模拟ArrayList容器的实现
实现一个容器,能够存放任意类型的数据,能够自动扩容,能够实现一系列方法。
下面是练习容器的程序的第一个版本:
package MyArrayListSimulation;
public class MyArrayList {
private Object[] value;//创建一个Object类的数组对象,所有的类都是Object类的子类,所以这个数组能够存储所有类型对象
private int size;//创建一个变量保存数组的长度
private int newCapacity;
public MyArrayList() {//无参构造器
// value = new Object[16];//默认长度是16
this(16);
}
public MyArrayList(int size) {//有参构造器
value = new Object[size];//创建指定长度的Object类的数组对象
}
public void add(Object object) {//向容器中添加成分
value[size] = object;
size++;
if (size >= 16) {
newCapacity = size << 1 + 2;
Object[] newValue = new Object[newCapacity];
for (int i = 0; i < value.length; i++) {
newValue[i] = value[i];
}
value = newValue;
}
}
public int getNewCapacity() {
return newCapacity;
}
public int getSize() {//获取容器当前大小
return size;
}
public Object getValue(int index) {
return value[index];
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
MyArrayList myArrayList = new MyArrayList();
myArrayList.add("ffd");
myArrayList.add("~!@#$%^&*()");
myArrayList.add("#");
myArrayList.add("^*fd*^");
myArrayList.add(new Human("奔驰", 1));
for (int i = 0; i < myArrayList.getSize(); i++) {
if (i == myArrayList.getSize() - 1) {
Human human = (Human) myArrayList.getValue(i);
System.out.println(human.name + " " + human.age);
} else {
System.out.println(myArrayList.getValue(i));
}
}
System.out.println("Now the ArrayList have "+myArrayList.getSize()+" babys");
int realCapacity = myArrayList.getSize()<myArrayList.getNewCapacity()?myArrayList.getNewCapacity():16;
System.out.println("Now the ArrayList's capacity is "+realCapacity);
}
}
package MyArrayListSimulation;
public class Human {
public String name;
public int age;
public Human(String name, int age) {
this.name = name;
this.age = age;
}
}
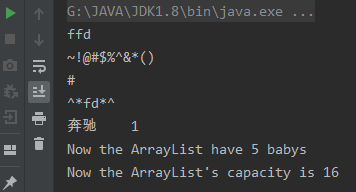
运行结果:
分析:容器的初始大小设为16,总共向容器中输入了5个不同类型的对象,经测试能够正常输出。
但是我在测试连续向容器中放入超过初试大小(16)的对象个数时,比如放入了18个对象,那么此时容器会自动扩容一次,根据规则扩容一次之后的大小应该为16*2+2=34,但是实际输出的容器大小却是38,这是为什么?
初步判断问题是出现在扩容的时候,所以我在扩容操作处设置了一个断点,然后进行debug,如下图:

当添加第16个对象时,size=15,然后size++,满足if语句条件,进入扩容操作,如上图所示,在执行完newCapacity = size * 2 + 2;后新的容器容量确实变成了16*2+2=34,然后把之前容器中的元素全部复制到新的容器中,到这里都没有问题,那么当调用add方法添加第17个对象时,size=16,size++之后仍满足if条件语句,又会执行扩容程序扩容一次,实际上此时并未溢出,接下来的几个元素也是会这样执行,当添加第18个对象时,size=18,newCapacity=18 x 2 + 2 =38,此时已经找到了问题的根源,解决办法也很简单,只需要在执行扩容语句的if条件语句多加一个判断条件即可,即:if ((size >= 16)&&(size>=newCapacity)),输出结果如下:

上面虽然基本实现了容器的功能,但是程序不够健壮,比如没有校验索引是否越界?下面进行完善并添加查找获取并返回容器中对象的索引位置、替换特定索引的对象等。
第二个版本如下:
package MyArrayListSimulation;
public class MyArrayList {
private Object[] value;//创建一个Object类的数组对象,所有的类都是Object类的子类,所以这个数组能够存储所有类型对象
private int size;//创建一个变量保存数组的长度
private int newCapacity;
public MyArrayList() {//无参构造器
// value = new Object[16];//默认长度是16
this(16);
}
public MyArrayList(int size) {//有参构造器
if (size < 0) {
try {
throw new Exception();
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
value = new Object[size];//创建指定长度的Object类的数组对象
}
public void add(Object object) {//向容器中添加成分
value[size] = object;
size++;
if ((size >= 16) && (size >= newCapacity)) {
newCapacity = size * 2 + 2;
Object[] newValue = new Object[newCapacity];
for (int i = 0; i < value.length; i++) {
newValue[i] = value[i];
}
value = newValue;
}
}
public int getNewCapacity() {
return newCapacity;
}
public int getSize() {//获取容器当前大小
return size;
}
public Object getValue(int index) {
if (index < 0 || index > size - 1) {
try {
throw new Exception();
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
return value[index];
}
public int getIndex(Object object) {//获取特定对象索引
if (object == null) {
return -1;
} else {
for (int i = 0; i < value.length; i++) {
if (value[i] == object)
return i;
}
}
return -1;
}
public Object getObject(int index) {//获取索引位置的对象
if (index < 0 || index > size - 1) {
try {
throw new Exception();
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
return value[index];
}
public void replaceObject(int index, Object object) {
if (index < 0 || index > size - 1) {
try {
throw new Exception();
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
} else {
value[index] = object;
}
}
public void outputArrayList() {
for (int i = 0; i < getSize(); i++) {
if (i == getSize() - 1) {
Human human = (Human) getValue(i);
System.out.println(human.name + " " + human.age);
} else {
System.out.println(getValue(i));
}
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
MyArrayList myArrayList = new MyArrayList();
myArrayList.add("ffd");
myArrayList.add("~!@#$%^&*()");
myArrayList.add("#");
myArrayList.add("^*fd*^");
myArrayList.add(new Human("奔驰", 1));
myArrayList.outputArrayList();
System.out.println("Now the ArrayList have " + myArrayList.getSize() + " babys");
int realCapacity = myArrayList.getSize() < myArrayList.getNewCapacity() ? myArrayList.getNewCapacity() : 16;
System.out.println("Now the ArrayList's capacity is " + realCapacity);
myArrayList.replaceObject(2, "12345");
System.out.println("The String (^*fd*^)'s index is: " + myArrayList.getIndex("ffd"));
System.out.println("The index of object is: " + myArrayList.getObject(1));
myArrayList.outputArrayList();
}
}
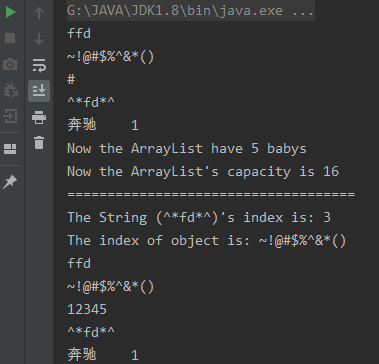
运行结果:
基本实现功能,当然还有很多待优化的内容,以后我再继续完善。