 import java.util.concurrent.ArrayBlockingQueue; 16 import java.util.concurrent.BlockingQueue; 17 import java.util.concurrent.TimeUnit; 18 19 public class Test_05_ArrayBlockingQueue { 20 21 final BlockingQueue<String> queue = new ArrayBlockingQueue<>(3); 22 23 public static void main(String[] args) { 24 final Test_05_ArrayBlockingQueue t = new Test_05_ArrayBlockingQueue(); 25 26 for(int i = 0; i < 5; i++){ 27 // System.out.println("add method : " + t.queue.add("value"+i)); 28 /*try { 29 t.queue.put("put"+i); 30 } catch (InterruptedException e) { 31 e.printStackTrace(); 32 } 33 System.out.println("put method : " + i);*/ 34 // System.out.println("offer method : " + t.queue.offer("value"+i)); 35 try { 36 System.out.println("offer method : " + 37 t.queue.offer("value"+i, 1, TimeUnit.SECONDS)); 38 } catch (InterruptedException e) { 39 e.printStackTrace(); 40 } 41 } 42 43 System.out.println(t.queue); 44 } 45 46 }
- DelayQueue 延时队列。根据比较机制,实现自定义处理顺序的队列。常用于定时任务。

1 /** 2 * 并发容器 - DelayQueue 3 * 无界容器。 4 */ 5 package concurrent.t06; 6 7 import java.util.concurrent.BlockingQueue; 8 import java.util.concurrent.DelayQueue; 9 import java.util.concurrent.Delayed; 10 import java.util.concurrent.TimeUnit; 11 12 public class Test_06_DelayQueue { 13 14 static BlockingQueue<MyTask_06> queue = new DelayQueue<>(); 15 16 public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException { 17 long value = System.currentTimeMillis(); 18 MyTask_06 task1 = new MyTask_06(value + 2000); 19 MyTask_06 task2 = new MyTask_06(value + 1000); 20 MyTask_06 task3 = new MyTask_06(value + 3000); 21 MyTask_06 task4 = new MyTask_06(value + 2500); 22 MyTask_06 task5 = new MyTask_06(value + 1500); 23 24 queue.put(task1); 25 queue.put(task2); 26 queue.put(task3); 27 queue.put(task4); 28 queue.put(task5); 29 30 System.out.println(queue); 31 System.out.println(value); 32 for(int i = 0; i < 5; i++){ 33 System.out.println(queue.take()); 34 } 35 } 36 37 } 38 39 class MyTask_06 implements Delayed { 40 41 private long compareValue; 42 43 public MyTask_06(long compareValue){ 44 this.compareValue = compareValue; 45 } 46 47 /** 48 * 比较大小。自动实现升序 49 * 建议和getDelay方法配合完成。 50 * 如果在DelayQueue是需要按时间完成的计划任务,必须配合getDelay方法完成。 51 */ 52 @Override 53 public int compareTo(Delayed o) { 54 return (int)(this.getDelay(TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS) - o.getDelay(TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS)); 55 } 56 57 /** 58 * 获取计划时长的方法。 59 * 根据参数TimeUnit来决定,如何返回结果值。 60 */ 61 @Override 62 public long getDelay(TimeUnit unit) { 63 return unit.convert(compareValue - System.currentTimeMillis(), TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS); 64 } 65 66 @Override 67 public String toString(){ 68 return "Task compare value is : " + this.compareValue; 69 } 70 71 }
- LinkedTransferQueue 转移队列,使用 transfer 方法,实现数据的即时处理。没有消费者,就阻塞。

