B - Mike and Shortcuts
Description
Recently, Mike was very busy with studying for exams and contests. Now he is going to chill a bit by doing some sight seeing in the city.
City consists of n intersections numbered from 1 to n. Mike starts walking from his house located at the intersection number 1 and goes along some sequence of intersections. Walking from intersection number i to intersection j requires |i - j| units of energy. The total energy spent by Mike to visit a sequence of intersections p1 = 1, p2, ..., pk is equal to 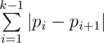
units of energy.
Of course, walking would be boring if there were no shortcuts. A shortcut is a special path that allows Mike walking from one intersection to another requiring only 1 unit of energy. There are exactly n shortcuts in Mike's city, the ith of them allows walking from intersection ito intersection ai (i ≤ ai ≤ ai + 1) (but not in the opposite direction), thus there is exactly one shortcut starting at each intersection. Formally, if Mike chooses a sequence p1 = 1, p2, ..., pk then for each 1 ≤ i < k satisfying pi + 1 = api and api ≠ pi Mike will spendonly 1 unit of energy instead of |pi - pi + 1| walking from the intersection pi to intersection pi + 1. For example, if Mike chooses a sequence p1 = 1, p2 = ap1, p3 = ap2, ..., pk = apk - 1, he spends exactly k - 1 units of total energy walking around them.
Before going on his adventure, Mike asks you to find the minimum amount of energy required to reach each of the intersections from his home. Formally, for each 1 ≤ i ≤ n Mike is interested in finding minimum possible total energy of some sequence p1 = 1, p2, ..., pk = i.
Input
The first line contains an integer n(1 ≤ n ≤ 200 000) — the number of Mike's city intersection.
The second line contains n integers a1, a2, ..., an(i ≤ ai ≤ n , , describing shortcuts of Mike's city, allowing to walk from intersection i to intersection ai using only 1 unit of energy. Please note that the shortcuts don't allow walking in opposite directions (from ai to i).
Output
In the only line print n integers m1, m2, ..., mn, where mi denotes the least amount of total energy required to walk from intersection 1to intersection i.
Sample Input
3
2 2 3
0 1 2
5
1 2 3 4 5
0 1 2 3 4
7
4 4 4 4 7 7 7
0 1 2 1 2 3 3
Hint
In the first sample case desired sequences are:
1: 1; m1 = 0;
2: 1, 2; m2 = 1;
3: 1, 3; m3 = |3 - 1| = 2.
In the second sample case the sequence for any intersection 1 < i is always 1, i and mi = |1 - i|.
In the third sample case — consider the following intersection sequences:
1: 1; m1 = 0;
2: 1, 2; m2 = |2 - 1| = 1;
3: 1, 4, 3; m3 = 1 + |4 - 3| = 2;
4: 1, 4; m4 = 1;
5: 1, 4, 5; m5 = 1 + |4 - 5| = 2;
6: 1, 4, 6; m6 = 1 + |4 - 6| = 3;
7: 1, 4, 5, 7; m7 = 1 + |4 - 5| + 1 = 3.
题意:
n个城市排成一排,起点是第一个城市,每次可以向左或者右相邻城市走,路程为1
每个城市有一个捷径ai 表示第i个城市可以直接到ai城市,路程为1.
问从第一个城市出发,到达每个城市的最短路。
分析:相当于每个城市有三条路可以选择,直接用bfs求最短路径。
#include <iostream> #include<cstdio> #include<cstring> using namespace std; const int MAXN=200005; int a[MAXN],b[MAXN],q[MAXN],d[MAXN]; int main() { int n,r=0,l=1; memset(q,0,sizeof(q)); memset(b,0x6f,sizeof(b)); scanf("%d",&n); for(int i=1;i<=n;i++) scanf("%d",&a[i]); b[1]=0;q[1]=1;d[++r]=1; for(;l<=r;l++) { if(d[l]>1&&!q[d[l]-1]) { q[d[l]-1]=1; b[d[l]-1]=b[d[l]]+1; d[++r]=d[l]-1; } if(d[l]<n&&!q[d[l]+1]) { q[d[l]+1]=1; b[d[l]+1]=b[d[l]]+1; d[++r]=d[l]+1; } if(!q[a[d[l]]]) { q[a[d[l]]]=1; b[a[d[l]]]=b[d[l]]+1; d[++r]=a[d[l]]; } } for(int i=1;i<n;i++) printf("%d ",b[i]); printf("%d ",b[n]); return 0; }