最小和

位运算知识点
12>>1 //6 a/2 等价为 a>>1
中间数 (L+R)/2 会出现溢出(溢出的意思就是超过了二进制)
L+(R-L)/2 最终改成 l+((r-l)>>1)
const smallSum = arr => { if (arr == null || arr.length < 2) { return 0; } return mergeSort(arr, 0, arr.length - 1) } const mergeSort = (arr, l, r) => { if (l == r) { return 0; } // let mid = Math.floor((l + r) / 2) let mid = l+((r-l)>>1) return mergeSort(arr, l, mid) + mergeSort(arr, mid + 1, r) + merge(arr, l, mid, r) } const merge = (arr, l, m, r) => { let help = []; let i = 0; let p1 = l; let p2 = m + 1; let res=0; while (p1 <= m && p2 <= r) { //如果左边小于右边,r开始到p2的个数*p1 //简单理解成 p1<p2 重复的加在一起 res+=arr[p1]<arr[p2]?(r-p2+1)*arr[p1]:0; help[i++] = arr[p1] < arr[p2] ? arr[p1++] : arr[p2++] } while (p1 <= m) { help[i+1]=arr[p1++] } while (p2 <= r) { help[i++]=arr[p2++] } for (let j = 0; j < help.length; j++) { arr[l + j] = help[j] } return res } console.log(smallSum([1, 2, 3]))
递归的理解
递归算法实际上是一种分而治之的方法,它把复杂问题分解为简单问题来求解。对于某些复杂问题(例如hanio塔问题),递归算法是一种自然且合乎逻辑的解决问题的方式,但是递归算法的执行效率通常比较差。因此,在求解某些问题时,常采用递归算法来分析问题,用非递归算法来求解问题
,递归会出问题的话,循环也一定会出问题,只不过递归是出了问题才告诉你,而循环则在执行前就可以知道有问题
循环和递归有种逆向思维关系, 循环通常来自底向上, 递归自顶向下。
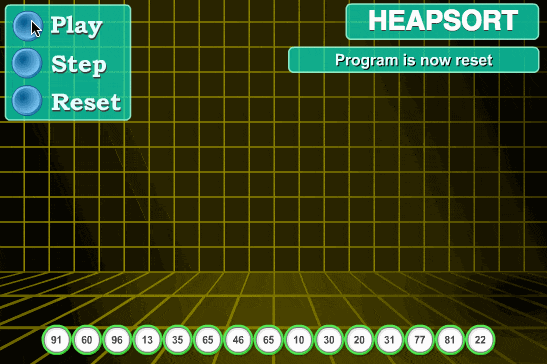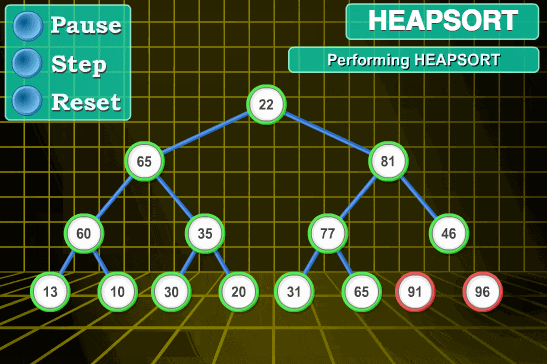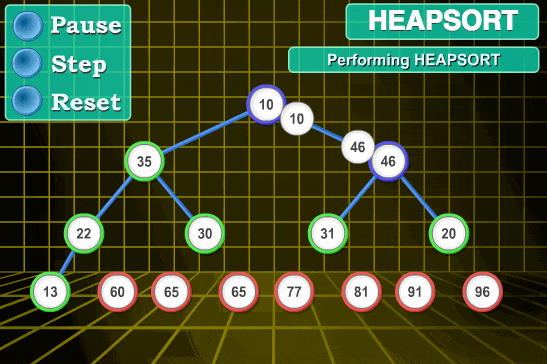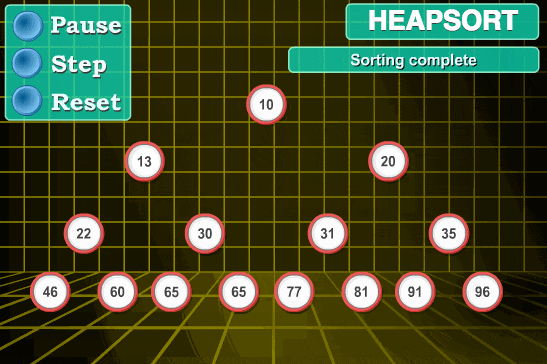
堆排序
将数组转化成二叉树
左节点
2*i+1右节点2*i+2父节点 (i-1)/2大根堆=>就是完全二叉树
// 堆 let len; //数组长度 //建立大堆顶 function builddMaxHeap(arr) { len = arr.length; for (let i = Math.floor(len / 2); i >= 0; i--) { heapify(arr, i) } } //堆调整 const heapify = (arr, i) => { let left = 2 * i + 1, right = 2 * i + 2, largest = i; if (left < len && arr[left] > arr[largest]) { largest=left; } if (right < len && arr[right] > arr[largest]) { largest=right; } if (largest != i) { swap(arr, i, largest) heapify(arr, largest) } } function swap(arr, i, j) { var temp = arr[i]; arr[i] = arr[j]; arr[j] = temp; } //排序 function heapSort(arr) { builddMaxHeap(arr) for (let i = arr.length-1; i >0 ; i--) { //0 i>0 最后一个和0交换 swap(arr, 0, i) len--; //0重新被排到最后 heapify(arr,0) } return arr; }
排序
let arr=[
{name:'张三',age:122,height:423},
{name:'张三',age:14,height:223},
{name:'张三',age:16,height:123},
]
console.log(arr.sort((a, b) => a.age - b.age))
矩阵算法
回型打印

let arr=[
[1,2,3,4],
[1,2,3,4],
[1,2,3,4],
[1,2,3,4]
]
const spiralOrder=(arr)=>{
let x1=0;
let y1=0;
let x2=arr.length-1;
let y2=arr[0].length-1;
//这个代码是直接找外层循环后再找内层循环
while (x1 <= x2 && y1 <= y2) {
printEdge(arr,x1++,y1++,x2--,y2--)
}
//下面这层代码是直接找外层循环
//printEdge(arr,x1,y1,x2,y2)
}
const printEdge = (arr,x1, y1, x2, y2) => {
// x轴相等
// 0 0 0 3
if(x1==x2){
for (let i = y1; i <=y2 ; i++) {
// [0][0] [0][1] [0][2] [0][3]
console.log(arr[x1][i])
}
//y轴相等
//0 0 3 0
}else if (y1 == y2) {
for (let i = x1; i <=x2 ; i++) {
console.log(arr[i][y1])
}
}else{
let cy1=y1;
let cx1=x1;
while (cy1 != y2) {
//(0,0) (0,1) (0,2)
console.log(arr[x1][cy1])
cy1++
}
while (cx1 != x2) {
//(0,3)(1,3)(2,3)
console.log(arr[cx1][y2])
cx1++
}
while (cy1 != y1) {
//(3,3)(3,2)(3,1)
console.log(arr[x2][cy1])
cy1--
}
while (cx1 != x1) {
//(3,0)(2,0)(1,0)
console.log(arr[cx1][y1])
cx1--
}
}
}
spiralOrder(arr)
打印Z形矩阵
宏观基础
一行是一横行
一列是一纵向
//虽然我懂了,但是我被这个行呀,列呀搞糊涂了
/**
* 将 AB连线上的元素打印出来
* @param {要打印的矩阵} m
* @param {A的横坐标} x1
* @param {A的纵坐标} y1
* @param {B的横坐标} x2
* @param {B的纵坐标} y2
* @param {打印方向} f
*/
printMatrizIGZag=(arr) =>{
let x1 = 0;
let y1 = 0;
let x2 = 0;
let y2 = 0;
let enx2 = arr.length - 1,
eny2 = arr[0].length - 1;
let fromUp = false;
// 判断条件:AB走到最后即结束循环
while (x1 != enx2 + 1) {
printLevel(arr, x1, y1, x2, y2, fromUp);
x1 = y1 == eny2 ? x1 + 1 : x1;
y1 = y1 == eny2 ? y1 : y1 + 1;
y2 = x2 == enx2 ? y2 + 1 : y2;
x2 = x2 == enx2 ? x2 : x2 + 1;
fromUp = !fromUp;
}
}
printLevel=(m, x1, y1, x2, y2, f)=> {
if (f) {
while (x1 != x2 + 1) {
console.log(m[x1++][y1--])
}
} else {
while (x2 != x1 - 1) {
console.log(m[x2--][y2++])
}
}
}
let arr = [
[1, 2, 3, 4],
[1, 2, 3, 4],
[1, 2, 3, 4],
[1, 2, 3, 4]
]
printMatrizIGZag(arr)
链表
链表是由一系列的节点组成的集合,每个节点都使用一个对象的引用指向他的后继,指向另一个节点的引用叫链
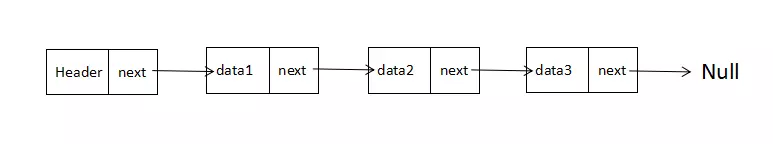
有点麻烦,先放放
二叉树遍历
定义一个初始化的二叉树
var nodes = {
node: 6,
left: {
node: 5,
left: {
node: 4
},
right: {
node: 3
}
},
right: {
node: 2,
right: {
node: 1
}
}
}
/*
* 6
* 5 2
* 4 3 1
* */
先序遍历
递归版
- 若二叉树为空,则算法结束,否则:
- 访问根节点
- 前序遍历根节点的左子树
- 前序遍历根节点的右子树
let result = []; const dfs = nodes => { if (nodes.node) { result.push(nodes.node) //先递归添加所有的左节点 nodes.left && dfs(nodes.left) //再递归添加所有的右节点 nodes.right && dfs(nodes.right) } } dfs(nodes) console.log(result) // [6, 5, 4, 3, 2, 1]非递归版
- 初始化一个栈,将根节点压入栈中
- 先判断右节点有没有,有就入栈,再判断左节点有没有,有就入栈
- 然后再出栈(pop), 先出左节点,再出右节点
var dfs = function(nodes) { var result = [] var stack = [] stack.push(nodes) while (stack.length) { var item = stack.pop() result.push(item.node) item.right && stack.push(item.right) item.left && stack.push(item.left) } return result } console.log(dfs(nodes)) // [6, 5, 4, 3, 2, 1]
中序遍历
左 中 右
递归版
- 先入栈6,5,4 出栈4,5,6再5节点的时候因为有右节点3,先入栈,添加到数组中,所以是4,5,3,6
- 再右节点入栈的时候,因为入栈一个就添加到数组中,所以是2,1
var result = [] var dfs = function(nodes) { if(nodes.node) { //也就是先入栈6,5,4,所有出栈是4,5,6 nodes.left && dfs(nodes.left) result.push(nodes.node)//(4,5) 3 6 nodes.right && dfs(nodes.right)//因为5有右节点(3) , // 然后就是右节点2入栈的时候就添加到数组中,右节点1入栈也被添加了 } } dfs(nodes) console.log(result) // [4, 5, 3, 6, 2, 1]非递归版
var dfs = function(nodes) { var result = [] var stack = [] var item = nodes stack.push(nodes) while (stack.length) { if(item.left && !item.touched) {//因为4的item.left没有直接跳出 item.touched = true item = item.left stack.push(item) //(6,5,4) continue } item.touched && delete item.touched // 清理标记 item = stack.pop() result.push(item.node) //4,5, item.right && stack.push(item.right) //然后把3入栈,因为3没有左节点直接出栈 } return result } console.log(dfs(nodes))
后序遍历
左右中
递归版
不用解释,打印下你就懂了 var result = [] var dfs = function(nodes) { if(nodes.node) { nodes.left && dfs(nodes.left) nodes.right && dfs(nodes.right) result.push(nodes.node) } } dfs(nodes) console.log(result)非递归版
function Stack() { var items = []; //用来保存栈里的元素 this.push = function (element) { items.push(element); } this.pop = function () { return items.pop(); } this.peek = function () { return items[items.length - 1]; } this.isEmpty = function () { return items.length == 0; } this.size = function () { return items.length; } this.clear = function () { items = []; } this.print = function () { console.log(items.toString()); } } //也就是先序遍历(中左右)换成中右左 const preOrder = (head) => { if (head != null) { const stack = new Stack() stack.push(head) while (!stack.isEmpty()) { head=stack.pop() console.log(head.node) if (head.right != null) { stack.push(head.right) } if (head.left != null) { stack.push(head.left) } } } } preOrder(nodes) 最简洁的方法 const preOrder = (head) => { if (head != null) { const stack = new Stack() stack.push(head) let c=null; while (!stack.isEmpty()) { //查看栈顶(就是最后一个) c=stack.peek() if (c.left != null && head != c.left && head != c.right) { stack.push(c.left) }else if (c.right != null && head != c.right) { stack.push(c.right) }else{ console.log(stack.pop().node) head=c } } } } preOrder(nodes)
打印直观的二叉树
给一个节点,找到这个节点的后继
直接用java代码吧比较直观
public static class Node {
public int value;
public Node left;
public Node right;
public Node parent;
public Node(int data) {
this.value = data;
}
}
public static Node getSuccessorNode(Node node) {
if (node == null) {
return node;
}
if (node.right != null) { //如果当前节点的右孩子节点不为空,说明有右子树,
return getLeftMost(node.right); //则找到并返回右子树上最左的节点
} else { //如果当前节点没有右子树
Node parent = node.parent;
while (parent != null && parent.left != node) {
node = parent;
parent = node.parent;
}
return parent;
}
}
public static Node getLeftMost(Node node) { //在这个函数里面,node是某个节点的头部
if (node == null) {
return node;
}
while (node.left != null) { //左子树不为空的情况下,一路向左
node = node.left;
}
return node;
}
记录的过程叫做序列化,把一个内容还原出内存中的树结构,就是反序列化
序列化二叉树

定义一个如图的二叉树
const symmetricalTree = { val: 1, left: { val: 2, left: { val: 4, left: null, right: null }, right: { val: 5, left: null, right: null } }, right: { val: 3, left: { val: 6, left: null, right: null }, right: { val: 7, left: null, right: null } } }先序序列化
//序列化 function Serialize(pRoot, arr = []) { if (!pRoot) { arr.push('#'); } else { arr.push(pRoot.val); Serialize(pRoot.left, arr); Serialize(pRoot.right, arr); } return arr.join(','); }反序列化
//反序列化 function Deserialize(str) { if (!str) { return null; } return deserialize(str.split(',')); } function deserialize (arr) { let node = null; const current = arr.shift(); if (current !== '#') { node = { val: current }; node.left = deserialize(arr); node.right = deserialize(arr); } return node; }可以去查查先序,中序,后序,层序的实现,还有其中的递归版和非递归版
###############################################################################################################################################################################................................................................................................................................................................