1 /** 2 * 并发容器 - LinkedTransferQueue 3 * 转移队列 4 * add - 队列会保存数据,不做阻塞等待。 5 * transfer - 是TransferQueue的特有方法。必须有消费者(take()方法的调用者)。 6 * 如果没有任意线程消费数据,transfer方法阻塞。一般用于处理即时消息。 7 */ 8 package concurrent.t06; 9 10 import java.util.concurrent.LinkedTransferQueue; 11 import java.util.concurrent.TimeUnit; 12 import java.util.concurrent.TransferQueue; 13 14 public class Test_07_TransferQueue { 15 16 TransferQueue<String> queue = new LinkedTransferQueue<>(); 17 18 public static void main(String[] args) { 19 final Test_07_TransferQueue t = new Test_07_TransferQueue(); 20 21 /*new Thread(new Runnable() { 22 @Override 23 public void run() { 24 try { 25 System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + " thread begin " ); 26 System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + " - " + t.queue.take()); 27 } catch (InterruptedException e) { 28 e.printStackTrace(); 29 } 30 } 31 }, "output thread").start(); 32 33 try { 34 TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(2); 35 } catch (InterruptedException e) { 36 e.printStackTrace(); 37 } 38 39 try { 40 t.queue.transfer("test string"); 41 } catch (InterruptedException e) { 42 e.printStackTrace(); 43 }*/ 44 45 new Thread(new Runnable() { 46 47 @Override 48 public void run() { 49 try { 50 t.queue.transfer("test string"); 51 // t.queue.add("test string"); 52 System.out.println("add ok"); 53 } catch (Exception e) { 54 e.printStackTrace(); 55 } 56 } 57 }).start(); 58 59 try { 60 TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(2); 61 } catch (InterruptedException e) { 62 e.printStackTrace(); 63 } 64 65 new Thread(new Runnable() { 66 @Override 67 public void run() { 68 try { 69 System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + " thread begin " ); 70 System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + " - " + t.queue.take()); 71 } catch (InterruptedException e) { 72 e.printStackTrace(); 73 } 74 } 75 }, "output thread").start(); 76 77 } 78 79 }
- SynchronusQueue 同步队列,是一个容量为 0 的队列。是一个特殊的 TransferQueue。必须现有消费线程等待,才能使用的队列。

1 /** 2 * 并发容器 - SynchronousQueue 3 * 必须现有消费线程等待,才能使用的队列。 4 * add 方法,无阻塞。若没有消费线程阻塞等待数据,则抛出异常。 5 * put 方法,有阻塞。若没有消费线程阻塞等待数据,则阻塞。 6 */ 7 package concurrent.t06; 8 9 import java.util.concurrent.BlockingQueue; 10 import java.util.concurrent.SynchronousQueue; 11 import java.util.concurrent.TimeUnit; 12 13 public class Test_08_SynchronusQueue { 14 15 BlockingQueue<String> queue = new SynchronousQueue<>(); 16 17 public static void main(String[] args) { 18 final Test_08_SynchronusQueue t = new Test_08_SynchronusQueue(); 19 20 new Thread(new Runnable() { 21 @Override 22 public void run() { 23 try { 24 System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + " thread begin " ); 25 try { 26 TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(2); 27 } catch (InterruptedException e) { 28 e.printStackTrace(); 29 } 30 System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + " - " + t.queue.take()); 31 } catch (InterruptedException e) { 32 e.printStackTrace(); 33 } 34 } 35 }, "output thread").start(); 36 37 /*try { 38 TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(3); 39 } catch (InterruptedException e) { 40 e.printStackTrace(); 41 }*/ 42 // t.queue.add("test add"); 43 try { 44 t.queue.put("test put"); 45 } catch (InterruptedException e) { 46 e.printStackTrace(); 47 } 48 49 System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + " queue size : " + t.queue.size()); 50 } 51 52 }
三、 ThreadPool&Executor
3.1 Executor
线程池顶级接口。定义方法,void execute(Runnable)。方法是用于处理任务的一个服务方法。调用者提供 Runnable 接口的实现,线程池通过线程执行这个 Runnable。服务方法无返回值的。是 Runnable 接口中的 run 方法无返回值。
常用方法 - void execute(Runnable)
作用是: 启动线程任务的。

