通过SLAM或其他方式构建的点云地图是无法直接用于导航的,我知道的解决方案有三种:
一、将点云地图二维投影,转换为可用于导航的二维栅格地图;
二、将点云转换为Octomap八叉树地图,即可使用导航算法,比如RRT*进行三维导航;
三、将实时点云数据转换为实时激光数据,这样就可以愉快的使用ROS的move_base和acml包了。
此博客为第一种方案的实现案例
构建点云地图
构建点云地图需要深度图和对应的位姿,这里使用高翔的<视觉SLAM14讲>的深度图和位姿。这里构建的是一个ROS功能包,代码如下:
#include <stdio.h>
#include <iostream>
#include <algorithm>
#include <fstream>
#include <Eigen/Core>
#include <Eigen/Geometry>
#include <Eigen/Dense>
#include <ros/ros.h>
#include <opencv2/opencv.hpp>
#include <opencv2/core/core.hpp>
#include <opencv2/core/eigen.hpp>
#include <opencv2/imgproc/imgproc.hpp>
#include <opencv2/highgui/highgui.hpp>
#include <pcl/common/common_headers.h>
#include <pcl/point_types.h>
#include <pcl/io/pcd_io.h>
#include <pcl/filters/voxel_grid.h>
//#include <pcl/visualization/pcl_visualizer.h>
//#include <pcl/visualization/cloud_viewer.h>
#include <pcl/filters/statistical_outlier_removal.h>
#include <pcl/point_cloud.h>
#include <pcl_conversions/pcl_conversions.h>
#include <pcl_ros/point_cloud.h>
#include <sensor_msgs/PointCloud2.h>
// 定义点云使用的格式:这里用的是XYZRGB
typedef pcl::PointXYZRGB PointT;
typedef pcl::PointCloud<PointT> PointCloud;
using namespace std;
void PCLTest();
ros::Publisher pub_pcs;
ros::Publisher pub_pcr;
int main(int argc, char** argv)
{
ros::init(argc, argv, "pcl_test_node");//初始化节点
ros::start();//启动节点
ros::NodeHandle nh;
pub_pcs=nh.advertise<sensor_msgs::PointCloud2>("/point_cloud",1);
pub_pcr=nh.advertise<PointCloud>("/point_cloud_raw",1);
ROS_INFO_STREAM("Initing");
PCLTest();
ROS_INFO_STREAM("pcl_test节点结束");
return 0;
}
void PCLTest()
{
vector<cv::Mat> colorImgs, depthImgs; // 彩色图和深度图
vector<Eigen::Isometry3d> poses; // 相机位姿
ifstream fin("./data/pose.txt");
if (!fin)
{
cerr<<"cannot find pose file"<<endl;
return;
}
for ( int i=0; i<5; i++ )
{
boost::format fmt( "./data/%s/%d.%s" ); //图像文件格式
colorImgs.push_back( cv::imread( (fmt%"color"%(i+1)%"png").str() ));
depthImgs.push_back( cv::imread( (fmt%"depth"%(i+1)%"pgm").str(), -1 )); // 使用-1读取原始图像
double data[7] = {0};
for ( int i=0; i<7; i++ )
{
fin>>data[i];
}
Eigen::Quaterniond q( data[6], data[3], data[4], data[5] );
Eigen::Isometry3d T(q);
T.pretranslate( Eigen::Vector3d( data[0], data[1], data[2] ));
poses.push_back( T );
}
// 计算点云并拼接
// 相机内参
double cx = 325.5;
double cy = 253.5;
double fx = 518.0;
