1.服务容错的核心知识
1.1雪崩效应
在微服务架构中,一个请求需要调用多个服务是非常常见的。如客户端访问A服务,而A服务需要调用B服务,B服务需要调用C服务,由于网络原因或者自身的原因,如果B服务或者C服务不能及时响应,A服务将处于阻塞状态,直到B服务C服务响应。此时若有大量的请求涌入,容器的线程资源会被消耗完毕,导致服务瘫痪。服务与服务之间的依赖性,故障会传播,造成连锁反应,会对整个微服务系统造成灾难性的严重后果,这就是服务故障的“雪崩”效应。

雪崩是系统中的蝴蝶效应导致其发生的原因多种多样,有不合理的容量设计,或者是高并发下某一个方法响应变慢,亦或是某台机器的资源耗尽。从源头上我们无法完全杜绝雪崩源头的发生,但是雪崩的根本原因来源于服务之间的强依赖,所以我们可以提前评估,做好熔断,隔离,限流。
1.2服务隔离
顾名思义,它是指将系统按照一定的原则划分为若干个服务模块,各个模块之间相对独立,无强依赖。当有故障发生时,能将问题和影响隔离在某个模块内部,而不扩散风险,不波及其它模块,不影响整体的系统服务。
1.3熔断降级
熔断这一概念来源于电子工程中的断路器(Circuit Breaker)。在互联网系统中,当下游服务因访问压力过大而响应变慢或失败,上游服务为了保护系统整体的可用性,可以暂时切断对下游服务的调用。这种牺牲局部,保全整体的措施就叫做熔断。
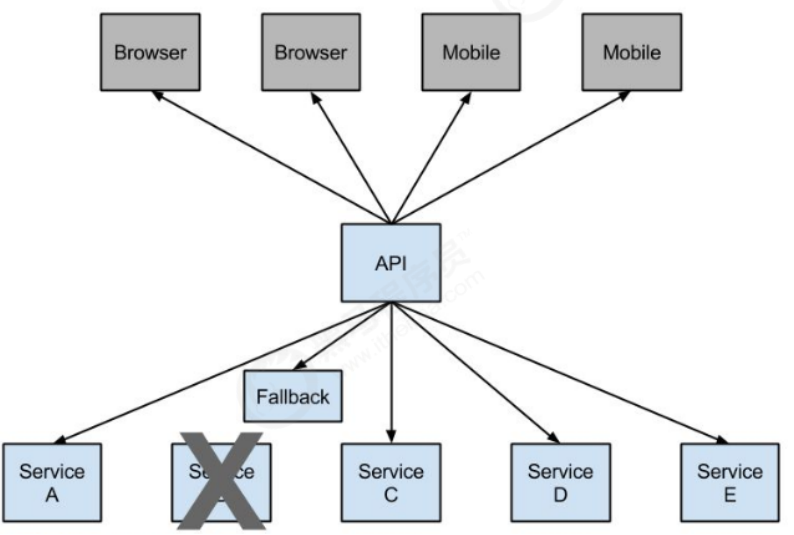
所谓降级,就是当某个服务熔断之后,服务器将不再被调用,此时客户端可以自己准备一个本地的fallback回调,返回一个缺省值。 也可以理解为兜底。
1.4服务限流
限流可以认为服务降级的一种,限流就是限制系统的输入和输出流量已达到保护系统的目的。一般来说系统的吞吐量是可以被测算的,为了保证系统的稳固运行,一旦达到的需要限制的阈值,就需要限制流量并采取少量措施以完成限制流量的目的。比方:推迟解决,拒绝解决,或者者部分拒绝解决等等。
2.Hystrix介绍

Hystrix 是由Netflix开源的一个延迟和容错库,用于隔离访问远程系统、服务或者第三方库,防止级联失败,从而提升系统的可用性与容错性。Hystrix主要通过以下几点实现延迟和容错。
- 包裹请求:使用 HystrixCommand包裹对依赖的调用逻辑,每个命令在独立线程中执行。这使用了设计模式中的“命令模式”。
- 跳闸机制:当某服务的错误率超过一定的阈值时, Hystrix可以自动或手动跳闸,停止请求该服务一段时间。
- 资源隔离: Hystrix为每个依赖都维护了一个小型的线程池(或者信号量)。如果该线程池已满,发往该依赖的请求就被立即拒绝,而不是排队等待,从而加速失败判定。
- 监控: Hystrix可以近乎实时地监控运行指标和配置的变化,例如成功、失败、超时、以及被拒绝的请求等。
- 回退机制:当请求失败、超时、被拒绝,或当断路器打开时,执行回退逻辑。回退逻辑由开发人员自行提供,例如返回一个缺省值。
- 自我修复:断路器打开一段时间后,会自动进入 “半开”状态。
3.Hystrix应用案例
3.1基础项目构建
- 新建服务消费者
cloud-provider-payment-hystrix-8001
- pom
<!--hystrix-->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.cloud</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-cloud-starter-netflix-hystrix</artifactId>
</dependency>
- yml
server:
port: 8001
spring:
application:
name: cloud-provider-hystrix-payment
eureka:
client:
register-with-eureka: true
fetch-registry: true
service-url:
#defaultZone: http://eureka7001.com:7001/eureka,http://eureka7002.com:7002/eureka
defaultZone: http://eureka7001.com:7001/eureka
- 主启动类
@SpringBootApplication
@EnableEurekaClient //本服务启动后会自动注册进eureka服务中
public class PaymentHystrixApplication {
public static void main(String[] args) {
SpringApplication.run(PaymentHystrixApplication.class, args);
}
}
- Servie
@Service
public class PaymentService
{
/**
* 正常访问,一切OK
* @param id
* @return
*/
public String paymentInfo_OK(Integer id)
{
return "线程池:"+Thread.currentThread().getName()+"paymentInfo_OK,id: "+id+" "+"O(∩_∩)O";
}
/**
* 超时访问,演示降级
* @param id
* @return
*/
public String paymentInfo_TimeOut(Integer id)
{
try { TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(5); } catch (InterruptedException e) { e.printStackTrace(); }
return "线程池:"+Thread.currentThread().getName()+"paymentInfo_TimeOut,id: "+id+" "+"O(∩_∩)O,耗费3秒";
}
}
- Controller
@RestController
@Slf4j
public class PaymentController
{
@Autowired
private PaymentService paymentService;
@Value("${server.port}")
private String serverPort;
@GetMapping("/payment/hystrix/ok/{id}")
public String paymentInfo_OK(@PathVariable("id") Integer id)
{
String result = paymentService.paymentInfo_OK(id);
log.info("****result: "+result);
return result;
}
@GetMapping("/payment/hystrix/timeout/{id}")
public String paymentInfo_TimeOut(@PathVariable("id") Integer id) throws InterruptedException
{
String result = paymentService.paymentInfo_TimeOut(id);
log.info("****result: "+result);
return result;
}
}
- 启动eureka7001
- 启动cloud-provider-payment-hystrix-8001
- 访问success方法 http://localhost:8001/payment/hystrix/ok/6
- 访问timeout方法 http://localhost:8001/payment/hystrix/timeout/6 (每次调用耗费5秒钟)
- 上述module均ok 以上述为根基平台,从正确->错误->降级熔断->恢复
3.2高并发测试
- 开启Jmeter,20000个并发压死8001,20000请求都去访问paymentInfo_TimeOut服务
- 再来一个访问 http://localhost:8001/payment/hystrix/ok/6
- 看演示结果,两个都在自己转圈圈
- 为什么会被卡死?
