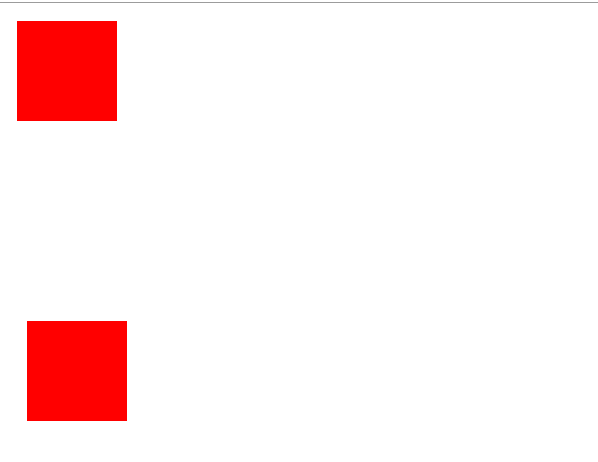
https://css-tricks.com/mega-list-svg-information/
rect 矩形
<svg width='200' height='200'>
<g transform="translate(10 50) rotate(-30)">
<!-- 移动 (10,50) 旋转 -30 -->
<rect x='50' y='50' width='100' height='50' fill='red' stroke='#000' stroke-width='5'>
<!-- x,y 位置 width,height 矩形的宽高 fill 填充的颜色 stroke 边框的颜色 stroke-width 边框的宽度 -->
</rect>
</g>
</svg>
rx='10' ry='10'
圆角
viewBox
视区盒子
viewBox="x, y, width, height"
// x:左上角横坐标,y:左上角纵坐标,宽度,height:高度

<svg width='200' height='200' style="border:1px solid #cd0000;" viewBox="0,0,100,100">
相当于在 0,0 的位置 把svg缩小了一倍
circle圆
<circle cx="50" cy="60" r="50"/>
cx,cy 圆点
r 半径
ellipse 椭圆
<svg width='200' height='200' style="border:1px solid #cd0000;margin: 100px">
<ellipse rx="10" ry="50" fill="none" stroke="red" stroke-width="2" transform="translate(100,100)"></ellipse>
</svg>
line 直线
<svg width='500' height='500' style="border:1px solid #cd0000;margin: 100px">
<g stroke="green">
<line x1="100" y1="300" x2="400" y2="480" stroke-width="3"></line>
</g>
</svg>
polyline 折线
<svg width='500' height='500' style="border:1px solid #cd0000;margin: 100px"> <polyline fill="none" stroke="blue" stroke-width="10" points="50 50,400 20,300 200," /> </svg>
polygon多边形
<svg width='500' height='500' style="border:1px solid #cd0000;margin: 100px">
<polygon points="20 30,50 60,350 100" fill="red" stroke="blue" stroke-width="2"></polygon>
</svg>
例子
M 100,200 L 400,300
M 100,200 L 400,300 L 123,44
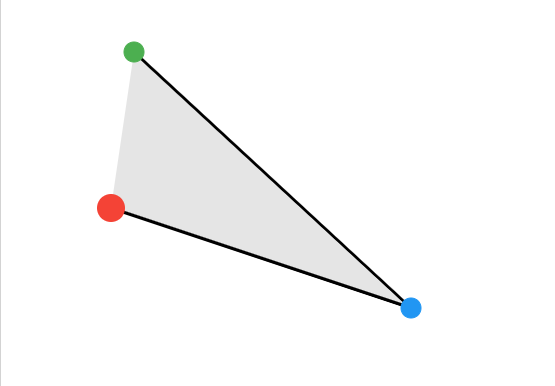
path
<svg width='500' height='500' style="border:1px solid #cd0000;margin: 100px">
<path d="路径" pathLenth="非负数"/>
// path 计算路径长度
</svg>
大小写
大写 M 绝对定位
小写 m 相对定位
(M m) 移动到新位置
(L l) 从当前坐标到新坐标绘制一条线
(H h) 将线绘制到新的水平坐标
(V v) 将线绘制新的垂直坐标
(Z z) 关闭当前路径
<svg width='500' height='500' style="border:1px solid #cd0000;margin: 100px">
<path d="M 50 50 L 0 300 L 200 200 V 50 H 40 L300 300 L 300 200 Z" fill="none" stroke-width="2" stroke="red"/>