1 /** 2 * 线程池 3 * Executor - 线程池底层处理机制。 4 * 在使用线程池的时候,底层如何调用线程中的逻辑。 5 */ 6 package concurrent.t08; 7 8 import java.util.concurrent.Executor; 9 10 public class Test_01_MyExecutor implements Executor { 11 public static void main(String[] args) { 12 new Test_01_MyExecutor().execute(new Runnable() { 13 @Override 14 public void run() { 15 System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + " - test executor"); 16 } 17 }); 18 } 19 20 @Override 21 public void execute(Runnable command) { 22 new Thread(command).start(); 23 } 24 }
3.2 ExecutorService
Executor 接口的子接口。提供了一个新的服务方法,submit。有返回值(Future 类型)。submit 方法提供了 overload 方法。其中有参数类型为 Runnable 的,不需要提供返回值的;有参数类型为 Callable,可以提供线程执行后的返回值。
Future,是 submit 方法的返回值。代表未来,也就是线程执行结束后的一种结果。如返回值。
常见方法 - void execute(Runnable), Future submit(Callable), Future submit(Runnable)
线程池状态: Running, ShuttingDown, Termitnaed
- Running - 线程池正在执行中。活动状态。
- ShuttingDown - 线程池正在关闭过程中。优雅关闭。一旦进入这个状态,线程池不再接收新的任务,处理所有已接收的任务,处理完毕后,关闭线程池。
- Terminated - 线程池已经关闭。
3.3 Future
未来结果,代表线程任务执行结束后的结果。获取线程执行结果的方式是通过 get 方法获取的。get 无参,阻塞等待线程执行结束,并得到结果。get 有参,阻塞固定时长,等待
线程执行结束后的结果,如果在阻塞时长范围内,线程未执行结束,抛出异常。
常用方法: T get() T get(long, TimeUnit)

1 /** 2 * 线程池 3 * 固定容量线程池 4 */ 5 package concurrent.t08; 6 7 import java.util.concurrent.Callable; 8 import java.util.concurrent.ExecutionException; 9 import java.util.concurrent.ExecutorService; 10 import java.util.concurrent.Executors; 11 import java.util.concurrent.Future; 12 import java.util.concurrent.FutureTask; 13 import java.util.concurrent.TimeUnit; 14 15 public class Test_03_Future { 16 17 public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException, ExecutionException { 18 /*FutureTask<String> task = new FutureTask<>(new Callable<String>() { 19 @Override 20 public String call() throws Exception { 21 return "first future task"; 22 } 23 }); 24 25 new Thread(task).start(); 26 27 System.out.println(task.get());*/ 28 29 ExecutorService service = Executors.newFixedThreadPool(1); 30 31 Future<String> future = service.submit(new Callable<String>() { 32 @Override 33 public String call() { 34 try { 35 TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS.sleep(500); 36 } catch (InterruptedException e) { 37 e.printStackTrace(); 38 } 39 System.out.println("aaa"); 40 return Thread.currentThread().getName() + " - test executor"; 41 } 42 }); 43 System.out.println(future); 44 System.out.println(future.isDone()); // 查看线程是否结束, 任务是否完成。 call方法是否执行结束 45 46 System.out.println(future.get()); // 获取call方法的返回值。 47 System.out.println(future.isDone()); 48 } 49 50 }
3.4 Callable
可执行接口。 类似 Runnable 接口。也是可以启动一个线程的接口。其中定义的方法是call。call 方法的作用和 Runnable 中的 run 方法完全一致。call 方法有返回值。
接口方法 : Object call();相当于 Runnable 接口中的 run 方法。区别为此方法有返回值。不能抛出已检查异常。
和 Runnable 接口的选择 - 需要返回值或需要抛出异常时,使用 Callable,其他情况可任意选择。
3.5 Executors
工具类型。为 Executor 线程池提供工具方法。可以快速的提供若干种线程池。如:固定容量的,无限容量的,容量为 1 等各种线程池。
线程池是一个进程级的重量级资源。默认的生命周期和 JVM 一致。当开启线程池后,直到 JVM 关闭为止,是线程池的默认生命周期。如果手工调用 shutdown 方法,那么线程池执行所有的任务后,自动关闭。
开始 - 创建线程池。
结束 - JVM 关闭或调用 shutdown 并处理完所有的任务。
类似 Arrays,Collections 等工具类型的功用。
3.6 FixedThreadPool
容量固定的线程池。活动状态和线程池容量是有上限的线程池。所有的线程池中,都有一个任务队列。使用的是 BlockingQueue<Runnable>作为任务的载体。当任务数量大于线程池容量的时候,没有运行的任务保存在任务队列中,当线程有空闲的,自动从队列中取出任务执行。
使用场景: 大多数情况下,使用的线程池,首选推荐 FixedThreadPool。OS 系统和硬件是有线程支持上限。不能随意的无限制提供线程池。
线程池默认的容量上限是 Integer.MAX_VALUE。
常见的线程池容量: PC - 200。 服务器 - 1000~10000
queued tasks - 任务队列
completed tasks - 结束任务队列