tomcat的默认的工作线程数被打满 了,没有多余的线程来分解压力和处理。 - 测试结论
上面还是服务提供者8001自己测试,假如此时外部的消费者80也来访问,那消费者只能干等,最终导致消费端80不满意,服务端8001直接被拖死。
3.3服务消费端加入
- 新建服务消费者
cloud-consumer-order-hystrix-80
- pom
<!--openfeign-->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.cloud</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-cloud-starter-openfeign</artifactId>
</dependency>
<!--hystrix-->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.cloud</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-cloud-starter-netflix-hystrix</artifactId>
</dependency>
<!--eureka client-->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.cloud</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-cloud-starter-netflix-eureka-client</artifactId>
</dependency>
- yml
server:
port: 80
eureka:
client:
register-with-eureka: false
service-url:
defaultZone: http://eureka7001.com:7001/eureka/
- 主启动类
@SpringBootApplication
@EnableFeignClients
public class OrderHystrixApplication {
public static void main(String[] args) {
SpringApplication.run(OrderHystrixApplication.class, args);
}
}
- Service
@Component
@FeignClient(value = "cloud-provider-hystrix-payment")
public interface PaymentHystrixService {
@GetMapping("/payment/hystrix/ok/{id}")
String paymentInfo_OK(@PathVariable("id") Integer id);
@GetMapping("/payment/hystrix/timeout/{id}")
String paymentInfo_TimeOut(@PathVariable("id") Integer id);
}
- Controller
@RestController
@Slf4j
public class OrderHystirxController
{
@Resource
private PaymentHystrixService paymentHystrixService;
@GetMapping("/consumer/payment/hystrix/ok/{id}")
public String paymentInfo_OK(@PathVariable("id") Integer id)
{
String result = paymentHystrixService.paymentInfo_OK(id);
return result;
}
@GetMapping("/consumer/payment/hystrix/timeout/{id}")
public String paymentInfo_TimeOut(@PathVariable("id") Integer id)
{
String result = paymentHystrixService.paymentInfo_TimeOut(id);
return result;
}
}
- 正常测试
http://localhost/consumer/payment/hystrix/ok/6 - 高并发测试
- 2W个线程压8001
- 消费端80微服务再去访问正常的OK微服务8001地址
http://localhost/consumer/payment/hystrix/ok/6 - 消费者80,转圈圈卡顿或者报超时错误
3.4故障现象和导致原因
- 8001同一层次的其它接口服务被困死,因为tomcat线程池里面的工作线程已经被挤占完毕。
- 80此时调用8001,客户端访问响应缓慢,转圈圈。
- 正因为有上述故障或不佳表现,才有降级/容错/限流等技术诞生
3.5如何解决?解决的要求
- 超时导致服务器变慢(转圈)
超时不再等待 - 出错(宕机或程序运行出错)
出错要有兜底 - 解决
- 对方服务(8001)超时了,调用者(80)不能一直死等待,必须有服务降级
- 对方服务(8001)宕机了,调用者(80)不能一直死等待,必须有服务降级
- 对方服务(8001)OK,调用者(80)自己出故障或有自我要求(自己的等待时间小于服务提供者),自己处理降级
4.服务降级
- 降级配置
@HystrixCommand - 8001先从自身找问题
设置自身调用超时时间的峰值,峰值内可以正常运行,超过了需要有兜底的方法处理,作服务降级fallback - 8001fallback
- 业务类启用
一旦调用服务方法失败并抛出了错误信息后,会自动调用@HystrixCommand标注好的fallbackMethod调用类中的指定方法
- 业务类启用
@Service
public class PaymentService
{
/**
* 正常访问,一切OK
* @param id
* @return
*/
public String paymentInfo_OK(Integer id)
{
return "线程池:"+Thread.currentThread().getName()+"paymentInfo_OK,id: "+id+" "+"O(∩_∩)O";
}
/**
* 超时访问,演示降级
* @param id
* @return
*/
@HystrixCommand(fallbackMethod = "paymentInfo_TimeOutHandler",commandProperties = {
@HystrixProperty(name="execution.isolation.thread.timeoutInMilliseconds",value="3000")
})
public String paymentInfo_TimeOut(Integer id)
{
int second = 5;
try { TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(second); } catch (InterruptedException e) { e.printStackTrace(); }
return "线程池:"+Thread.currentThread().getName()+"paymentInfo_TimeOut,id: "+id+" "+"O(∩_∩)O,耗费秒: "+second;
}
public String paymentInfo_TimeOutHandler(Integer id){
return "/(ㄒoㄒ)/调用支付接口超时或异常: "+ " 当前线程池名字" + Thread.currentThread().getName();
}
}
* 主启动类激活
添加新注解@EnableCircuitBreaker
@SpringBootApplication
@EnableEurekaClient //本服务启动后会自动注册进eureka服务中
@EnableCircuitBreaker
public class PaymentHystrixApplication {
public static void main(String[] args) {
SpringApplication.run(PaymentHystrixApplication.class, args);
}
}
- 80fallback
- yml
server:
port: 80
eureka:
client:
register-with-eureka: false
service-url:
defaultZone: http://eureka7001.com:7001/eureka/
feign:
hystrix:
enabled: true
* 主启动类
@SpringBootApplication
@EnableFeignClients
@EnableHystrix
public class OrderHystrixApplication {
public static void main(String[] args) {
SpringApplication.run(OrderHystrixApplication.class, args);
}
}
* 业务类
@RestController
@Slf4j
public class PaymentHystirxController
{
@Resource
private PaymentHystrixService paymentHystrixService;