</svg>
有三组命令绘制弯曲的路径: 三次贝塞尔曲线(C,S),二次贝塞尔曲线(Q,T) 和椭圆弧(A)
C
三次贝塞尔曲线(x1,y1,x2,y2,x,y)
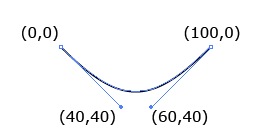
<path d="M0 0 C40 40,60 40,100,0" stroke="black" fill="none"/>
S
在原本的点后方建立一个带有贝塞尔曲线
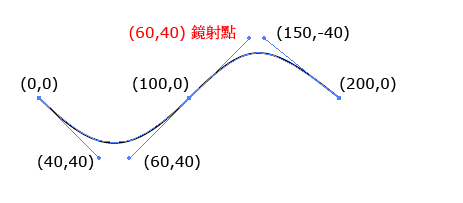
<path d="M0 0 C40 40,60 40,100,0 S150 -40, 200 0" stroke="black" fill="none"/>
Q
Q简单些, 起点和终点的贝塞尔曲线公用一个控制点,只需要提供贝塞尔控制点坐标和终点坐标
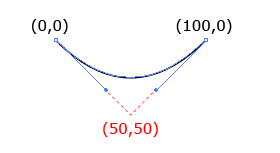
<path d="M0 0 Q50 50, 100 0" stroke="black" fill="none"/>
T
只有一组参数x,y ,表示终点的坐标,所以T的前方接上Q,才能画出对应的坐标线
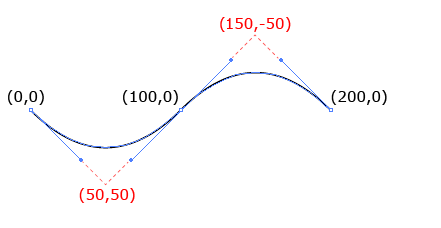
<path d="M0 0 Q50 50, 100 0 T200 0" stroke="black" fill="none"/>
A
工具网址https://mavo.io/demos/svgpath/
椭圆弧(rx,ry,x-axis-rotation,large-arc-flag, sweep-flag)
- rx : 椭圆的x 轴半径( 根据不同的终点换算成比例 )
- ry : 椭圆的y 轴半径( 根据不同的终点换算成比例 )
- x-axis-rotation : 弧线与x 轴的夹角
- large-arc-flag : 1 为大角度弧线,0 为小角度弧线( 必须有三个点 )
- sweep-flag : 1 为顺时针方向,0 为逆时针方向
- x : 终点x 座标
- y : 终点y 座标
path太复杂了,我这种小可爱理解有点困难
线上网址
https://jxnblk.github.io/paths/
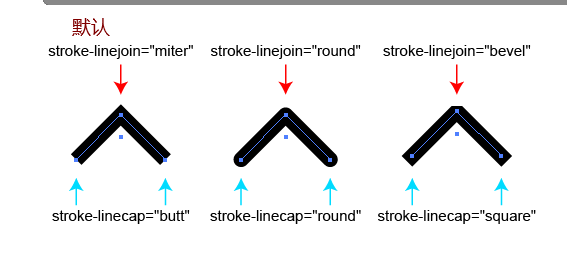
stroke 边框
- stroke:边框的颜色
- stroke-width:边框的宽度
- stroke-linecap:边框端点的属性( butt (预设)、square、round )
- stroke-linejoin:边框接合尖角的属性( miter (预设)、round、bevel )
- stroke-dasharray:虚线
<polyline fill="none" stroke="#000000" stroke-width="10" stroke-linecap="round" stroke-linejoin="round" points="193.546,119.133
223.245,89.434 252.943,119.133 "/>
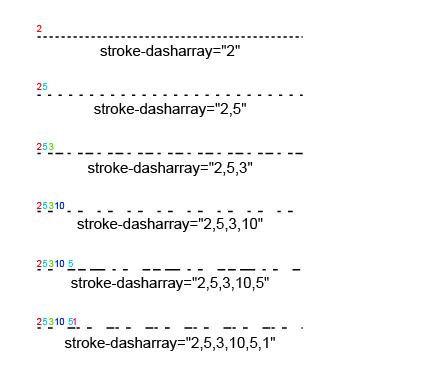
<line fill="none" stroke="#000000" stroke-dasharray="2" x1="0" y1="0" x2="100" y2="0"/>
鼠标悬浮过渡
fill 填色
<rect x="290" y="50" width="100" height="100" stroke="#000" stroke-width="10" fill="#09f"></rect>
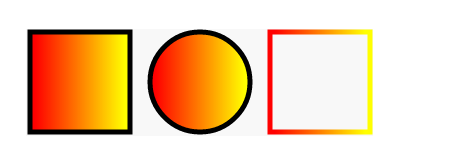
渐变
左到右
<defs>
<linearGradient id="a1">
<stop offset="5%" stop-color="#F00" />
<stop offset="95%" stop-color="#ff0" />
</linearGradient>
</defs>
<rect x="50" y="250" width="100" height="100" stroke="#000" stroke-width="5" fill="url(#a1)"></rect>
