###########说明1:
1 Swingbench 简述
1.1 概述
这是Oracle UK的一个员工在一个被抛弃的项目的基础上开发的。目前稳定版本2.2,最新版本2.3,基于JDK1.5。该工具是免费的,可以在作者的网站上自由下载,并且拥有详细的使用文档。除了Swingbench,作者还开发了两个相关工具:测试数据生成工具DataGenerator和跟踪文件分析工具Trace Analyzer。
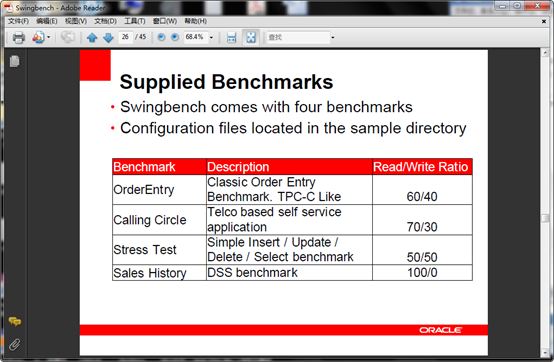
Swingbench可 以执行4种不同的标准测试(benchmark),拥有三种前端展示方式Swingbench/Charbench/Minibench,其中 Charbench是字符模式的,另外两种是GUI模式的。另外还可以通过ClusterOverview可以聚合显示所有的结果。Swingbench的开发目的主要是用来展示RAC的负载和测试,但也可用于单实例环境。最新的2.3版本开始支持TimesTen内存数据库。
下载地址:http://www.dominicgiles.com/downloads.html
作者博客:http://www.dominicgiles.com/blog/blog.html
目前网络上开源的oracle压力测试工具主要是orabm和swingbench,由于orabm不支持oracle 11g版本,因此本次测试使用了swingben进行了压力测试。另外,swingbench还能对rac进行测试。swingbench是UK based oracle Database Solutions group开发的一个oracle压力测试工具,好像是官方废弃的一个项目,官方页面http://dominicgiles.com/swingbench.html上可以下载最新的软件版本。swingbench可以运行在windows和linux平台,本次以windows为例。
2. 环境配置
测试客户端需要安装JDK,无需安装oracle client端
swingbench的版本为2.4 ,直接解压软件压缩包,解压后路劲如下,因是windows下做测试 所以使用 winbin目录下的批处理文件
主要使用到的是如下四个bat文件
主要的bat文件作用如下:
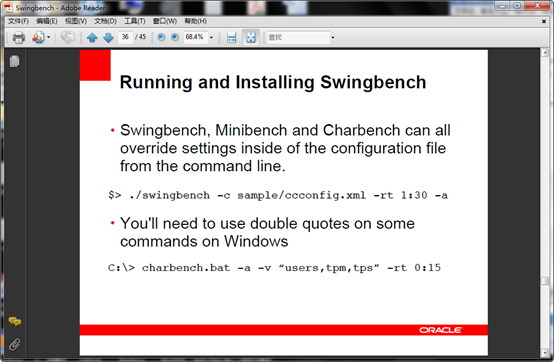
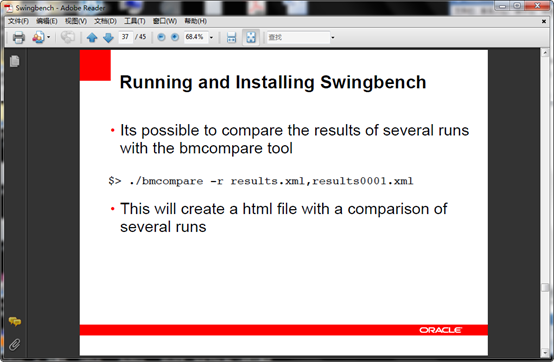
1、 bmcompare 用来对比测试结果
2、 ccwizard 是以CC种子为模板创建的运行测试数据
3、 clusteroverview 用来启动集群的压力测试,并查看测试结果
4、 coordinator 用来启动协调服务器
5、 minibench 用来注册节点到协调服务器
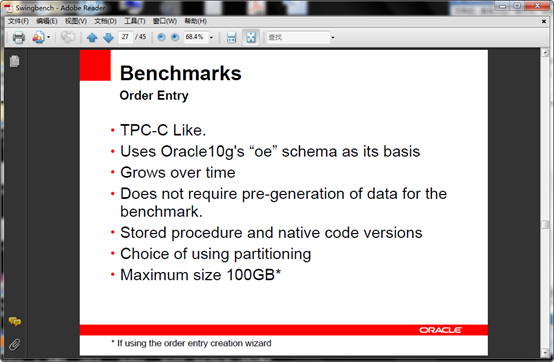
6、 oewizard 是以OE种子为模板创建运行测试数据
7、 shwizard 是以SH种子为模板创建运行测试数据
8、 swingbench 执行基准测试
3.测试
3.1 创建测试数据
swingbench不使用客户数据,而是按自己的规则创建测试数据,(生成的测试数据只能使用一次,测试过后 需要再次测试的话,需要重新创建测试数据,这点做的不好)
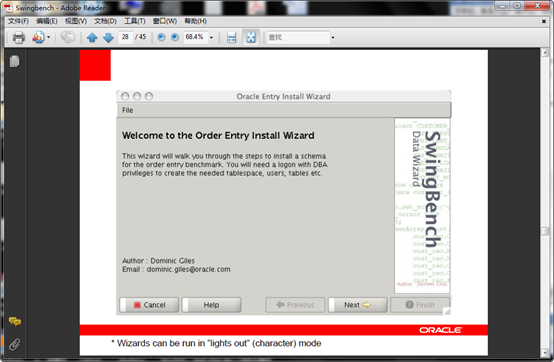
到目标目录下 运行oewizard.bat批处理文件,也可以在目录下双机oewizard.bat批处理文件运行
会看到如下界面
下一步
下一步,输入你需要测试的数据库的 //ip/sid 以及sys用户的密码
下一步,前三项不需要修改,为swingbench自动创建的schema,只需要修改datafile的存放路径即可。
下一步,选择创建数据的数据量 最小100M 最大1TB, 我选择为100GB 一般需要4-7小时,(和你硬件io性能有关)
PS:做测试时要确定对生产库没有影响,用swingbench测试,会占用大量的IO,我使用的是新核心系统的新存储,和旧的环境完全独立,所以swingbench测试对旧生产环境没有任何影响。
下一步,
下一步,数据开始插入,100G的数据大概要7个小时左右完成。
4、启动swingbench配置
4.1、Winbin目录下运行coordinator–g 启动协调服务器,如下
4.2、启动swingbench配置相关压力测试参数
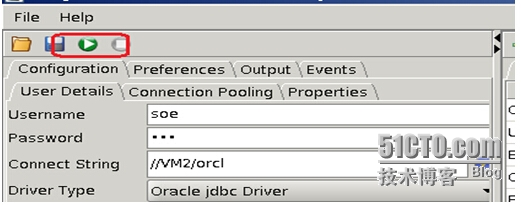
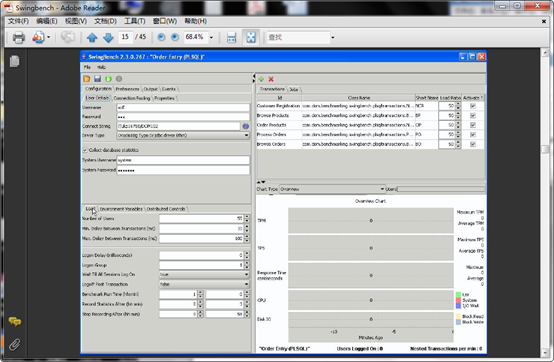
出现如此主界面 主要参数设置 好对应的connect string,其他的参数建附录A
设置图上vhfs1节点圈圈内的参数,节点2同样操作。
将数据库OS 的ssh打开 则可以统计主机的cpu disk IO 信息
也可以拉出AWR报表
设置 insert,update ,select的比例
4.3 注册节点到注册服务器(这一步很重要,如果不填写协调服务器主机名,则无法使用cluster view集群进程)
完成后点击保存(两个节点都要填写协调服务器主机名),退出。
5、测试
5.1、打开集群的两个节点,命令如下,
swingbench.bat -c
C:swingbenchconfigsoeconfig.xml -cs 192.192.5.106:1521:vhfs1 -g vhfs1 -dt
thin
swingbench.bat -c C:swingbenchconfigsoeconfig.xml -cs
192.192.5.107:1521:vhfs2 -g vhfs2 -dt thin
保持集群下两节点的swingbench 图形进程处于打开状态。
5.2、运行./clusteroverview进行测试,依次启动oracleRAC的两个节点数据库连接,如下,可以在运行选项栏里选择自动负载均衡。
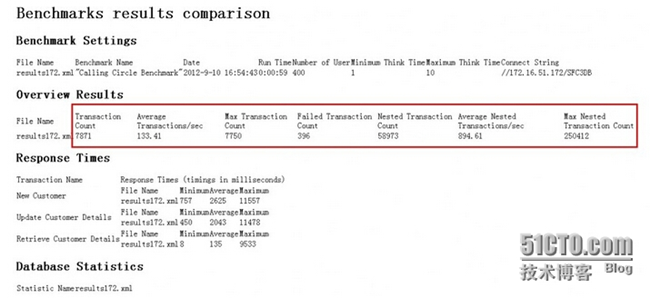
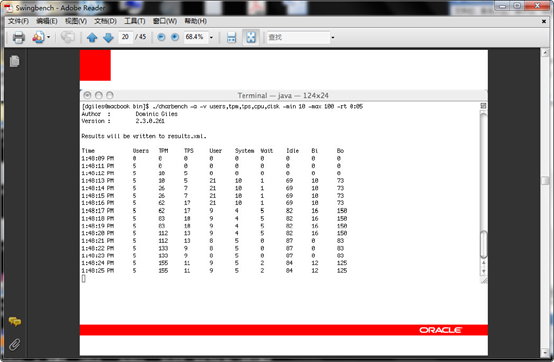
压力测试结果如下,
6、测试结果统计对比
结果为XML文档
############## sample 1:
#######section 4:
java虚拟机内存不足,“Could not create the Java Virtual Machine”问题解决方案
在运行java程序时,遇到问题"Could not create the Java Virtual Machine."如下截图:
大概原因,就是java堆内存不足以运行JVM,需要增加内存。
网上搜索此问题,大部分都是针对某个程序进行修改JVM内存的解决方法,比如eclipse,等。试问,若是其他程序出现问题了呢?
