一、Vuex演示(mutations同步方法)
通过const state定义变量方式,在new Vuex.Store是引用的写法
1、main.js
//sotre中的变量为所有组件共享变量,即全局变量 import Vue from 'vue';//引用vue import Vuex from 'vuex';//引用vuex Vue.use(Vuex);//使用vuex //一、格式 /*const store = new Vuex.Store(); export default store;*/ //////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////// //2、示例 // 定义数据 // state在vuex中是用于储存数据的 const state={ name : 100 } // 定义方法 mutation同步,因为能改变state的方法是mutations // mutations 里面方的是方法,主要用于改变state中的数据源 const mutations ={ addNumber(){ state.name+=100 }, reduceNumber(){ state.name+=100 }, }, //定义方法 actions异步 使用场景:异步操作比如数据请求,则需要放在 action 中 // 实例化 Vuex.store,用到什么引什么,用到actions就引入actions,用到getters就引入getters,本文只用到这两个 const store = new Vuex.Store({ state, mutations }) export default store; //1、页面中用this.$store.state来获取到state中的某个值。 //2、页面中使用this.$store.commit来调用vuex中mutations里的某个方法 //3、页面中使用this.$store.dispatch来调用vuex中actions里的某个方法 //actions和mutation的区别 //Action 提交的是 mutation,而不是直接变更状态
页面调用
<template>
<div>{{this.$store.state.name}}
<button @click="add">增加100</button>
<button @click="reduce">减少100</button>
</div>
</template>
<script>
export default {
components: {
},
data() {
return {
active: 2
};
},
methods: {
add(){
this.$store.commit('addNumber')
},
reduce(){
this.$store.commit('reduceNumber')
},
}
}
</script>
二、演示(action示例异步调用)
store.js文件
//sotre中的变量为所有组件共享变量,即全局变量 import Vue from 'vue';//引用vue import Vuex from 'vuex';//引用vuex Vue.use(Vuex);//使用vuex const store = new Vuex.Store({ state: { count: 0 }, mutations: { increment (state) { state.count++ } }, actions: { increment (context) { context.commit('increment') } } }) export default store //1、页面中用this.$store.state来获取到state中的某个值。 //2、页面中使用this.$store.commit来调用vuex中mutations里的某个方法 //3、页面中使用this.$store.dispatch来调用vuex中actions里的某个方法 //actions和mutation的区别 //Action 提交的是 mutation,而不是直接变更状态
页面调用
<template>
<div>{{this.$store.state.count}}
<button @click="add">增加100</button>
</div>
</template>
<script>
export default {
components: {
},
data() {
return {
active: 2
};
},
methods: {
add(){
this.$store.dispatch('increment')
},
}
}
</script>
三、演示(action示例异步调用扩展)
1、扩展回调参数
store.js页面
//sotre中的变量为所有组件共享变量,即全局变量 import Vue from 'vue';//引用vue import Vuex from 'vuex';//引用vuex Vue.use(Vuex);//使用vuex const store = new Vuex.Store({ state: { count: 0 }, mutations: { increment (state) { state.count++ } }, actions: { increment (context,param) { context.commit('increment') //action执行后回调 if (param.success) param.success() } } }) export default store //1、页面中用this.$store.state来获取到state中的某个值。 //2、页面中使用this.$store.commit来调用vuex中mutations里的某个方法 //3、页面中使用this.$store.dispatch来调用vuex中actions里的某个方法 //actions和mutation的区别 //Action 提交的是 mutation,而不是直接变更状态
页面调用
<template>
<div>{{this.$store.state.count}}
<button @click="add">增加100</button>
</div>
</template>
<script>
export default {
components: {
},
data() {
return {
active: 2
};
},
methods: {
add(){
this.$store.dispatch("increment", {
success() {
alert("incremented!")
}
})
},
}
}
</script>
关键点
payload里面添加一个回调函数的变量

2、扩展回调参数+属性一起使用
store页面
//sotre中的变量为所有组件共享变量,即全局变量 import Vue from 'vue';//引用vue import Vuex from 'vuex';//引用vuex Vue.use(Vuex);//使用vuex const store = new Vuex.Store({ state: { count: 0, list:[] }, mutations: { //这里的state对应着上面这个state,param则是传过来的参数 //因为是new在一个store里面的所以需要参数, increment (state,param) { state.count++; state.list=param; } }, actions: { //这里的context和我们使用的$store拥有相同的对象和方法,param则是传过来的参数变量(具有两个属性) increment (context,param) { context.commit('increment',param.list) //action执行后回调 if (param.success) param.success() } } }) export default store //1、页面中用this.$store.state来获取到state中的某个值。 //2、页面中使用this.$store.commit来调用vuex中mutations里的某个方法 //3、页面中使用this.$store.dispatch来调用vuex中actions里的某个方法 //actions和mutation的区别 //Action 提交的是 mutation,而不是直接变更状态
调用页面
<template>
<div>
{{this.$store.state.count}}
{{this.$store.state.list}}
<button @click="add">增加100</button>
</div>
</template>
<script>
export default {
components: {
},
data() {
return {
active: 2
};
},
methods: {
add(){
this.$store.dispatch("increment", {
//定义匿名变量参数内加两个属性,一个list变量,一个回调函数
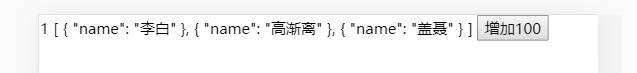
list: [{name: '李白'}, {name: '高渐离'}, {name: '盖聂'}],
success() {
alert("incremented!")
}
})
},
}
}
</script>
效果图: