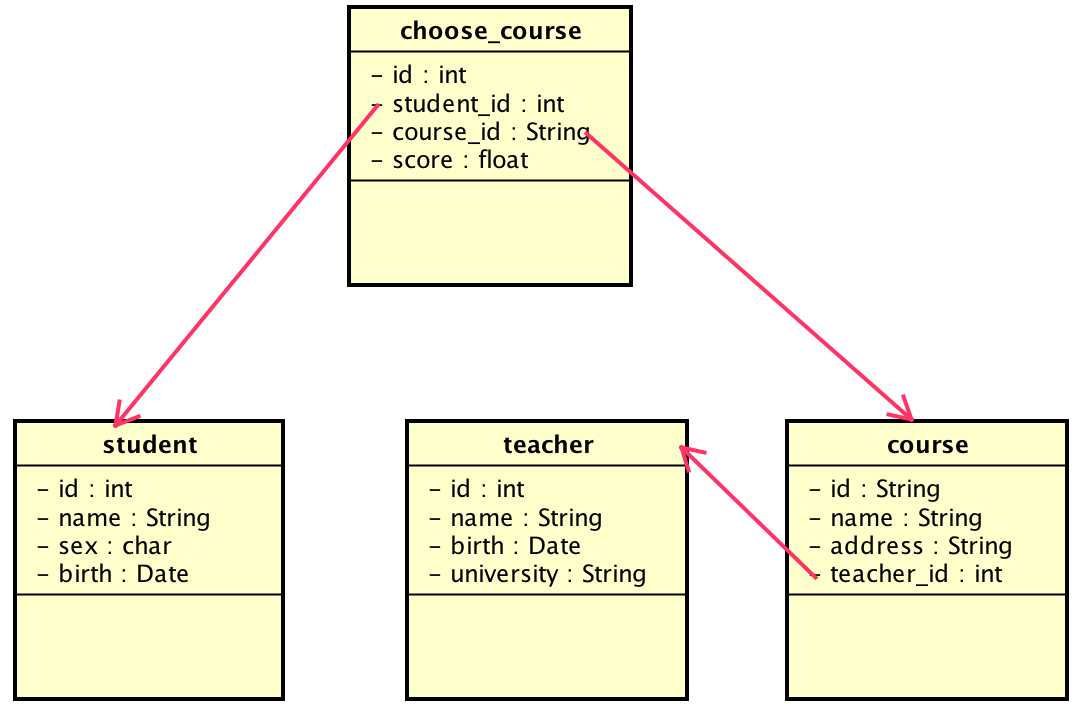
以一个实际例子来说明mysql数据库的常用操作。学生选课系统,基本表包括student表、teacher表、course表,每门课程都有固定的老师;以及学生选课表,字段包括id(主键),学生id,课程id,以及分数score。如图所示:
1、服务器的连接
shell> mysql -h host -u user -p Enter password: ****** host : 服务器运行的主机名 user : mysql账号用户名
2、数据库的创建和使用
create database course_choosing; alter database course_choosing character set utf8; use course_choosing;
3、表相关操作
create table student(id int NOT NULL primary key, name varchar(12), sex varchar(1), birth DATE); create table teacher(id int NOT NULL primary key, name varchar(12), birth date, university varchar(32)); create table course(id varchar(3) NOT NULL primary key, name varchar(16) NOT NULL, address varchar(20), teacher_id int, UNIQUE (name)); create table choose_course(id int NOT NULL primary key, student_id int, course_id varchar(3), score float(4,1));
4、插入数据
 insert into table values();
insert into table values();
insert into student values(1001, '王小明', 'm', '1990-02-12'); insert into student values(1002, '张晓丽', 'f', '1990-09-28'); insert into student values(1003, '周婷', 'f', '1989-03-29'); insert into student values(1004, '叶大勇', 'm', '1991-11-02'); insert into student values(1005, '安卓', 'm', '1990-01-20'); insert into teacher values(101, '祝大师', '1970-09-11', '北京大学'); insert into teacher values(102, '李大卫', '1973-11-01', '北京大学'); insert into teacher values(103, '乔明湘', '1980-02-11', ‘北京大学'); insert into course values('003', '经济学', '梅园区东教学楼101室', 101); insert into course values('009', '建筑学', '桃园区东教学楼304室', 103); insert into course values('011', '金融学', '梅园区东教学楼103室', 101); insert into course values('022', '软件工程', '桃园区西教学楼203室', 102); insert into choose_course values(1, 1001, '003', 80.0); insert into choose_course values(2, 1001, '009', 59.5); insert into choose_course values(3, 1001, '011', 92.0); insert into choose_course values(4, 1002, '009', 89.0); insert into choose_course values(5, 1002, '022', 67.5); insert into choose_course values(6, 1003, '022', 80.0); insert into choose_course values(7, 1004, '003', 90.0); insert into choose_course values(8, 1005, '009', 80.0); insert into choose_course values(9, 1004, '011', 62.0);
5、select语句
#limit mysql> select * from student limit 3; --等价于select * from student limit 0,3; +------+-----------+------+------------+ | id | name | sex | birth | +------+-----------+------+------------+ | 1001 | 王小明 | m | 1990-02-24 | | 1002 | 张晓丽 | f | 1990-09-28 | | 1003 | 周婷 | f | 1989-03-29 | +------+-----------+------+------------+ #order by mysql> select * from choose_course order by score desc, id asc limit 6; --按分数由高到低排列,如果相同,则按id从小到大排序 +----+------------+-----------+-------+ | id | student_id | course_id | score | +----+------------+-----------+-------+ | 3 | 1001 | 011 | 92.0 | | 7 | 1004 | 003 | 90.0 | | 4 | 1002 | 009 | 89.0 | | 1 | 1001 | 003 | 80.0 | | 6 | 1003 | 022 | 80.0 | | 8 | 1005 | 009 | 80.0 | +----+------------+-----------+-------+ #in mysql> select * from student where id in(1001, 1004); --等价于select * from student where id=1001 or id=1004; +------+-----------+------+------------+ | id | name | sex | birth | +------+-----------+------+------------+ | 1001 | 王小明 | m | 1990-02-24 | | 1004 | 叶大勇 | m | 1991-11-02 | +------+-----------+------+------------+ #between and mysql> select * from student where birth between '1990-01-01' and '1990-12-30'; +------+-----------+------+------------+ | id | name | sex | birth | +------+-----------+------+------------+ | 1001 | 王小明 | m | 1990-02-24 | | 1002 | 张晓丽 | f | 1990-09-28 | | 1005 | 安卓 | m | 1990-01-20 | +------+-----------+------+------------+ #as mysql> select * from choose_course as cc where cc.score >= 90; --等价于select * from choose_course cc where cc.score >= 90; +----+------------+-----------+-------+ | id | student_id | course_id | score | +----+------------+-----------+-------+ | 3 | 1001 | 011 | 92.0 | | 7 | 1004 | 003 | 90.0 | +----+------------+-----------+-------+ #join --JOIN: 如果表中有至少一个匹配,则返回行 --LEFT JOIN: 即使右表中没有匹配,也从左表返回所有的行 --RIGHT JOIN: 即使左表中没有匹配,也从右表返回所有的行 mysql> select t1.*,t2.course_id,t2.score from student t1 join choose_course t2 on t2.score>80 and t1.id=t2.student_id; +------+-----------+------+------------+-----------+-------+ | id | name | sex | birth | course_id | score | +------+-----------+------+------------+-----------+-------+ | 1001 | 王小明 | m | 1990-02-24 | 011 | 92.0 | | 1002 | 张晓丽 | f | 1990-09-28 | 009 | 89.0 | | 1004 | 叶大勇 | m | 1991-11-02 | 003 | 90.0 | +------+-----------+------+------------+-----------+-------+ mysql> select t1.*,t2.course_id,t2.score from student t1 left join choose_course t2 on t2.score>80 and t1.id=t2.student_id; +------+-----------+------+------------+-----------+-------+ | id | name | sex | birth | course_id | score | +------+-----------+------+------------+-----------+-------+ | 1001 | 王小明 | m | 1990-02-24 | 011 | 92.0 | | 1002 | 张晓丽 | f | 1990-09-28 | 009 | 89.0 | | 1003 | 周婷 | f | 1989-03-29 | NULL | NULL | | 1004 | 叶大勇 | m | 1991-11-02 | 003 | 90.0 | | 1005 | 安卓 | m | 1990-01-20 | NULL | NULL | | 1006 | 陈路 | f | 1989-01-23 | NULL | NULL | +------+-----------+------+------------+-----------+-------+ #union (all) mysql> select name from student limit 2 union select name from teacher; +-----------+ | name | +-----------+ | 王小明 | | 张晓丽 | | 祝大师 | | 李大卫 | | 乔明湘 | +-----------+
#having
--HAVING子句可以让我们筛选成组后的各组数据.
WHERE子句在聚合前先筛选记录.也就是说作用在GROUP BY 子句和HAVING子句前.
而HAVING子句在聚合后对组记录进行筛选。
举例:选出所有10个以上学生选择的课程id以及学生人数。
mysql> select course_id, count(*) as c from choose_course group by course_id having c>10 order by c desc;
6、其他常用操作
安装mysql后给root账号设置密码 mysqladmin -u root -p password 新增用户并且设置权限 GRANT ALL PRIVILEGES ON blog.* TO 'blog'@'%' IDENTIFIED BY 'blog';
flush privileges; ##表相关 查看默认引擎 show engines; 或者 show variables like 'table_type'; 更改表名 alter table student rename to student_new; 查看表结构 desc student; 清空表数据 delete from student; 删除表 drop table student; 查看建表语句 show create table student; ##列相关 添加列 alter table student add column age int; 删除列 alter table student drop column age; 修改列名或属性 alter table student change username name varchar(12); 添加、删除主键/外健约束 alter table course add primary key(id); alter table course add foreign key(teacher_id) references teacher(id); alter table course drop foreign key teacher_id; 多列唯一索引 alter table course add unique index (address, teacher_id); 如果不存在则插入,如果存在则更新on duplicate key update insert into course(id, name, address, teacher_id) values('111', '王晓明', '123', 129) on duplicate key update name='张晓丽';