现在给出一个全局的java虚拟机修改内存的方法。在WIN XP,WIN 7,WIN8都可以。
解决方案:增加一个系统环境变量
变量名:_JAVA_OPTIONS
变量值:-Xmx512M
保存后,就OK!!
下面给出关于java堆内存的一个介绍,这是一个英文网页的翻译过来的。
关于java堆内存:
可以利用bmcompare.bat 对比两个测试结果,语法如图,结果会生产在本地。
c:swingbenchwinbin>bmcompare.bat -r results00003 results00013
https://www.cnblogs.com/jyzhao/p/6185463.html?utm_source=itdadao&utm_medium=referral
我们可以使用swingbench这个工具对数据库性能进行压力测试,得到一些性能指标作为参考。
SwingBench下载:
http://www.dominicgiles.com/downloads.html
参考相关文章:
http://www.linuxidc.com/Linux/2016-04/130297.htm
http://blog.csdn.net/xiaofan23z/article/details/7978998
实验环境:
RHEL 6.5 + Oracle 11.2.0.4 RAC + SwingBench 2.5.0.971
1. 生成swingbench配置文件
swingbench解压即可使用,第一次需要配置,本次只是简单熟悉swingbench的使用,配置基本按照默认。
[oracle@jyrac1 bin]$ pwd
/home/oracle/swingbench/bin
[oracle@jyrac1 bin]$ ./oewizard 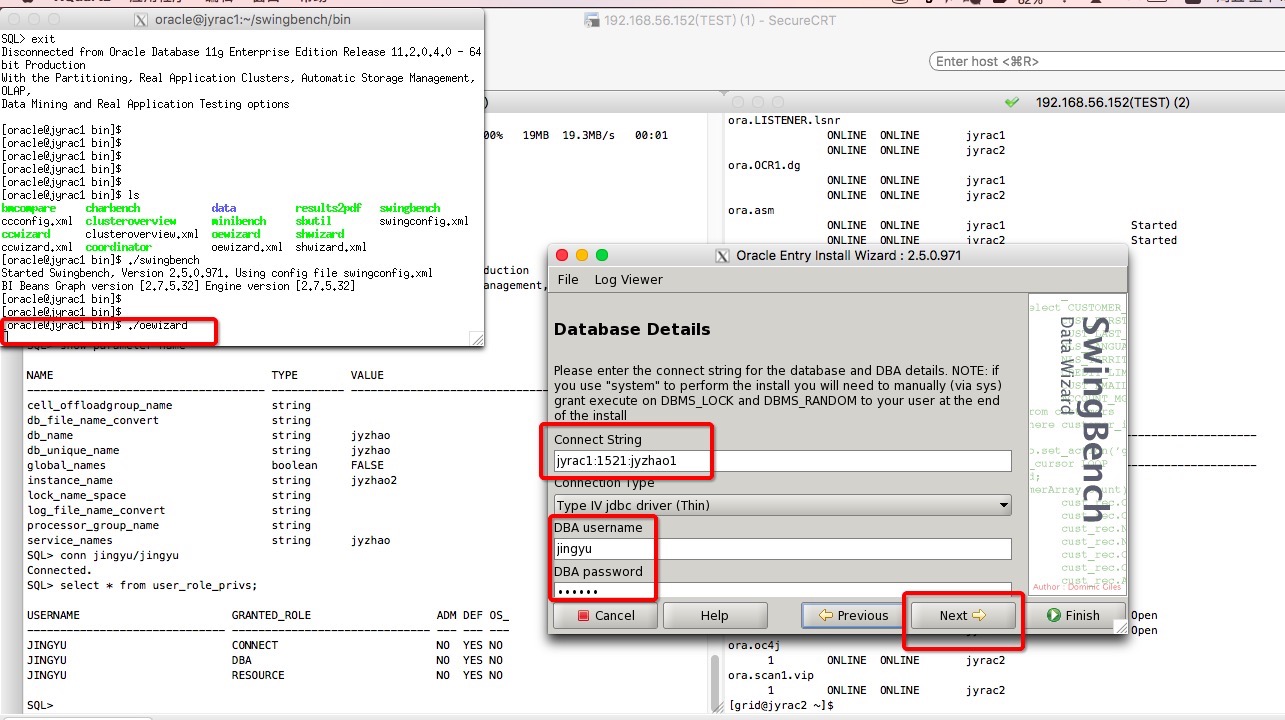
注意,上面的connect string,根据需求填写,比如:
--如果压测只连接实例1
jyrac1:1521:jyzhao1
--如果压测只连接实例2
jyrac2:1521:jyzhao2
--如果压测连接RAC集群,LB到各个实例
//jyrac1/jyzhao
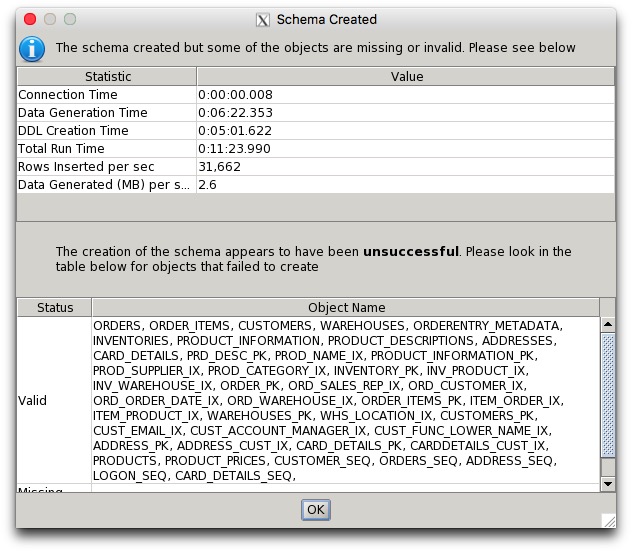
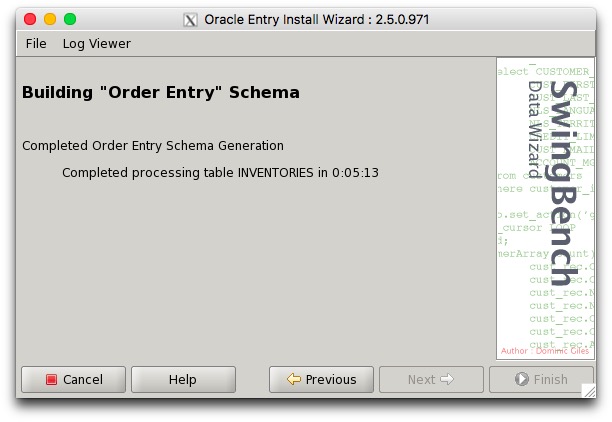
2. 运行swingbench压力测试
可以大致看到压力测试中,数据库可以达到的TPM,TPS等性能指标,作为今后系统正式上线后的一个参考依据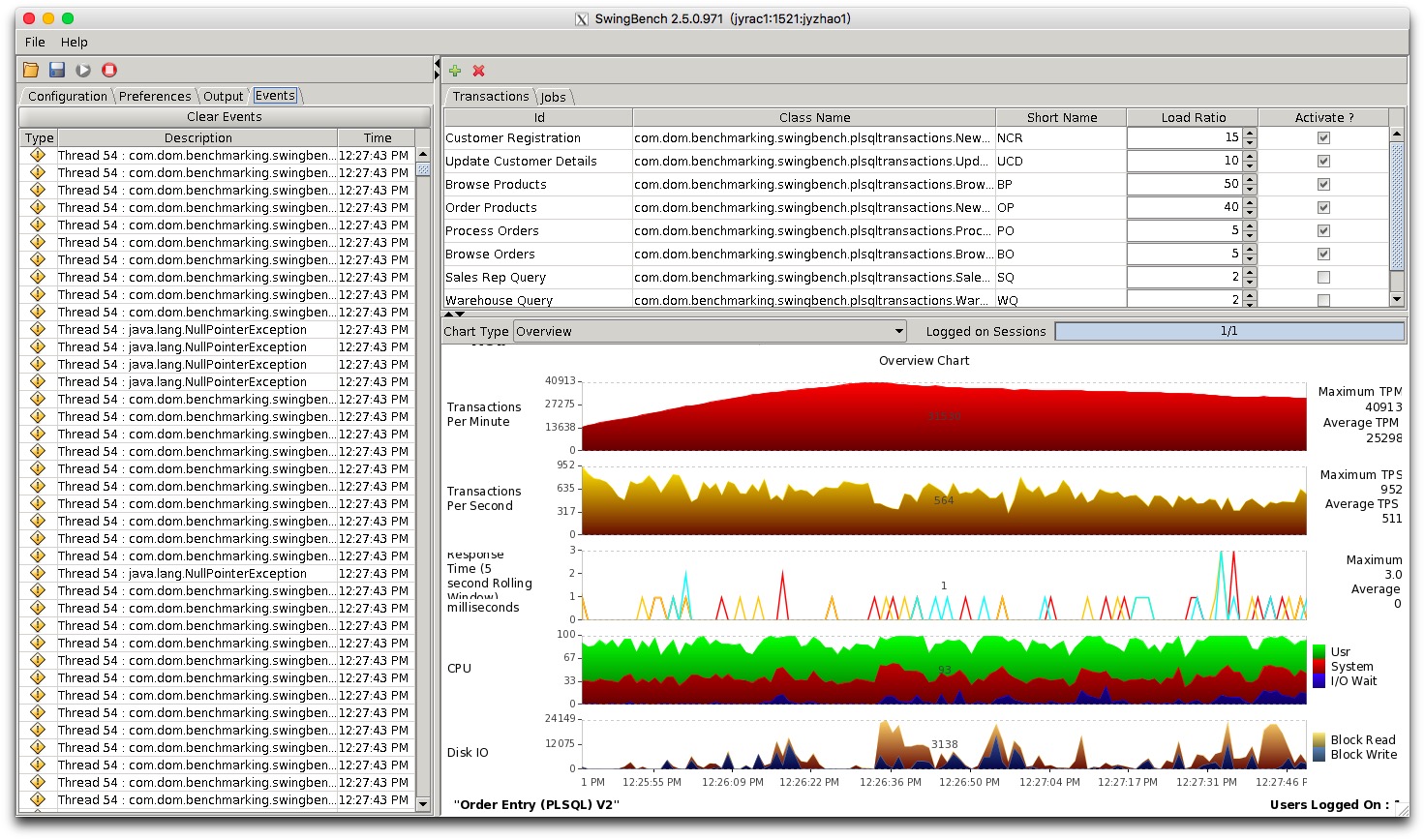
补充:最好使用sys用户直接连接,确认没有无效对象,避免后续再次赋权:
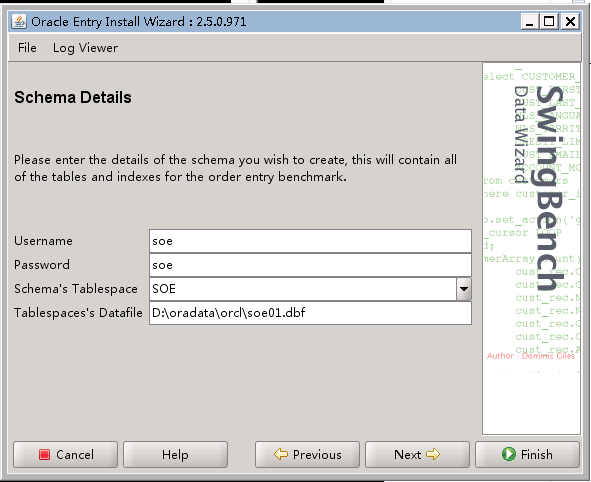
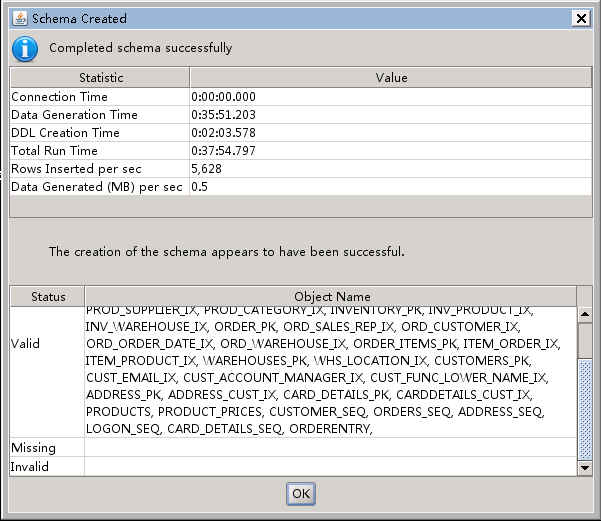
下面附几张单实例压测配置的截图: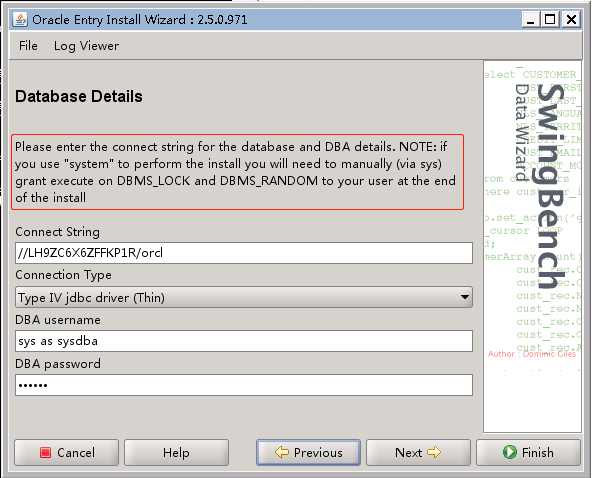
--linux 测试环境 8G 数据实际完成时间为 3小时50分
-AIX 1G ,1G 数据库实际完成时间20分钟
-如果使用非system的dba 用户创建,需要执行grant execute on dbms_lock to soe;
数据导完之后在该目录下运行swingbench执行测试,修改数据库连接名,用户连接数设置为350,测试时间设置为10分钟
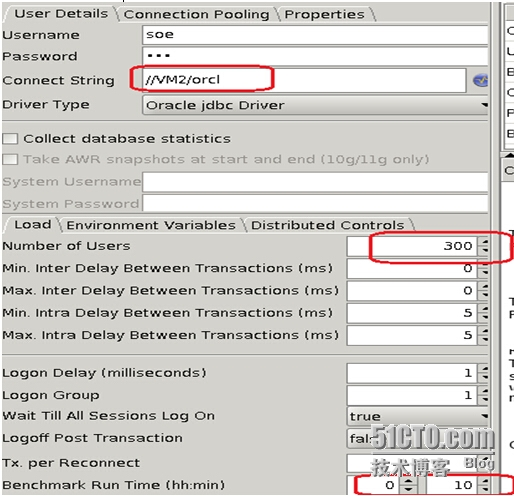
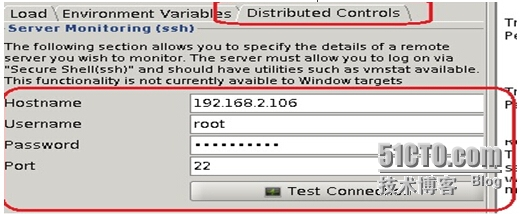
修改Distributed Controls用于测试过程中搜集测试监控信息,修改完之后测试连接是否正常,并可以统计主机的cpu disk IO 信息
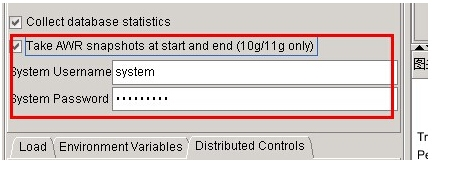
还可以拉出AWR报表
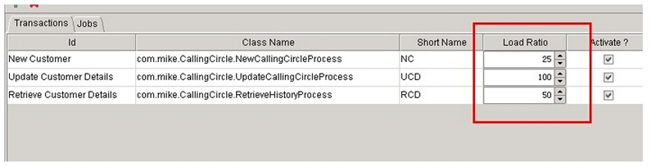
设置 insert,update ,select的比例
设置完成之后,点击左上角绿色按钮执行测试
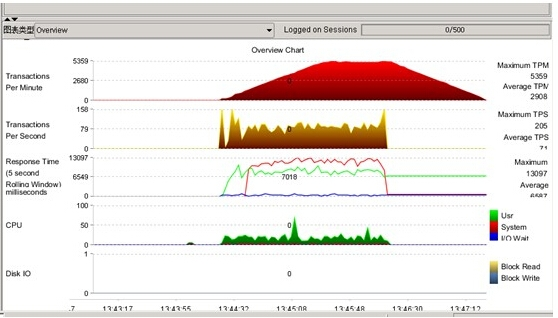
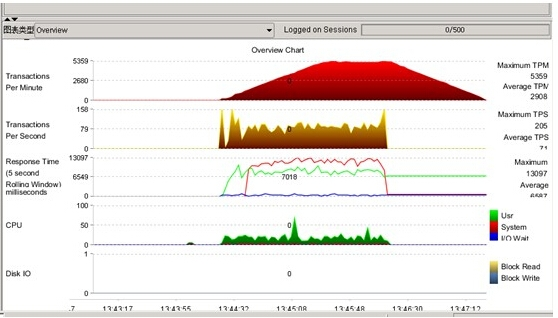
试结果可保持为XML文档,最后查看显示如下, 我的测试发现第一次运行压力测试正常,后面跑几次总是hang 在3分钟,左右,不知道什么原因
原因如下: 这是正常的测试 ,没有黄色的告警
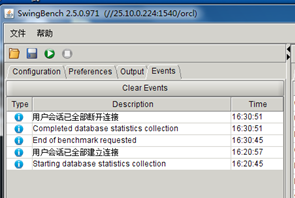
这是有问题 ,

###官方文档
http://www.dominicgiles.com/Swingbench.pdf
1.
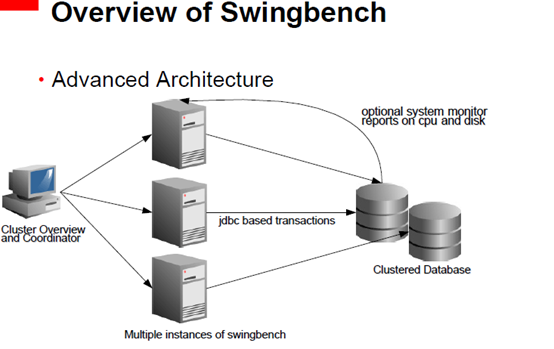
Overview of Swingbench
• Typically used as a standalone load generator
• However a Coordinator process allows multiple
load generators to work together.
• ClusterOverview aggregates all of the results
together.
• Its free....
2.
For windows
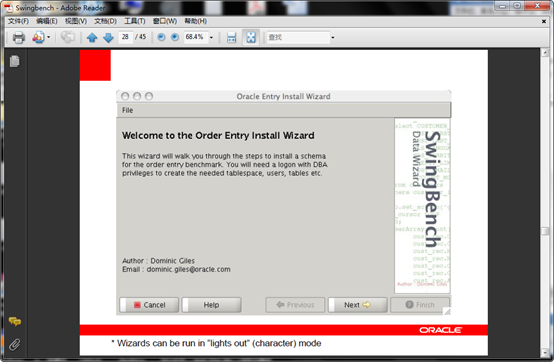
1.
Overview of Swingbench
• Typically used as a standalone load generator
• However a Coordinator process allows multiple
load generators to work together.
• ClusterOverview aggregates all of the results
together.
• Its free....
For windows
---恢复内容结束---
############## sample 1:
#######section 4:
