1. 数组中无重复元素
Suppose an array sorted in ascending order is rotated at some pivot unknown to you beforehand. (i.e., [0,1,2,4,5,6,7] might become [4,5,6,7,0,1,2]).
You are given a target value to search. If found in the array return its index, otherwise return -1.
You may assume no duplicate exists in the array.
Your algorithm's runtime complexity must be in the order of O(log n).
Example 1:
Input: nums = [4,5,6,7,0,1,2], target = 0
Output: 4
Example 2:
Input: nums = [4,5,6,7,0,1,2], target = 3
Output: -1
1.1 寻找最小值所在的点
建立模型求解
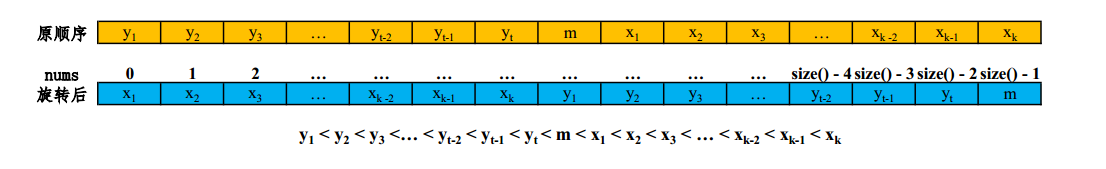
本题关键在于求解 最小值所在的索引,再通过二分法求解即可。
选择right作为比较的轴值,原因在于nums[right] 永远不会等于nums[mid],分一下三种情况讨论。
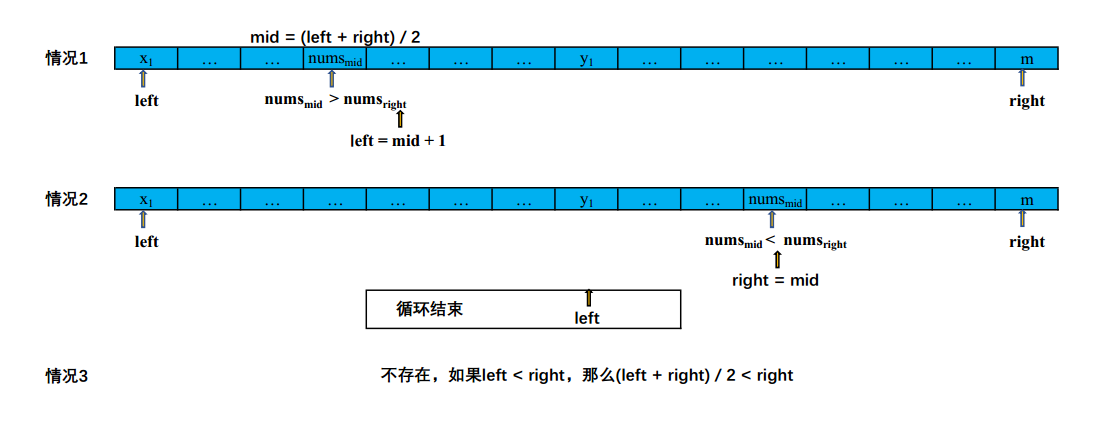
如果中间值比最右端的值大,那么应该让 left = mid + 1,如果中间值比最右端小,那么应该让right = mid,因为nums[mid] = y1时也是满足中间值比最右端小,不应该让right = mid - 1.
循环结束时left = right = index(y1)
1.2 二分法求解
先按照标准的二分法思路求解,不同的是,旋转以后,中间值与未旋转之前总是向后偏移最小值索引个单位。
int search(vector<int>& nums, int target) { int left = 0; int right = nums.size() - 1; int mid = 0; while (left < right) { mid = (left + right) / 2; if (nums[mid] <= nums[right]) { right = mid; } else { left = mid + 1; } } int point = left; left = 0; right = nums.size() - 1; while (left <= right) { int medium = (left + right) / 2; mid = (medium + point) % nums.size(); if (nums[mid] < target) { left = medium + 1; } else if (nums[mid] > target) { right = medium - 1; } else { return mid; } } return -1; }