@GetMapping("/consumer/payment/hystrix/ok/{id}")
public String paymentInfo_OK(@PathVariable("id") Integer id)
{
String result = paymentHystrixService.paymentInfo_OK(id);
return result;
}
@GetMapping("/consumer/payment/hystrix/timeout/{id}")
@HystrixCommand(fallbackMethod = "paymentTimeOutFallbackMethod",commandProperties = {
@HystrixProperty(name="execution.isolation.thread.timeoutInMilliseconds",value="1500")
})
public String paymentInfo_TimeOut(@PathVariable("id") Integer id)
{
String result = paymentHystrixService.paymentInfo_TimeOut(id);
return result;
}
public String paymentTimeOutFallbackMethod(@PathVariable("id") Integer id)
{
return "我是消费者80,对方支付系统繁忙请10秒钟后再试或者自己运行出错请检查自己,o(╥﹏╥)o";
}
}
- 目前问题
每个业务方法对应一个兜底的方法,代码膨胀,统一和自定义的分开 - 解决问题
- @DefaultProperties(defaultFallback = "")
@RestController
@Slf4j
@DefaultProperties(defaultFallback = "payment_Global_FallbackMethod")
public class PaymentHystirxController
{
@Resource
private PaymentHystrixService paymentHystrixService;
@GetMapping("/consumer/payment/hystrix/ok/{id}")
public String paymentInfo_OK(@PathVariable("id") Integer id)
{
String result = paymentHystrixService.paymentInfo_OK(id);
return result;
}
@GetMapping("/consumer/payment/hystrix/timeout/{id}")
@HystrixCommand //加了@DefaultProperties属性注解,并且没有写具体方法名字,就用统一全局的
public String paymentInfo_TimeOut(@PathVariable("id") Integer id)
{
String result = paymentHystrixService.paymentInfo_TimeOut(id);
return result;
}
public String paymentTimeOutFallbackMethod(@PathVariable("id") Integer id)
{
return "paymentTimeOutFallbackMethod,对方系统繁忙,请10秒钟后再次尝试/(ㄒoㄒ)/";
}
public String payment_Global_FallbackMethod()
{
return "Global异常处理信息,请稍后再试,/(ㄒoㄒ)/~~";
}
}
* @FeignClient 添加fallback
@Component
@FeignClient(value = "CLOUD-PROVIDER-HYSTRIX-PAYMENT",fallback = PaymentFallbackService.class)
public interface PaymentFeignClientService
{
@GetMapping("/payment/hystrix/{id}")
public String getPaymentInfo(@PathVariable("id") Integer id);
}
4.服务熔断
断路器:一句话就是家里的保险丝
熔断是什么?
熔断机制概述:
熔断机制是应对雪崩效应的一种微服务链路保护机制。当扇出链路的某个微服务出错不可用或者响应时间太长时,会进行服务的降级,进而熔断该节点微服务的调用,快速返回错误的响应信息。当检测到该节点微服务调用响应正常后,恢复调用链路。
在Spring Cloud框架里,熔断机制通过Hystrix实现。Hystrix会监控微服务间调用的状况,当失败的调用到一定阈值,缺省是5秒内20次调用失败,就会启动熔断机制。熔断机制的注解是@HystrixCommand。
4.1实操
- 修改cloud-provider-payment-hystrix-8001 PaymentService
//=========服务熔断
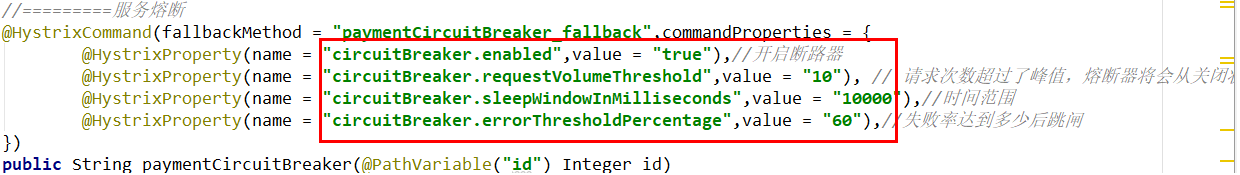
@HystrixCommand(fallbackMethod = "paymentCircuitBreaker_fallback", commandProperties = {
@HystrixProperty(name = "circuitBreaker.enabled", value = "true"),
@HystrixProperty(name = "circuitBreaker.requestVolumeThreshold", value = "10"),
@HystrixProperty(name = "circuitBreaker.sleepWindowInMilliseconds", value = "10000"),
@HystrixProperty(name = "circuitBreaker.errorThresholdPercentage", value = "60"),
})
public String paymentCircuitBreaker(@PathVariable("id") Integer id) {
if (id < 0) {
throw new RuntimeException("******id 不能负数");
}
String serialNumber = IdUtil.simpleUUID();
return Thread.currentThread().getName() + " " + "调用成功,流水号: " + serialNumber;
}
public String paymentCircuitBreaker_fallback(@PathVariable("id") Integer id) {
return "id 不能负数,请稍后再试,/(ㄒoㄒ)/~~ id: " + id;
}
- Controller
@GetMapping("/payment/circuit/{id}")
public String paymentCircuitBreaker(@PathVariable("id") Integer id) {
String result = paymentService.paymentCircuitBreaker(id);
log.info("****result: " + result);
return result;
}
- 测试
正确:http://localhost:8001/payment/circuit/31
错误:http://localhost:8001/payment/circuit/-31 - 一次正确一次错误测试
- 重点测试
多次错误,然后慢慢正确,发现刚开始不满足条件,就算是正确的访问地址也不能进行
4.2原理
熔断类型
- 熔断打开:请求不再进行调用当前服务,内部设置时钟一般为MTTR(平均故障处理时间),当打开时长达到所设时钟则进入半熔断状态。
- 熔断关闭:熔断关闭不会对服务进行熔断。
- 熔断半开:部分请求根据规则调用当前服务,如果请求成功且符合规则则认为当前服务恢复正常,关闭熔断。
官网断路器流程图
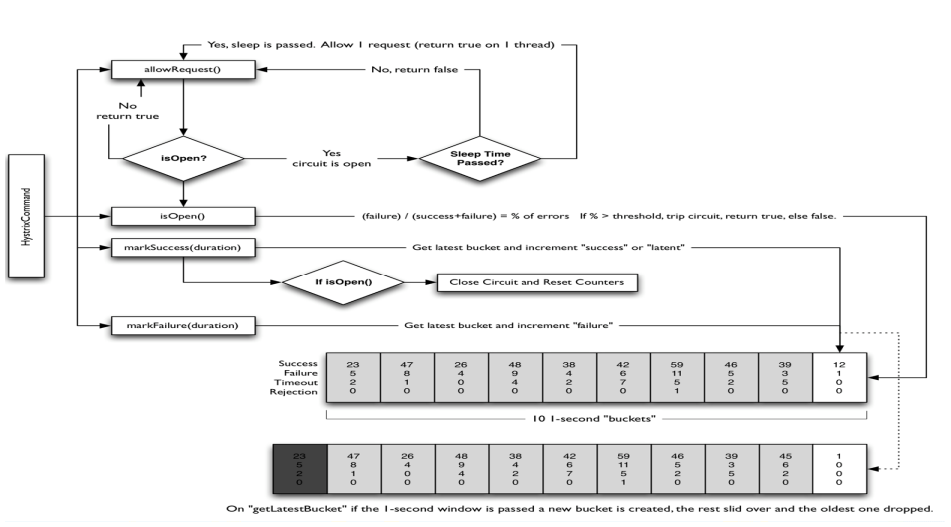
断路器在什么情况下开始起作用
涉及到断路器的三个重要参数:快照时间窗、请求总数阀值、错误百分比阀值。
1:快照时间窗:断路器确定是否打开需要统计一些请求和错误数据,而统计的时间范围就是快照时间窗,默认为最近的10秒。
2:请求总数阀值:在快照时间窗内,必须满足请求总数阀值才有资格熔断。默认为20,意味着在10秒内,如果该hystrix命令的调用次数不足20次,即使所有的请求都超时或其他原因失败,断路器都不会打开。
3:错误百分比阀值:当请求总数在快照时间窗内超过了阀值,比如发生了30次调用,如果在这30次调用中,有15次发生了超时异常,也就是超过50%的错误百分比,在默认设定50%阀值情况下,这时候就会将断路器打开。
断路器开启或者关闭的条件
- 当满足一定的阈值的时候(默认10秒内超过20个请求次数)
- 当失败率达到一定的时候(默认10秒内超过50%的请求失败)
- 到达以上阈值,断路器将会开启
- 当开启的时候,所有请求都不会进行转发
- 一段时间之后(默认是5秒),这个时候断路器是半开状态,会让其中一个请求进行转发。如果成功,断路器会关闭,若失败,继续开启重复4和5
断路器打开之后
1:再有请求调用的时候,将不会调用主逻辑,而是直接调用降级fallback。通过断路器,实现了自动地发现错误并将降级逻辑切换为主逻辑,减少响应延迟的效果。
2:原来的主逻辑要如何恢复呢?