1 /** 2 * 线程池 3 * 固定容量线程池 4 * FixedThreadPool - 固定容量线程池。创建线程池的时候,容量固定。 5 * 构造的时候,提供线程池最大容量 6 * new xxxxx -> 7 * ExecutorService - 线程池服务类型。所有的线程池类型都实现这个接口。 8 * 实现这个接口,代表可以提供线程池能力。 9 * shutdown - 优雅关闭。 不是强行关闭线程池,回收线程池中的资源。而是不再处理新的任务,将已接收的任务处理完毕后 10 * 再关闭。 11 * Executors - Executor的工具类。类似Collection和Collections的关系。 12 * 可以更简单的创建若干种线程池。 13 */ 14 package concurrent.t08; 15 16 import java.util.concurrent.ExecutorService; 17 import java.util.concurrent.Executors; 18 import java.util.concurrent.TimeUnit; 19 20 public class Test_02_FixedThreadPool { 21 22 public static void main(String[] args) { 23 ExecutorService service = 24 Executors.newFixedThreadPool(5); 25 for(int i = 0; i < 6; i++){ 26 service.execute(new Runnable() { 27 @Override 28 public void run() { 29 try { 30 TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS.sleep(500); 31 } catch (InterruptedException e) { 32 e.printStackTrace(); 33 } 34 System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + " - test executor"); 35 } 36 }); 37 } 38 39 System.out.println(service); 40 41 service.shutdown(); 42 // 是否已经结束, 相当于回收了资源。 43 System.out.println(service.isTerminated()); 44 // 是否已经关闭, 是否调用过shutdown方法 45 System.out.println(service.isShutdown()); 46 System.out.println(service); 47 48 try { 49 TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(2); 50 } catch (InterruptedException e) { 51 e.printStackTrace(); 52 } 53 54 // service.shutdown(); 55 System.out.println(service.isTerminated()); 56 System.out.println(service.isShutdown()); 57 System.out.println(service); 58 } 59 60 }
3.7 CachedThreadPool
缓存的线程池。容量不限(Integer.MAX_VALUE)。自动扩容。容量管理策略:如果线程池中的线程数量不满足任务执行,创建新的线程。每次有新任务无法即时处理的时候,都会创建新的线程。当线程池中的线程空闲时长达到一定的临界值(默认 60 秒),自动释放线程。默认线程空闲 60 秒,自动销毁。
应用场景: 内部应用或测试应用。 内部应用,有条件的内部数据瞬间处理时应用,如:
电信平台夜间执行数据整理(有把握在短时间内处理完所有工作,且对硬件和软件有足够的信心)。 测试应用,在测试的时候,尝试得到硬件或软件的最高负载量,用于提供FixedThreadPool 容量的指导。

1 /** 2 * 线程池 3 * 无容量限制的线程池(最大容量默认为Integer.MAX_VALUE) 4 */ 5 package concurrent.t08; 6 7 import java.util.concurrent.ExecutorService; 8 import java.util.concurrent.Executors; 9 import java.util.concurrent.TimeUnit; 10 11 public class Test_05_CachedThreadPool { 12 13 public static void main(String[] args) { 14 ExecutorService service = Executors.newCachedThreadPool(); 15 System.out.println(service); 16 17 for(int i = 0; i < 5; i++){ 18 service.execute(new Runnable() { 19 @Override 20 public void run() { 21 try { 22 TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS.sleep(500); 23 } catch (InterruptedException e) { 24 e.printStackTrace(); 25 } 26 System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + " - test executor"); 27 } 28 }); 29 } 30 31 System.out.println(service); 32 33 try { 34 TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(65); 35 } catch (InterruptedException e) { 36 e.printStackTrace(); 37 } 38 39 System.out.println(service); 40 } 41 42 }
3.8 ScheduledThreadPool
计划任务线程池。可以根据计划自动执行任务的线程池。
scheduleAtFixedRate(Runnable, start_limit, limit, timeunit)
runnable - 要执行的任务。
start_limit - 第一次任务执行的间隔。
limit - 多次任务执行的间隔。
timeunit - 多次任务执行间隔的时间单位。
使用场景: 计划任务时选用(DelaydQueue),如:电信行业中的数据整理,没分钟整理,没消失整理,每天整理等。

