day2:python的简介与认识
day2:# 1、写一个登录程序
# username
# passwd
# 让用户输入账号和密码,输入用户和密码输入正确的话
# 提示你 xxx,欢迎登录,今天的日期是xxx,程序结束
# 错误的话,提示账号/密码输入错误
# 最多输入3次,如果输入3次都没有登录成功,提示失败次数过多。
# 需要判断输入是否为空。
# http://www.nnzhp.cn/archives/162 参考这个博客

count=0 username = 'fancy' passwd = 123456 import datetime today = datetime.date.today() welcome = '%s 欢迎登录,今天的日期是 %s' %(username,today) while count<3: username = input('请输入用户名:') passwd = input('请输入密码:') if username == 'fancy' and passwd == '123456': print(welcome) break elif username.strip() ==''or passwd.strip() =='': print('账号或密码不能为空') elif username!='fancy' or passwd !='123456': print ('账号/密码输入错误') count+=1 else: print('失败次数超过3次')
day3:python数据类型
day3-1:#第一个作业
# 1、校验密码是否合法的程序。
# 输入一个密码
# 1、长度5-10位
# 2、密码里面必须包含,大写字母、小写字母和数字
# # http://www.nnzhp.cn/archives/160 取交集的这种方式可以实现
# 3、最多输入5次

lower_letter = [] upper_letter = [] for i in range(ord('a'),ord('z')+1): lower_letter.append(chr(i)) for i in range(ord('A'),ord('Z')+1): upper_letter.append(chr(i)) num = {'0','1','2','3','4','5','6','7','8','9'} num = set(num) lower_letter = set(lower_letter) upper_letter = set(upper_letter) # print(num) # print(lower_letter) # print(upper_letter) for i in range(5): passwd = input('输入密码:').strip() pd = set(passwd) if 4<len(passwd)<11: if pd & lower_letter and pd & upper_letter and pd & num: print('密码输入成功') break else: print('密码必须包含大小写和数字') else: print('密码长度应该为5-10') continue else: print('您输入次数超过5次')
day3-2:
# 写一个录入学生作业情况的一个程序
# 1、查看学生作业情况
# 2、录入学生作业情况
# 3、可以让输入3次,需要为空的情况
# homeworks = {
# '张三':
# {'2018.3.22':"未交",'2018.3.23':'wei交'},
# '田雨':{'2018.3.22':"未交",'2018.3.23':'wei交'},
# }

homeworks = { '张三': {'已交':'2018.1.23'}, '李四': {'已交':'2018.2.13'}, '王五': {'未交':'2018.3.01'} } for i in range(3): name = input('学生姓名: ').strip() submit = input('是否交作业: ').strip() date = input('交作业日期:').strip() if name==''or submit==''or date=='': print('录入信息不能为空') elif name in homeworks: homeworks[name]={submit:date} print(homeworks) break else: homeworks.setdefault(name,{submit:date}) print(homeworks) else: print('输入超过三次,机会已用完')
day4:字符串,文件的操作
day4-1
#1、写一个自动生成密码文件的程序
# 1、你输入几,文件里面就给你产生多少条密码
# 2、密码必须包括,大写字母、小写字母、数字、特殊字符
# 3、密码不能重复
# 4、密码都是随机产生的
# 5、密码长度6-11
# http://www.nnzhp.cn/archives/150
# 随机数怎么用 参考 random模块怎么用

import random,string #导入random,string模块 lower = string.ascii_lowercase digits = string.digits upper = string.ascii_uppercase pun = string.punctuation x = lower + digits +upper + pun #定义含大写,小写,数字和特殊字符的字符串 f = open('text.txt','a+') #以a+方式打开文件 num= input('输入您要生成密码的条数:') for i in range(int(num)): lens = random.randint(2, 7) #随机选择2—7位长度 other = random.sample(x, lens) #定义other变量为连接随机位数的字符串,从x中截取 passwd =[random.choice(lower), random.choice(digits), random.choice(upper), random.choice(pun)]+other #密码的组成,其中分别从大小写,数字及特殊字符中随机选一个 random.shuffle(passwd) #打乱密码顺序 new_passwd = ''.join(passwd) #将列表转换成字符串 f.write(new_passwd+' ') #把密码写入文件 f.close() #关闭文件
day4-2
# 写一个注册的程序,账号和密码都存在文件里面。
# choice = input('请输入你的选择:1,注册2、删除用户3、登录')
# #注册
# 输入
# 账号
# 密码
# 密码确认
# # #需要校验用户是否存在,两次输入的密码,是否一致,为空的情况
# #账号和密码都存在文件里面
# #删除
# 输入一个用户名
# #需要校验用户是否存在
# #登录
# 输入账号密码登录

user_info = {} #定义一个字典,存放username,pwd
with open('users.txt') as f:
for line in f:
line = line.strip() #第一行取到:fancy,123456
所以需要把‘
’去掉
temp = line.split(',') #将取到的每一行放在一个列表里,以逗号分隔
username = temp[0] #取列表的username
pwd = temp[1] #取列表的password
user_info[username] = pwd
for i in range(3):
choice = input('请输入你的选择:1.注册2.删除用户3.登录
').strip()
if choice =='1':
username = input('账号:
').strip()
pwd = input('密码:
').strip()
cpwd = input('重复密码:
').strip()
if username and pwd and cpwd:
if username in user_info:
print('用户名已存在,请重新注册')
else:
if pwd == cpwd:
user_info[username] = pwd #字典里username的值(即密码)与输入的密码进行比较
print('恭喜你,%s注册成功' %username)
else:
print('两次输入的密码不一致')
else:
print('用户名或密码不能为空')
elif choice == '2':
username = input('请输入账号:').strip()
if username:
if username in user_info:
user_info.pop(username)
print(user_info)
print('删除成功')
else:
print('用户名不能为空')
elif choice =='3':
username = input('请输入账号:').strip()
pwd = input('请输入密码:').strip()
if username and pwd:
if username in user_info:
if user_info.get(username) ==pwd: #从字典里取password跟输入的密码比对
print('登录成功')
else:
print('账号密码错误')
else:
print('用户名不存在')
else:
print('用户名或密码不能为空')
else:
with open('users.txt','w') as fw: #循环3次结束后,清空文件写进新内容
for uname,pwd in user_info.items(): #把文件清空,写入字典里的最新内容
fw.write(uname+','+pwd+'
')
day5:函数,文件操作的补充
day5-1
#1、写一个生成双色球号码的一个程序,生成的号码写到文件里面
# 中奖号码由6个红色球号码和1个蓝色球号码组成
# 篮球范围:01-16
# 红球范围:01-33
# def swq(num):
# random.ranint(1,16)
# #tikti.txt
# 篮球:xx 红球号码是xx 01 08 09 12 13 19
# 篮球:xx 红球号码是xx 01 08 09 12 13 19

import random def ssq(): str_red = [] while len(str_red)!=6: red = str(random.randint(1, 33)).zfill(2) if red not in str_red: str_red.append(red) blue = str(random.randint(1,16)).zfill(2) str_reds = ' '.join(str_red) res = '篮球:%s''�00''红球号码是:%s ' %(blue,str_reds) return res def file(l): with open('ssq.txt','w',encoding='utf-8') as fa: fa.writelines(l) def main(): all_res = [] num = input('输入要生成的条数:').strip() if num.isdigit(): while int(num)!=len(all_res): res = ssq() if res not in all_res: all_res.append(res) else: print('请输入整数') file(all_res) main()
day5-2
商品管理的程序,商品信息都存在一个json串里面
1、查询商品信息 #校验商品是否存在
2、新增商品 # #校验商品是否存在 #校验价格是否合法
3、修改商品信息 ##校验商品是否存在
if chice =="1":
query_goods()
elif choice = ="2":
add_goods()

import json FILE_NAME = 'goods.json' def op_file(name,content=None): if content: with open(name,'w',encoding='utf-8') as fw: json.dump(content,fw,indent=4,ensure_ascii=False) else: with open(name,encoding='utf-8') as fr: res = json.load(fr) return res all_goods = op_file(FILE_NAME) def check_price(price): price = str(price) if price.isdigit(): price = int(price) if price>0: return True else: if price.count('.')==1: tmp = price.split('.') #0.0 left = tmp[0] right = tmp[1] # 1.00 if left.isdigit() and right.isdigit() and int(right)>0: #1.0 return True elif left.isdigit() and right.isdigit() and int(left)>0: # 0.1 return True return False def get_good_info(): while True: good_name = input('商品名称:').strip() price = input('price:').strip() count = input('count:').strip() color = input('color:').strip() if good_name and price and count and color: if not check_price(price): print('价格输入不合法,必须大于0') elif not count.isdigit() and int(count)<1: print('数量不合法') else: return good_name,price,count,color else: print('输入不能为空!') def add_good(): good_name,price,count,color = get_good_info() if good_name not in all_goods: all_goods[good_name]= { 'price':price, 'count':count, 'color':color } op_file(FILE_NAME,all_goods) print('添加完成!') else: print('商品已经存在!') def update_good(): good_name,price,count,color = get_good_info() if good_name in all_goods: all_goods[good_name]= { 'price':price, 'count':count, 'color':color } op_file(FILE_NAME,all_goods) print('修改完成!') else: print('商品不存在!') def query_good(): good_name = input('商品名称:').strip() if good_name in all_goods: print(all_goods.get(good_name)) else: print('商品不存在') def delete_good(): good_name = input('商品名称:').strip() if good_name in all_goods: all_goods.pop(good_name) op_file(FILE_NAME,all_goods) else: print('商品不存在') def main(): for i in range(3): choice = input('请输入你的选择' '1、添加' '2、修改' '3、删除' '4、查看' '5、退出') if choice=="1": add_good() elif choice=="2": update_good() elif choice=="3": delete_good() elif choice=="4": query_good() elif choice=="5": quit('程序退出') else: print('输入错误,请重新输入!') return main() main()
day6:操作数据库及常用模块
day6-1
# logs目录下,有一部分文件是空的
# 1、删除log目录下,所有的空文件
# 2、删除5天前的文件

import os,datetime,time def strToTimestamp(str=None,format='%Y-%m-%d'): if str: #如果传时间 tp = time.strptime(str,format) #把格式化时间转成时间元组 res = time.mktime(tp) #把时间元组转成时间戳 else: res = time.time() return int(res) def getDate(): before = datetime.datetime.today() + datetime.timedelta(days=-5) #获取5天前的格式化时间 bef = before.strftime('%Y-%m-%d') #截取年月日%Y-%m-%d new_bef = strToTimestamp(bef) # 5天前的时间,把格式化时间转成时间戳 for abs_path,dir,file in os.walk(r'C:UsersFancyDesktopliuyulingday6logs'): for f in file: files = os.path.join(abs_path,f) #拼接文件的绝对路径 size = os.path.getsize(files) #获取文件的size new_f = f.split('.')[0].split('_')[1] #截取文件名xxxx.log if size==0: os.remove(os.path.abspath(files)) continue if strToTimestamp(new_f)<new_bef: os.remove(os.path.abspath(files)) print('有内容的文件为:%s' %files) getDate()
day6-2
# 写代码实现,把我的数据库里面的stu表中的数据,导出到excel中
#编号 名字 性别
#编号 名字 性别

import pymysql,xlwt def conSql(host,user,passwd,db,sql,port=3306,charset='utf8'): coon = pymysql.connect( host='118.24.3.40',user='jxz',passwd='123456', port=3306,db='jxz',charset='utf8' ) cur = coon.cursor() #建立游标 cur.execute('select * from stu') #执行查询语句 data = cur.fetchall() #获取所有结果 return data cur.close() coon.close() def importExcel(): book = xlwt.Workbook() #新建一个excel sheet = book.add_sheet('导入信息') #加sheet页名 data = conSql('118.24.3.40','jxz','123456','jxz','select * from stu') # print(type(data)) #打印data的类型为元组 title = ['编号','名字','性别'] for i in range(len(title)): #获取表头的长度 sheet.write(0, i, title[i]) #写表头,0表示写入的是第一行即表头,i表示列,title[i]表示写入的值 for i in range(len(data)):#写内容 if i != 0:#判断如果不是表头,即写内容 for j in range(len(title)): sheet.write(i, j, data[i][j]) #循环写入每行数据 book.save('importData.xls') #结尾要用.xls结尾 importExcel()
day6-3
# 注册
# 登录
# 数据都存在数据库里面
# id username passwd
# 注册的时候,密码存的是加密之后的密码
# username pwd cpwd, 都是必填的
# 用户不能重复
# 登录
# 账号
# 密码
# 登录成功之后打印当前的日期

import hashlib,time,datetime def pdMd5(str): new_str = str.encode() #把字符串转成bytes类型 m=hashlib.md5() #实例化对象 m.update(new_str) #对转换好的bytes类型进行加密 return m.hexdigest() def usersSelect(): #实现从数据库查出username,passwd import pymysql coon = pymysql.connect( host='118.24.3.40', user='jxz', passwd='123456', port=3306, db='jxz', charset='utf8' ) cur = coon.cursor() select =cur.execute("select username,passwd from lyl") users = cur.fetchall() #获取sql查询结果,结果是一个二维元组 users = dict(users) #将元组转化成字典,方便后面判断username和password return users return select cur.close() coon.close() def insertSql(username,passwd): import pymysql coon = pymysql.connect( host='118.24.3.40',user='jxz',passwd='123456', port=3306,db='jxz',charset='utf8' ) cur = coon.cursor() insert = cur.execute("insert into lyl(username,passwd)VALUES('%s','%s')" %(username,passwd)) data = cur.fetchall() coon.commit() #insert语句时,要使用.commit()方法 # print(data) cur.close() coon.close() def main(): import hashlib for choice in range(3): choice = input('请输入你的选择:1注册,2登录').strip() if choice=='1': username=input('输入用户名:').strip() if username in usersSelect().keys(): #users要调用 print('该账号已存在,请重新注册') else: passwd = input('输入密码:').strip() cpwd = input('再次输入密码:').strip() if passwd==cpwd: md5_pwd = pdMd5(passwd) insertSql(username,md5_pwd) #把用户名,密码写进数据库,密码加密 print(md5_pwd) print('恭喜,注册成功') else: print('两次密码输入不一致,请重新输入') if choice=='2': username = input('请输入用户名:').strip() if username in usersSelect().keys(): #判断username是否存在,存在的话输入密码 passwd = input('请输入密码:').strip() if usersSelect().get(username)==passwd: print('恭喜,登录成功%s' %datetime.date.today()) else: print('密码输入错误,请重新输入') else: print('用户名不存在,请重新输入') main()
优化版本:

import hashlib,pymysql,datetime def my_db(sql): import pymysql coon = pymysql.connect( host='118.24.3.40', user='jxz', passwd='123456', port=3306, db='jxz', charset='utf8') cur = coon.cursor() #建立游标 cur.execute(sql)#执行sql if sql.strip()[:6].upper()=='SELECT': res = cur.fetchall() else: coon.commit() res = 'ok' cur.close() coon.close() return res def my_md5(str): import hashlib new_str = str.encode() #把字符串转成bytes类型 # new_str = b'%s'%str #把字符串转成bytes类型 m = hashlib.md5() #实例化md5对象 m.update(new_str) #加密 return m.hexdigest() #获取结果返回 def reg(): username = input('username:').strip() pwd = input('pwd:').strip() cpwd = input('cpwd:').strip() if username and pwd and cpwd: sql = 'select * from nhy where name="%s";'%username # select * from nhy where name='nhy'; res = my_db(sql) if res: print('该用户已经存在!') else: if pwd == cpwd: md5_pwd = my_md5(pwd) insert_sql = 'insert into nhy (name,pwd) value ("%s","%s");'%(username,md5_pwd) my_db(insert_sql) print('注册成功!') else: print('两次输入的密码不一致') else: print('必填项不能为空!') def login(): username = input('username:').strip() pwd = input('pwd:').strip() if username and pwd: md5_pwd = my_md5(pwd) sql = 'select * from nhy where name="%s" and pwd="%s";'%(username,md5_pwd) # select * from nhy where name='nhy'; res = my_db(sql) if res: print('欢迎,登录成功!今天是%s'%datetime.date.today()) else: print('账号/密码错误!') else: print('必填项不能为空!') login()
day7:操作数据库,Redis,接口开发,操作excel
day7-1:
# 修改excel,把app_student.xls里面的数据,
# 1、如果这一行数据里面有乱码,那么就给他删掉
# 2、再加上一列,是否毕业
# 3、如果班级是天蝎座的话,毕业这一列写成毕业
# 4、其他班级的写成未毕业