对于这一问题,hystrix也为我们实现了自动恢复功能。
当断路器打开,对主逻辑进行熔断之后,hystrix会启动一个休眠时间窗,在这个时间窗内,降级逻辑是临时的成为主逻辑,当休眠时间窗到期,断路器将进入半开状态,释放一次请求到原来的主逻辑上,如果此次请求正常返回,那么断路器将继续闭合,主逻辑恢复,如果这次请求依然有问题,断路器继续进入打开状态,休眠时间窗重新计时。
@HystrixCommand ALL配置
//========================All
@HystrixCommand(fallbackMethod = "str_fallbackMethod",
groupKey = "strGroupCommand",
commandKey = "strCommand",
threadPoolKey = "strThreadPool",
commandProperties = {
// 设置隔离策略,THREAD 表示线程池 SEMAPHORE:信号池隔离
@HystrixProperty(name = "execution.isolation.strategy", value = "THREAD"),
// 当隔离策略选择信号池隔离的时候,用来设置信号池的大小(最大并发数)
@HystrixProperty(name = "execution.isolation.semaphore.maxConcurrentRequests", value = "10"),
// 配置命令执行的超时时间
@HystrixProperty(name = "execution.isolation.thread.timeoutinMilliseconds", value = "10"),
// 是否启用超时时间
@HystrixProperty(name = "execution.timeout.enabled", value = "true"),
// 执行超时的时候是否中断
@HystrixProperty(name = "execution.isolation.thread.interruptOnTimeout", value = "true"),
// 执行被取消的时候是否中断
@HystrixProperty(name = "execution.isolation.thread.interruptOnCancel", value = "true"),
// 允许回调方法执行的最大并发数
@HystrixProperty(name = "fallback.isolation.semaphore.maxConcurrentRequests", value = "10"),
// 服务降级是否启用,是否执行回调函数
@HystrixProperty(name = "fallback.enabled", value = "true"),
// 是否启用断路器
@HystrixProperty(name = "circuitBreaker.enabled", value = "true"),
// 该属性用来设置在滚动时间窗中,断路器熔断的最小请求数。例如,默认该值为 20 的时候,
// 如果滚动时间窗(默认10秒)内仅收到了19个请求, 即使这19个请求都失败了,断路器也不会打开。
@HystrixProperty(name = "circuitBreaker.requestVolumeThreshold", value = "20"),
// 该属性用来设置在滚动时间窗中,表示在滚动时间窗中,在请求数量超过
// circuitBreaker.requestVolumeThreshold 的情况下,如果错误请求数的百分比超过50,
// 就把断路器设置为 "打开" 状态,否则就设置为 "关闭" 状态。
@HystrixProperty(name = "circuitBreaker.errorThresholdPercentage", value = "50"),
// 该属性用来设置当断路器打开之后的休眠时间窗。 休眠时间窗结束之后,
// 会将断路器置为 "半开" 状态,尝试熔断的请求命令,如果依然失败就将断路器继续设置为 "打开" 状态,
// 如果成功就设置为 "关闭" 状态。
@HystrixProperty(name = "circuitBreaker.sleepWindowinMilliseconds", value = "5000"),
// 断路器强制打开
@HystrixProperty(name = "circuitBreaker.forceOpen", value = "false"),
// 断路器强制关闭
@HystrixProperty(name = "circuitBreaker.forceClosed", value = "false"),