java虚拟机内存不足,“Could not create the Java Virtual Machine”问题解决方案
在运行java程序时,遇到问题"Could not create the Java Virtual Machine."如下截图:
大概原因,就是java堆内存不足以运行JVM,需要增加内存。
网上搜索此问题,大部分都是针对某个程序进行修改JVM内存的解决方法,比如eclipse,等。试问,若是其他程序出现问题了呢?
现在给出一个全局的java虚拟机修改内存的方法。在WIN XP,WIN 7,WIN8都可以。
解决方案:增加一个系统环境变量
变量名:_JAVA_OPTIONS
变量值:-Xmx512M
保存后,就OK!!
下面给出关于java堆内存的一个介绍,这是一个英文网页的翻译过来的。
关于java堆内存:
3、进入swingbench/bin目录执行oewizard导入1G测试数据,并修改数据库连接名和DBA密码

注意,上面的connect string,根据需求填写,比如:
--如果压测只连接实例1
jyrac1:1521:jyzhao1
--如果压测只连接实例2
jyrac2:1521:jyzhao2
--如果压测连接RAC集群,LB到各个实例
//jyrac1/jyzhao
输入导入数据文件存放位置:
选择导入1G数据:
--linux 测试环境 8G 数据实际完成时间为 3小时50分
数据导完之后在该目录下运行swingbench执行测试,修改数据库连接名,用户连接数设置为300,测试时间设置为10分钟
修改Distributed Controls用于测试过程中搜集测试监控信息,修改完之后测试连接是否正常,并可以统计主机的cpu disk IO 信息
还可以拉出AWR报表
设置 insert,update ,select的比例
设置完成之后,点击左上角绿色按钮执行测试
测试过程截图
测试结果可保持为XML文档,最后查看显示如下
------------
我们可以使用swingbench这个工具对数据库性能进行压力测试,得到一些性能指标作为参考。
SwingBench下载:
http://www.dominicgiles.com/downloads.html
参考相关文章:
http://www.linuxidc.com/Linux/2016-04/130297.htm
http://blog.csdn.net/xiaofan23z/article/details/7978998
###########说明1:
1 Swingbench 简述
1.1 概述
这是Oracle UK的一个员工在一个被抛弃的项目的基础上开发的。目前稳定版本2.2,最新版本2.3,基于JDK1.5。该工具是免费的,可以在作者的网站上自由下载,并且拥有详细的使用文档。除了Swingbench,作者还开发了两个相关工具:测试数据生成工具DataGenerator和跟踪文件分析工具Trace Analyzer。
Swingbench可 以执行4种不同的标准测试(benchmark),拥有三种前端展示方式Swingbench/Charbench/Minibench,其中 Charbench是字符模式的,另外两种是GUI模式的。另外还可以通过ClusterOverview可以聚合显示所有的结果。Swingbench的开发目的主要是用来展示RAC的负载和测试,但也可用于单实例环境。最新的2.3版本开始支持TimesTen内存数据库。
下载地址:http://www.dominicgiles.com/downloads.html
作者博客:http://www.dominicgiles.com/blog/blog.html
目前网络上开源的oracle压力测试工具主要是orabm和swingbench,由于orabm不支持oracle 11g版本,因此本次测试使用了swingben进行了压力测试。另外,swingbench还能对rac进行测试。swingbench是UK based oracle Database Solutions group开发的一个oracle压力测试工具,好像是官方废弃的一个项目,官方页面http://dominicgiles.com/swingbench.html上可以下载最新的软件版本。swingbench可以运行在windows和linux平台,本次以windows为例。
2. 环境配置
测试客户端需要安装JDK,无需安装oracle client端
swingbench的版本为2.4 ,直接解压软件压缩包,解压后路劲如下,因是windows下做测试 所以使用 winbin目录下的批处理文件
主要使用到的是如下四个bat文件
主要的bat文件作用如下:
1、 bmcompare 用来对比测试结果
2、 ccwizard 是以CC种子为模板创建的运行测试数据
3、 clusteroverview 用来启动集群的压力测试,并查看测试结果
4、 coordinator 用来启动协调服务器
5、 minibench 用来注册节点到协调服务器
6、 oewizard 是以OE种子为模板创建运行测试数据
7、 shwizard 是以SH种子为模板创建运行测试数据
8、 swingbench 执行基准测试
3.测试
3.1 创建测试数据
swingbench不使用客户数据,而是按自己的规则创建测试数据,(生成的测试数据只能使用一次,测试过后 需要再次测试的话,需要重新创建测试数据,这点做的不好)
到目标目录下 运行oewizard.bat批处理文件,也可以在目录下双机oewizard.bat批处理文件运行
会看到如下界面
下一步
下一步,输入你需要测试的数据库的 //ip/sid 以及sys用户的密码
下一步,前三项不需要修改,为swingbench自动创建的schema,只需要修改datafile的存放路径即可。
下一步,选择创建数据的数据量 最小100M 最大1TB, 我选择为100GB 一般需要4-7小时,(和你硬件io性能有关)
PS:做测试时要确定对生产库没有影响,用swingbench测试,会占用大量的IO,我使用的是新核心系统的新存储,和旧的环境完全独立,所以swingbench测试对旧生产环境没有任何影响。
下一步,
下一步,数据开始插入,100G的数据大概要7个小时左右完成。
4、启动swingbench配置
4.1、Winbin目录下运行coordinator–g 启动协调服务器,如下