import xlrd,xlwt,os # def main(): book = xlrd.open_workbook('app_student.xls') #读文件 sheet = book.sheet_by_index(0) #获取第一页 book1 = xlwt.Workbook() #新建 sheet1 = book1.add_sheet('sheet1') header = sheet.row_values(0) #获取表头 header.append('是否毕业') #加一列 for index,h in enumerate(header): #写表头 sheet1.write(0,index,h) row = 1 for i in range(1,sheet.nrows): #获取每行数据,为一个list,从2行开始循环 line = sheet.row_values(i) if '?'in str(line):#判断每一行里是否有? continue else: if line[5]=='天蝎座': line.append('毕业') else: line.append('未毕业') for index,col in enumerate(line): #写入没有乱码的内容 sheet1.write(row,index,col) row +=1 os.remove('app_student.xls') book1.save('app_student.xls') # main()
day7-2:
# 改写注册接口的:
# 1、改写我的注册接口,让它的密码存成密文的。
# 2、数据不再存在mysql里面,存到redis里面,redis的key就用string类型
# 3、lyl 7869d295e566295b51eec5d6bed67c14
# 4、校验用户是否存在
# user:lyl
将实现该功能的文件分类,便于管理和调用,目录列表如下:
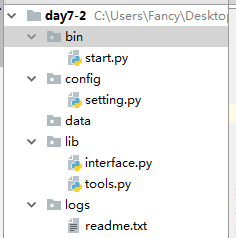
分别介绍下各个文件的作用:
1.start.py:启动文件,该程序运行时,只需要运行start.py即可。
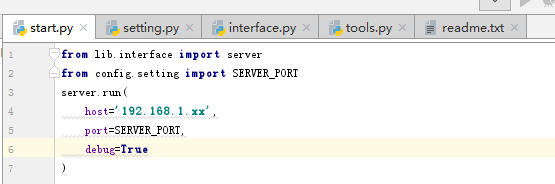
2.setting.py:配置文件,把一些具体的配置信息都写在该文件里,其他文件用到时,直接导入后调用即可。
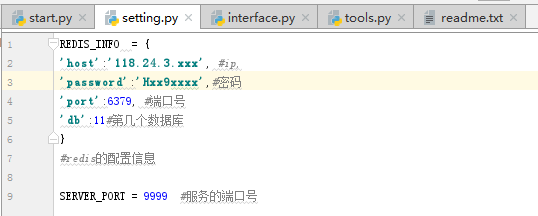
3.interface.py:接口文件,把所有的接口写在该文件里。
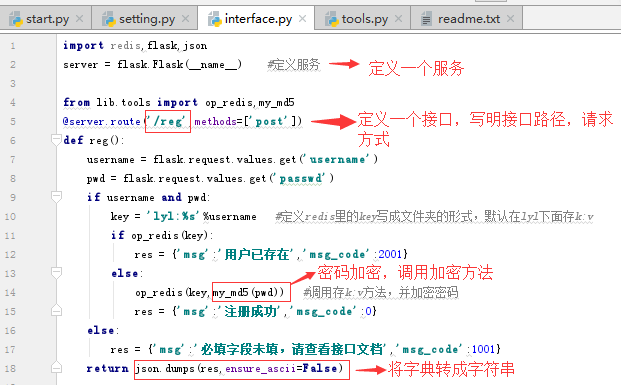
4.tools.py:该文件写各种方法,提供被调用,比如该文件里:连接redis函数,加密函数。

5.readme.txt:该文件写一些说明信息,接口信息等。
day8:requests模块,urllib,及异常处理
day8-1:
# http://doc.****.cn/index.php?s=/5&page_id=17
# 这个抽奖接口,每天只能抽奖3次,而且必须先登录才能抽奖
# 写一个函数,让他自动抽奖
# 1、先登录,获取到sign
# 2、然后再调用抽奖接口
# 3、抽奖接口每天只能抽3次,抽奖的时候如果提示你抽奖次数已经用完
# 那么你就连上redis,修改抽奖次数