// 滚动时间窗设置,该时间用于断路器判断健康度时需要收集信息的持续时间
@HystrixProperty(name = "metrics.rollingStats.timeinMilliseconds", value = "10000"),
// 该属性用来设置滚动时间窗统计指标信息时划分"桶"的数量,断路器在收集指标信息的时候会根据
// 设置的时间窗长度拆分成多个 "桶" 来累计各度量值,每个"桶"记录了一段时间内的采集指标。
// 比如 10 秒内拆分成 10 个"桶"收集这样,所以 timeinMilliseconds 必须能被 numBuckets 整除。否则会抛异常
@HystrixProperty(name = "metrics.rollingStats.numBuckets", value = "10"),
// 该属性用来设置对命令执行的延迟是否使用百分位数来跟踪和计算。如果设置为 false, 那么所有的概要统计都将返回 -1。
@HystrixProperty(name = "metrics.rollingPercentile.enabled", value = "false"),
// 该属性用来设置百分位统计的滚动窗口的持续时间,单位为毫秒。
@HystrixProperty(name = "metrics.rollingPercentile.timeInMilliseconds", value = "60000"),
// 该属性用来设置百分位统计滚动窗口中使用 “ 桶 ”的数量。
@HystrixProperty(name = "metrics.rollingPercentile.numBuckets", value = "60000"),
// 该属性用来设置在执行过程中每个 “桶” 中保留的最大执行次数。如果在滚动时间窗内发生超过该设定值的执行次数,
// 就从最初的位置开始重写。例如,将该值设置为100, 滚动窗口为10秒,若在10秒内一个 “桶 ”中发生了500次执行,
// 那么该 “桶” 中只保留 最后的100次执行的统计。另外,增加该值的大小将会增加内存量的消耗,并增加排序百分位数所需的计算时间。
@HystrixProperty(name = "metrics.rollingPercentile.bucketSize", value = "100"),
// 该属性用来设置采集影响断路器状态的健康快照(请求的成功、 错误百分比)的间隔等待时间。
@HystrixProperty(name = "metrics.healthSnapshot.intervalinMilliseconds", value = "500"),
// 是否开启请求缓存
@HystrixProperty(name = "requestCache.enabled", value = "true"),
// HystrixCommand的执行和事件是否打印日志到 HystrixRequestLog 中
@HystrixProperty(name = "requestLog.enabled", value = "true"),
},
threadPoolProperties = {
// 该参数用来设置执行命令线程池的核心线程数,该值也就是命令执行的最大并发量
@HystrixProperty(name = "coreSize", value = "10"),
// 该参数用来设置线程池的最大队列大小。当设置为 -1 时,线程池将使用 SynchronousQueue 实现的队列,
// 否则将使用 LinkedBlockingQueue 实现的队列。
@HystrixProperty(name = "maxQueueSize", value = "-1"),
// 该参数用来为队列设置拒绝阈值。 通过该参数, 即使队列没有达到最大值也能拒绝请求。
// 该参数主要是对 LinkedBlockingQueue 队列的补充,因为 LinkedBlockingQueue
// 队列不能动态修改它的对象大小,而通过该属性就可以调整拒绝请求的队列大小了。
@HystrixProperty(name = "queueSizeRejectionThreshold", value = "5"),
}
)
public String strConsumer() {
return "hello 2020";
}
public String str_fallbackMethod()
{
return "*****fall back str_fallbackMethod";
}
5.Hystrix执行流程
官网图例
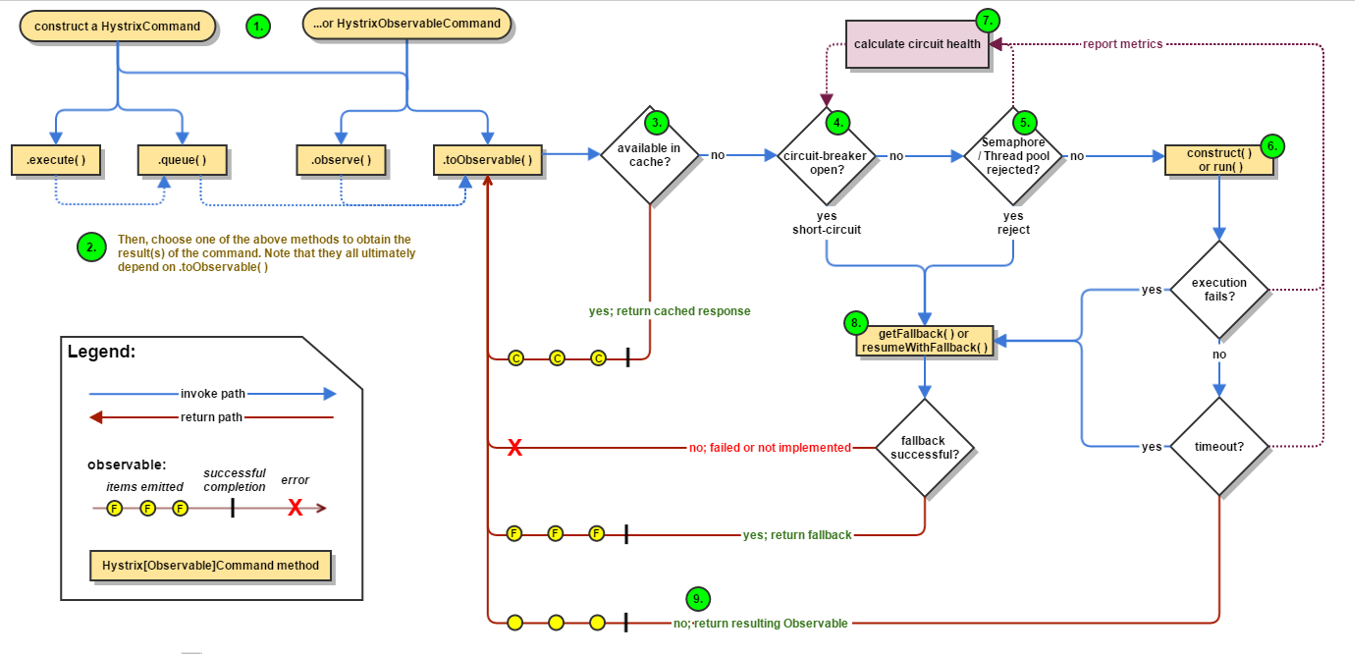
步骤说明
- 创建 HystrixCommand(用在依赖的服务返回单个操作结果的时候) 或 HystrixObserableCommand(用在依赖的服务返回多个操作结果的时候) 对象。
