
每次进入源码的世界,就像完成一场奇妙的旅行!
1. 属性赋值概述
上一篇讲述了bean实例化中的创建实例过程,实例化后就需要对类中的属性进行依赖注入操作,本篇将重点分析属性赋值相关流程。其中属性赋值,体现在AbstractAutowireCapableBeanFactory类中的doCreateBean方法中的populateBean(beanName, mbd, instanceWrapper)这行代码;在赋值之前还做了收集属性的相关操作,下面就通过源码来分析。
2. 流程概览
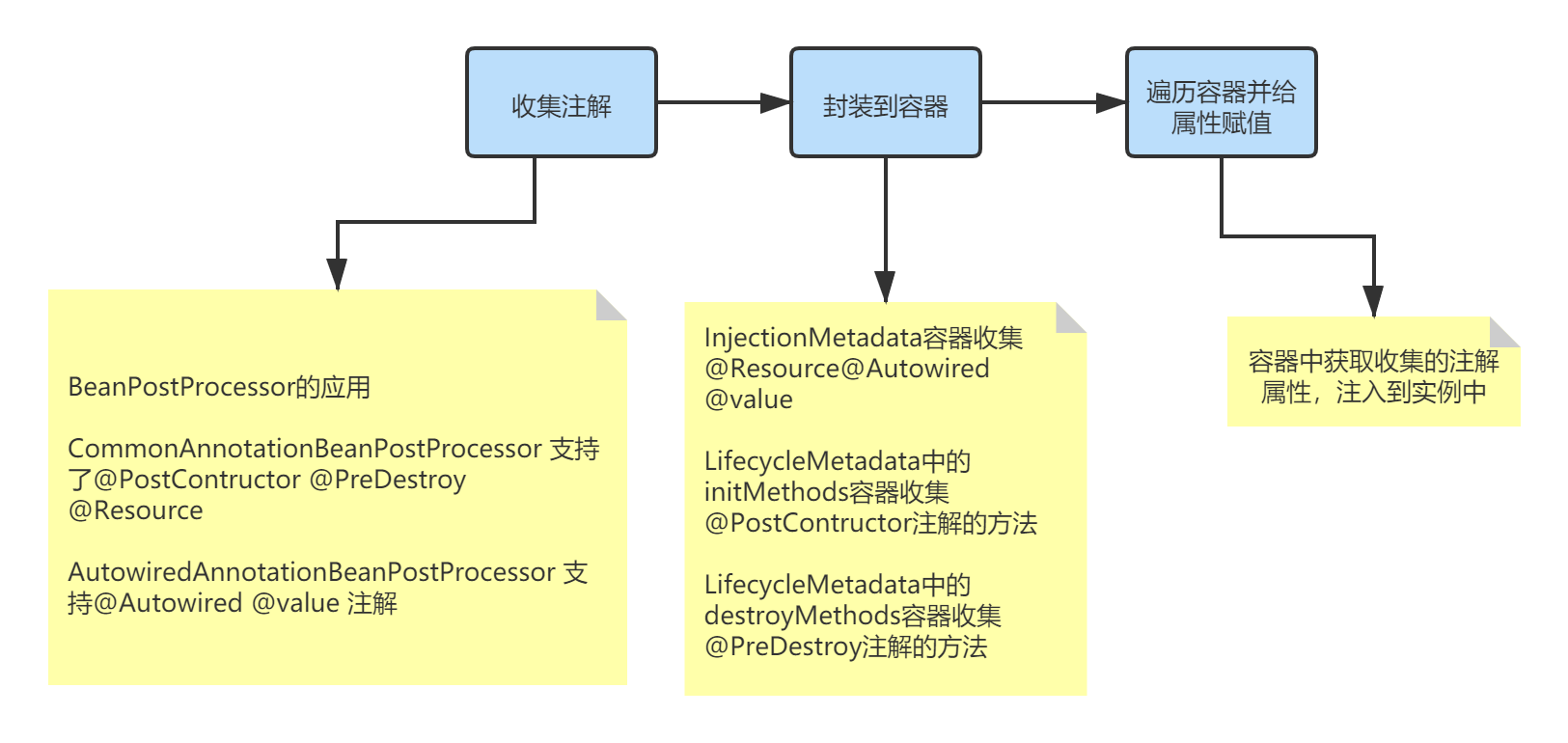
流程中分为三步:
step1:通过BeanPostProcessor的实现类,实现了带注解的属性收集,CommonAnnotationBeanPostProcessor 支持了@PostContructor、@PreDestroy、@Resource的收集;AutowiredAnnotationBeanPostProcessor支持@Autowired、@value注解的属性收集;
step2:将收集有注解属性和方法封装到对应的容器中;
step3:遍历容器中的属性,注入到对应的bean实例中。
3. 源码分析
3.1 收集@PostConstruct @PreDestroy注解的方法
首先AbstractAutowireCapableBeanFactory类中的doCreateBean方法:
protected Object doCreateBean(String beanName, RootBeanDefinition mbd, @Nullable Object[] args)
throws BeanCreationException {
// Instantiate the bean.