double fy = 519.0;
double depthScale = 1000.0;
cout<<"正在将图像转换为点云..."<<endl;
// 新建一个点云
PointCloud::Ptr pointCloud( new PointCloud );
//pcl::visualization::CloudViewer viewer("pcd viewer");
for ( int i=0; i<5; i++ )
{
PointCloud::Ptr current( new PointCloud );
cout<<"转换图像中: "<<i+1<<endl;
cv::Mat color = colorImgs[i];
cv::Mat depth = depthImgs[i];
Eigen::Isometry3d T = poses[i];
for ( int v=0; v<color.rows; v++ )
for ( int u=0; u<color.cols; u++ )
{
unsigned int d = depth.ptr<unsigned short> ( v )[u]; // 深度值
if ( d==0 ) continue; // 为0表示没有测量到
if ( d >= 3500 ) continue; // 深度太大时不稳定,去掉
Eigen::Vector3d point;
point[2] = double(d)/depthScale;
point[0] = (u-cx)*point[2]/fx;
point[1] = (v-cy)*point[2]/fy;
Eigen::Vector3d pointWorld = T*point;
PointT p ;
p.x = pointWorld[0];
p.y = pointWorld[1];
p.z = pointWorld[2];
p.b = color.data[ v*color.step+u*color.channels() ];
p.g = color.data[ v*color.step+u*color.channels()+1 ];
p.r = color.data[ v*color.step+u*color.channels()+2 ];
current->points.push_back( p );
}
//利用统计滤波器方法去除孤立点。
PointCloud::Ptr tmp ( new PointCloud );
pcl::StatisticalOutlierRemoval<PointT> statistical_filter;
statistical_filter.setMeanK(50);
statistical_filter.setStddevMulThresh(1.0);
statistical_filter.setInputCloud(current);
statistical_filter.filter( *tmp );
(*pointCloud) += *tmp;
//viewer.showCloud(pointCloud);
//getchar();
}
getchar();
pointCloud->is_dense = false;
cout<<"点云共有"<<pointCloud->size()<<"个点."<<endl;
//体素滤波器(Voxel Filter)进行降采样
pcl::VoxelGrid<PointT> voxel_filter;
voxel_filter.setLeafSize( 0.01, 0.01, 0.01 ); //分辨率
PointCloud::Ptr tmp ( new PointCloud );
voxel_filter.setInputCloud( pointCloud );
voxel_filter.filter( *tmp );
tmp->swap(*pointCloud);
cout<<"滤波之后,点云共有"<<pointCloud->size()<<"个点."<<endl;
sensor_msgs::PointCloud2 pmsg;
pcl::toROSMsg(*pointCloud, pmsg);
pmsg.header.frame_id = "map";
pub_pcs.publish(pmsg);
pub_pcr.publish(*pointCloud);
getchar();
//while (!viewer.wasStopped ())
//{
//}
pcl::io::savePCDFileBinary("map.pcd", *pointCloud );
}
PCLTest函数是构建点云的函数,首先从pose.txt中读取位姿,然后读取rgb图像和深度图像,接着将像素坐标转换为世界坐标,在存入点云中,每张图片构建的点云都进行统计滤波。构建完成点云之后,进行体素滤波。最后发布点云。这里发布两个消息:sensor_msgs::PointCloud2 和 PointCloud,其中sensor_msgs::PointCloud2类型的点云用于rviz点云可视化,而PointCloud则用于给cloud_to_map包转换为二维地图。