1 /** 2 * 线程池 3 * 计划任务线程池。 4 */ 5 package concurrent.t08; 6 7 import java.util.concurrent.Executors; 8 import java.util.concurrent.ScheduledExecutorService; 9 import java.util.concurrent.TimeUnit; 10 11 public class Test_07_ScheduledThreadPool { 12 13 public static void main(String[] args) { 14 ScheduledExecutorService service = Executors.newScheduledThreadPool(3); 15 System.out.println(service); 16 17 // 定时完成任务。 scheduleAtFixedRate(Runnable, start_limit, limit, timeunit) 18 // runnable - 要执行的任务。 19 service.scheduleAtFixedRate(new Runnable() { 20 @Override 21 public void run() { 22 try { 23 TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS.sleep(500); 24 } catch (InterruptedException e) { 25 e.printStackTrace(); 26 } 27 System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()); 28 } 29 }, 0, 300, TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS); 30 31 } 32 33 }
3.9 SingleThreadExceutor
单一容量的线程池。使用场景: 保证任务顺序时使用。如: 游戏大厅中的公共频道聊天。秒杀。

1 /** 2 * 线程池 3 * 容量为1的线程池。 顺序执行。 4 */ 5 package concurrent.t08; 6 7 import java.util.concurrent.ExecutorService; 8 import java.util.concurrent.Executors; 9 import java.util.concurrent.TimeUnit; 10 11 public class Test_06_SingleThreadExecutor { 12 13 public static void main(String[] args) { 14 ExecutorService service = Executors.newSingleThreadExecutor(); 15 System.out.println(service); 16 17 for(int i = 0; i < 5; i++){ 18 service.execute(new Runnable() { 19 @Override 20 public void run() { 21 try { 22 TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS.sleep(500); 23 } catch (InterruptedException e) { 24 e.printStackTrace(); 25 } 26 System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + " - test executor"); 27 } 28 }); 29 } 30 31 } 32 33 }
3.10 ForkJoinPool
分支合并线程池(mapduce 类似的设计思想)。适合用于处理复杂任务。
初始化线程容量与 CPU 核心数相关。
线程池中运行的内容必须是 ForkJoinTask 的子类型(RecursiveTask,RecursiveAction)。ForkJoinPool - 分支合并线程池。 可以递归完成复杂任务。要求可分支合并的任务必须是 ForkJoinTask 类型的子类型。其中提供了分支和合并的能力。ForkJoinTask 类型提供了两个抽象子类型,RecursiveTask 有返回结果的分支合并任务,RecursiveAction 无返回结果的分支合并任务。(Callable/Runnable)compute 方法:就是任务的执行逻辑。
ForkJoinPool 没有所谓的容量。默认都是 1 个线程。根据任务自动的分支新的子线程。当子线程任务结束后,自动合并。所谓自动是根据 fork 和 join 两个方法实现的。
应用: 主要是做科学计算或天文计算的。数据分析的。