BeanWrapper instanceWrapper = null;
if (mbd.isSingleton()) {
instanceWrapper = this.factoryBeanInstanceCache.remove(beanName);
}
if (instanceWrapper == null) {
//创建对象实例
instanceWrapper = createBeanInstance(beanName, mbd, args);
}
Object bean = instanceWrapper.getWrappedInstance();
Class<?> beanType = instanceWrapper.getWrappedClass();
if (beanType != NullBean.class) {
mbd.resolvedTargetType = beanType;
}
// Allow post-processors to modify the merged bean definition.
synchronized (mbd.postProcessingLock) {
if (!mbd.postProcessed) {
try {
// 收集注解
// BeanPostProcessor典型应用
// CommonAnnotationBeanPostProcessor 支持了@PostContructor @PreDestroy @Resource
// AutowiredAnnotationBeanPostProcessor 支持@Autowired @value 注解
applyMergedBeanDefinitionPostProcessors(mbd, beanType, beanName);
}
catch (Throwable ex) {
throw new BeanCreationException(mbd.getResourceDescription(), beanName,
"Post-processing of merged bean definition failed", ex);
}
mbd.postProcessed = true;
}
}
// Eagerly cache singletons to be able to resolve circular references
// even when triggered by lifecycle interfaces like BeanFactoryAware.
boolean earlySingletonExposure = (mbd.isSingleton() && this.allowCircularReferences &&
isSingletonCurrentlyInCreation(beanName));
if (earlySingletonExposure) {
if (logger.isTraceEnabled()) {
logger.trace("Eagerly caching bean '" + beanName +
"' to allow for resolving potential circular references");
}
addSingletonFactory(beanName, () -> getEarlyBeanReference(beanName, mbd, bean));
}
// Initialize the bean instance.
Object exposedObject = bean;
try {
// 属性赋值
populateBean(beanName, mbd, instanceWrapper);
// 初始化bean
exposedObject = initializeBean(beanName, exposedObject, mbd);
}
catch (Throwable ex) {
if (ex instanceof BeanCreationException && beanName.equals(((BeanCreationException) ex).getBeanName())) {
throw (BeanCreationException) ex;
}
else {
throw new BeanCreationException(
mbd.getResourceDescription(), beanName, "Initialization of bean failed", ex);
}
}
if (earlySingletonExposure) {
Object earlySingletonReference = getSingleton(beanName, false);
if (earlySingletonReference != null) {
if (exposedObject == bean) {
exposedObject = earlySingletonReference;
}
else if (!this.allowRawInjectionDespiteWrapping && hasDependentBean(beanName)) {
String[] dependentBeans = getDependentBeans(beanName);
Set<String> actualDependentBeans = new LinkedHashSet<>(dependentBeans.length);
for (String dependentBean : dependentBeans) {
if (!removeSingletonIfCreatedForTypeCheckOnly(dependentBean)) {
actualDependentBeans.add(dependentBean);
}
}
if (!actualDependentBeans.isEmpty()) {
throw new BeanCurrentlyInCreationException(beanName,
"Bean with name '" + beanName + "' has been injected into other beans [" +
StringUtils.collectionToCommaDelimitedString(actualDependentBeans) +
"] in its raw version as part of a circular reference, but has eventually been " +
"wrapped. This means that said other beans do not use the final version of the " +
"bean. This is often the result of over-eager type matching - consider using " +
"'getBeanNamesForType' with the 'allowEagerInit' flag turned off, for example.");
}
}
}
}
// Register bean as disposable.