需要注意的是,若想直接发布点云类型 pcl::PointCloud#include <pcl_ros/point_cloud.h>。若想将pcl::PointCloud
#include <pcl_conversions/pcl_conversions.h>。
程序的最后将点云地图保存为map.pcd。我们可以使用pcl_viewer查看:
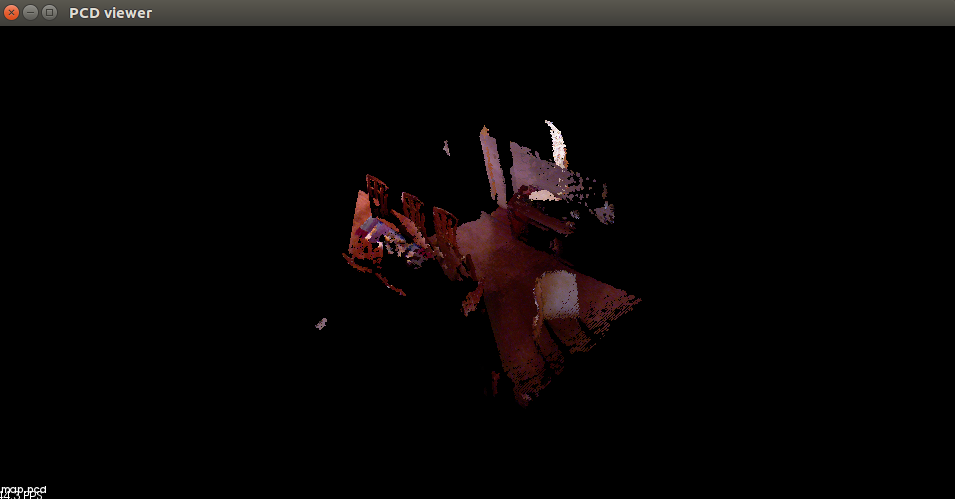

点云地图的二维投影
这里通过cloud_to_map功能包将点云地图转换二维地图。cloud_to_map好象是北达科他大学( North Dakota State University),更具体的信息我不知道了。下载地址为:PointCloud-to-grid-map上下载的,但是直接使用貌似有点问题,而且这个程序为了动态调参,写的太复杂了,我将其简化了。其主程序如下:
#include <iostream>
#include <fstream>
#include <stdint.h>
#include <math.h>
#include <ros/ros.h>
#include <pcl_ros/point_cloud.h>
#include <nav_msgs/OccupancyGrid.h>
#include <pcl_conversions/pcl_conversions.h>
#include <pcl/point_cloud.h>
#include <pcl/point_types.h>
#include <pcl/common/common_headers.h>
#include <pcl/io/pcd_io.h>
#include <pcl/point_types.h>
#include <pcl/features/normal_3d.h>
#include <pcl/console/parse.h>
#include <pcl/filters/passthrough.h>
typedef pcl::PointXYZRGB PointT;
typedef pcl::PointCloud<pcl::PointXYZRGB> PointCloud;
typedef pcl::PointCloud<pcl::Normal> NormalCloud;
using namespace std;
/* 全局变量 */
PointCloud::ConstPtr currentPC;
bool newPointCloud = false;
double cellResolution=0.05;
double deviation = 0.785398;
int buffer_size=50;//每个栅格法线垂直的阈值
ros::Publisher pub;
void calcSize(double *xMax, double *yMax, double *xMin, double *yMin)
{
pcl::PointXYZRGB minPt, maxPt;
pcl::getMinMax3D(*currentPC, minPt, maxPt);
*xMax=maxPt.x;
*yMax=maxPt.y;
*xMin=minPt.x;
*yMin=minPt.y;
}
//得到栅格地图
void computeGrid( std::vector<signed char> &ocGrid, double xMin, double yMin,int xCells, int yCells)
{
cout<<"开始计算法线"<<endl;
//计算点云的法线
NormalCloud::Ptr cloud_normals(new NormalCloud);
pcl::NormalEstimation<pcl::PointXYZRGB, pcl::Normal> ne;
ne.setInputCloud(currentPC);
pcl::search::KdTree<pcl::PointXYZRGB>::Ptr tree(new pcl::search::KdTree<pcl::PointXYZRGB>());
ne.setSearchMethod(tree);
ne.setRadiusSearch(0.06);
ne.compute(*cloud_normals);
cout<<"判断法线是否垂直"<<endl;
int size=xCells*yCells;
std::vector<int> countGrid(size);
//判断每个点云的法向量是否垂直
for (size_t i = 0; i < currentPC->size(); i++)
{
double x = currentPC->points[i].x;
double y = currentPC->points[i].y;
double z = cloud_normals->points[i].normal_z;
int xc = (int) ((x - xMin) / cellResolution); //取整后默认按照cellResolution将点分配到cell
int yc = (int) ((y - yMin) / cellResolution);
/*
法线是单位向量,z是发现的z值,z越接近于1,表明法线越垂直。
而acos(z)使得z值越接近于1,结果越小.