4.2、启动swingbench配置相关压力测试参数
出现如此主界面 主要参数设置 好对应的connect string,其他的参数建附录A
设置图上vhfs1节点圈圈内的参数,节点2同样操作。
将数据库OS 的ssh打开 则可以统计主机的cpu disk IO 信息
也可以拉出AWR报表
设置 insert,update ,select的比例
4.3 注册节点到注册服务器(这一步很重要,如果不填写协调服务器主机名,则无法使用cluster view集群进程)
完成后点击保存(两个节点都要填写协调服务器主机名),退出。
5、测试
5.1、打开集群的两个节点,命令如下,
swingbench.bat -c
C:swingbenchconfigsoeconfig.xml -cs 192.192.5.106:1521:vhfs1 -g vhfs1 -dt
thin
swingbench.bat -c C:swingbenchconfigsoeconfig.xml -cs
192.192.5.107:1521:vhfs2 -g vhfs2 -dt thin
保持集群下两节点的swingbench 图形进程处于打开状态。
5.2、运行./clusteroverview进行测试,依次启动oracleRAC的两个节点数据库连接,如下,可以在运行选项栏里选择自动负载均衡。
压力测试结果如下,
6、测试结果统计对比
结果为XML文档
#######################
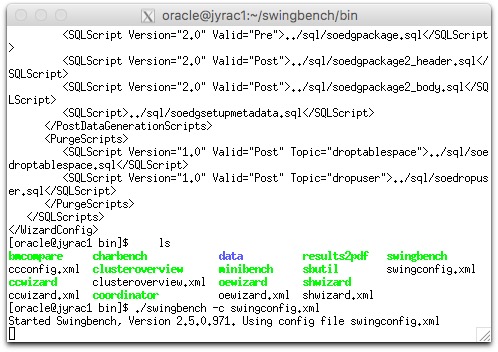
可以利用bmcompare.bat 对比两个测试结果,语法如图,结果会生产在本地。
c:swingbenchwinbin>bmcompare.bat -r results00003 results00013
https://www.cnblogs.com/jyzhao/p/6185463.html?utm_source=itdadao&utm_medium=referral
我们可以使用swingbench这个工具对数据库性能进行压力测试,得到一些性能指标作为参考。
SwingBench下载:
http://www.dominicgiles.com/downloads.html
参考相关文章:
http://www.linuxidc.com/Linux/2016-04/130297.htm
http://blog.csdn.net/xiaofan23z/article/details/7978998
实验环境:
RHEL 6.5 + Oracle 11.2.0.4 RAC + SwingBench 2.5.0.971
1. 生成swingbench配置文件
swingbench解压即可使用,第一次需要配置,本次只是简单熟悉swingbench的使用,配置基本按照默认。
[oracle@jyrac1 bin]$ pwd
/home/oracle/swingbench/bin
[oracle@jyrac1 bin]$ ./oewizard 
注意,上面的connect string,根据需求填写,比如:
--如果压测只连接实例1
jyrac1:1521:jyzhao1
--如果压测只连接实例2
jyrac2:1521:jyzhao2
--如果压测连接RAC集群,LB到各个实例
//jyrac1/jyzhao


2. 运行swingbench压力测试

可以大致看到压力测试中,数据库可以达到的TPM,TPS等性能指标,作为今后系统正式上线后的一个参考依据
补充:最好使用sys用户直接连接,确认没有无效对象,避免后续再次赋权:
下面附几张单实例压测配置的截图:


###sample 2
https://www.cnblogs.com/wxzhe/p/10026569.html
MySQL基准测试工具--sysbench
我们需要知道的是sysbench并不是一个压力测试工具,是一个基准测试工具。linux自带的版本比较低,我们需要自己安装sysbench。
[root@test2 ~]# sysbench --version sysbench 0.4.12
安装sysbench,sysbench的源码托管在GitHub上,下载源码:
unzip sysbench-master.zip #解压源码 yum -y install make automake libtool pkgconfig libaio-devel #下载依赖包 cd sysbench-master sh autogen.sh 编译: ./configure --with-mysql-includes=/usr/local/mysql/include --with-mysql-libs=/usr/local/mysql/lib #根据安装的MySQL的位置,设置目录位置 make make install 这样安装之后使用sysbench命令时会报错。 [root@test3 sysbench-master]# sysbench --version sysbench: error while loading shared libraries: libmysqlclient.so.20: cannot open shared object file: No such file or directory 解决办法: 在/etc/profile文件中加入一行: export LD_LIBRARY_PATH=/usr/local/mysql/lib source /etc/profile 命令可以正常使用 [root@test3 sysbench-master]# sysbench --version sysbench 1.1.0
查看sysbench的一些帮助信息:
[root@test3 ~]# sysbench --help Usage: sysbench [options]... [testname] [command] Commands implemented by most tests: prepare run cleanup help General options: --threads=N number of threads to use [1] #线程的数量,默认是1 --events=N limit for total number of events [0] #限制的最大事件数量,默认是0,不限制 --time=N limit for total execution time in seconds [10] #整个测试执行的时间 --warmup-time=N #在进行基准测试多少秒之后启用统计信息--forced-shutdown=STRING #超过--time时间限制后,强制中断,默认是【off】 --thread-stack-size=SIZE size of stack per thread [64K] --thread-init-timeout=N wait time in seconds for worker threads to initialize [30] --rate=N average transactions rate. 0 for unlimited rate [0] --report-interval=N #打印出中间的信念,N表示每隔N秒打印一次,0表示禁用--report-checkpoints=[LIST,...] #转储完全统计信息并在指定时间点复位所有计数器,参数是逗号分隔值的列表,表示从必须执行报告检查点的测试开始所经过的时间(以秒为单位)。 默认情况下,报告检查点处于关闭状态[off]。--debug[=on|off] print more debugging info [off] --validate[=on|off] #在可能情况下执行验证检查,默认是[off] --help[=on|off] print help and exit [off] --version[=on|off] print version and exit [off] --config-file=FILENAME File containing command line options --luajit-cmd=STRING perform LuaJIT control command. This option is equivalent to 'luajit -j'. See LuaJIT documentation for more information
#上面是一些通用的配置信息,在具体测试某个测试时,会再详细说明参数设置
首先来进行IO测试
[root@test3 ~]# sysbench fileio help #查看IO测试的文档
sysbench 1.1.0 (using bundled LuaJIT 2.1.0-beta3)
fileio options:
--file-num=N number of files to create [128] #文件的数量
--file-block-size=N block size to use in all IO operations [16384] #文件块的大小,如果要是针对INNODB的测试,可以设置为innodb_page_size的大小
--file-total-size=SIZE total size of files to create [2G] #文件的总大小
--file-test-mode=STRING test mode {seqwr【顺序写】, seqrewr【顺序读写】, seqrd【顺序读】, rndrd【随机读】, rndwr【随机写】, rndrw【随机读写】} #文件测试模式
--file-io-mode=STRING file operations mode {sync【同步】,async【异步】,mmap【map映射】} [默认为:sync] #文件的io模式
--file-async-backlog=N number of asynchronous operatons to queue per thread [128] #打开文件时的选项,这是与API相关的参数。
--file-extra-flags=[LIST,...] #打开文件时的选项,这是与API相关的参数。可选有sync,dsync,direct。--file-fsync-freq=N #执行fsync函数的频率,fsync主要是同步磁盘文件,因为可能有系统和磁盘缓冲的关系。默认为100,如果为0表示不使用fsync。
--file-fsync-all[=on|off] #每执行完一次写操作,就执行一次fsync,默认未off。--file-fsync-end[=on|off] #在测试结束时,执行fsync,默认为on。--file-fsync-mode=STRING #文件同步函数的选择,同样是和API相关的参数,由于多个操作对fdatasync支持的不同,因此不建议使用fdatasync。默认为fsync。--file-merged-requests=N #尽可能合并此数量的io请求(0-不合并),默认为[0]。
--file-rw-ratio=N #测试时的读写比例,默认是2:1。
在使用sysbench进行测试的时候,通常分为三个步骤prepare,run,cleanup阶段。
第一步准备数据(prepare阶段):
[root@test3 systext]# sysbench fileio --file-num=10 --file-total-size=50G prepare sysbench 1.1.0 (using bundled LuaJIT 2.1.0-beta3) 10 files, 5242880Kb each, 51200Mb total Creating files for the test... Extra file open flags: (none) Creating file test_file.0 Creating file test_file.1 Creating file test_file.2 Creating file test_file.3 Creating file test_file.4 Creating file test_file.5 Creating file test_file.6 Creating file test_file.7 Creating file test_file.8 Creating file test_file.9 53687091200 bytes written in 489.55 seconds (104.59 MiB/sec).