try {
registerDisposableBeanIfNecessary(beanName, bean, mbd);
}
catch (BeanDefinitionValidationException ex) {
throw new BeanCreationException(
mbd.getResourceDescription(), beanName, "Invalid destruction signature", ex);
}
return exposedObject;
}
createBeanInstance上一篇已经讲完,完成bean的创建,创建完后,bean只是在堆内存中申请了一块内存空间,还没有对其属性赋值,而在属性赋值前,优先收集标注了注解的属性,收集过程在applyMergedBeanDefinitionPostProcessors方法中完成,进入该方法:
protected void applyMergedBeanDefinitionPostProcessors(RootBeanDefinition mbd, Class<?> beanType, String beanName) {
// 遍历当前类中的所有BeanPostProcessors
for (BeanPostProcessor bp : getBeanPostProcessors()) {
if (bp instanceof MergedBeanDefinitionPostProcessor) {
MergedBeanDefinitionPostProcessor bdp = (MergedBeanDefinitionPostProcessor) bp;
bdp.postProcessMergedBeanDefinition(mbd, beanType, beanName);
}
}
}
遍历当前类中的实现了BeanPostProcessor接口的类,再次进入postProcessMergedBeanDefinition方法,会看到有几个典型的实现类,首先是 CommonAnnotationBeanPostProcessor类,这个类完成了@Resource注解的属性或者方法的收集,这个类还对@PostConstruct和@PreDestory支持。具体的收集过程如下:
public void postProcessMergedBeanDefinition(RootBeanDefinition beanDefinition, Class<?> beanType, String beanName) {
// 扫描@PostConstructor @PreDestroy
super.postProcessMergedBeanDefinition(beanDefinition, beanType, beanName);
// 扫描属性与方法上的@Resource注解,收集到InjectionMetadata容器中
InjectionMetadata metadata = findResourceMetadata(beanName, beanType, null);
metadata.checkConfigMembers(beanDefinition);
}
回到CommonAnnotationBeanPostProcessor类的构造方法,完成@PostConstruct和@PreDestory注解的设值,分别塞到initAnnotationType与destroyAnnotationType属性中:
public CommonAnnotationBeanPostProcessor() {
setOrder(Ordered.LOWEST_PRECEDENCE - 3);
setInitAnnotationType(PostConstruct.class);
setDestroyAnnotationType(PreDestroy.class);
ignoreResourceType("javax.xml.ws.WebServiceContext");
}
点击进入其父类InitDestroyAnnotationBeanPostProcessor的postProcessMergedBeanDefinition方法
public void postProcessMergedBeanDefinition(RootBeanDefinition beanDefinition, Class<?> beanType, String beanName) {
LifecycleMetadata metadata = findLifecycleMetadata(beanType);
metadata.checkConfigMembers(beanDefinition);
}
点击findLifecycleMetadata进入方法:
private LifecycleMetadata findLifecycleMetadata(Class<?> clazz) {
if (this.lifecycleMetadataCache == null) {
// Happens after deserialization, during destruction...
return buildLifecycleMetadata(clazz);
}
// Quick check on the concurrent map first, with minimal locking.