<circle cx="220" cy="300" r="50" stroke="#000" stroke-width="5" fill="url(#a1)"></circle>
<rect x="290" y="250" width="100" height="100" stroke="url(#a1)" stroke-width="5" fill="none"></rect>
放射状
<defs>
<radialGradient id="a1">
<stop offset="5%" stop-color="#ff0" />
<stop offset="95%" stop-color="#f00" />
</radialGradient>
</defs>

垂直渐变
<defs>
<linearGradient id="a1" x1="0%" y1="0%" x2="0%" y2="100%">
<stop offset="5%" stop-color="#F00" />
<stop offset="95%" stop-color="#ff0" />
</linearGradient>
</defs>
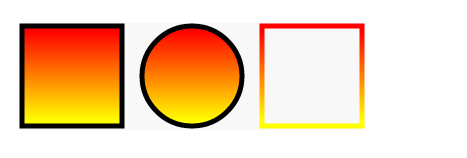
倾斜渐变
<defs>
<linearGradient id="a1" x1="0%" y1="0%" x2="100%" y2="100%">
<stop offset="5%" stop-color="#F00" />
<stop offset="95%" stop-color="#ff0" />
</linearGradient>
</defs>
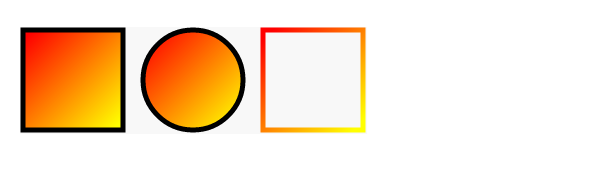
修改中心点的渐变
<defs>
<radialGradient id="a1" cx="20%" cy="40%">
<stop offset="5%" stop-color="#ff0" />
<stop offset="95%" stop-color="#f00" />
</radialGradient>
</defs>

pattern
用于fill
通过x轴或y轴方向以固定间隔平铺,然后通过id引用
属性
- patternUnits = "userSpaceOnUse | objectBoundingBox"
- patternContentUnits = "userSpaceOnUse | objectBoundingBox"
- patternTransform
- x
- y
- width
- height
- xlink:href
- preserveAspectRatio = "[defer] []"
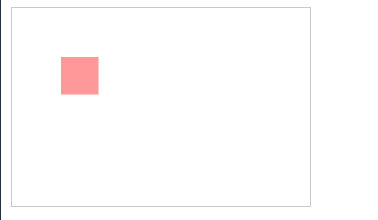
patternUnits=userSpaceOnUse
表示以使用者的坐标为主
<svg width="240" height="160" >
<defs>
<pattern id="p" patternUnits="userSpaceOnUse" width="60" height="60">
<rect width="30" height="30" fill="#f99" x="0" y="0"/>
</pattern>
</defs>
<rect width="240" height="160" fill="url(#p)" stroke="#aaa" />
</svg>
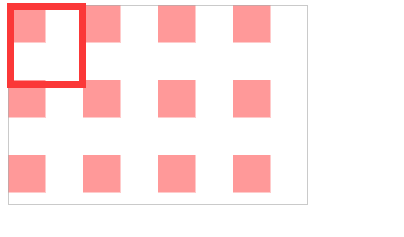
完整版,你可以把每一个注释下,方便自己理解
<svg width="240" height="160" >
<defs>
<pattern id="p" patternUnits="userSpaceOnUse" width="60" height="60">
<rect width="40" height="40" fill="#f99" x="0" y="0"/>
</pattern>
</defs>
<rect width="240" height="160" fill="url(#p)" stroke="#aaa" />
<circle cx="150" cy="80" r="50" stroke="#000" fill="url(#p)" />
