java用 @interface Annotation{ } 定义一个注解 @Annotation,一个注解是一个类。
@Override,@Deprecated,@SuppressWarnings为常见的3个注解。
注解相当于一种标记,在程序中加上了注解就等于为程序加上了某种标记,以后,
JAVAC编译器,开发工具和其他程序可以用反射来了解你的类以及各种元素上有无任何标记,看你有什么标记,就去干相应的事。
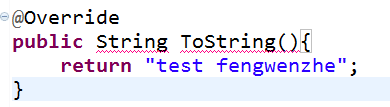
注解@Override用在方法上,当我们想重写一个方法时,在方法上加@Override,当我们方法
的名字出错时,编译器就会报错,如下图:
注解@Deprecated,用来表示某个类的属性或方法已经过时,不想别人再用时,在属性和方法
上用@Deprecated修饰,如图:

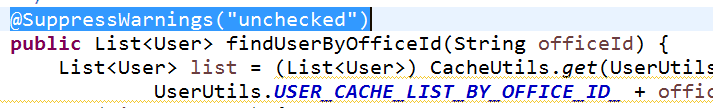
注解@SuppressWarnings用来压制程序中出来的警告,比如在没有用泛型或是方法已经过时的时候:
注解@Retention可以用来修饰注解,是注解的注解,称为元注解。
Retention注解有一个属性value,是RetentionPolicy类型的,Enum RetentionPolicy是一个枚举类型,
这个枚举决定了Retention注解应该如何去保持,也可理解为Rentention 搭配 RententionPolicy使用。RetentionPolicy有3个值:CLASS RUNTIME SOURCE
用@Retention(RetentionPolicy.CLASS)修饰的注解,表示注解的信息被保留在class文件(字节码文件)中当程序编译时,但不会被虚拟机读取在运行的时候;
用@Retention(RetentionPolicy.SOURCE )修饰的注解,表示注解的信息会被编译器抛弃,不会留在class文件中,注解的信息只会留在源文件中;
用@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME )修饰的注解,表示注解的信息被保留在class文件(字节码文件)中当程序编译时,会被虚拟机保留在运行时,
所以他们可以用反射的方式读取。RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME 可以让你从JVM中读取Annotation注解的信息,以便在分析程序的时候使用。
package com.self; import java.lang.annotation.Retention; import java.lang.annotation.RetentionPolicy; @Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME) public @interface MyTarget { } 定义个一注解@MyTarget,用RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME修饰; package com.self; import java.lang.reflect.Method; public class MyTargetTest { @MyTarget public void doSomething() { System.out.println("hello world"); } public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception { Method method = MyTargetTest.class.getMethod("doSomething",null); if(method.isAnnotationPresent(MyTarget.class))//如果doSomething方法上存在注解@MyTarget,则为true { System.out.println(method.getAnnotation(MyTarget.class)); } } } 上面程序打印:@com.self.MyTarget(),如果RetentionPolicy值不为RUNTIME,则不打印。 @Retention(RetentionPolicy.SOURCE ) public @interface Override @Retention(RetentionPolicy.SOURCE ) public @interface SuppressWarnings @Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME ) public @interface Deprecated 由上可以看出,只有注解@Deprecated在运行时可以被JVM读取到 注解中可以定义属性,看例子: @Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME) public @interface MyAnnotation { String hello() default "gege"; String world(); int[] array() default { 2, 4, 5, 6 }; EnumTest.TrafficLamp lamp() ; TestAnnotation lannotation() default @TestAnnotation(value = "ddd"); Class style() default String.class; } 上面程序中,定义一个注解@MyAnnotation,定义了6个属性,他们的名字为: hello,world,array,lamp,lannotation,style. 属性hello类型为String,默认值为gege 属性world类型为String,没有默认值 属性array类型为数组,默认值为2,4,5,6 属性lamp类型为一个枚举,没有默认值 属性lannotation类型为注解,默认值为@TestAnnotation,注解里的属性是注解 属性style类型为Class,默认值为String类型的Class类型 看下面例子:定义了一个MyTest类,用注解@MyAnnotation修饰,注解@MyAnnotation定义的属性都赋了值 @MyAnnotation(hello = "beijing", world="shanghai",array={},lamp=TrafficLamp.RED,style=int.class) public class MyTest { @MyAnnotation(lannotation=@TestAnnotation(value="baby"), world = "shanghai",array={1,2,3},lamp=TrafficLamp.YELLOW) @Deprecated @SuppressWarnings("") public void output() { System.out.println("output something!"); } } 接着通过反射读取注解的信息: public class MyReflection { public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception { MyTest myTest = new MyTest(); Class<MyTest> c = MyTest.class; Method method = c.getMethod("output", new Class[] {}); //如果MyTest类名上有注解@MyAnnotation修饰,则为true if(MyTest.class.isAnnotationPresent(MyAnnotation.class)) { System.out.println("have annotation"); } if (method.isAnnotationPresent(MyAnnotation.class)) { method.invoke(myTest, null); //调用output方法 //获取方法上注解@MyAnnotation的信息 MyAnnotation myAnnotation = method.getAnnotation(MyAnnotation.class); String hello = myAnnotation.hello(); String world = myAnnotation.world(); System.out.println(hello + ", " + world);//打印属性hello和world的值 System.out.println(myAnnotation.array().length);//打印属性array数组的长度 System.out.println(myAnnotation.lannotation().value()); //打印属性lannotation的值 System.out.println(myAnnotation.style()); } //得到output方法上的所有注解,当然是被RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME修饰的 Annotation[] annotations = method.getAnnotations(); for (Annotation annotation : annotations) { System.out.println(annotation.annotationType().getName()); } } } 上面程序打印: have annotation output something! gege, shanghai 3 baby class java.lang.String com.heima.annotation.MyAnnotation java.lang.Deprecated 如果注解中有一个属性名字叫value,则在应用时可以省略属性名字不写。 可见,@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME )注解中,RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME是注解属性值,属性名字是value, 属性的返回类型是RetentionPolicy,如下: public @interface MyTarget { String value(); } 可以这样用: @MyTarget("aaa") public void doSomething() { System.out.println("hello world"); } 注解@Target也是用来修饰注解的元注解,它有一个属性ElementType也是枚举类型, 值为:ANNOTATION_TYPE CONSTRUCTOR FIELD LOCAL_VARIABLE METHOD PACKAGE PARAMETER TYPE 如@Target(ElementType.METHOD) 修饰的注解表示该注解只能用来修饰在方法上。 @Target(ElementType.METHOD) @Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME) public @interface MyTarget { String value() default "hahaha"; } 如把@MyTarget修饰在类上,则程序报错,如: @MyTarget public class MyTargetTest 注解大都用在开发框架中吧,好了有关注解就学习那么多了,谢谢。