1 /** 2 * 线程池 3 * 分支合并线程池。 4 */ 5 package concurrent.t08; 6 7 import java.io.IOException; 8 import java.util.Random; 9 import java.util.concurrent.ExecutionException; 10 import java.util.concurrent.ForkJoinPool; 11 import java.util.concurrent.Future; 12 import java.util.concurrent.RecursiveTask; 13 14 public class Test_08_ForkJoinPool { 15 16 final static int[] numbers = new int[1000000]; 17 final static int MAX_SIZE = 50000; 18 final static Random r = new Random(); 19 20 21 static{ 22 for(int i = 0; i < numbers.length; i++){ 23 numbers[i] = r.nextInt(1000); 24 } 25 } 26 27 static class AddTask extends RecursiveTask<Long>{ // RecursiveAction 28 int begin, end; 29 public AddTask(int begin, int end){ 30 this.begin = begin; 31 this.end = end; 32 } 33 34 // 35 protected Long compute(){ 36 if((end - begin) < MAX_SIZE){ 37 long sum = 0L; 38 for(int i = begin; i < end; i++){ 39 sum += numbers[i]; 40 } 41 // System.out.println("form " + begin + " to " + end + " sum is : " + sum); 42 return sum; 43 }else{ 44 int middle = begin + (end - begin)/2; 45 AddTask task1 = new AddTask(begin, middle); 46 AddTask task2 = new AddTask(middle, end); 47 task1.fork();// 就是用于开启新的任务的。 就是分支工作的。 就是开启一个新的线程任务。 48 task2.fork(); 49 // join - 合并。将任务的结果获取。 这是一个阻塞方法。一定会得到结果数据。 50 return task1.join() + task2.join(); 51 } 52 } 53 } 54 55 public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException, ExecutionException, IOException { 56 long result = 0L; 57 for(int i = 0; i < numbers.length; i++){ 58 result += numbers[i]; 59 } 60 System.out.println(result); 61 62 ForkJoinPool pool = new ForkJoinPool(); 63 AddTask task = new AddTask(0, numbers.length); 64 65 Future<Long> future = pool.submit(task); 66 System.out.println(future.get()); 67 68 } 69 70 }
3.11 ThreadPoolExecutor
线程池底层实现。除 ForkJoinPool 外,其他常用线程池底层都是使用 ThreadPoolExecutor实现的。
public ThreadPoolExecutor (int corePoolSize, // 核心容量,创建线程池的时候,默认有多少线程。也是线程池保持的最少线程数 int maximumPoolSize, // 最大容量,线程池最多有多少线程 long keepAliveTime, // 生命周期,0 为永久。当线程空闲多久后,自动回收。 TimeUnit unit, // 生命周期单位,为生命周期提供单位,如:秒,毫秒 BlockingQueue<Runnable> workQueue // 任务队列,阻塞队列。注意,泛型必须是 Runnable ); //使用场景: 默认提供的线程池不满足条件时使用。如:初始线程数据 4,最大线程数200,线程空闲周期 30 秒。

1 /** 2 * 线程池 3 * 固定容量线程池 4 */ 5 package concurrent.t08; 6 7 import java.util.ArrayList; 8 import java.util.concurrent.ExecutorService; 9 import java.util.concurrent.LinkedBlockingQueue; 10 import java.util.concurrent.ThreadPoolExecutor; 11 import java.util.concurrent.TimeUnit; 12 13 public class Test_09_ThreadPoolExecutor { 14 15 public static void main(String[] args) { 16 // 模拟fixedThreadPool, 核心线程5个,最大容量5个,线程的生命周期无限。 17 ExecutorService service = 18 new ThreadPoolExecutor(5, 5, 0L, TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS, 19 new LinkedBlockingQueue<Runnable>()); 20 21 for(int i = 0; i < 6; i++){ 22 service.execute(new Runnable() { 23 @Override 24 public void run() { 25 try { 26 TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS.sleep(500); 27 } catch (InterruptedException e) { 28 e.printStackTrace(); 29 } 30 System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + " - test executor"); 31 } 32 }); 33 } 34 35 System.out.println(service); 36 37 service.shutdown(); 38 System.out.println(service.isTerminated()); 39 System.out.println(service.isShutdown()); 40 System.out.println(service); 41 42 try { 43 TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(2); 44 } catch (InterruptedException e) { 45 e.printStackTrace(); 46 } 47 48 service.shutdown(); 49 System.out.println(service.isTerminated()); 50 System.out.println(service.isShutdown()); 51 System.out.println(service); 52 53 } 54 55 }