- 命令执行。其中 HystrixComand 实现了下面前两种执行方式;而 HystrixObservableCommand 实现了后两种执行方式:execute():同步执行,从依赖的服务返回一个单一的结果对象, 或是在发生错误的时候抛出异常。queue():异步执行, 直接返回 一个Future对象, 其中包含了服务执行结束时要返回的单一结果对象。observe():返回 Observable 对象,它代表了操作的多个结果,它是一个 Hot Obserable(不论 "事件源" 是否有 "订阅者",都会在创建后对事件进行发布,所以对于 Hot Observable 的每一个 "订阅者" 都有可能是从 "事件源" 的中途开始的,并可能只是看到了整个操作的局部过程)。toObservable(): 同样会返回 Observable 对象,也代表了操作的多个结果,但它返回的是一个Cold Observable(没有 "订阅者" 的时候并不会发布事件,而是进行等待,直到有 "订阅者" 之后才发布事件,所以对于 Cold Observable 的订阅者,它可以保证从一开始看到整个操作的全部过程)。
- 若当前命令的请求缓存功能是被启用的, 并且该命令缓存命中, 那么缓存的结果会立即以 Observable 对象的形式 返回。
- 检查断路器是否为打开状态。如果断路器是打开的,那么Hystrix不会执行命令,而是转接到 fallback 处理逻辑(第 8 步);如果断路器是关闭的,检查是否有可用资源来执行命令(第 5 步)。
- 线程池/请求队列/信号量是否占满。如果命令依赖服务的专有线程池和请求队列,或者信号量(不使用线程池的时候)已经被占满, 那么 Hystrix 也不会执行命令, 而是转接到 fallback 处理逻辑(第8步)。
- Hystrix 会根据我们编写的方法来决定采取什么样的方式去请求依赖服务。HystrixCommand.run() :返回一个单一的结果,或者抛出异常。HystrixObservableCommand.construct(): 返回一个Observable 对象来发射多个结果,或通过 onError 发送错误通知。
- Hystrix会将 "成功"、"失败"、"拒绝"、"超时" 等信息报告给断路器, 而断路器会维护一组计数器来统计这些数据。断路器会使用这些统计数据来决定是否要将断路器打开,来对某个依赖服务的请求进行 "熔断/短路"。
- 当命令执行失败的时候, Hystrix 会进入 fallback 尝试回退处理, 我们通常也称该操作为 "服务降级"。而能够引起服务降级处理的情况有下面几种:第4步: 当前命令处于"熔断/短路"状态,断路器是打开的时候。第5步: 当前命令的线程池、 请求队列或 者信号量被占满的时候。第6步:HystrixObservableCommand.construct() 或 HystrixCommand.run() 抛出异常的时候。
- 当Hystrix命令执行成功之后, 它会将处理结果直接返回或是以Observable 的形式返回。
tips:如果我们没有为命令实现降级逻辑或者在降级处理逻辑中抛出了异常, Hystrix 依然会返回一个 Observable 对象, 但是它不会发射任何结果数据, 而是通过 onError 方法通知命令立即中断请求,并通过onError()方法将引起命令失败的异常发送给调用者。
6.服务监控Hystrix Dashboard
除了隔离依赖服务的调用以外,Hystrix还提供了准实时的调用监控(Hystrix Dashboard),Hystrix会持续地记录所有通过Hystrix发起的请求的执行信息,并以统计报表和图形的形式展示给用户,包括每秒执行多少请求多少成功,多少失败等。Netflix通过hystrix-metrics-event-stream项目实现了对以上指标的监控。Spring Cloud也提供了Hystrix Dashboard的整合,对监控内容转化成可视化界面。
- 新建cloud-consumer-hystrix-dashboard-9001
- pom
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.cloud</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-cloud-starter-netflix-hystrix-dashboard</artifactId>
</dependency>
- yml
server:
port: 9001
- 主启动类
@SpringBootApplication
@EnableHystrixDashboard
public class HystrixDashboardMain9001
{