LifecycleMetadata metadata = this.lifecycleMetadataCache.get(clazz);
if (metadata == null) {
synchronized (this.lifecycleMetadataCache) {
metadata = this.lifecycleMetadataCache.get(clazz);
if (metadata == null) {
// 构建生命周期相关的元数据
metadata = buildLifecycleMetadata(clazz);
this.lifecycleMetadataCache.put(clazz, metadata);
}
return metadata;
}
}
return metadata;
}
再次进入构建生命周期相关的元数据的方法buildLifecycleMetadata:
private LifecycleMetadata buildLifecycleMetadata(final Class<?> clazz) {
if (!AnnotationUtils.isCandidateClass(clazz, Arrays.asList(this.initAnnotationType, this.destroyAnnotationType))) {
return this.emptyLifecycleMetadata;
}
List<LifecycleElement> initMethods = new ArrayList<>();
List<LifecycleElement> destroyMethods = new ArrayList<>();
Class<?> targetClass = clazz;
do {
final List<LifecycleElement> currInitMethods = new ArrayList<>();
final List<LifecycleElement> currDestroyMethods = new ArrayList<>();
//遍历类中的方法,找到@PostConstruct注解的方法
ReflectionUtils.doWithLocalMethods(targetClass, method -> {
if (this.initAnnotationType != null && method.isAnnotationPresent(this.initAnnotationType)) {
LifecycleElement element = new LifecycleElement(method);
currInitMethods.add(element);
if (logger.isTraceEnabled()) {
logger.trace("Found init method on class [" + clazz.getName() + "]: " + method);
}
}
//遍历类中的方法,找到@PreDestroy注解的方法
if (this.destroyAnnotationType != null && method.isAnnotationPresent(this.destroyAnnotationType)) {
currDestroyMethods.add(new LifecycleElement(method));
if (logger.isTraceEnabled()) {
logger.trace("Found destroy method on class [" + clazz.getName() + "]: " + method);
}
}
});
// @PostConstruct注解的方法加到initMethods
initMethods.addAll(0, currInitMethods);
// @PreDestroy注解的方法加到destroyMethods
destroyMethods.addAll(currDestroyMethods);
targetClass = targetClass.getSuperclass();
}
while (targetClass != null && targetClass != Object.class);
return (initMethods.isEmpty() && destroyMethods.isEmpty() ? this.emptyLifecycleMetadata :
new LifecycleMetadata(clazz, initMethods, destroyMethods));
}
循环遍历类中的所有的方法,判断方法上是否有@PostConstruct注解如果有的话加入到initMethods集合,判断方法上是否有@PreDestroy注解,如果有加入到destroyMethods集合中去。
3.2 收集@Resource注解的属性与方法
进入上述findResourceMetadata方法:
private InjectionMetadata findResourceMetadata(String beanName, final Class<?> clazz, @Nullable PropertyValues pvs) {
// Fall back to class name as cache key, for backwards compatibility with custom callers.
String cacheKey = (StringUtils.hasLength(beanName) ? beanName : clazz.getName());
// 查看缓存里面有没有InjectionMetadata实例.
InjectionMetadata metadata = this.injectionMetadataCache.get(cacheKey);
if (InjectionMetadata.needsRefresh(metadata, clazz)) {
synchronized (this.injectionMetadataCache) {
metadata = this.injectionMetadataCache.get(cacheKey);
if (InjectionMetadata.needsRefresh(metadata, clazz)) {
if (metadata != null) {
metadata.clear(pvs);
}
// 构建@Resource元数据
metadata = buildResourceMetadata(clazz);
this.injectionMetadataCache.put(cacheKey, metadata);
}
}
}
return metadata;
}
step1:看缓存里面有没有 InjectionMetadata 对象;
step2:构建@Resource元数据;
再次进入buildResourceMetadata方法:
private InjectionMetadata buildResourceMetadata(final Class<?> clazz) {
if (!AnnotationUtils.isCandidateClass(clazz, resourceAnnotationTypes)) {
return InjectionMetadata.EMPTY;
}
List<InjectionMetadata.InjectedElement> elements = new ArrayList<>();
Class<?> targetClass = clazz;
do {
final List<InjectionMetadata.InjectedElement> currElements = new ArrayList<>();
// 遍历所有field,判断有没有Resource注解
ReflectionUtils.doWithLocalFields(targetClass, field -> {
if (webServiceRefClass != null && field.isAnnotationPresent(webServiceRefClass)) {
if (Modifier.isStatic(field.getModifiers())) {
throw new IllegalStateException("@WebServiceRef annotation is not supported on static fields");
}