即acos(z)的结果越大,z越不垂直
*/
double normal_value = acos(fabs(z));//值域 0--phi 地面fabs(z)应该是1 acos是0,最小值
if (normal_value > deviation) //根据acos函数的递减性质,非地面点的值应该都比地面点大。可以设置deviation值,决定障碍物点的阈值
countGrid[yc * xCells + xc]++; //统计一个cell中垂直方向满足条件的点数
}
cout<<"计算占据概率"<<endl;
//根据阈值计算占据概率
for (int i = 0; i < size; i++) //size:xCells * yCells
{
if (countGrid[i] < buffer_size && countGrid[i]>0)
ocGrid[i] = 0;
else if (countGrid[i] > buffer_size)
ocGrid[i] = 100;
else if (countGrid[i] == 0)
ocGrid[i] = 0; // TODO Should be -1
}
}
void updateGrid(nav_msgs::OccupancyGridPtr grid, int xCells, int yCells,
double originX, double originY, std::vector<signed char> *ocGrid)
{
static int seq=0;
grid->header.frame_id = "map";
grid->header.seq=seq++;
grid->header.stamp.sec = ros::Time::now().sec;
grid->header.stamp.nsec = ros::Time::now().nsec;
grid->info.map_load_time = ros::Time::now();
grid->info.resolution = cellResolution;
grid->info.width = xCells;
grid->info.height = yCells;
grid->info.origin.position.x = originX; //minx
grid->info.origin.position.y = originY; //miny
grid->info.origin.position.z = 0;
grid->info.origin.orientation.w = 1;
grid->info.origin.orientation.x = 0;
grid->info.origin.orientation.y = 0;
grid->info.origin.orientation.z = 0;
grid->data = *ocGrid;
}
void callback(const PointCloud::ConstPtr& msg)
{
currentPC=msg;
ROS_INFO_STREAM("Convertor节点——接收到点云");
/*计算点云的最大和最小值*/
double xMax = 0, yMax = 0, xMin = 0, yMin = 0;
calcSize(&xMax, &yMax, &xMin, &yMin);
cout<<"极值:"<<xMax<<" "<<yMax<<" "<<xMin<<" "<<yMin<<" "<<endl;
/* 确定栅格地图的长和宽 */
int xCells = ((int) ((xMax - xMin) / cellResolution)) + 1;
int yCells = ((int) ((yMax - yMin) / cellResolution)) + 1;
cout<<"地图大小:"<<xCells<<" "<<yCells<<endl;
/*计算栅格地图*/
std::vector<signed char> ocGrid(yCells * xCells); //存储每个cell的值 0或者100
