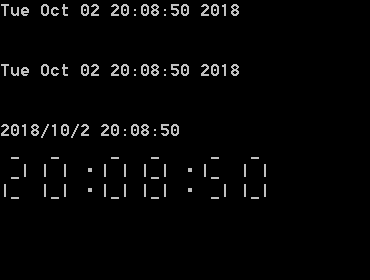
/********************************** * Name : timeDisplay.cpp * Purpose: Display digital clock according to current system time. * Author : feicaixian ***********************************/ #include <stdio.h> #include <time.h> #include <stdlib.h> void segDisp(int n); void numToArr(int n, int *a); /*********************** * 7段码笔画编号,编号可以随意,不同编号方案对应不同7段码 * _0 * 5|_6| 1 * 4|_3| 2 * ***********************/ //将0~9的7段码存入数组,0表示不显示笔画,1表示显示笔画 const int segments[10][7] = { {1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 0},//0 {0, 1, 1, 0, 0, 0, 0},//1 {1, 1, 0, 1, 1, 0, 1},//2 {1, 1, 1, 1, 0, 0, 1},//3 {0, 1, 1, 0, 0, 1, 1},//4 {1, 0, 1, 1, 0, 1, 1},//5 {1, 0, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1},//6 {1, 1, 1, 0, 0, 0, 0},//7 {1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1},//8 {1, 1, 1, 1, 0, 1, 1} //9 }; int main() { /* Use time() to get system time.The function prototype is: #include <time.h> time_t time(time_t *); function type is time_t, function name is time, parameter is pointer, whose type is time_t. time(time_t *timer) returns the number of seconds between January 1, 1970 and the current system time to timer, which can be print as long int. */ time_t t;//define a time_t type variable time(&t);//Pass time_t type pointer to time() printf("The number of seconds: %d ",t);//print the seconds from January 1, 1970 to now. /*Use functions followed to convert seconds to a structure: struct tm *gmtime(const time_t *timer); //convert seconds to Greenwich Mean Time(GMT) struct tm *localtime(const time_t * timer); //convert seconds to localtime struct tm * means that the type of return value is a struct tm type pointer. struct tm { int tm_sec;//seconds 0-61 int tm_min;//minutes 1-59 int tm_hour;//hours 0-23 int tm_mday;//day of the month 1-31 int tm_mon;//months since jan 0-11, so add 1 to get the real months. int tm_year;//years from 1900, add 1900 to get the real years. int tm_wday;//days since Sunday, 0-6 int tm_yday;//days since Jan 1, 0-365 int tm_isdst;//Daylight Saving time indicator }; */ struct tm *p = localtime(&t);//不一定要把当前系统时间传给指针,你也可以自定义各成员的值。 int oldSeconds; while(1) { system("cls");//clear screen. /* 方法一: char *asctime(const struct tm *timeptr) 返回一个表示当地时间的字符串,它代表了timeptr的日期和时间。 */ printf("%s ",asctime(p));//输出结果像这样:Sat Mar 25 06:10:10 1989 /* 方法二: char *ctime(const time_t *timer) 返回一个表示当地时间的字符串,当地时间是基于参数 timer。 */ printf("%s ",ctime(&t));//输出结果和asctime一样 /* 方法三: 也可以自己输出日期和时间,自定义格式 */ int a[6]; int timeToInt = p->tm_hour * 10000 + p->tm_min * 100 + p->tm_sec; printf("%d/%d/%d ",1900+p->tm_year,p->tm_mon + 1, p->tm_mday);//date numToArr(timeToInt, a); printf("%d%d:%d%d:%d%d ",a[5],a[4],a[3],a[2],a[1],a[0]); //使用7段码显示时间 segDisp(timeToInt); //不断获取当前时间,直到秒钟刷新,跳出循环,更新显示 oldSeconds = p->tm_sec; do { time(&t); p = localtime(&t); }while (p->tm_sec == oldSeconds); } return 0; } void numToArr(int n, int *a) { int k = 0; //数组a[]的下标 do { a[k++] = n % 10; n /= 10; }while (n != 0); } void segDisp(int n) { int i; //打印7段码时形参n的各位的序号 int k = 0; //数组a[]的下标 int a[6]; //存储形参的各个位的数字 const int num = 6;//时间显示的所需数字个数 //将形参n的各位存入数组a[] numToArr(n, a); //------------------------------------- //--- 按行显示数字的7段码,共3行。 //--- 第一行显示编号0,第二行显示编号5 6 1,第三行显示编号4 3 2. //------------------------------------- //显示编号0 for (i = num-1; i >= 0; i--) { if (i == 4 | i == 2){ //在第二个数字和第四个数字后面要显示冒号,如12:34:43。由于使用中文下的·号,采用全角模式,占两个字符宽度, //所以额外增加两个空格。 if (segments[a[i]][0]) printf(" _ "); else printf(" "); } else { if (segments[a[i]][0]) printf(" _ "); //附加两个空格,显示下一个数字的笔画。 //第一个空格是因为本数字右边还有一个笔画,第二个空格是因为两个数字之间应有间隔。 else printf(" ");//用空格代替下划线 } } printf(" ");//在下一行打印 //显示编号5 6 1 for (i = num-1; i >= 0; i--) { if (segments[a[i]][5]) printf("|"); else printf(" "); if (segments[a[i]][6]) printf("_"); else printf(" "); if (segments[a[i]][1]) printf("| "); else printf(" "); if (i == 4 | i == 2) printf("·");//显示冒号 } printf(" ");//在下一行打印 //显示编号4 3 2 for (i = num-1; i >= 0; i--) { if (segments[a[i]][4]) printf("|"); else printf(" "); if (segments[a[i]][3]) printf("_"); else printf(" "); if (segments[a[i]][2]) printf("| "); else printf(" "); if (i == 4 | i == 2) printf("·"); } }