1、K-近邻算法(Knn)
其原理为在一个样本空间中,有一些已知分类的样本,当出现一个未知分类的样本,则根据距离这个未知样本最近的k个样本来决定。
举例:爱情电影和动作电影,它们中都存在吻戏和动作,出现一个未知分类的电影,将根据以吻戏数量和动作数量建立的坐标系中距离未知分类所在点的最近的k个点来决定。
2、算法实现步骤
(1)计算所有点距离未知点的欧式距离
(2)对所有点进行排序
(3)找到距离未知点最近的k个点
(4)计算这k个点所在分类出现的频率
(5)选择频率最大的分类即为未知点的分类
3、java实现
Point类
public class Point { private long id; private double x; private double y; private String type; public Point(long id,double x, double y) { this.x = x; this.y = y; this.id = id; } public Point(long id,double x, double y, String type) { this.x = x; this.y = y; this.type = type; this.id = id; } //get、set方法省略 }
Distance类
public class Distance {
// 已知点id
private long id;
// 未知点id
private long nid;
// 二者之间的距离
private double disatance;
public Distance(long id, long nid, double disatance) {
this.id = id;
this.nid = nid;
this.disatance = disatance;
}
//get、set方法省略
}
比较器CompareClass类
import java.util.Comparator;
//比较器类
public class CompareClass implements Comparator<Distance>{
public int compare(Distance d1, Distance d2) {
return d1.getDisatance()>d2.getDisatance()?20 : -1;
}
}
KNN主类
/** * 1、输入所有已知点 2、输入未知点 3、计算所有已知点到未知点的欧式距离 4、根据距离对所有已知点排序 5、选出距离未知点最近的k个点 6、计算k个点所在分类出现的频率 7、选择频率最大的类别即为未知点的类别 * * @author fzj * */ public class KNN { public static void main(String[] args) { // 一、输入所有已知点 List<Point> dataList = creatDataSet(); // 二、输入未知点 Point x = new Point(5, 1.2, 1.2); // 三、计算所有已知点到未知点的欧式距离,并根据距离对所有已知点排序 CompareClass compare = new CompareClass(); Set<Distance> distanceSet = new TreeSet<Distance>(compare); for (Point point : dataList) { distanceSet.add(new Distance(point.getId(), x.getId(), oudistance(point, x))); } // 四、选取最近的k个点 double k = 5; /** * 五、计算k个点所在分类出现的频率 */ // 1、计算每个分类所包含的点的个数 List<Distance> distanceList= new ArrayList<Distance>(distanceSet); Map<String, Integer> map = getNumberOfType(distanceList, dataList, k); // 2、计算频率 Map<String, Double> p = computeP(map, k); x.setType(maxP(p)); System.out.println("未知点的类型为:"+x.getType()); } // 欧式距离计算 public static double oudistance(Point point1, Point point2) { double temp = Math.pow(point1.getX() - point2.getX(), 2) + Math.pow(point1.getY() - point2.getY(), 2); return Math.sqrt(temp); } // 找出最大频率 public static String maxP(Map<String, Double> map) { String key = null; double value = 0.0; for (Map.Entry<String, Double> entry : map.entrySet()) { if (entry.getValue() > value) { key = entry.getKey(); value = entry.getValue(); } } return key; } // 计算频率 public static Map<String, Double> computeP(Map<String, Integer> map, double k) { Map<String, Double> p = new HashMap<String, Double>(); for (Map.Entry<String, Integer> entry : map.entrySet()) { p.put(entry.getKey(), entry.getValue() / k); } return p; } // 计算每个分类包含的点的个数 public static Map<String, Integer> getNumberOfType( List<Distance> listDistance, List<Point> listPoint, double k) { Map<String, Integer> map = new HashMap<String, Integer>(); int i = 0; System.out.println("选取的k个点,由近及远依次为:"); for (Distance distance : listDistance) { System.out.println("id为" + distance.getId() + ",距离为:" + distance.getDisatance()); long id = distance.getId(); // 通过id找到所属类型,并存储到HashMap中 for (Point point : listPoint) { if (point.getId() == id) { if (map.get(point.getType()) != null) map.put(point.getType(), map.get(point.getType()) + 1); else { map.put(point.getType(), 1); } } } i++; if (i >= k) break; } return map; } public static ArrayList<Point> creatDataSet(){ Point point1 = new Point(1, 1.0, 1.1, "A"); Point point2 = new Point(2, 1.0, 1.0, "A"); Point point3 = new Point(3, 1.0, 1.2, "A"); Point point4 = new Point(4, 0, 0, "B"); Point point5 = new Point(5, 0, 0.1, "B"); Point point6 = new Point(6, 0, 0.2, "B"); ArrayList<Point> dataList = new ArrayList<Point>(); dataList.add(point1); dataList.add(point2); dataList.add(point3); dataList.add(point4); dataList.add(point5); dataList.add(point6); return dataList; } }
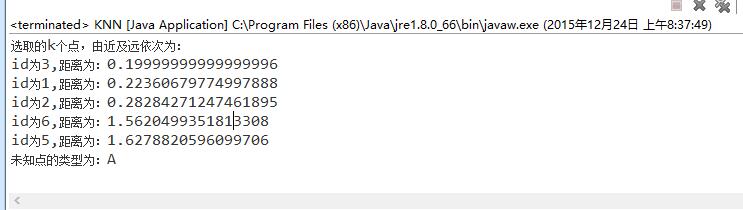
4、运行结果
参考
[1] 《机器学习实战》