currElements.add(new WebServiceRefElement(field, field, null));
}
else if (ejbClass != null && field.isAnnotationPresent(ejbClass)) {
if (Modifier.isStatic(field.getModifiers())) {
throw new IllegalStateException("@EJB annotation is not supported on static fields");
}
currElements.add(new EjbRefElement(field, field, null));
}
else if (field.isAnnotationPresent(Resource.class)) {
if (Modifier.isStatic(field.getModifiers())) {
throw new IllegalStateException("@Resource annotation is not supported on static fields");
}
if (!this.ignoredResourceTypes.contains(field.getType().getName())) {
currElements.add(new ResourceElement(field, field, null));
}
}
});
// 遍历所有方法,判断有没有@Resource注解
ReflectionUtils.doWithLocalMethods(targetClass, method -> {
Method bridgedMethod = BridgeMethodResolver.findBridgedMethod(method);
if (!BridgeMethodResolver.isVisibilityBridgeMethodPair(method, bridgedMethod)) {
return;
}
if (method.equals(ClassUtils.getMostSpecificMethod(method, clazz))) {
if (webServiceRefClass != null && bridgedMethod.isAnnotationPresent(webServiceRefClass)) {
if (Modifier.isStatic(method.getModifiers())) {
throw new IllegalStateException("@WebServiceRef annotation is not supported on static methods");
}
if (method.getParameterCount() != 1) {
throw new IllegalStateException("@WebServiceRef annotation requires a single-arg method: " + method);
}
PropertyDescriptor pd = BeanUtils.findPropertyForMethod(bridgedMethod, clazz);
currElements.add(new WebServiceRefElement(method, bridgedMethod, pd));
}
else if (ejbClass != null && bridgedMethod.isAnnotationPresent(ejbClass)) {
if (Modifier.isStatic(method.getModifiers())) {
throw new IllegalStateException("@EJB annotation is not supported on static methods");
}
if (method.getParameterCount() != 1) {
throw new IllegalStateException("@EJB annotation requires a single-arg method: " + method);
}
PropertyDescriptor pd = BeanUtils.findPropertyForMethod(bridgedMethod, clazz);
currElements.add(new EjbRefElement(method, bridgedMethod, pd));
}
else if (bridgedMethod.isAnnotationPresent(Resource.class)) {
if (Modifier.isStatic(method.getModifiers())) {
throw new IllegalStateException("@Resource annotation is not supported on static methods");
}
Class<?>[] paramTypes = method.getParameterTypes();
if (paramTypes.length != 1) {
throw new IllegalStateException("@Resource annotation requires a single-arg method: " + method);
}
if (!this.ignoredResourceTypes.contains(paramTypes[0].getName())) {
PropertyDescriptor pd = BeanUtils.findPropertyForMethod(bridgedMethod, clazz);
currElements.add(new ResourceElement(method, bridgedMethod, pd));
}
}
}
});
elements.addAll(0, currElements);
targetClass = targetClass.getSuperclass();
}
while (targetClass != null && targetClass != Object.class);
return InjectionMetadata.forElements(elements, clazz);
}
step1:从类中获取所有 Field 对象,循环 field 对象,判断 field 有没有@Resource 注解,如果有注解封装成 ResourceElement 对象;
step2:从类中获取所有 Method对象,循环 Method对象,判断 Method有没有@Resource 注解,如果有注解封装成 ResourceElement 对象;
step3:最终把两个 field 和 Method 封装的对象集合封装到 InjectionMetadata 对象中。
3.3 @Autowired注解的属性与方法收集
AutowiredAnnotationBeanPostProcessor类对@Autowired和@Value注解的属性和方法的收集,收集支持的注解类型可以在构造函数或者 Static 静态块中找。收集过程基本上跟@Resource注解的收集差不多。下面先看AutowiredAnnotationBeanPostProcessor的构造函数:
public AutowiredAnnotationBeanPostProcessor() {
this.autowiredAnnotationTypes.add(Autowired.class);
this.autowiredAnnotationTypes.add(Value.class);
try {
this.autowiredAnnotationTypes.add((Class<? extends Annotation>)
ClassUtils.forName("javax.inject.Inject", AutowiredAnnotationBeanPostProcessor.class.getClassLoader()));
logger.trace("JSR-330 'javax.inject.Inject' annotation found and supported for autowiring");
}
catch (ClassNotFoundException ex) {
// JSR-330 API not available - simply skip.
