内部类的拓展
定义类or方法内部的类
最外层的类只能使用public和默认修饰
class Demo { class A { } public static void main(String[] args) { class B { } int a; } }
示例2:
class Demo { //成员变量属于类的对象,只有类的对象存在时成员变量才存在 private int bb; class A { } public static void main(String[] args) { Demo demo = new Demo(); A a = demo.new A(); A a2 = new Demo().new A(); } }
匿名内部类
语法规则
new 接口名/父类名(参数值){
//…… 抽象方法的实现or父类方法的重写
}
示例:
public interface A { void fun(); } //***************************** public static void main(String[] args) { class AAA implements A{ @Override public void fun() { System.out.println("haha"); } } A a = new AAA(); a.fun(); //假如整个系统只使用到了类AAA的一个对象,我们就可以采用匿名内部类的方式简化代码 A a2 = new A() { @Override public void fun() { System.out.println("22"); } }; a2.fun(); new A() { @Override public void fun() { System.out.println("33333333"); } }.fun(); }
示例2:【定义对象的同时重写方法】
public class AAA extends A { @Override public void fun2() { System.out.println("A fun22222"); } } public static void main(String[] args) { A a = new A(); a.fun1(); a.fun2(); AAA aaa = new AAA(); aaa.fun1(); aaa.fun2(); A a2 = new A() { @Override public void fun2() { System.out.println("A fun22222"); } }; a2.fun1(); a2.fun2(); }
示例3:
public class A { private int sth; public int getSth() { return sth; } public void setSth(int sth) { this.sth = sth; } public A(int sth) { super(); this.sth = sth; } public void fun1() { System.out.println("A fun1 " + sth); } public void fun2() { System.out.println("A fun2 " + sth); } } public static void main(String[] args) { A a = new A(1); a.fun1(); a.fun2(); A a2 = new A(1234) { public void fun1() { System.out.println(super.getSth()); }; }; a2.fun1(); a2.fun2(); new A(1234) { public void fun1() { System.out.println(getSth()); }; }.fun2(); }
File
在Java中不管是文件还是文件夹都用File类表示
示例1:
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException { File file = new File("abc321.txt"); if(!file.exists()) { file.createNewFile(); } File file2 = new File("aaa"); file2.mkdir(); File file3= new File("aaa/bb/cc");//相对路径 file3.mkdirs(); File file4 = new File("D:/abc/efg/dd.txt");//绝对路径 String path = file4.getPath(); System.out.println(path); String parent = file4.getParent(); System.out.println(parent); File parentFile = new File(parent); if(!parentFile.exists()) { parentFile.mkdirs(); } if(!file4.exists()) { file4.createNewFile(); } }
示例2:
private static void fun1() { //列举出来某一个文件夹下面所有的文件 File file = new File("C:\Users\lenovo\Documents\Tencent Files\369950806\FileRecv\Demp"); File[] listFiles = file.listFiles(); //Stream.of:将数据转换成Stream, Stream.of(listFiles).forEach(item->System.out.println(item.getName())); }
示例3:
public class Demo { public static void main(String[] args) { //列举某目录下面所有的文件,包含子文件夹下的文件 File file = new File("C:\Users\lenovo\Documents\Tencent Files\369950806\FileRecv\Demp"); fun(file); } public static void fun(File file) { File[] listFiles = file.listFiles(); for(File item : listFiles) { if(!item.isDirectory()) { System.out.println(item.getName()); }else { fun(item); } } } }
示例4:
import java.io.*; public class FileCopyDemo{ public static void main(String[] args)throws IOException{ BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader(new FileReader("D:\1.txt")); BufferedWriter bw = new BufferedWriter(new FileWriter("D:\copy.txt")); String line = ""; while((line=br.readLine())!=null){ bw.write(line); bw.newLine(); bw.flush(); } bw.close(); br.close(); }
IO
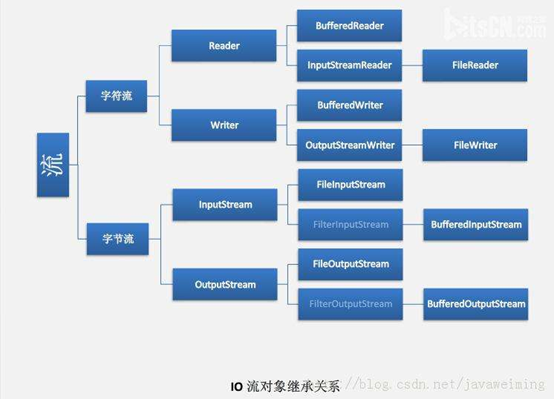
输入输出的参考坐标:计算机内存。
示例:将指定的字符写到文件中。
public static void main(String[] args) { try { //1、创建一个空的文件 File file = new File("abc.txt"); if (!file.exists()) { file.createNewFile(); } //2、准备数据 StringBuffer data = new StringBuffer(); for(int i = 0;i<8000;i++) { data.append(UUID.randomUUID().toString()); } data.append("4321*"); System.out.println(data); //往文件中写入数据 FileWriter writer = new FileWriter(file); writer.write(data.toString()); writer.flush();//刷新 //释放资源 writer.close(); } catch (Exception e) { System.out.println("haha"); } }

设计模式
单例设计模式
套路,经验的沉淀
目的:保证系统中某个类只能产生一个对象。
生成类的对象:通过new调用构造方法产生。
饿汉式
public class Boss { private Boss() { } //static类型的成员变量属于类,在类中只有一份拷贝 private static Boss boss = new Boss(); public static Boss getInstance() { return boss; } }
懒汉式
public class Boss2 { private Boss2() { } //static类型的成员变量属于类,在类中只有一份拷贝 private static Boss2 boss ; public static Boss2 getInstance() { if(boss == null) boss = new Boss2(); return boss; } }