<rect width="60" height="60" x="1" y="1" stroke="#00f" stroke-width="2" fill="url(#p)" />
</svg>
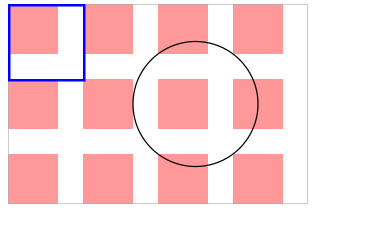
优先级从上到下一次递增的
<defs>
<pattern id="p" patternUnits="userSpaceOnUse" width="40" height="40">
<rect width="30" height="30" fill="#f99" x="30" y="0"></rect>
</pattern>
</defs>
我们会发现当我们把pattern里的rect,位置超过了pattern 的范围,就会发现rect会被裁剪
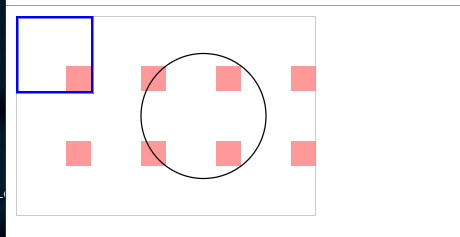
patternUnits=userSpaceOnUse
设置是以我们画出来的形状为基准, 设置pattern长宽,就变成了比例而不是数值
如果宽高为1,1 那么画出来的就是等于图形长宽
<svg width="240" height="160" >
<defs>
<pattern id="p" patternUnits="objectBoundingBox" width="1" height="1">
<rect width="30" height="30" fill="#f99" x="40" y="40"/>
</pattern>
</defs>
<!-- 长宽比 1:1-->
<rect width="240" height="160" fill="url(#p)" stroke="#aaa" />
<!--x=40,y=40,w30h30 fill #f99 填充一个小矩形-->
</svg>
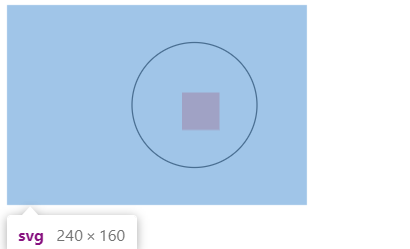
<svg width="240" height="160" >
<defs>
<pattern id="p" patternUnits="objectBoundingBox" width="1" height="1">
<rect width="30" height="30" fill="#f99" x="40" y="40"/>
</pattern>
</defs>
<!-- 长宽比 1:1-->
<circle cx="150" cy="80" r="50" stroke="#000" fill="url(#p)" />
<!--
那么这个元素的起步位置原点应该是 100,30
由于x=40,y=40
所以 填充的矩形的其实位置是140,70
-->
</svg>
<svg width="240" height="160">
<defs>
<pattern id="p" patternUnits="objectBoundingBox" width="1" height="1">
<rect width="30" height="30" fill="#f99" x="0" y="0"/>
</pattern>
</defs>
<!-- 长宽比 1:1-->
<rect width="100" height="100" stroke-width="2" stroke="red" fill="url(#p)" x="20" y="20"/>
<circle r="30" cx="200" cy="80" fill="url(#p)" stroke-width="2" stroke="red"/>
</svg>
如果把width设为.4, height设置为0.4,那么在100*100的图形中,则是40 * 40 的pattern,
如果rect 为 width 30 height 30 则背景图案是带有10的宽度间距的重复图案
<svg width="240" height="160">
<defs>
<pattern id="p" patternUnits="objectBoundingBox" width=".4" height=".4">
<rect width="30" height="30" fill="#f99" x="0" y="0"></rect>
</pattern>
</defs>
<circle cx="180" cy="80" r="50" stroke="#0a0" stroke-width="2" fill="url(#p)" />
<rect width="100" height="100" x="10" y="30" stroke="#000" stroke-width="2" fill="url(#p)" />
</svg>
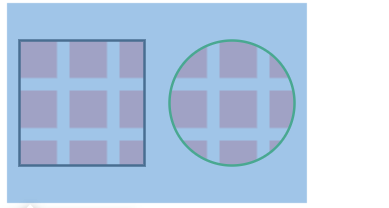
不同的矩形的套用,出来的结果不同
<svg width="240" height="160">
<defs>
<pattern id="p" patternUnits="objectBoundingBox" width=".4" height=".4">
<rect width="30" height="30" fill="#f99" x="0" y="0"></rect>
</pattern>
</defs>
<rect width="80" height="80" x="120" y="30" stroke="#000" stroke-width="2" fill="url(#p)" />
<rect width="100" height="100" x="10" y="30" stroke="#000" stroke-width="2" fill="url(#p)" />
</svg>
设定为userSpaceOnUse实际的宽度的高度: 比例乘上实际套用的图像的长/宽
当为width/height 80px 80*0.4=32 由于他们每一个宽度是30那么空隙就是2
patternTransform
让我们直接对pattern 下大 transform
倾斜45度
<svg width="240" height="160">
<defs>
<pattern id="p1" patternUnits="objectBoundingBox" width=".2" height=".4" patternTransform="rotate(45)">
<rect width="10" height="50" fill="#000" x="0" y="0"></rect>
<rect width="10" height="50" fill="#fa0" x="10" y="0"></rect>
</pattern>
</defs>
<rect width="100" height="100" x="10" y="30" stroke="#000" stroke-width="2" fill="url(#p1)" />
</svg>

要记得的点在于userSpaceOnUse 就是标准的长度数值,objectBoundingBox 就是比例
xlink:href
二次引入
<defs>
<pattern id="r1">
<rect width="20" height="20" fill="#0c0" x="0" y="0"></rect>
</pattern>
<pattern id="p1" patternUnits="objectBoundingBox" width=".4" height=".4" xlink:href="#r1" />
<pattern id="p2" patternUnits="objectBoundingBox" width=".25" height=".25" xlink:href="#r1" />
</defs>
<rect width="100" height="100" x="10" y="30" stroke="#000" stroke-width="2" fill="url(#p1)" />
<rect width="100" height="100" x="120" y="30" stroke="#000" stroke-width="2" fill="url(#p2)" />
defs
把一些重复利用的物体放在defs元素内
再use 把元素呈现出来
use 的属性有 x,y 的坐标
<svg width="500px" height="500px" > <defs> <rect id="ccc" width="100" height="100" x="10" y="10" fill="red"/> </defs> <use xlink:href="#ccc"/> <use xlink:href="#ccc" x="10" y="300"/> </svg>
