1昨日回顾
2作业讲解
3 结构体的基本定义
//1
struct teacher
{
int id;
char name[64];
};
struct teacher t5 = { 5, "laoshi5" };
//2
struct {
int id;
char name[64];
} t3, t4;//匿名的结构体类型 类型只能定义一次, 不能通过函数传参
//3
typedef struct _teacher
{
int id;
char name[64];
} teacher_t; //最常用的写法
/*
struct _teacher
{
int id;
char name[64];
};
typedef struct _teacher teacher_t;
*/
void print_teacher(struct teacher* p1)
{
printf("id = %d ", p1->id);
printf("name = %s ", p1->name);
}
void print_teacher2(struct teacher t) //t = t1 int a = b; struct teacher t1 = t2
{
printf("===== print_teacher2=== ");
printf("id = %d ", t.id);
printf("name = %d ", t.name);
}
void copy(struct teacher to, struct teacher from)
{
to = from;
}
void copy2(struct teacher *to, struct teacher *from)
{
*to = *from;
}
/*
void print_teacher2(struct {
int id;
char name[64];
})
*/
int main(void)
{
struct teacher t1;
struct teacher t8;
teacher_t t6 = {6, "laoshi6"};
//teacher t7; // C语言中 定义一个结构体 必须加上struct 关键字 C++不用加
t1.id = 10;
strcpy(t1.name, "laoshi1");
print_teacher(&t1);
print_teacher(&t5);
print_teacher2(t1); //
printf("===== ");
copy2(&t8, &t1);
print_teacher(&t8);
struct teacher t9 = t1; //int a = b;
return 0;
}
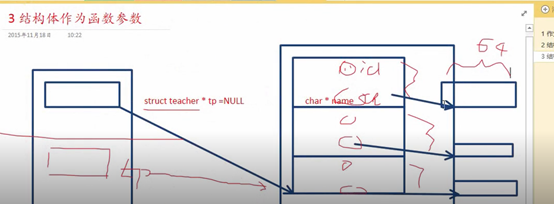
4 结构体作为函数参数
5结构体嵌套一级指针
#define _CRT_SECURE_NO_WARNINGS
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <string.h>
#define NAME_LEN (64)
struct teacher
{
int id;
char *name;
};
int create_teachers(struct teacher **tpp, int num)
{
if (tpp == NULL) return;
struct teacher *tp;
int i = 0;
// 在堆上分配空间
tp = (struct teacher*) malloc(sizeof(struct teacher)* num);
if (tp == NULL)
{
fprintf(stderr, "malloc tp error ");
return -1;
}
memset(tp, 0, sizeof(struct teacher) * num);
for (i = 0; i < num; i++)
{
// 在堆上给name分配空间
tp[i].name = (char *)malloc(sizeof(char)*NAME_LEN);
memset(tp[i].name, 0, sizeof(char)*NAME_LEN);
}
// 开辟完之后把指针传出去
*tpp = tp;
return 0;
}
void sort_teacher(struct teacher *tp,int num)
{
int i = 0;
int j = 0;
struct teacher temp_teacher;
for (i = 0;i<num-1;i++)
{
for (j = i; j < num; j++)
{
// 每次把最小的放到数组最开始的位置
if (tp[i].id > tp[j].id) {
temp_teacher = tp[i];
tp[i] = tp[j];
tp[j] = temp_teacher;
}
}
}
}
void print_teacher(struct teacher* p, int num)
{
int i = 0;
for (i = 0; i < num; i++)
{
printf("========= ");
printf("id:%d ", p[i].id);
printf("name:%s ", p[i].name);
}
}
// 内存释放
void free_teachers(struct teacher **tpp,int num)
{
if (tpp == NULL)
{
return;
}
struct teacher *tp = *tpp;
int i = 0;
if (tp != NULL)
{
for (i = 0; i < num; i++) {
if (tp[i].name != NULL)
{
free(tp[i].name);
tp[i].name = NULL;
}
}
free(tp);
*tpp = NULL;
printf("free success ");
}
}
int main(int argc,char* argv[])
{
// 创建两个老师
// 创建结构体指针
struct teacher *tp = NULL;
int num = 2;
int i = 0;
int ret = 0;
// 传入指针,通过二级指针接收来对此指针所指向内存区域进行修改
ret = create_teachers(&tp, num);
if (ret < 0) return -1;
// 为堆上的name的位置赋值
for (i = 0; i < num; i++)
{
printf("enter tp[%d]'s id :", i);
scanf("%d", &tp[i].id);
printf("enter tp[%d]'s name :", i);
scanf("%s", tp[i].name);
}
print_teacher(tp, num);
sort_teacher(tp, num);
print_teacher(tp, num);
free_teachers(&tp, num);
return 0;
}
6结构体深拷贝和浅拷贝问题
// 结构体可以通过变量直接赋值,但不要使用这种方法
// 要给结构体中的成员 一个一个的拷贝
如果结构体中有指针,浅拷贝后可能会造成重复释放的问题
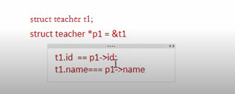
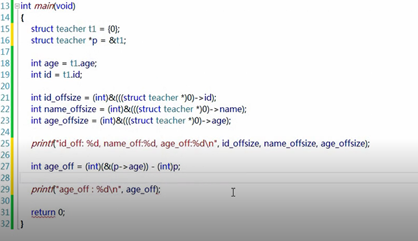
7结构体内部成员的偏移量

