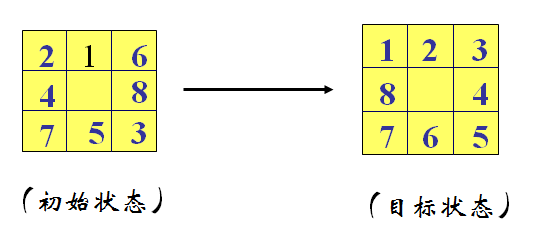
八数码问题
利用启发式搜索,找出以下问题的最优解。
#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
#include <algorithm>
using namespace std;
const int BLANK = 0;
const int R = 3;
const int C = 3;
pair<int, int> find_blank(const vector<vector<int>> &m) {
for (int r = 0; r < m.size(); r++) {
for (int c = 0; c < m[r].size(); c++) {
if (m[r][c] == BLANK) {
return make_pair(r, c);
}
}
}
return make_pair(-1, -1);
}
vector<pair<int, int>> address_derive(const pair<int, int> &father) {
vector<pair<int, int>> addresses;
const int r = father.first, c = father.second;
if (r - 1 >= 0) {
addresses.push_back(make_pair(r - 1, c));
}
if (r + 1 < R) {
addresses.push_back(make_pair(r + 1, c));
}
if (c - 1 >= 0) {
addresses.push_back(make_pair(r, c - 1));
}
if (c + 1 < C) {
addresses.push_back(make_pair(r, c + 1));
}
return addresses;
}
vector<vector<vector<int>>> matrix_derive(const vector<vector<int>> &father) {
vector<vector<vector<int>>> matrices;
pair<int, int> address = find_blank(father);
vector<pair<int, int>> addresses = address_derive(address);
for (const auto e : addresses) {
int r = e.first, c = e.second;
vector<vector<int>> son = father;
swap(son[address.first][address.second], son[r][c]);
matrices.push_back(son);
}
return matrices;
}
int evaluate(const vector<vector<int>> &m, const vector<vector<int>> &goal) {
int difference = 0;
for (int r = 0; r < goal.size(); r++) {
for (int c = 0; c < goal[r].size(); c++) {
if (goal[r][c] == BLANK) {
continue;
}
difference = m[r][c] != goal[r][c] ? difference + 1 : difference;
}
}
return difference;
}
struct Block {
int g;
int h;
vector<vector<int>> m;
Block(int g = 0, int h = 0, vector<vector<int>> m = vector<vector<int>>())
:g(g), h(h), m(m) {};
};
void print(const Block &b) {
for (const auto r : b.m) {
for (const auto c : r) {
cout << c << " ";
}
cout << endl;
}
cout << b.g << " " << b.h << endl;
cout << endl;
}
bool in_close(const vector<vector<vector<int>>> &close, const vector<vector<int>> &m) {
for (auto e : close) {
if (e == m) {
return true;
}
}
return false;
}
bool in_open(const vector<Block> &open, const vector<vector<int>> &m) {
for (auto e : open) {
if (e.m == m) {
return true;
}
}
return false;
}
void search(const vector<vector<int>> &begin, const vector<vector<int>> &goal) {
vector<Block> open;
vector<vector<vector<int>>> close;
open.push_back(Block(0, evaluate(begin, goal), begin));
int g = 0;
while (open.size()){
sort(open.begin(), open.end(), [](const Block &lhs, const Block &rhs) {
return (lhs.g + lhs.h) < (rhs.g + rhs.h);
});
Block cur = open.front();
open.erase(open.begin());
close.push_back(cur.m);
print(cur);
if (cur.m == goal) {
break;
}
vector<vector<vector<int>>> matrices = matrix_derive(cur.m);
for (auto e : matrices) {
if(!in_open(open, e)){
if (!in_close(close, e)) {
open.push_back(Block(cur.g+1, evaluate(e, goal), e));
}
}
}
}
}
int main() {
vector<vector<int>> begin = { {2,1,6},{4,0,8},{7,5,3} };
vector<vector<int>> goal = { {1,2,3}, {8,0,4}, {7,6,5} };
search(begin, goal);
return 0;
}