vue的组件
什么是组件:说白了,就是自定义标签。
vue为什么有组件的概念:不止是vue,目前流行的框架都有组件这个概念,比如angular中的自定义指令,其实就是组件。
怎么使用组件:使用组件之前,先要创建一个组件
var MyComponent = Vue.extend({ // 选项... })
然后是注册组件
需要用Vue.component(tag,constructor) 注册
// 全局注册组件,tag 为 my-component Vue.component('my-component', MyComponent)
组件在注册之后,便可以在父实例的模块中以自定义元素 <my-component> 的形式使用。要确保在初始化根实例之前注册了组件:
<div id="example"> <my-component></my-component> </div>
// 定义 var MyComponent = Vue.extend({ template: '<div>A custom component!</div>' }) // 注册 Vue.component('my-component', MyComponent) // 创建根实例 new Vue({ el: '#example' })
当然,这样写还是有些累,好在Vue给我们提供了注册组件的“语法糖”
<!DOCTYPE html> <html lang="en"> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0"> <meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="ie=edge"> <title>Document</title> </head> <body> <div id="app"> <explane></explane> </div> </body> <script src="../js/vue.js"></script> <script> Vue.component('explane',{ template:'<p>this is firest component</p>' }); new Vue({ el:'#app' }) </script> </html>
在chrome中显示:
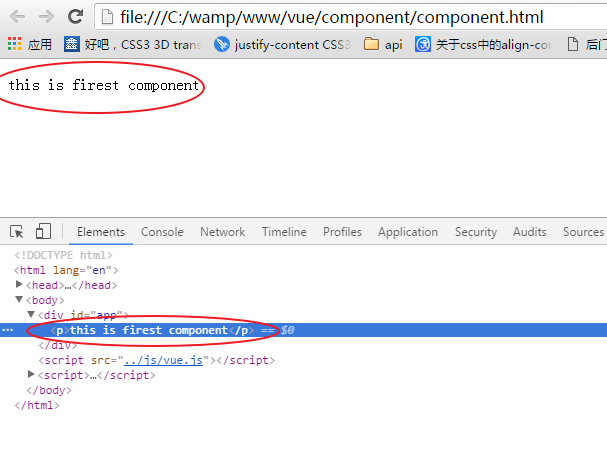
这种写法Vue.component()的第1个参数是标签名称,第2个参数是一个选项对象,使用选项对象的template属性定义组件模板。
使用这种方式,Vue在背后会自动地调用Vue.extend()。
调用Vue.component()注册组件时[实际上是在vue的prototype对象里添加component()],注册的组件是全局的。这意味着该组件在任意Vue实例都可以使用,如果不需要全局注册,或者是让组件使用在其它组件[组件的嵌套]内,可以用选项对象的components属性实现局部注册。
<!DOCTYPE html> <html lang="en"> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0"> <meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="ie=edge"> <title>Document</title> </head> <body> <div id="app"> <first-comp></first-comp> <explane></explane> </div> </body> <script src="../js/vue.js"></script> <script> var cpt = Vue.extend({ template:"<p>第一个组件</p>" }); new Vue({ el:"#app", components: { "firstComp":cpt, "explane":{ template:"<p>第二个组件</p>" } } }) </script> </html>
在chrome中显示:
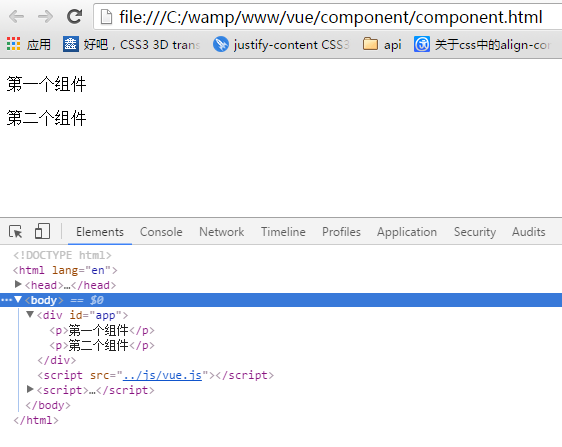
尽管语法糖简化了组件注册,但在template选项中拼接HTML元素比较麻烦,这也导致了HTML和JavaScript的高耦合性。
庆幸的是,Vue.js提供了两种方式将定义在JavaScript中的HTML模板分离出来。
第一种:使用script标签
<!DOCTYPE html> <html lang="en"> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0"> <meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="ie=edge"> <title>Document</title> </head> <body> <div id="app"> <first-cpt></first-cpt> </div> <script type="text/x-template" id="myCpt"> <p>script标签引入模版</p> </script> </body> <script src="../js/vue.js"></script> <script> Vue.component("firstCpt",{ template:"#myCpt" }); new Vue({ el:"#app" }) </script> </html>
在chrome中显示:
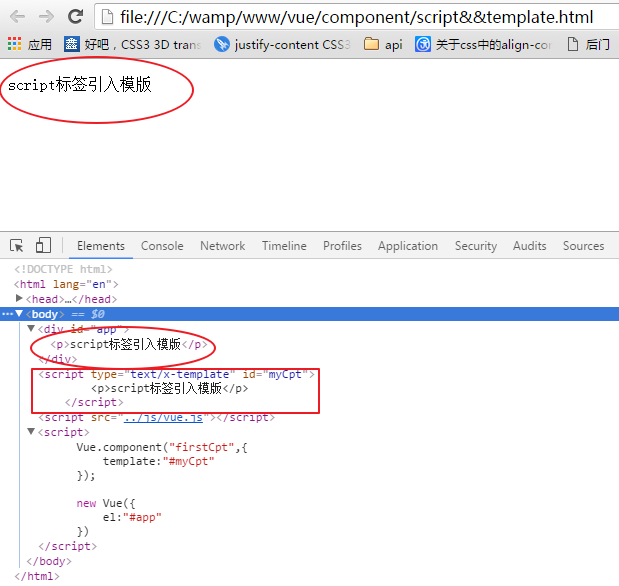
template选项现在不再是HTML元素,而是一个id,Vue.js根据这个id查找对应的元素,然后将这个元素内的HTML作为模板进行编译。
注意:使用<script>标签时,type指定为text/x-template,意在告诉浏览器这不是一段js脚本,浏览器在解析HTML文档时会忽略<script>标签内定义的内容。
