1 链表的概念及结构
概念:链表是一种物理存储结构上非连续、非顺序的存储结构,数据元素的逻辑顺序是通过链表中的指针链接次序实现的。
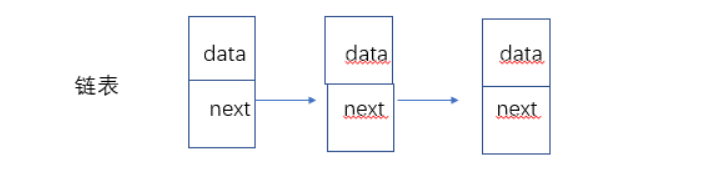
实际中链表的结构非常多样,以下情况组合起来就有8种链表结构: 1. 单向、双向 2. 带头、不带头 3. 循环、非循环。
常用的有无头单向非循环链表、带头双向循环链表。
1. 无头单向非循环链表:结构简单,一般不会单独用来存数据。实际中更多是作为其他数据结构的子结 构,如哈希桶、图的邻接表等等。另外这种结构在笔试面试中出现很多。
2. 带头双向循环链表:结构最复杂,一般用在单独存储数据。实际中使用的链表数据结构,都是带头双向 循环链表。另外这个结构虽然结构复杂,但是使用代码实现以后会发现结构会带来很多优势,实现反而 简单了,后面我们代码实现了就知道了。
下面是无头单向非循环链表的一些基本操作代码:
//NodeList.c #include"NodeList2.h" //遍历 void print(Node* head) { Node* cur = head; //声明一个新指针用来进行遍历 while (cur) { //cur为NULL时链表遍历完 printf("%d-->", cur->val); cur = cur->next; } printf(" "); } //销毁链表 Node* NodeListDestory(Node* head) { Node* cur = head; while (cur) //每一个节点都要销毁 { Node* node = cur->next; free(cur); cur = node; } head = NULL; return head; } //头插 Node* NodeListPushFront(Node* head, DataType x) { Node* node = (Node*)malloc(sizeof(Node)); //申请节点 node->val = x; // 将数据放入节点中 node->next = head; //新节点的下一个节点置为原链表的头结点 return node; //返回新的头结点 //head=node;return head; } //尾插 Node* NodeListPushBack(Node* head,DataType x) { if (NULL == head) { head=NodeListPushFront(head, x); //如果原链表为空,插入第一个元素用头插 } else { //原链表不为空,申请新节点 Node* node = (Node*)malloc(sizeof(Node)); node->val = x; //将要插入的数据放入节点 node->next = NULL; //因为是尾插,所以插入的节点的下一个一定为空节点 Node* cur = head; //声明一个变量来进行遍历 while (cur->next != NULL) //cur的next为NULL时说明cur是最后一个节点 { cur = cur->next; } cur->next = node; //循环结束,cur遍历到链表最后一项的位置,使next指向新节点,完成尾插 } return head; } //头删 Node* NodeListPopFront(Node* head) { assert(head); if (NULL == head->next) //链表的第一个节点的next为空时说明链表只有一个节点 { free(head); head = NULL; return head; } else //链表不止一个节点时 { Node* node = head->next; //定义一个新指针指向head的next free(head); //释放head节点 return node; //返回node节点,即为将原链表的第二个节点返回,外部接收使其成为新的头结点 } } //尾删 Node* NodeListPopBack(Node* head) { assert(head); if (NULL == head->next) //链表只有一个节点 { free(head); head = NULL; } else //链表不止一个节点时 { Node* cur = head; while (NULL != cur->next->next) //节点的next的next为空,说明当前节点在倒数第二个节点 { cur = cur->next; } //循环结束则说明cur已经是倒数第二个节点,它的下一个是最后一个节点,也就是要删除的节点 free(cur->next); //释放cur的下一个节点,即删除最后一个节点 cur->next = NULL; //cur的next置为空,防止野指针 } return head; } //查找x并第一次在链表中出现的位置,没有该元素则输出提示信息 Node* NodeListFind(Node* head, DataType x) { assert(head); int count = 0; for (Node* cur = head; cur != NULL; cur = cur->next) { ++count; if (x == cur->val) { printf("%d ", count); //记录x是链表中的第几个元素 return cur; //如果找到x第一次出现的位置,返回其所在的节点地址 } } count = 0; printf("链表中没有%d ", x); return NULL; //如果会跳出循环,说明链表中没有x,返回NULL表示该元素不存在链表中 } //删除x第一次出现的节点 Node* NodeListRemove(Node* head, DataType x) { assert(head); if (x == head->val) { Node *node = head->next; free(head); return node; } else { Node* cur = head; while (cur) { if (x == cur->next->val) //第一个元素已经在前面判断过,所以从第二个元素的值开始判断 { //当前节点的next节点的值为x时进行删除操作 Node* node = cur->next; //记录下要删除的节点,以免断开链接后失去地址,无法释放 cur->next = cur->next->next; //当前节点的next指向next的next,完成删除 free(node); //释放删除的节点的空间 return head; } cur = cur->next; } } }
//NodeList.h typedef int DataType; typedef struct Node { DataType val; struct Node* next; }Node; //销毁链表 Node* NodeListDestory(Node* head); //头插 Node* NodeListPushFront(Node* head, DataType x); //遍历 void print(Node* head); //尾插 Node* NodeListPushBack(Node* head, DataType x); //头删 Node* NodeListPopFront(Node* head); //尾删 Node* NodeListPopBack(Node* head); ////查找x并第一次在链表中出现的位置 Node* NodeListFind(Node* head, DataType x); //删除x第一次出现的节点 Node* NodeListRemove(Node* head, DataType x); //删除值为x的所有节点 Node* NodeListRemoveAll(Node* head, DataType x);
//test.c #include"NodeList2.h" void test() { Node* head; head = NULL; //链表为空即为初始化 head = NodeListPushFront(head, 5); head = NodeListPushFront(head, 4); head = NodeListPushFront(head, 3); head = NodeListPushFront(head, 2); head = NodeListPushFront(head, 1); head = NodeListPushFront(head, 5); print(head); head = NodeListPushBack(head, 6); head = NodeListPushBack(head, 7); head = NodeListPushBack(head, 8); head = NodeListPushFront(head, 5); //head=NodeListDestory(head); print(head); //head = NodeListPopFront(head); //print(head); //head = NodeListPopFront(head); //print(head); //head = NodeListPopBack(head); //print(head); //head = NodeListPopBack(head); //print(head); //Node* pos = NodeListFind(head, 11); //head=NodeListRemove(head, 5); //print(head); system("pause"); } int main() { test(); return 0; }