public static void main(String[] args)
{
SpringApplication.run(MainApp9001.class,args);
}
}
- 所有Provider微服务提供类都需要监控依赖配置
<!-- actuator监控信息完善 -->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-actuator</artifactId>
</dependency>
-
启动cloud-consumer-hystrix-dashboard-9001
访问http://localhost:9001/hystrix

-
修改cloud-provider-payment-hystrix-8001
注意:新版本Hystrix需要在主启动类MainAppHystrix8001中指定监控路径
@EnableEurekaClient //本服务启动后会自动注册进eureka服务中
@EnableCircuitBreaker//对hystrixR熔断机制的支持
public class MainAppHystrix8001
{
public static void main(String[] args)
{
SpringApplication.run(MainAppHystrix8001.class,args);
}
/**
*此配置是为了服务监控而配置,与服务容错本身无关,springcloud升级后的坑
*ServletRegistrationBean因为springboot的默认路径不是"/hystrix.stream",
*只要在自己的项目里配置上下面的servlet就可以了
*/
@Bean
public ServletRegistrationBean getServlet() {
HystrixMetricsStreamServlet streamServlet = new HystrixMetricsStreamServlet();
ServletRegistrationBean registrationBean = new ServletRegistrationBean(streamServlet);
registrationBean.setLoadOnStartup(1);
registrationBean.addUrlMappings("/hystrix.stream");
registrationBean.setName("HystrixMetricsStreamServlet");
return registrationBean;
}
}
-
9001监控8001
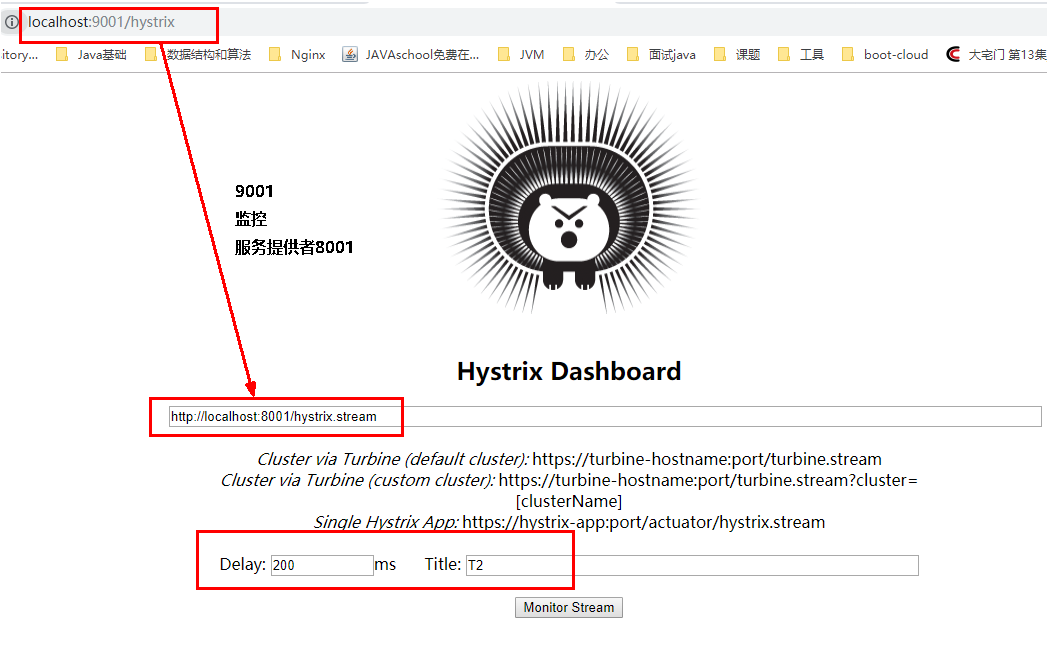
-
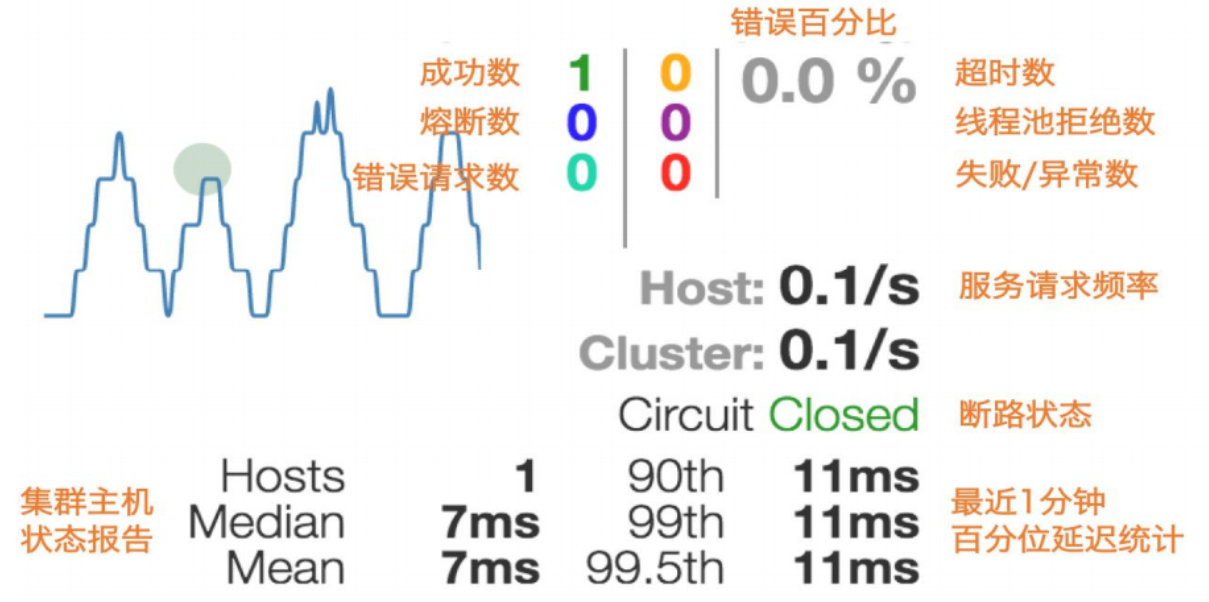
1圈
实心圆:共有两种含义。它通过颜色的变化代表了实例的健康程度,它的健康度从绿色<黄色<橙色<红色递减。
该实心圆除了颜色的变化之外,它的大小也会根据实例的请求流量发生变化,流量越大该实心圆就越大。所以通过该实心圆的展示,就可以在大量的实例中快速的发现故障实例和高压力实例。 -
1线
曲线:用来记录2分钟内流量的相对变化,可以通过它来观察到流量的上升和下降趋势。 -
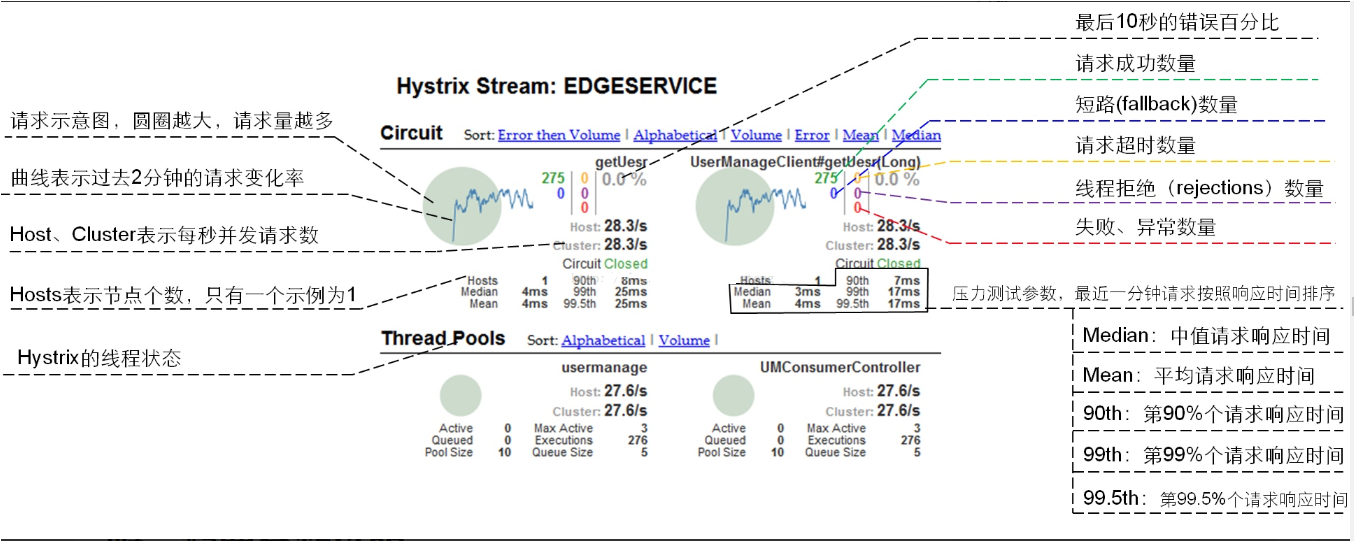
整图说明
-
整图说明2
7.Hystrix的核心源码
Hystrix 底层基于 RxJava,RxJava 是响应式编程开发库,因此Hystrix的整个实现策略简单说即:把一个HystrixCommand封装成一个Observable(待观察者),针对自身要实现的核心功能,对Observable进行各种装饰,并在订阅各步装饰的Observable,以便在指定事件到达时,添加自己的业务。
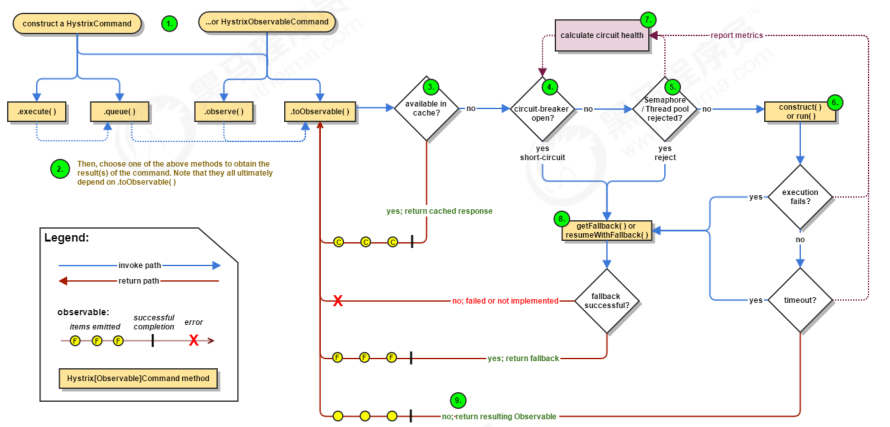
Hystrix 主要有4种调用方式:
- toObservable() 方法 :未做订阅,只是返回一个Observable 。
- observe() 方法 :调用 #toObservable() 方法,并向 Observable 注册 rx.subjects.ReplaySubject发起订阅。
- queue() 方法 :调用 #toObservable() 方法的基础上,调用:Observable#toBlocking() 和BlockingObservable#toFuture() 返回 Future 对象
- execute() 方法 :调用 #queue() 方法的基础上,调用 Future#get() 方法,同步返回 #run() 的执行结果。
主要的执行逻辑:
- 每次调用创建一个新的HystrixCommand,把依赖调用封装在run()方法中.