}
}
收集了@Autowired和@Value注解并设置到autowiredAnnotationTypes类型中。后面流程与@Resource收集一样,也是收集Field和Method上面的注解,然后放到InjectionMetadata对象中。
private InjectionMetadata buildAutowiringMetadata(final Class<?> clazz) {
if (!AnnotationUtils.isCandidateClass(clazz, this.autowiredAnnotationTypes)) {
return InjectionMetadata.EMPTY;
}
List<InjectionMetadata.InjectedElement> elements = new ArrayList<>();
Class<?> targetClass = clazz;
do {
final List<InjectionMetadata.InjectedElement> currElements = new ArrayList<>();
// 循环收集Field上面是否有@Autowired注解
ReflectionUtils.doWithLocalFields(targetClass, field -> {
MergedAnnotation<?> ann = findAutowiredAnnotation(field);
if (ann != null) {
if (Modifier.isStatic(field.getModifiers())) {
if (logger.isInfoEnabled()) {
logger.info("Autowired annotation is not supported on static fields: " + field);
}
return;
}
boolean required = determineRequiredStatus(ann);
currElements.add(new AutowiredFieldElement(field, required));
}
});
// 循环收集Method上面是否有@Autowired注解
ReflectionUtils.doWithLocalMethods(targetClass, method -> {
Method bridgedMethod = BridgeMethodResolver.findBridgedMethod(method);
if (!BridgeMethodResolver.isVisibilityBridgeMethodPair(method, bridgedMethod)) {
return;
}
MergedAnnotation<?> ann = findAutowiredAnnotation(bridgedMethod);
if (ann != null && method.equals(ClassUtils.getMostSpecificMethod(method, clazz))) {
if (Modifier.isStatic(method.getModifiers())) {
if (logger.isInfoEnabled()) {
logger.info("Autowired annotation is not supported on static methods: " + method);
}
return;
}
if (method.getParameterCount() == 0) {
if (logger.isInfoEnabled()) {
logger.info("Autowired annotation should only be used on methods with parameters: " +
method);
}
}
boolean required = determineRequiredStatus(ann);
PropertyDescriptor pd = BeanUtils.findPropertyForMethod(bridgedMethod, clazz);
currElements.add(new AutowiredMethodElement(method, required, pd));
}
});
// 放入容器elements,而elements本身是InjectionMetadata类型下的InjectedElement属性
elements.addAll(0, currElements);
targetClass = targetClass.getSuperclass();
}
while (targetClass != null && targetClass != Object.class);
return InjectionMetadata.forElements(elements, clazz);
}
3.4 属性赋值
收集完@Resource和@Autowired注解以后就开始依赖注入,进入populateBean方法:
protected void populateBean(String beanName, RootBeanDefinition mbd, @Nullable BeanWrapper bw) {
if (bw == null) {
if (mbd.hasPropertyValues()) {
throw new BeanCreationException(
mbd.getResourceDescription(), beanName, "Cannot apply property values to null instance");
}
else {
// Skip property population phase for null instance.
return;
}
}
// Give any InstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessors the opportunity to modify the
// state of the bean before properties are set. This can be used, for example,
// to support styles of field injection.
if (!mbd.isSynthetic() && hasInstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessors()) {
for (BeanPostProcessor bp : getBeanPostProcessors()) {
if (bp instanceof InstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor) {
InstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor ibp = (InstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor) bp;
if (!ibp.postProcessAfterInstantiation(bw.getWrappedInstance(), beanName)) {
return;
}
}
}
}
PropertyValues pvs = (mbd.hasPropertyValues() ? mbd.getPropertyValues() : null);
int resolvedAutowireMode = mbd.getResolvedAutowireMode();
if (resolvedAutowireMode == AUTOWIRE_BY_NAME || resolvedAutowireMode == AUTOWIRE_BY_TYPE) {
MutablePropertyValues newPvs = new MutablePropertyValues(pvs);
// Add property values based on autowire by name if applicable.
if (resolvedAutowireMode == AUTOWIRE_BY_NAME) {
autowireByName(beanName, mbd, bw, newPvs);
}
// Add property values based on autowire by type if applicable.
if (resolvedAutowireMode == AUTOWIRE_BY_TYPE) {
autowireByType(beanName, mbd, bw, newPvs);
}
pvs = newPvs;
}
boolean hasInstAwareBpps = hasInstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessors();
boolean needsDepCheck = (mbd.getDependencyCheck() != AbstractBeanDefinition.DEPENDENCY_CHECK_NONE);
PropertyDescriptor[] filteredPds = null;
if (hasInstAwareBpps) {
if (pvs == null) {
pvs = mbd.getPropertyValues();
}
for (BeanPostProcessor bp : getBeanPostProcessors()) {
if (bp instanceof InstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor) {
InstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor ibp = (InstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor) bp;
// 依赖注入的过程,@Autowired支持 @Resource支持
PropertyValues pvsToUse = ibp.postProcessProperties(pvs, bw.getWrappedInstance(), beanName);
if (pvsToUse == null) {
if (filteredPds == null) {
filteredPds = filterPropertyDescriptorsForDependencyCheck(bw, mbd.allowCaching);
}
pvsToUse = ibp.postProcessPropertyValues(pvs, filteredPds, bw.getWrappedInstance(), beanName);
if (pvsToUse == null) {
return;
}
}
pvs = pvsToUse;
}
}
}
if (needsDepCheck) {
if (filteredPds == null) {
filteredPds = filterPropertyDescriptorsForDependencyCheck(bw, mbd.allowCaching);
}
checkDependencies(beanName, mbd, filteredPds, pvs);
}
if (pvs != null) {
applyPropertyValues(beanName, mbd, bw, pvs);
}
}
该方法的核心工作就是完成依赖注入,进入postProcessProperties方法:
public PropertyValues postProcessProperties(PropertyValues pvs, Object bean, String beanName) {
InjectionMetadata metadata = findAutowiringMetadata(beanName, bean.getClass(), pvs);
try {
// 依赖注入
metadata.inject(bean, beanName, pvs);
}
catch (BeanCreationException ex) {
throw ex;
}
catch (Throwable ex) {
throw new BeanCreationException(beanName, "Injection of autowired dependencies failed", ex);
}
return pvs;
}
最后通过metadata.inject方法把容器中收集的属性注入:
public void inject(Object target, @Nullable String beanName, @Nullable PropertyValues pvs) throws Throwable {
Collection<InjectedElement> checkedElements = this.checkedElements;
Collection<InjectedElement> elementsToIterate =
(checkedElements != null ? checkedElements : this.injectedElements);
if (!elementsToIterate.isEmpty()) {
for (InjectedElement element : elementsToIterate) {
if (logger.isTraceEnabled()) {
logger.trace("Processing injected element of bean '" + beanName + "': " + element);
}
// 循环调用每个方法依赖一次处理
element.inject(target, beanName, pvs);
}
}
}
点击进入inject方法:
protected void inject(Object target, @Nullable String requestingBeanName, @Nullable PropertyValues pvs)
throws Throwable {
if (this.isField) {
Field field = (Field) this.member;
ReflectionUtils.makeAccessible(field);
// 设置属性,getResourceToInject会触发getBean
field.set(target, getResourceToInject(target, requestingBeanName));
}
else {
if (checkPropertySkipping(pvs)) {
return;
}
try {
Method method = (Method) this.member;
ReflectionUtils.makeAccessible(method);
// 设置方法
method.invoke(target, getResourceToInject(target, requestingBeanName));
}
catch (InvocationTargetException ex) {
throw ex.getTargetException();
}
}
}
看到属性与方法通过反射的注入到所需的实例中,如果注入的是引用类型,会通过调用getResourceToInject方法优先拿到引用类型的实例,底层是通过BeanFactory.getBean方式拿到应用的属性的:
protected Object getResourceToInject(Object target, @Nullable String requestingBeanName) {
if (StringUtils.hasLength(this.beanName)) {
if (beanFactory != null && beanFactory.containsBean(this.beanName)) {
// Local match found for explicitly specified local bean name.
// 通过getBean方式拿引用类型的值
Object bean = beanFactory.getBean(this.beanName, this.lookupType);
if (requestingBeanName != null && beanFactory instanceof ConfigurableBeanFactory) {
((ConfigurableBeanFactory) beanFactory).registerDependentBean(this.beanName, requestingBeanName);
}
return bean;
}
else if (this.isDefaultName && !StringUtils.hasLength(this.mappedName)) {
throw new NoSuchBeanDefinitionException(this.beanName,
"Cannot resolve 'beanName' in local BeanFactory. Consider specifying a general 'name' value instead.");
}
}
4. 总结
本篇讲述了实例化后属性的收集与赋值过程,通过典型的BeanPostProccessor应用,完成相关注解的收集,并完成依赖注入,最终完成属性赋值,后续将继续分析初始化流程。