粒子群优化(PSO, particle swarm optimization) 是由Kennedy和Eberhart在1995年提出的一 种群智能优化方法。
优点:好理解容易实现,适合解决极值问题
缺点:容易过早收敛,容易陷入局部最优解,(如果初始点选的不好,可能就会被某个粒子带偏了= =/)
(Java实现):

1 package pso; 2 3 import java.util.Random; 4 5 /** 6 * 粒子类 7 * 8 * @see dimension 9 * @author Flyuz 10 */ 11 public class Particle { 12 // 维数 13 public int dimension = 2; 14 // 粒子的位置 15 public double[] X = new double[dimension]; 16 // 粒子的速度 17 public double[] V = new double[dimension]; 18 // 局部最好位置 19 public double[] pbest = new double[dimension]; 20 // 最大速度 21 public double Vmax = 2; 22 // 最大位置 23 public double[] Xmax = { 2, 2 }; 24 // 最小位置 25 public double[] Xmin = { -2, -2 }; 26 // 适应值 27 public double fitness; 28 29 /** 30 * 根据当前位置计算适应值 本例子求式子最大值 31 * 32 * @return newFitness 33 */ 34 public double calculateFitness() { 35 36 double newFitness = 0; 37 if (X[0] == 0 && X[1] == 0) 38 newFitness = Math.exp((Math.cos(2 * Math.PI * X[0]) + Math.cos(2 * Math.PI * X[1])) / 2) - 2.71289; 39 else 40 newFitness = Math.sin(Math.sqrt(Math.pow(X[0], 2) + Math.pow(X[1], 2))) 41 / Math.sqrt(Math.pow(X[0], 2) + Math.pow(X[1], 2)) 42 + Math.exp((Math.cos(2 * Math.PI * X[0]) + Math.cos(2 * Math.PI * X[1])) / 2) - 2.71289; 43 return newFitness; 44 } 45 46 /** 47 * 初始化自己的位置和pbest 48 */ 49 public void initialX() { 50 for (int i = 0; i < dimension; i++) { 51 X[i] = new Random().nextDouble() * (Xmax[i] - Xmin[i]) + Xmin[i]; 52 pbest[i] = X[i]; 53 } 54 } 55 56 /** 57 * 初始化自己的速度 58 */ 59 public void initialV() { 60 for (int i = 0; i < dimension; i++) { 61 V[i] = new Random().nextDouble() * Vmax * 0.5; 62 } 63 } 64 }
 算法类
算法类针对缺点,提出了 Multi-start PSO 算法,即每迭代若干次后,都保留历史优粒子,粒子全部初始化,以提高粒子的多样性,扩大搜索 空间。又提出了一种动态惯性权重的粒子群优化算法,惯性权重随着迭代次数的增加而降低,在开始阶段具有较强的全局搜索能力,而在后期以 较小的惯性权重能够收敛到优解。

1 package pso; 2 3 import java.util.ArrayList; 4 import java.util.List; 5 import java.util.Random; 6 7 public class NormalPSO { 8 9 private static double[] gbest;// 全局最优位置 10 private static double gbest_fitness = -0x3f3f3f;// 全局最优位置对应的fitness 11 private static int particle_num = 10;// 粒子数 12 private static int N = 100;// 迭代次数 13 private static int c1, c2 = 2; 14 private static double w = 1.4;// 惯性因子 15 private static List<Particle> particles = new ArrayList<Particle>();// 粒子群 16 17 /** 18 * 初始化所有粒子 19 */ 20 public static void initialParticles() { 21 for (int i = 0; i < particle_num; i++) { 22 Particle particle = new Particle(); 23 particle.initialX(); 24 particle.initialV(); 25 particle.fitness = particle.calculateFitness(); 26 particles.add(particle); 27 } 28 } 29 30 /** 31 * 更新 gbest 32 */ 33 public static void updateGbest() { 34 double fitness = -0x3f3f3f; 35 int index = 0; 36 for (int i = 0; i < particle_num; i++) { 37 if (particles.get(i).fitness > fitness) { 38 index = i; 39 fitness = particles.get(i).fitness; 40 } 41 } 42 if (fitness > gbest_fitness) { 43 gbest = particles.get(index).pbest.clone(); 44 gbest_fitness = fitness; 45 } 46 } 47 48 /** 49 * 更新每个粒子的速度 50 */ 51 public static void updateV() { 52 for (Particle particle : particles) { 53 for (int i = 0; i < particle.dimension; i++) { 54 double v = w * particle.V[i] + c1 * rand() * (particle.pbest[i] - particle.X[i]) 55 + c2 * rand() * (gbest[i] - particle.X[i]); 56 if (v > particle.Vmax) 57 v = particle.Vmax * rand(); 58 else if (v < -particle.Vmax) 59 v = -particle.Vmax * rand(); 60 particle.V[i] = v;// 更新Vi 61 } 62 } 63 } 64 65 /** 66 * 更新每个粒子的位置和pbest 67 */ 68 public static void updateX() { 69 for (Particle particle : particles) { 70 for (int i = 0; i < particle.dimension; i++) { 71 particle.X[i] = particle.X[i] + particle.V[i]; 72 if (particle.X[i] > particle.Xmax[i]) 73 particle.X[i] = new Random().nextDouble() * (particle.Xmax[i] - particle.Xmin[i]) 74 + particle.Xmin[i]; 75 if (particle.X[i] < particle.Xmin[i]) 76 particle.X[i] = new Random().nextDouble() * (particle.Xmax[i] - particle.Xmin[i]) 77 + particle.Xmin[i]; 78 } 79 double newFitness = particle.calculateFitness();// 新的适应值 80 if (newFitness > particle.fitness) { 81 particle.pbest = particle.X.clone(); 82 particle.fitness = newFitness; 83 } 84 } 85 } 86 87 /** 88 * 算法主要流程 89 */ 90 public static void process() { 91 int n = 0; 92 initialParticles(); 93 updateGbest(); 94 while (n++ < N) { 95 /* 96 * Multi-start PSO 算法,即每迭代若干次后,都保留历史优粒子, 粒子全部初始化,以提高粒子的多样性,扩大搜索 空间。 97 */ 98 if (n == N / 2) { 99 initialParticles(); 100 updateGbest(); 101 } 102 updateV(); 103 updateX(); 104 updateGbest(); 105 w -= 0.01; // 动态惯性权重 106 System.out.println(n + ". 当前gbest:(" + gbest[0] + "," + gbest[1] + ") fitness = " + gbest_fitness); 107 } 108 } 109 110 public static double rand() { 111 return new Random().nextDouble(); 112 } 113 114 public static void main(String[] args) { 115 process(); 116 } 117 }
改进后,虽然有一定的效果,但是效果不太明显。
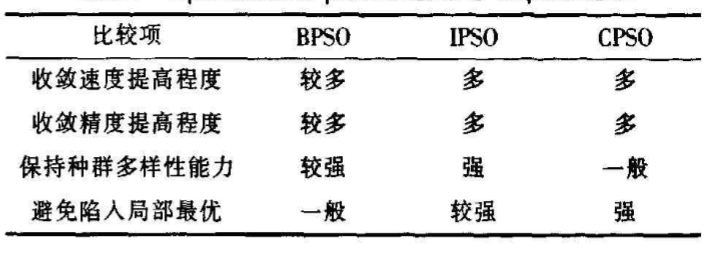
后来又提出许多混合粒子群算法,比如遗传粒子群(BPSO)、免疫粒子群(IPSO)、混沌粒子群等(CPSO),针对不同的领域,需选用适合的优化算法。