- 执行execute()/queue做同步或异步调用.
- 判断熔断器(circuit-breaker)是否打开,如果打开跳到步骤8,进行降级策略,如果关闭进入步骤.
- 判断线程池/队列/信号量是否跑满,如果跑满进入降级步骤8,否则继续后续步骤.
- 调用HystrixCommand的run方法.运行依赖逻辑,依赖逻辑调用超时,进入步骤8.
- 判断逻辑是否调用成功。返回成功调用结果;调用出错,进入步骤8.
- 计算熔断器状态,所有的运行状态(成功, 失败, 拒绝,超时)上报给熔断器,用于统计从而判断熔断器状态.
- getFallback()降级逻辑。以下四种情况将触发getFallback调用:
1. run()方法抛出非HystrixBadRequestException异常。
2. run()方法调用超时
3. 熔断器开启拦截调用
4. 线程池/队列/信号量是否跑满
5. 没有实现getFallback的Command将直接抛出异常,fallback降级逻辑调用成功直接返回,降级逻辑调用失败抛出异常. - 返回执行成功结果
HystrixCommand注解
在实际应用过程通过@HystrixCommand注解能够更加简单快速的实现Hystrix的应用,那么我们就直接从@HystrixCommand注解入手,其中包含了诸多参数配置,如执行隔离策略,线程池定义等,这些参数就不一一说明了,我们来看看其是如何实现服务降级的。
public @interface HystrixCommand {
String groupKey() default "";
String commandKey() default "";
String threadPoolKey() default "";
String fallbackMethod() default "";
HystrixProperty[] commandProperties() default {};
HystrixProperty[] threadPoolProperties() default {};
Class<? extends Throwable>[] ignoreExceptions() default {};
ObservableExecutionMode observableExecutionMode() default ObservableExecutionMode.EAGER;
HystrixException[] raiseHystrixExceptions() default {};
String defaultFallback() default "";
}
其定义了 fallbackMethod方法名,正如其名,其提供了一个定义回退方法映射,在异常触发时此方法名对应的method将被触发执行,从而实现服务的降级。那么@HystrixCommand注解又是如何被执行的呢,我们找到 HystrixCommandAspect.java ,其切点定义如下
@Aspect
public class HystrixCommandAspect {
private static final Map<HystrixCommandAspect.HystrixPointcutType,HystrixCommandAspect.MetaHolderFactory> META_HOLDER_FACTORY_MAP;
public HystrixCommandAspect() {
}
@Pointcut("@annotation(com.netflix.hystrix.contrib.javanica.annotation.HystrixCommand)")
public void hystrixCommandAnnotationPointcut() {
}
@Pointcut("@annotation(com.netflix.hystrix.contrib.javanica.annotation.HystrixCollapser)")
public void hystrixCollapserAnnotationPointcut() {
}
@Around("hystrixCommandAnnotationPointcut() || hystrixCollapserAnnotationPointcut()")
public Object methodsAnnotatedWithHystrixCommand(ProceedingJoinPoint joinPoint) throws Throwable {
//略
}
可以看到被 @HystrixCommand 注解的方法将会执行切面处理。
环绕通知增强
在HystrixCommandAspect的methodsAnnotatedWithHystrixCommand方法中我们可以看到如下
@Around("hystrixCommandAnnotationPointcut() || hystrixCollapserAnnotationPointcut()")
public Object methodsAnnotatedWithHystrixCommand(ProceedingJoinPoint joinPoint) throws Throwable {
Method method = AopUtils.getMethodFromTarget(joinPoint);
Validate.notNull(method, "failed to get method from joinPoint: %s", new Object[]{joinPoint});
if (method.isAnnotationPresent(HystrixCommand.class) && method.isAnnotationPresent(HystrixCollapser.class)) {
throw new IllegalStateException("method cannot be annotated with HystrixCommand and HystrixCollapser annotations at the same time");
} else {
HystrixCommandAspect.MetaHolderFactory metaHolderFactory = (HystrixCommandAspect.MetaHolderFactory)META_HOLDER_FACTORY_MAP.get(HystrixCommandAspect.HystrixPointcutType.of(method));
MetaHolder metaHolder = metaHolderFactory.create(joinPoint);
HystrixInvokable invokable = HystrixCommandFactory.getInstance().create(metaHolder);
ExecutionType executionType = metaHolder.isCollapserAnnotationPresent() ? metaHolder.getCollapserExecutionType() : metaHolder.getExecutionType();
try {
Object result;
if (!metaHolder.isObservable()) {
result = CommandExecutor.execute(invokable, executionType, metaHolder);
} else {
result = this.executeObservable(invokable, executionType, metaHolder);
}
return result;
} catch (HystrixBadRequestException var9) {
throw var9.getCause();
} catch (HystrixRuntimeException var10) {
throw this.hystrixRuntimeExceptionToThrowable(metaHolder,var10);
}
}
}
此方法通过环绕通知的形式对目标方法进行增强,主要作用如下:
- HystrixInvokable :定义了后续真正执行HystrixCommand的GenericCommand实例
- 定义 metaHolder,包含了当前被注解方法的所有相关有效信息
- 执行方法: 在进入执行体前,其有一个判断条件,判断其是否是一个Observable模式(在Hystrix中,其实现大量依赖RXJAVA,会无处不在的看到Observable,其是一种观察者模式的实现,具体可以到RxJava项目官方做更多了解)
9.服务熔断Hystrix的替换方案
18年底Netflix官方宣布Hystrix 已经足够稳定,不再积极开发 Hystrix,该项目将处于维护模式。就目前来看Hystrix是比较稳定的,并且Hystrix只是停止开发新的版本,并不是完全停止维护,Bug什么的依然会维护的。因此短期内,Hystrix依然是继续使用的。但从长远来看,Hystrix总会达到它的生命周期,那么Spring Cloud生态中是否有替代产品呢?
Alibaba Sentinel
Sentinel 是阿里巴巴开源的一款断路器实现,目前在Spring Cloud的孵化器项目 Spring Cloud Alibaba中的一员Sentinel本身在阿里内部已经被大规模采用,非常稳定。因此可以作为一个较好的替代品。
Resilience4J
Resilicence4J 一款非常轻量、简单,并且文档非常清晰、丰富的熔断工具,这也是Hystrix官方推荐的替代产品。不仅如此,Resilicence4j还原生支持Spring Boot 1.x/2.x,而且监控也不像Hystrix一样弄Dashboard/Hystrix等一堆轮子,而是支持和Micrometer(Pivotal开源的监控门面,Spring Boot 2.x中的Actuator就是基于Micrometer的)、prometheus(开源监控系统,来自谷歌的论文)、以及Dropwizard metrics(Spring Boot曾经的模仿对象,类似于Spring Boot)进行整合。