computeGrid(ocGrid, xMin, yMin, xCells, yCells);
cout<<"成功计算得到栅格地图"<<endl;
//发布地图消息
nav_msgs::OccupancyGridPtr grid(new nav_msgs::OccupancyGrid);
updateGrid(grid, xCells, yCells, xMin, yMin, &ocGrid);
pub.publish(grid);
ROS_INFO_STREAM("Convertor节点——发布栅格地图");
}
int main(int argc, char** argv)
{
setlocale(LC_ALL, "");
ros::init(argc, argv, "convertor_node");
ros::NodeHandle nh;
ros::Subscriber sub = nh.subscribe<PointCloud>("/point_cloud/raw", 1, callback);
pub = nh.advertise<nav_msgs::OccupancyGrid>("/map", 1);
//构造占据网格消息
nav_msgs::OccupancyGridPtr grid(new nav_msgs::OccupancyGrid);
grid->header.seq = 1;
grid->header.frame_id = "map";//父坐标系
grid->info.origin.position.z = 0;
grid->info.origin.orientation.w = 1;
grid->info.origin.orientation.x = 0;
grid->info.origin.orientation.y = 0;
grid->info.origin.orientation.z = 0;
ROS_INFO_STREAM("Convertor节点初始化完成");
ros::Rate loop_rate(0.2);
ros::Duration t(10);
while (ros::ok())
{
ros::spinOnce();
t.sleep();
}
}
cloud_to_map订阅点云:/point_cloud_raw,发布的栅格地图:/map。而且dynamic_reconfigure功能包动态配置参数。
在rviz中显示栅格地图:
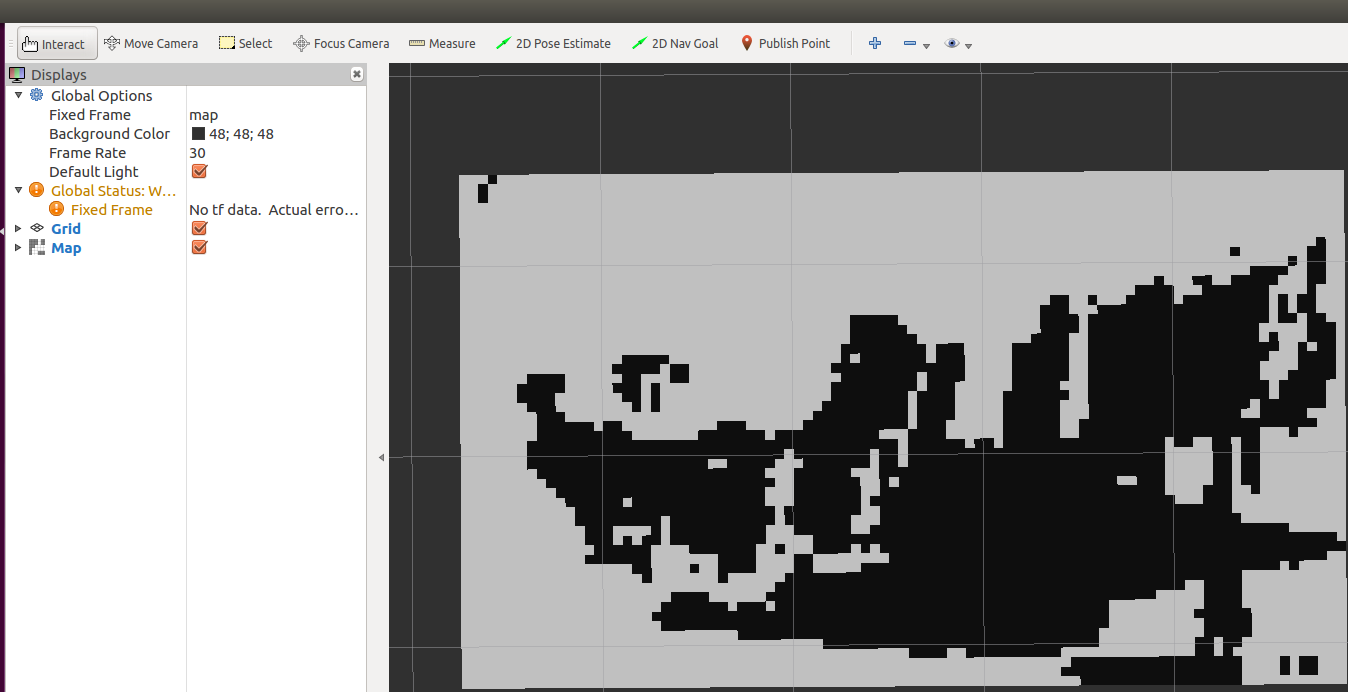
这个程序通过判断法向量的方法获得地图,但我觉得这种方法计算量大,而是感觉效果一半。我这里提出一种更简单的方法,直接将z轴0-0.5范围内的点云投影,得到栅格地图,程序如下:
#include <iostream>
#include <fstream>
#include <stdint.h>
#include <math.h>
#include <ros/ros.h>
#include <pcl_ros/point_cloud.h>
#include <nav_msgs/OccupancyGrid.h>
#include <pcl_conversions/pcl_conversions.h>
#include <pcl/point_cloud.h>
#include <pcl/point_types.h>
#include <pcl/common/common_headers.h>
#include <pcl/io/pcd_io.h>
#include <pcl/point_types.h>
#include <pcl/features/normal_3d.h>
#include <pcl/console/parse.h>
#include <dynamic_reconfigure/server.h>
#include <cloud_to_map/cloud_to_map_nodeConfig.h> //autogenerated for the cloud_to_map package by the dynamic_reconfigure package.
/* Define the two point cloud types used in this code */
typedef pcl::PointCloud<pcl::PointXYZRGB> PointCloud;
typedef pcl::PointCloud<pcl::Normal> NormalCloud;
/* Global */
PointCloud::ConstPtr currentPC;
bool newPointCloud = false;
bool reconfig = false;
// -----------------------------------------------
// -----Define a structure to hold parameters-----
// -----------------------------------------------
struct Param
{
std::string frame;
double searchRadius;
double deviation;
int buffer;
double loopRate;
double cellResolution;
};
// -----------------------------------
// -----Define default parameters-----
//If the value cannot be retrieved from the server, default_val is used instead.
// -----------------------------------
Param param;
boost::mutex mutex; //多线程
void loadDefaults(ros::NodeHandle& nh)
{
nh.param<std::string>("frame", param.frame, "world");
nh.param("search_radius", param.searchRadius, 0.05);
nh.param("deviation", param.deviation, 0.78539816339);
nh.param("buffer", param.buffer, 5);
nh.param("loop_rate", param.loopRate, 10.0);
nh.param("cell_resolution", param.cellResolution, 0.05);
}
// ------------------------------------------
// -----Callback for Dynamic Reconfigure-----调用动态参数配置
// ------------------------------------------
void callbackReconfig(cloud_to_map::cloud_to_map_nodeConfig &config, uint32_t level)
{
boost::unique_lock<boost::mutex>(mutex);
param.frame = config.frame.c_str();
param.searchRadius = config.search_radius;
param.deviation = config.deviation;
param.buffer = config.buffer;
param.loopRate = config.loop_rate;
//param.cellResolution = config.cell_resolution;
param.cellResolution=0.05;
reconfig = true;
ROS_INFO("
Reconfigure Request:
frame:%s
deviation:%f
loop_rate:%f
cell_resolution:%f
search_radius:%f",
param.frame.c_str(), param.deviation,param.loopRate,param.cellResolution, param.searchRadius);
}
// ------------------------------------------------------
// -----Update current PointCloud if msg is received-----
// ------------------------------------------------------
void callback(const PointCloud::ConstPtr& msg)
{
boost::unique_lock<boost::mutex>(mutex); //unique_lock是write lock。被锁后不允许其他线程执行被shared_lock或unique_lock的代码。
//在写操作时,一般用这个,可以同时限制unique_lock的写和share_lock的读。
//ROS_INFO("callback is finshed
");
currentPC = msg;
newPointCloud = true;
}
// ----------------------------------------------------------------
// -----Calculate surface normals with a search radius of 0.05-----
// ----------------------------------------------------------------
void calcSurfaceNormals(PointCloud::ConstPtr& cloud, pcl::PointCloud<pcl::Normal>::Ptr normals)
{
pcl::NormalEstimation<pcl::PointXYZRGB, pcl::Normal> ne;
ne.setInputCloud(cloud);
pcl::search::KdTree<pcl::PointXYZRGB>::Ptr tree(new pcl::search::KdTree<pcl::PointXYZRGB>());
ne.setSearchMethod(tree);
ne.setRadiusSearch(param.searchRadius);
ne.compute(*normals);
}
// ---------------------------------------
// -----Initialize Occupancy Grid Msg-----
// ---------------------------------------
void initGrid(nav_msgs::OccupancyGridPtr grid)
{
grid->header.seq = 1;
grid->header.frame_id = param.frame; //参考frame
grid->info.origin.position.z = 0;
grid->info.origin.orientation.w = 1;
grid->info.origin.orientation.x = 0;
grid->info.origin.orientation.y = 0;
grid->info.origin.orientation.z = 0;
std::cout<<"initGrid finshed!
"<< std::endl;
/* nav_msgs/OccupancyGrid
# This represents a 2-D grid map, in which each cell represents the probability of occupancy.
Header header
#MetaData for the map
MapMetaData info
# The map data, in row-major order, starting with (0,0). Occupancy
# probabilities are in the range [0,100]. Unknown is -1.
int8[] data
Header header
uint32 seq
time stamp
string frame_id
MapMetaData info
time map_load_time
float32 resolution
uint32 width
uint32 height
geometry_msgs/Pose origin
geometry_msgs/Point position
float64 x
float64 y
float64 z
geometry_msgs/Quaternion orientation
float64 x
float64 y
float64 z
float64 w
int8[] data */
}
// ------------------------------------------
// -----Calculate size of Occupancy Grid-----
// ------------------------------------------
void calcSize(double *xMax, double *yMax, double *xMin, double *yMin)
{
for (size_t i = 0; i < currentPC->size(); i++)
{
double x = currentPC->points[i].x;
double y = currentPC->points[i].y;
if (*xMax < x) {
*xMax = x;
}
if (*xMin > x) {
*xMin = x;
}
if (*yMax < y) {
*yMax = y;
}
if (*yMin > y) {
*yMin = y;
}
}
}
// ---------------------------------------
// -----Populate 填充 map with cost values-----
// ---------------------------------------
void populateMap(NormalCloud::Ptr cloud_normals, std::vector<int> &countGrid, double xMin, double yMin,
double cellResolution, int xCells, int yCells)
{
double deviation = param.deviation;
for (size_t i = 0; i < currentPC->size(); i++) //遍历每个点
{
double x = currentPC->points[i].x;
double y = currentPC->points[i].y;
double z = cloud_normals->points[i].normal_z;
int xCell, yCell;
//TODO implement cutoff height
xCell = (int) ((x - xMin) / cellResolution); //取整后默认按照cellResolution将点分配到cell
yCell = (int) ((y - yMin) / cellResolution);
if ((yCell * xCells + xCell) > (xCells * yCells))
std::cout << "x: " << x << ", y: " << y << ", xCell: " << xCell << ", yCell: " << yCell<< "
";
double normal_value = acos(fabs(z));//值域 0--phi 地面fabs(z)应该是1 acos是0,最小值
if (normal_value > deviation) //根据acos函数的递减性质,非地面点的值应该都比地面点大。可以设置deviation值,决定障碍物点的阈值
countGrid[yCell * xCells + xCell]++; //统计一个cell中垂直方向满足条件的点数
//else
//countGrid[yCell * xCells + xCell]--;
}
}
// ---------------------------------
// -----Generate Occupancy Grid-----
// ---------------------------------
void genOccupancyGrid(std::vector<signed char> &ocGrid, std::vector<int> &countGrid, int size)
{
int buf = param.buffer;
for (int i = 0; i < size; i++) //size:xCells * yCells
{
if (countGrid[i] < buf && countGrid[i]>0)
ocGrid[i] = 0;
else if (countGrid[i] > buf)
ocGrid[i] = 100;
else if (countGrid[i] == 0)
ocGrid[i] = 0; // TODO Should be -1
}
//std::cout<<" genOccupancyGrid finshed!"<< std::endl;
}
// -----------------------------------
// -----Update Occupancy Grid Msg-----
// -----------------------------------
void updateGrid(nav_msgs::OccupancyGridPtr grid, double cellRes, int xCells, int yCells,
double originX, double originY, std::vector<signed char> *ocGrid)
{
grid->header.seq++;
grid->header.stamp.sec = ros::Time::now().sec;
grid->header.stamp.nsec = ros::Time::now().nsec;
grid->info.map_load_time = ros::Time::now();
grid->info.resolution = cellRes;
grid->info.width = xCells;
grid->info.height = yCells;
grid->info.origin.position.x = originX; //minx
grid->info.origin.position.y = originY; //miny
grid->data = *ocGrid;
std::cout<<"updateGrid finshed!!"<< std::endl;
}
int main(int argc, char** argv)
{
/* Initialize ROS */
ros::init(argc, argv, "cloud_to_map_node");
ros::NodeHandle nh;
ros::Subscriber sub = nh.subscribe<PointCloud>("/point_cloud_raw", 1, callback);
ros::Publisher pub = nh.advertise<nav_msgs::OccupancyGrid>("/map", 1);
/* Initialize Dynamic Reconfigure ROS动态参数配置*/
dynamic_reconfigure::Server<cloud_to_map::cloud_to_map_nodeConfig> server;
dynamic_reconfigure::Server<cloud_to_map::cloud_to_map_nodeConfig>::CallbackType f;
f = boost::bind(&callbackReconfig, _1, _2);
//std::cout<<"*************************
"; //test
server.setCallback(f);
/* Initialize Grid */
nav_msgs::OccupancyGridPtr grid(new nav_msgs::OccupancyGrid);
initGrid(grid);
/* Finish initializing ROS */
mutex.lock();
ros::Rate loop_rate(param.loopRate);
mutex.unlock();
/* Wait for first point cloud */
while(ros::ok() && newPointCloud == false)
{
ros::spinOnce();//ROS消息回调处理函数。它俩通常会出现在ROS的主循环中,程序需要不断调用ros::spin() 或 ros::spinOnce(),
//两者区别在于前者调用后不会再返回,也就是你的主程序到这儿就不往下执行了,而后者在调用后还可以继续执行之后的程序。
//所接到的消息并不是立刻就被处理,而是必须要等到ros::spin()或ros::spinOnce()执行的时候才被调用,
loop_rate.sleep();
}
/* Begin processing point clouds */
while (ros::ok())
{
ros::spinOnce();//用后还可以继续执行之后的程序。
boost::unique_lock<boost::mutex> lck(mutex);
if (newPointCloud || reconfig)
{
/* Update configuration status */
reconfig = false; //调用动态参数配置时 =true
newPointCloud = false; //在回调函数=true
/* Record start time */
uint32_t sec = ros::Time::now().sec; //秒
uint32_t nsec = ros::Time::now().nsec;//纳秒
/* Calculate Surface Normals */
NormalCloud::Ptr cloud_normals(new NormalCloud);
calcSurfaceNormals(currentPC, cloud_normals);
/* Figure out size of matrix needed to store data. */
double xMax = 0, yMax = 0, xMin = 0, yMin = 0;
calcSize(&xMax, &yMax, &xMin, &yMin); //Calculate size of Occupancy Grid
//std::cout <<"size of matrix needed to store data:"<<"xMax: " << xMax << ", yMax: " << yMax << ", xMin: " << xMin << ", yMin: "<< yMin << "
";
/* Determine resolution of grid (m/cell) */
double cellResolution = param.cellResolution;
int xCells = ((int) ((xMax - xMin) / cellResolution)) + 1;
int yCells = ((int) ((yMax - yMin) / cellResolution)) + 1;
std::cout <<"the number of cells: " <<xCells*yCells<<"
";
/* Populate Map */
std::vector<int> countGrid(yCells * xCells);
populateMap(cloud_normals, countGrid, xMin, yMin, cellResolution, xCells, yCells);
/* Generate OccupancyGrid Data Vector */
std::vector<signed char> ocGrid(yCells * xCells); //存储每个cell的值 0或者100
genOccupancyGrid(ocGrid, countGrid, xCells * yCells);
/* Update OccupancyGrid Object */
updateGrid(grid, cellResolution, xCells, yCells, xMin, yMin, &ocGrid);
/* Release lock */
lck.unlock();
/* Record end time */
uint32_t esec = ros::Time::now().sec;
uint32_t ensec = ros::Time::now().nsec;
std::cout << "Seconds: " << esec - sec << " NSeconds: " << ensec - nsec << "
";
/* Publish Occupancy Grid */
pub.publish(grid);
}
loop_rate.sleep();
}
}
有了栅格地图,就可以进行全局路径规划了,完整的代码可以在此处获取;
总结
此案例其实就是一个有限有高度范围内的点云按照分辨率投影的案例,相较之下octomap在动态障碍物环境下优势明显。