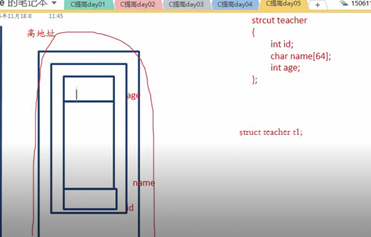
偏移:

8中午回顾
9结构体嵌套二级指针开辟内存空间
10结构体嵌套二级指针释放空间
11结构体字节对齐
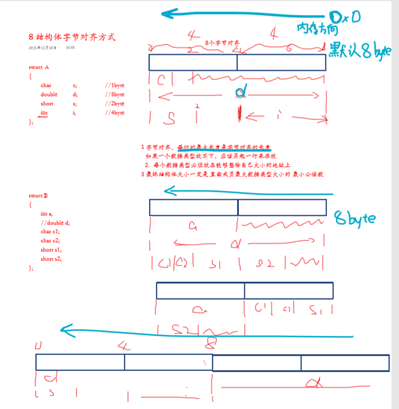
举个例子:
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 |
struct { char a; //1byte int b; //4byte char c[2] //2byte double d; //8byte }Struct_A; |
在计算机内存中,结构体变量的存储通常是按字长对齐的,比如8位机里就按字节对齐,那么上述结构体共占用1+4+2+8=15byte。
在16位机里,变量就按照2字节对齐,比如a这个成员,虽然是个char类型,地址在0x80000000本身只占1字节,但是下一个成员b却不能使用0x80000001这个地址,而必须使用0x80000002,这就是按字长对齐。以上结构体占用的空间也就是2+4+2+8=16字节
同理,在32位机中,如果a在0x80000000的话,b只能放在0x80000004,因为这里的字长是4个字节。以上结构体占用空间4+4+4+8=20字节
也就是说总有一些字节是浪费掉的,这样做的目的很简单,就是因为在大多数计算机体系结构中,对内存操作时按整字存取才能达到最高效率,相当于是以空间换取时间。当然在某些计算机体系结构中,比如ARM,是支持非对齐字传输的,也就是说变量并不一定要按照字长对齐,尽管这样可能会降低效率,但换来的是存储空间上的节约。对于程序员来讲,则需要将结构体声明为紧凑型结构体。声明的关键字依编译器不同而异,你可以去查一下__packed关键字,可以得到更详细的说明。使用紧凑型结构体,则会强制编译器将结构体成员按1字节对齐,则以上结构体占用空间仍为15字节。
资料:
https://bbs.csdn.net/topics/392057821
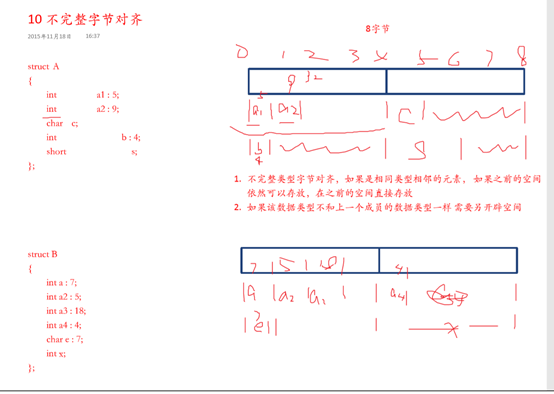
12不完整类型字节序对齐
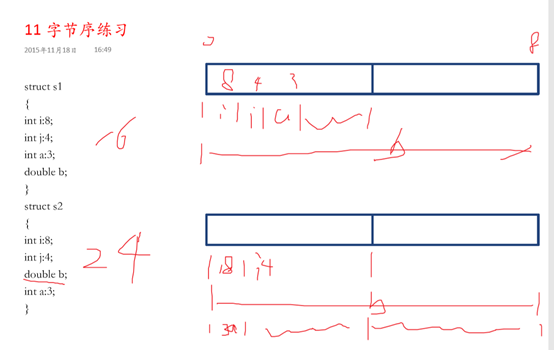
13位移操作符


14掩码
~按位取反运算符



题目:从八位开始找四位。。。这个函数实现


0按位取反编程全1 然后向左偏移n位 然后再全部取反 与 源数据x向右偏移position位 相与
?
9.文件的操作
mysql oracle 存到硬盘中的数据库
redis mongodb 内存型数据库
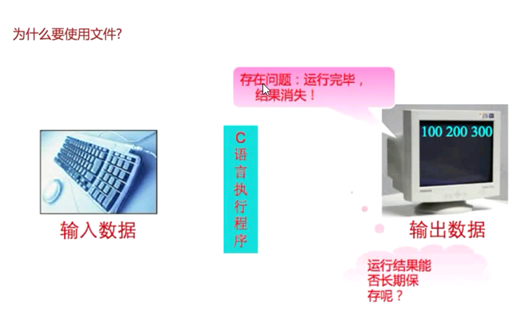

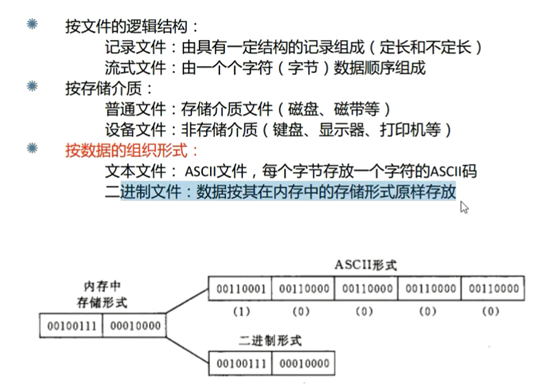


(缓冲区满了以后刷新缓冲区,存到文件中

cpu在不同进程间不停切换 ,如果没有缓冲区 cpu直接把100k放到磁盘中,然后切换进程2 然后切换进程1
现在有了缓冲区,cpu可以先把100k放到内存中(很快),然后就可以去切换进程2,后面让内存与磁盘进行交互io 效率提升
文件结构体:

操作系统通过限制文件描述符fd的数目来限制打开文件的个数



standard C I/O
fputc:
#define _CRT_SECURE_NO_WARNINGS
#include <stdio.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#define FILE_NAME "C:/Users/lg/Desktop/1.txt"
// 字符的写操作
void test_write_char()
{
char *buf = "abcdefghij";
int i = 0;
FILE *fp = fopen(FILE_NAME, "w+");
if (fp == NULL) {
fprintf(stderr, "open %s error ", FILE_NAME);
return -1;
}
for (i = 0; i < (int)strlen(buf); i++)
{
if (fputc(buf[i], fp) == EOF) {
fprintf(stderr, "fput %c error ", buf[i]);
break;
}
}
if (fp != NULL)
{
fclose(fp);
}
return 0;
}
int test_read_char()
{
FILE *fp = NULL;
char buf[128] = { 0 };
char ch = 0;
int i = 0;
fp = fopen(FILE_NAME, "r+");
if (fp == NULL)
{
fprintf(stderr, "fopen %s error ",FILE_NAME);
}
while ( (ch = fgetc(fp)) != EOF)
{
buf[i] = ch;
i++;
}
printf("buf:%s ",buf);
if (fp != NULL)
{
fclose(fp);
}
return 0;
}
int main(void)
{
test_write_char();
test_read_char();
return 0;
}
fputs fgets: 操作str
fputs不会把’ ’写进去

注意:1.fputs不会把字符串的�写进去
2.fputs不会写

注意:fgets不是根据�来从文件区分一行,而是通过 ,并会把 读进去



总结一下:
int fputc(ch,fp) (返回值是字符ascii码)
int fgetc(fp) (返回值是字符ascii 码)
int fputs(buf,fp)
char * fgets(buf,len,fp)
文件的随机存取操作
ftell
fseek
配置文件的测试框架
多文件形式编程
配置文件的写配置实现