第二种:使用template标签
<!DOCTYPE html> <html lang="en"> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0"> <meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="ie=edge"> <title>Document</title> </head> <body> <div id="app"> <first-cpt></first-cpt> </div> <template id="myCpt"> <p>script标签引入模版</p> </template> </body> <script src="../js/vue.js"></script> <script> Vue.component("firstCpt",{ template:"#myCpt" }); new Vue({ el:"#app" }) </script> </html>
在chrome中显示:
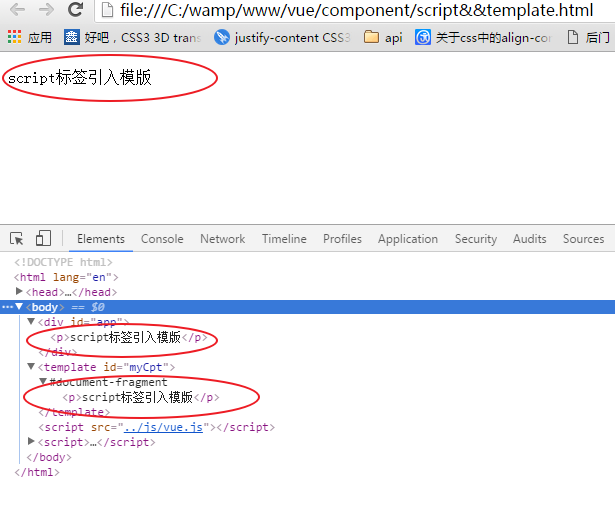
跟script标签用法一样。推荐使用这种方法。
组件的选项
传入Vue构造器的多数选项也可以用在 Vue.extend() 或Vue.component()中,不过有两个特例:data 和el。
Vue.js规定:在定义组件的选项时,data和el选项必须使用函数,否则会报错。
<!DOCTYPE html> <html lang="en"> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0"> <meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="ie=edge"> <title>Document</title> </head> <body> <div id="app"> <first-cpt></first-cpt> <second-cpt></second-cpt> </div> <template id="myCpt"> <p>姓名:{{name}}</p> </template> </body> <script src="../js/vue.js"></script> <script> Vue.component("firstCpt",{ template:"#myCpt", data:function(){ return { name:"hk" } } }); new Vue({ el:"#app", data:{ name:"jjk" }, components: { "secondCpt":{ template:"<p>姓名:{{name}}</p>", data:function(){ return { name:"dk" } } } } }) </script> </html>
在chrome中显示:
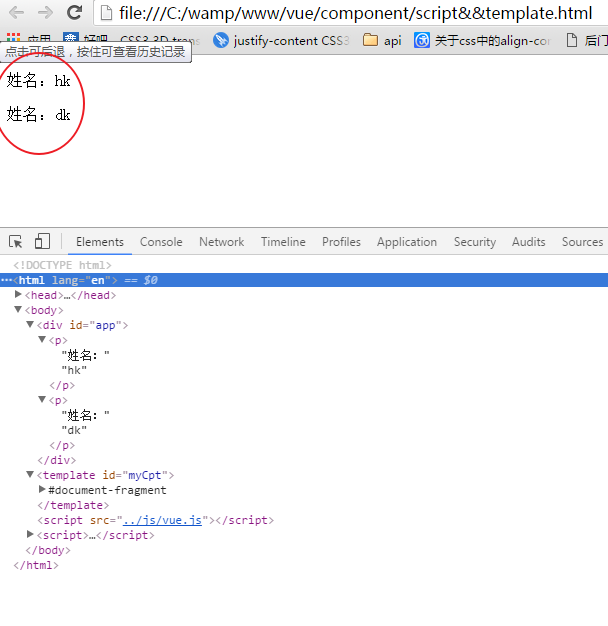
可以看出每个组件都有自己的作用域,互不干扰。Vue实例的中data选项也不会影响组件。
有时候,组件之间需要通信。这时就需要用到props选项了。
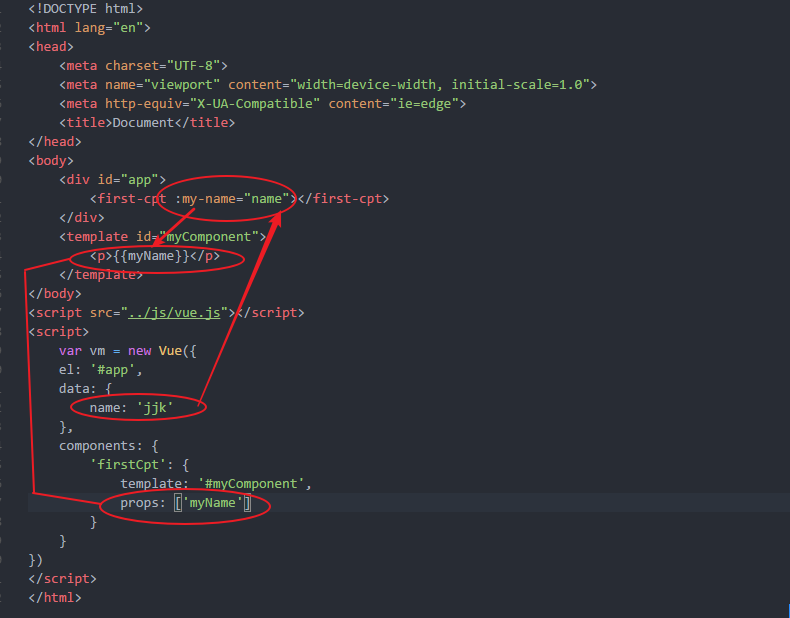
在·chrome中显示:
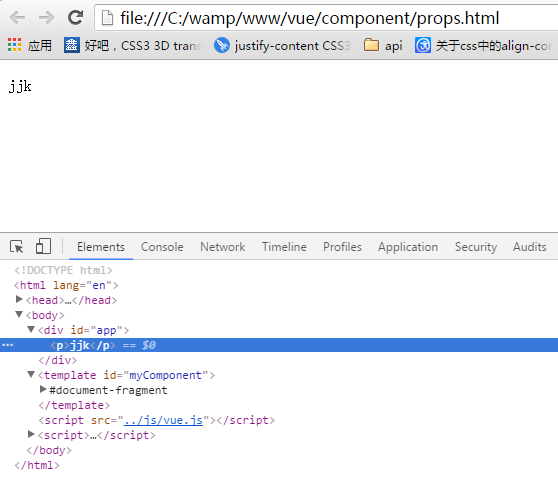
为了便于理解,你可以将这个Vue实例看作my-component的父组件。如果想要获取父组件的数据,必须在子组件中设置props选项(其实跟angular的@很相似)
注意:方法是不能通过props选项获取的。
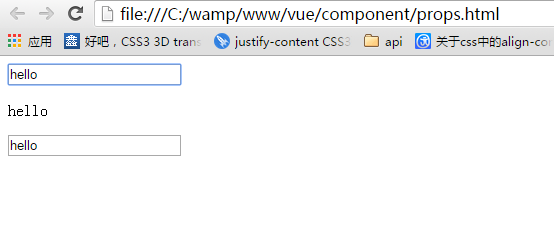
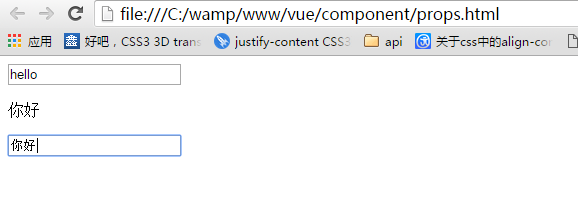
props默认是单向绑定:修改了子组件的数据,没有影响父组件的数据。修改了父组件的数据,会影响子组件的数据
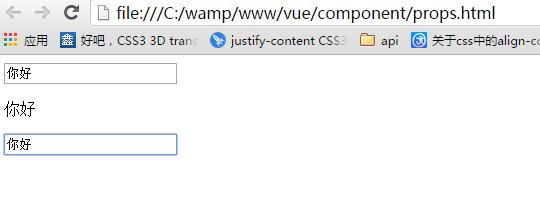
<!DOCTYPE html> <html lang="en"> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0"> <meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="ie=edge"> <title>Document</title> </head> <body> <div id="app"> <input v-model="name"> <first-cpt :my-name="name" my-send="send"></first-cpt> </div> <template id="myComponent"> <p>{{myName}}</p> <input v-model="myName"> </template> </body> <script src="../js/vue.js"></script> <script> var vm = new Vue({ el: '#app', data: { name: 'jjk' }, methods: { send:function(){ alert('666') } }, components: { 'firstCpt': { template: '#myComponent', props: ['myName',"mySend"] } } }) </script> </html>
一开始:
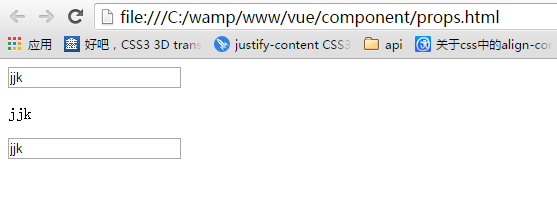
当修改了父组件时:
当修改了子组件时:
可以使用.sync显式 指定双向绑定,可以使子组件的数据修改可以传回给父组件
<first-cpt :my-name.sync="name" my-send="send"></first-cpt>
修改子组件数据时,父组件的数据也相应改变