#这里给出一个每秒写入的数据量104.59MB/s, 这里的写入是顺序写入的,表示磁盘的吞吐量为104.59MB/s。
【一般对顺序的读写称为吞吐量,对随机的IO使用IOPS来表示】
[root@test3 systext]# ll -h #文件大小为5个G
total 50G
-rw------- 1 root root 5.0G Nov 27 09:30 test_file.0
-rw------- 1 root root 5.0G Nov 27 09:31 test_file.1
-rw------- 1 root root 5.0G Nov 27 09:32 test_file.2
-rw------- 1 root root 5.0G Nov 27 09:32 test_file.3
-rw------- 1 root root 5.0G Nov 27 09:33 test_file.4
-rw------- 1 root root 5.0G Nov 27 09:34 test_file.5
-rw------- 1 root root 5.0G Nov 27 09:35 test_file.6
-rw------- 1 root root 5.0G Nov 27 09:36 test_file.7
-rw------- 1 root root 5.0G Nov 27 09:36 test_file.8
-rw------- 1 root root 5.0G Nov 27 09:37 test_file.9
数据准备好之后,进行测试:
#这里进行随机读写测试
[root@test3 systext]# sysbench fileio --file-num=10 --file-total-size=50G --file-block-size=16384 --file-test-mode=rndrw --file-io-mode=sync --file-extra-flags=direct --time=100 --threads=16 --report-interval=10 run sysbench 1.1.0 (using bundled LuaJIT 2.1.0-beta3) Running the test with following options: #设定的一些参数数值 Number of threads: 16 Report intermediate results every 10 second(s) Initializing random number generator from current time Extra file open flags: directio 10 files, 5GiB each 50GiB total file size Block size 16KiB Number of IO requests: 0 Read/Write ratio for combined random IO test: 1.50 Periodic FSYNC enabled, calling fsync() each 100 requests. Calling fsync() at the end of test, Enabled. Using synchronous I/O mode Doing random r/w test Initializing worker threads... Threads started! [ 10s ] reads: 3.24 MiB/s writes: 2.16 MiB/s fsyncs: 34.08/s latency (ms,95%): 80.025 #每隔10s输出一次报告 [ 20s ] reads: 3.49 MiB/s writes: 2.32 MiB/s fsyncs: 36.70/s latency (ms,95%): 73.135 [ 30s ] reads: 3.45 MiB/s writes: 2.29 MiB/s fsyncs: 37.00/s latency (ms,95%): 75.817 [ 40s ] reads: 3.43 MiB/s writes: 2.29 MiB/s fsyncs: 36.00/s latency (ms,95%): 75.817 [ 50s ] reads: 3.57 MiB/s writes: 2.38 MiB/s fsyncs: 37.40/s latency (ms,95%): 73.135 [ 60s ] reads: 3.08 MiB/s writes: 2.06 MiB/s fsyncs: 32.30/s latency (ms,95%): 86.002 [ 70s ] reads: 3.41 MiB/s writes: 2.27 MiB/s fsyncs: 36.40/s latency (ms,95%): 75.817 [ 80s ] reads: 3.47 MiB/s writes: 2.31 MiB/s fsyncs: 36.20/s latency (ms,95%): 73.135 [ 90s ] reads: 3.46 MiB/s writes: 2.31 MiB/s fsyncs: 36.20/s latency (ms,95%): 77.194 [ 100s ] reads: 3.10 MiB/s writes: 2.07 MiB/s fsyncs: 33.50/s latency (ms,95%): 75.817 Throughput: read: IOPS=215.57 3.37 MiB/s (3.53 MB/s) #通常的机械磁盘随机IOPS也就是200多一点。 write: IOPS=143.72 2.25 MiB/s (2.35 MB/s) #随机写入的速度明显要低很多。 fsync: IOPS=37.13 Latency (ms): min: 0.08 avg: 40.51 max: 1000.31 95th percentile: 77.19 sum: 1601329.71
#随机读大概是2.10M/s,文件块的大小为16KB,可以大概估计磁盘转速: 2.10*1024KB*60s/16KB=7560n/m, 大概就是7500转每分
 顺序读的测试
顺序读的测试可以更改--file-test-mode的模式,改变测试的模式。
测试阶段完成之后,需要进行最后的cleanup阶段,
[root@test3 systext]# sysbench fileio --file-num=10 --file-total-size=50 cleanup sysbench 1.1.0 (using bundled LuaJIT 2.1.0-beta3) Removing test files... [root@test3 systext]# ls [root@test3 systext]# df -h Filesystem Size Used Avail Use% Mounted on /dev/vda3 29G 8.4G 20G 31% / tmpfs 3.9G 44K 3.9G 1% /dev/shm /dev/vda1 190M 30M 151M 17% /boot /dev/vdb 100G 25G 76G 25% /data cgroup_root 3.9G 0 3.9G 0% /cgroup #看到磁盘空间已经释放
测试MySQL的OLTP
sysbench新版的用法和之前的旧版本有所不同,先来看测试数据库时的一些参数:
General database options:
--db-driver=STRING specifies database driver to use ('help' to get list of available drivers) [mysql] #指定数据库驱动,默认是mysql
--db-ps-mode=STRING prepared statements usage mode {auto, disable} [auto] #
--db-debug[=on|off] print database-specific debug information [off] #dubug模式
Compiled-in database drivers:
mysql - MySQL driver
mysql options:
--mysql-host=[LIST,...] MySQL server host [localhost]
--mysql-port=[LIST,...] MySQL server port [3306]
--mysql-socket=[LIST,...] MySQL socket
--mysql-user=STRING MySQL user [sbtest]
--mysql-password=STRING MySQL password []
--mysql-db=STRING MySQL database name [sbtest] #数据库名字,默认是sbtest
--mysql-ssl[=on|off] use SSL connections, if available in the client library [off] #以下是ssl的连接测试
--mysql-ssl-key=STRING path name of the client private key file
--mysql-ssl-ca=STRING path name of the CA file
--mysql-ssl-cert=STRING path name of the client public key certificate file
--mysql-ssl-cipher=STRING use specific cipher for SSL connections []
--mysql-compression[=on|off] use compression, if available in the client library [off] #压缩测试
--mysql-debug[=on|off] trace all client library calls [off]
--mysql-ignore-errors=[LIST,...] list of errors to ignore, or "all" [1213,1020,1205] #忽略的错误
--mysql-dry-run[=on|off] Dry run, pretend that all MySQL client API calls are successful without executing them [off]
MySQL测试的lua脚本:
#因为是源码安装,索引目录在这里 [root@test3 lua]# pwd /data/sysbench-master/src/lua [root@test3 lua]# ls bulk_insert.lua Makefile oltp_common.lua oltp_point_select.lua oltp_update_index.lua prime-test.lua empty-test.lua Makefile.am oltp_delete.lua oltp_read_only.lua oltp_update_non_index.lua select_random_points.lua internal Makefile.in oltp_insert.lua oltp_read_write.lua oltp_write_only.lua select_random_ranges.lua #根据脚本的名字可以选择对应的基本
#查看某个lua脚本的用法
[root@test3 lua]# sysbench oltp_common.lua help
sysbench 1.1.0 (using bundled LuaJIT 2.1.0-beta3)
oltp_common.lua options:
--auto_inc[=on|off] Use AUTO_INCREMENT column as Primary Key (for MySQL), or its alternatives in other DBMS. When disabled, use client-generated IDs [on]
--create_secondary[=on|off] Create a secondary index in addition to the PRIMARY KEY [on]
--create_table_options=STRING Extra CREATE TABLE options []
--delete_inserts=N Number of DELETE/INSERT combinations per transaction [1]
--distinct_ranges=N Number of SELECT DISTINCT queries per transaction [1]
--index_updates=N Number of UPDATE index queries per transaction [1]
--mysql_storage_engine=STRING Storage engine, if MySQL is used [innodb]
--non_index_updates=N Number of UPDATE non-index queries per transaction [1]
--order_ranges=N Number of SELECT ORDER BY queries per transaction [1]
--pgsql_variant=STRING Use this PostgreSQL variant when running with the PostgreSQL driver. The only currently supported variant is 'redshift'. When enabled, create_secondary is automatically disabled, and delete_inserts is set to 0
--point_selects=N Number of point SELECT queries per transaction [10]
--range_selects[=on|off] Enable/disable all range SELECT queries [on]
--range_size=N Range size for range SELECT queries [100]
--secondary[=on|off] Use a secondary index in place of the PRIMARY KEY [off]
--simple_ranges=N Number of simple range SELECT queries per transaction [1]
--skip_trx[=on|off] Don't start explicit transactions and execute all queries in the AUTOCOMMIT mode [off]
--sum_ranges=N Number of SELECT SUM() queries per transaction [1]
--table_size=N Number of rows per table [10000]
--tables=N Number of tables [1]
prepare阶段:
创建默认的测试库:
mysql> create database sbtest; #创建数据库 Query OK, 1 row affected (0.11 sec) #准备数据,时间比较长,可以把table_size设置的小一点 [root@test3 lua]# sysbench /data/sysbench-master/src/lua/oltp_read_write.lua --tables=3 --table_size=10000000 --mysql-user=root --mysql-password=123456 --mysql-host=10.0.102.214 --mysql-port=3306 --mysql-db=sbtest prepare sysbench 1.1.0 (using bundled LuaJIT 2.1.0-beta3) Creating table 'sbtest1'... Inserting 10000000 records into 'sbtest1' Creating a secondary index on 'sbtest1'... Creating table 'sbtest2'... Inserting 10000000 records into 'sbtest2' Creating a secondary index on 'sbtest2'... Creating table 'sbtest3'... Inserting 10000000 records into 'sbtest3' Creating a secondary index on 'sbtest3'...
#在MySQL shel1中查看数据
mysql> select count(*) from sbtest1;
+----------+
| count(*) |
+----------+
| 10000000 |
+----------+
1 row in set (1.89 sec)
mysql> show tables;
+------------------+
| Tables_in_sbtest |
+------------------+
| sbtest1 |
| sbtest2 |
| sbtest3 |
+------------------+
3 rows in set (0.00 sec)
run阶段
选择一个合适的lua脚本进行测试:
[root@test3 lua]# sysbench /data/sysbench-master/src/lua/oltp_point_select.lua --tables=3 --table_size=10000000 --mysql-user=root --mysql-password=123456 --mysql-host=10.0.102.214 --mysql-port=3306 --mysql-db=sbtest --threads=128 --time=100 --report-interval=5 run
sysbench 1.1.0 (using bundled LuaJIT 2.1.0-beta3)
Running the test with following options:
Number of threads: 128
Report intermediate results every 5 second(s)
Initializing random number generator from current time
Initializing worker threads...
Threads started!
[ 5s ] thds: 128 tps: 15037.47 qps: 15037.47 (r/w/o: 15037.47/0.00/0.00) lat (ms,95%): 41.10 err/s: 0.00 reconn/s: 0.00
[ 10s ] thds: 128 tps: 18767.43 qps: 18767.43 (r/w/o: 18767.43/0.00/0.00) lat (ms,95%): 46.63 err/s: 0.00 reconn/s: 0.00
[ 15s ] thds: 128 tps: 22463.68 qps: 22463.68 (r/w/o: 22463.68/0.00/0.00) lat (ms,95%): 40.37 err/s: 0.00 reconn/s: 0.00
[ 20s ] thds: 128 tps: 26848.42 qps: 26848.42 (r/w/o: 26848.42/0.00/0.00) lat (ms,95%): 28.67 err/s: 0.00 reconn/s: 0.00
[ 25s ] thds: 128 tps: 27005.57 qps: 27005.57 (r/w/o: 27005.57/0.00/0.00) lat (ms,95%): 15.00 err/s: 0.00 reconn/s: 0.00
[ 30s ] thds: 128 tps: 26965.62 qps: 26965.62 (r/w/o: 26965.62/0.00/0.00) lat (ms,95%): 1.82 err/s: 0.00 reconn/s: 0.00
[ 35s ] thds: 128 tps: 27626.74 qps: 27626.74 (r/w/o: 27626.74/0.00/0.00) lat (ms,95%): 0.42 err/s: 0.00 reconn/s: 0.00
[ 40s ] thds: 128 tps: 27244.27 qps: 27244.27 (r/w/o: 27244.27/0.00/0.00) lat (ms,95%): 0.33 err/s: 0.00 reconn/s: 0.00
[ 45s ] thds: 128 tps: 26522.56 qps: 26522.56 (r/w/o: 26522.56/0.00/0.00) lat (ms,95%): 1.42 err/s: 0.00 reconn/s: 0.00
[ 50s ] thds: 128 tps: 26791.43 qps: 26791.43 (r/w/o: 26791.43/0.00/0.00) lat (ms,95%): 5.57 err/s: 0.00 reconn/s: 0.00
[ 55s ] thds: 128 tps: 27088.42 qps: 27088.42 (r/w/o: 27088.42/0.00/0.00) lat (ms,95%): 1.42 err/s: 0.00 reconn/s: 0.00
[ 60s ] thds: 128 tps: 28056.06 qps: 28056.06 (r/w/o: 28056.06/0.00/0.00) lat (ms,95%): 0.22 err/s: 0.00 reconn/s: 0.00
[ 65s ] thds: 128 tps: 27296.11 qps: 27296.11 (r/w/o: 27296.11/0.00/0.00) lat (ms,95%): 0.73 err/s: 0.00 reconn/s: 0.00
[ 70s ] thds: 128 tps: 28621.60 qps: 28621.60 (r/w/o: 28621.60/0.00/0.00) lat (ms,95%): 0.19 err/s: 0.00 reconn/s: 0.00
[ 75s ] thds: 128 tps: 28992.29 qps: 28992.29 (r/w/o: 28992.29/0.00/0.00) lat (ms,95%): 0.19 err/s: 0.00 reconn/s: 0.00
[ 80s ] thds: 128 tps: 28279.88 qps: 28279.88 (r/w/o: 28279.88/0.00/0.00) lat (ms,95%): 0.20 err/s: 0.00 reconn/s: 0.00
[ 85s ] thds: 128 tps: 28612.84 qps: 28612.84 (r/w/o: 28612.84/0.00/0.00) lat (ms,95%): 0.20 err/s: 0.00 reconn/s: 0.00
[ 90s ] thds: 128 tps: 28031.47 qps: 28031.47 (r/w/o: 28031.47/0.00/0.00) lat (ms,95%): 0.20 err/s: 0.00 reconn/s: 0.00
[ 95s ] thds: 128 tps: 28734.66 qps: 28734.66 (r/w/o: 28734.66/0.00/0.00) lat (ms,95%): 0.20 err/s: 0.00 reconn/s: 0.00
[ 100s ] thds: 128 tps: 28767.20 qps: 28767.20 (r/w/o: 28767.20/0.00/0.00) lat (ms,95%): 2.39 err/s: 0.00 reconn/s: 0.00
SQL statistics:
queries performed:
read: 2638920 #总的select数量
write: 0
other: 0
total: 2638920
transactions: 2638920 (26382.71 per sec.) #TPS
queries: 2638920 (26382.71 per sec.) #QPS
ignored errors: 0 (0.00 per sec.) #忽略的错误
reconnects: 0 (0.00 per sec.) #重新连接
Throughput:
events/s (eps): 26382.7081 #每秒的事件数,一般和TPS一样
time elapsed: 100.0246s #测试的总时间
total number of events: 2638920 #总的事件数,一般和TPS一样
Latency (ms):
min: 0.11 #最小响应时间
avg: 4.85 #平均响应时间
max: 649.29 #最大响应时间
95th percentile: 25.74 #95%的响应时间是这个数据
sum: 12796148.28
Threads fairness:
events (avg/stddev): 20616.5625/196.08
execution time (avg/stddev): 99.9699/0.00
#在这个测试中,可以看到TPS与QPS的大小基本一致,说明这个lua脚本中的一个查询一般就是一个事务!
