实验代码:
1 #include<stdio.h> 2 #include<string.h> 3 #define PASSWORD "1234567" 4 5 int verify_password(char *password) 6 { 7 int authenticated; 8 char buffer[8]; // add local buf to be overflowed 9 authenticated=strcmp(password,PASSWORD); 10 strcpy(buffer, password); // overflow here 11 return authenticated; 12 } 13 14 int main() 15 { 16 int valid_flag=0; 17 char password[1024]; 18 while(1){ 19 printf("Please input password: "); 20 scanf("%s",password); 21 valid_flag=verify_password(password); 22 if(valid_flag){ 23 printf("Incorrect password! "); 24 } 25 else 26 { 27 printf("Congratulation! You have passed the verification! "); 28 break; 29 } 30 } 31 return 0; 32 }
注意以上第 8 行和第 10 行的代码,对于猜测变量在内存的相对位置和溢出尝试有用。
栈帧
程序执行到 int verify_password(char *password) 时的栈帧如图:
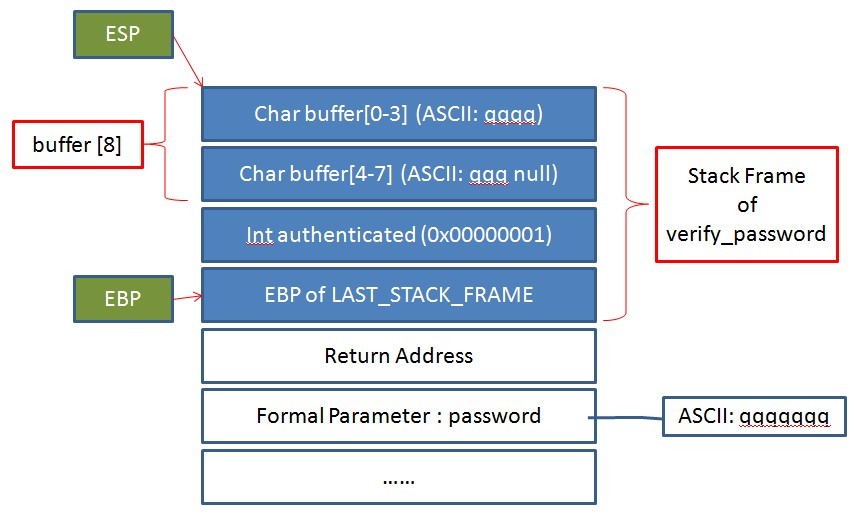
(变量在内存中的位置可能因编译优化而与上图不一致)
可见 authenticated (int 类型,内存中为 DWORD,占 4 字节)恰在 buffer 的 “下方”,如果 buffer 越界,那么 buffer[8..11] 刚好能覆盖 authenticated !
如果输入的字符超过 7 个字符(null 会占第 8 个字符),则越界字符会覆盖 authenticated。若 authenticated 被覆盖为 0,则溢出成功。
TIPS:用 OllyDBG 调试时可在栈区用【右键→Go to EBP】快速定位当前的 EBP,如图:
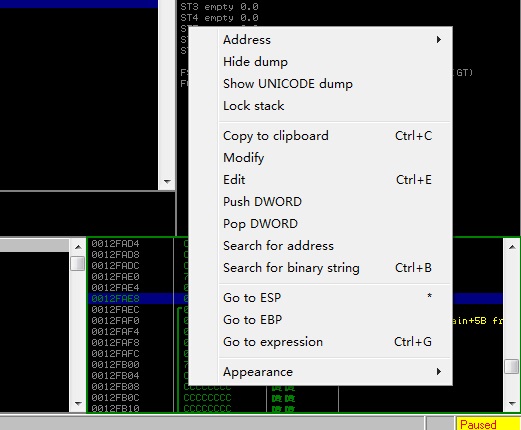
TIPS:用 OllyDBG 调试时可用 F2 设置断点。
OllyDbg 调试可见,输入 8 位密码 12345678,当程序执行完第 10 行后,authenticated 的值恰好被 password 的第九位字符串结束符 � 覆盖为 0x00000000
但需注意 authenticated 的值来源于第 9 行的 strcpy,如果输入的密码是 01234567,则 strcpy 返回 -1,authenticated 为 -1 的补码 0xFFFFFFFF,此时溢出后不能欺骗成功。