我们一般关注的指标主要有:
- response time avg:平均响应时间(后面的95%的大小可以通过–percentile=98的方式去更改)。
- transactions:精确的说是这一项后面的TPS,但如果使用了–skip-trx=on,这项事务数为0,需要用total number of events去除以总时间,得到tps(其实还可以分为读tps和写tps)。
- queries:用它除以总时间,得到吞吐量QPS。
因为上面的TPS与QPS是一样的,因此只绘了TPS的图,如下:
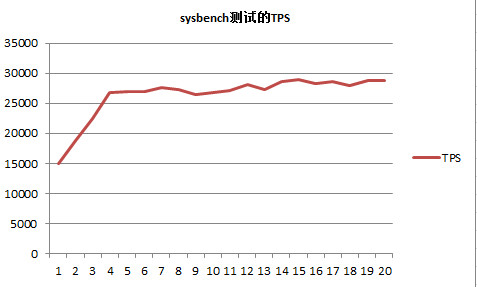
刚开始的时候有一个明显的上升,这时候是因为在bp中没有缓存数据,需要从磁盘中读数据,也就是预热阶段!
清理数据
[root@test3 lua]# sysbench /data/sysbench-master/src/lua/oltp_read_write.lua --tables=3 --table_size=10000000 --mysql-user=root --mysql-password=123456 --mysql-host=10.0.102.214 --mysql-port=3306 --mysql-db=sbtest cleanup sysbench 1.1.0 (using bundled LuaJIT 2.1.0-beta3) Dropping table 'sbtest1'... Dropping table 'sbtest2'... Dropping table 'sbtest3'... [root@test3 lua]#
sysbench除了以上的测试之外,还可以测试:
Compiled-in tests: fileio - File I/O test cpu - CPU performance test memory - Memory functions speed test threads - Threads subsystem performance test mutex - Mutex performance test See 'sysbench <testname> help' for a list of options for each test
sample mysql 压力测试
task 8: sysbech 压力测试
源码安装:
https://github.com/akopytov/sysbench
RHEL/CentOS
yum -y install make automake libtool pkgconfig libaio-devel
# For MySQL support, replace with mysql-devel on RHEL/CentOS 5
yum -y install mariadb-devel openssl-devel
# For PostgreSQL support
yum -y install postgresql-devel
unzip sysbench-master.zip
cd sysbench-master
./autogen.sh
# Add --with-pgsql to build with PostgreSQL support
./configure
make -j
make install
sysbench --help
调试:
cd /tmp/dba/sysbench-master/src/lua
sysbench oltp_common.lua help
mysql -uroot -p -h10.241.21.113 -P 3306
mysql> create database sbtest; #创建数据库
prepare阶段:
#准备数据,时间比较长,可以把table_size设置的小一点
sysbench /tmp/dba/sysbench-master/src/lua/oltp_read_write.lua --tables=3 --table_size=10000000 --mysql-user=dba --mysql-password=db1234DBA --mysql-host=10.241.21.113 --mysql-port=3306 --mysql-db=sbtest prepare
use sbtest;
select count(*) from sbtest1;
run阶段:
##--threads=N number of threads to use [1] #线程的数量,默认是1
##--time=N limit for total execution time in seconds [10] #整个测试执行的时间
## --report-interval=N #打印出中间的信念,N表示每隔N秒打印一次,
sysbench /tmp/dba/sysbench-master/src/lua/oltp_read_write.lua --tables=3 --table_size=10000000 --mysql-user=dba --mysql-password=db1234DBA --mysql-host=10.241.21.113 --mysql-port=3306 --mysql-db=sbtest --threads=128 --time=100 --report-interval=5 run
清理数据:
sysbench /tmp/dba/sysbench-master/src/lua/oltp_read_write.lua --tables=3 --table_size=10000000 --mysql-user=dba --mysql-password=db1234DBA --mysql-host=10.241.21.113 --mysql-port=3306 --mysql-db=sbtest cleanup
SQL statistics:
queries performed:
read: 2638920 #总的select数量
write: 0
other: 0
total: 2638920
transactions: 2638920 (26382.71 per sec.) #TPS
queries: 2638920 (26382.71 per sec.) #QPS
ignored errors: 0 (0.00 per sec.) #忽略的错误
reconnects: 0 (0.00 per sec.) #重新连接
Throughput:
events/s (eps): 26382.7081 #每秒的事件数,一般和TPS一样
time elapsed: 100.0246s #测试的总时间
total number of events: 2638920 #总的事件数,一般和TPS一样
Latency (ms):
min: 0.11 #最小响应时间
avg: 4.85 #平均响应时间
max: 649.29 #最大响应时间
95th percentile: 25.74 #95%的响应时间是这个数据
sum: 12796148.28
Threads fairness:
events (avg/stddev): 20616.5625/196.08
execution time (avg/stddev): 99.9699/0.00
#在这个测试中,可以看到TPS与QPS的大小基本一致,说明这个lua脚本中的一个查询一般就是一个事务!
我们一般关注的指标主要有:
- response time avg:平均响应时间(后面的95%的大小可以通过–percentile=98的方式去更改)。
- transactions:精确的说是这一项后面的TPS,但如果使用了–skip-trx=on,这项事务数为0,需要用total number of events去除以总时间,得到tps(其实还可以分为读tps和写tps)。
- queries:用它除以总时间,得到吞吐量QPS。
因为上面的TPS与QPS是一样的,因此只绘了TPS的图,如下:

####更多解释:
https://www.cnblogs.com/zhoujinyi/archive/2013/04/19/3029134.html
③:使用说明
初始化数据:prepare。在本地数据库的dba_test库中,初始化三张表(sbtest1、sbtest2、sbtest3),存储引擎是innodb,每张表50万数据。
sysbench --test=/usr/share/doc/sysbench/tests/db/oltp.lua --mysql-table-engine=innodb --mysql-host=127.0.0.1 --mysql-db=dba_test --oltp-table-size=500000 --oltp_tables_count=3 --rand-init=on --mysql-user=zjy --mysql-password=zjy prepare
因为是本机测试,所以也可以用也可以使用--mysql-socket指定socket文件来连接。
测试:run。模拟对3个表并发OLTP测试,每个表50万行记录,持续压测时间为5分钟。
sysbench --test=/usr/share/doc/sysbench/tests/db/oltp.lua --mysql-table-engine=innodb --mysql-host=127.0.0.1 --mysql-db=dba_test --num-threads=8 --oltp-table-size=500000 --oltp_tables_count=3 --oltp-read-only=off --report-interval=10 --rand-type=uniform --max-time=600 --max-requests=0 --percentile=99 --mysql-user=zjy --mysql-password=zjy run
上面跑完会出一个结果:
#每10秒钟报告一次测试结果,tps、每秒读、每秒写、95%以上的响应时长统计
[ 10s] threads: 8, tps: 66.60, reads: 943.67, writes: 269.62, response time: 431.72ms (95%), errors: 0.00, reconnects: 0.00
[ 20s] threads: 8, tps: 34.30, reads: 480.20, writes: 137.20, response time: 598.28ms (95%), errors: 0.00, reconnects: 0.00
[ 30s] threads: 8, tps: 36.60, reads: 512.40, writes: 146.40, response time: 494.87ms (95%), errors: 0.00, reconnects: 0.00
OLTP test statistics:
queries performed:
read: 941248 #读总数
write: 268928 #写总数
other: 134464 #其他操作总数(SELECT、INSERT、UPDATE、DELETE之外的操作,例如COMMIT等)
total: 1344640 #全部总数
transactions: 67232 (112.04 per sec.) #总事务数(每秒事务数)
read/write requests: 1210176 (2016.73 per sec.) #读写总数(每秒读写次数)
other operations: 134464 (224.08 per sec.) #其他操作总数(每秒其他操作次数)
ignored errors: 0 (0.00 per sec.)
reconnects: 0 (0.00 per sec.)
General statistics:
total time: 600.0698s #总耗时
total number of events: 67232 #共发生多少事务数
total time taken by event execution: 4799.8569s # 所有事务耗时相加(不考虑并行因素)
response time:
min: 2.09ms #最小耗时
avg: 71.39ms #平均耗时
max: 839.32ms #最大耗时
approx. 95 percentile: 309.40ms 超过95%平均耗时
Threads fairness:
events (avg/stddev): 8404.0000/17.56
execution time (avg/stddev): 599.9821/0.02
