总体概况
持久化存储操作:
a. 磁盘文件
a) 基于终端指令
i. 保证parse方法返回一个可迭代类型的对象(存储解析到的页面内容)
ii. 使用终端指令完成数据存储到制定磁盘文件中的操作
1. scrapy crawl 爬虫文件名称 –o 磁盘文件.后缀
b) 基于管道
i. items:存储解析到的页面数据
ii. pipelines:处理持久化存储的相关操作
iii. 代码实现流程:
1. 将解析到的页面数据存储到items对象
2. 使用yield关键字将items提交给管道文件进行处理
3. 在管道文件中编写代码完成数据存储的操作
4. 在配置文件中开启管道操作
b. 数据库
a) mysql
b) redis
c) 编码流程:
1. 将解析到的页面数据存储到items对象
2. 使用yield关键字将items提交给管道文件进行处理
3. 在管道文件中编写代码完成数据存储的操作
4. 在配置文件中开启管道操作
需求:将爬取到的数据值分别存储到本地磁盘、redis数据库、mysql数据。
1. 需要在管道文件中编写对应平台的管道类
2. 在配置文件中对自定义的管道类进行生效操作
***问题:针对多个url进行数据的爬取
解决方案:请求的手动发送
----------------------
磁盘文件
基于终端指令
a. 磁盘文件
a) 基于终端指令
i. 保证parse方法返回一个可迭代类型的对象(存储解析到的页面内容)
ii. 使用终端指令完成数据存储到制定磁盘文件中的操作
1. scrapy crawl 爬虫文件名称 –o 磁盘文件.后缀
class QiubaiSpider(scrapy.Spider): name = 'qiubai' #allowed_domains = ['www.qiushibaike.com/text'] start_urls = ['https://www.qiushibaike.com/text/'] def parse(self, response): # 建议大家使用xpath进行解析(框架集成了xpath解析的接口) div_list = response.xpath("//div[@id='content-left']/div") # 存储到的解析到的页面数据 data_list = [] for div in div_list: author = div.xpath('./div/a[2]/h2/text()').extract_first() content = div.xpath(".//div[@class='content']/span/text()").extract_first() #print(author+' '+content) dict = {'author':author,'content':content} data_list.append(dict) return data_list
scrapy crawl qiubai -o qiubai.csv --nolog # qiubai.csv 如果不存在自动创建
出现qiubai.csv文件
基于管道
items.py:数据结构模板文件。定义数据属性。
pipelines.py:管道文件。接收数据(items),进行持久化操作。
b) 基于管道
i. items:存储解析到的页面数据
ii. pipelines:处理持久化存储的相关操作
iii. 代码实现流程:
1. 将解析到的页面数据存储到items对象
2. 使用yield关键字将items提交给管道文件进行处理
3. 在管道文件中编写代码完成数据存储的操作
4. 在配置文件中开启管道操作
爬虫文件代码:
qiubai.py
import scrapy from qiubaiPro.items import QiubaiproItem class QiubaiSpider(scrapy.Spider): name = 'qiubai' #allowed_domains = ['www.qiushibaike.com/text'] start_urls = ['https://www.qiushibaike.com/text/'] def parse(self, response): #建议大家使用xpath进行指定内容的解析(框架集成了xpath解析的接口) # 段子的内容和作者 div_list = response.xpath('//div[@id="content-left"]/div') for div in div_list: #xpath解析到的指定内容被存储到了Selector对象 #extract()该方法可以将Selector对象中存储的数据值拿到 #author = div.xpath('./div/a[2]/h2/text()').extract()[0] #extract_first() == extract()[0] author = div.xpath('./div/a[2]/h2/text()').extract_first() content = div.xpath('.//div[@class="content"]/span/text()').extract_first() #1.将解析到的数据值(author和content)存储到items对象 item = QiubaiproItem() item['author'] = author item['content'] = content #2.将item对象提交给管道 yield item
1、将解析到的页面数据存储到items对象
在items.py 中封装两个属性对象
class QiubaiproItem(scrapy.Item): # define the fields for your item here like: # name = scrapy.Field() # 属性声明 author = scrapy.Field() content = scrapy.Field()
# 1.将解析到数据值(author和content)储存到items对象 item = QiubaiproItem() item['author'] = author item['content'] = content # 2.将item对象提交给管道 yield item
3、在管道文件中编写代码完成数据存储的操作
class QiubaiproPipeline(object): # 该方法可以接受爬虫文件中提交过来的item对象,并且对item对象的页面数据进行持久化处理 # 参数:item表示的就是接受到的item对象 def process_item(self, item, spider): author = item['author'] content = item['content'] # 持久化存储io操作 with open('./qiubai_pipe.txt','w',encoding='utf-8')as f: f.write(author+':'+content+' ') return item
4、在配置文件settings.py中开启管道操作
# 300 数字表示优先级 ITEM_PIPELINES = { 'qiubaipro.pipelines.QiubaiproPipeline': 300, }
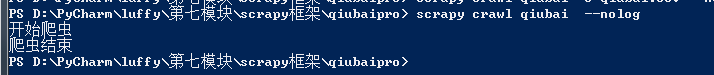
在命令行执行程序
scrapy crawl qiubai --nolog
第三步有个bug每次调用管道都会进行数据读取的操作,造成数据存储不完整
pipelines.py
class QiubaiproPipeline(object): def open_spider(self,spider): print('开始爬虫') self.fp = open('./qiubai_pipe.txt', 'w', encoding='utf-8') # 该方法可以接受爬虫文件中提交过来的item对象,并且对item对象的页面数据进行持久化处理 # 参数:item表示的就是接受到的item对象 def process_item(self, item, spider): author = item['author'] content = item['content'] # 持久化存储io操作 self.fp.write(author+':'+content+' ') return item # 该方法只会在爬虫结束的时候被调用一次 def close_spider(self,spider): print('爬虫结束') self.fp.close()
测试成功:
将数据存到数据库中
1、mysql数据库
b. 数据库 a) mysql b) redis
c) 编码流程: 1. 将解析到的页面数据存储到items对象 2. 使用yield关键字将items提交给管道文件进行处理 3. 在管道文件中编写代码完成数据存储的操作 4. 在配置文件中开启管道操作
1、将解析到的页面数据存储到items对象
在items.py 中封装两个属性对象
class QiubaiproItem(scrapy.Item): # define the fields for your item here like: # name = scrapy.Field() # 属性声明 author = scrapy.Field() content = scrapy.Field()
qiubai.py
2.使用yield关键字将items提交给管道文件进行处理
qiubai.py
import scrapy from qiubaipro.items import QiubaiproItem class QiubaiSpider(scrapy.Spider): name = 'qiubai' #allowed_domains = ['www.qiushibaike.com/text'] start_urls = ['https://www.qiushibaike.com/text/'] def parse(self, response): # 建议大家使用xpath进行解析(框架集成了xpath解析的接口) div_list = response.xpath("//div[@id='content-left']/div") # 存储到的解析到的页面数据 data_list = [] for div in div_list: author = div.xpath('./div/a[2]/h2/text()').extract_first() content = div.xpath(".//div[@class='content']/span/text()").extract_first() # 1.将解析到数据值(author和content)储存到items对象 item = QiubaiproItem() item['author'] = author item['content'] = content # 2.将item对象提交给管道 yield item
pipelines.py
import pymysql class QiubaiproPipeline(object): conn = None # mysql的连接对象声明 cursor = None # mysql游标对象声明 def open_spider(self,spider): print('开始爬虫') # 链接数据库 # host 本机的ip地址 # 在命令行输入 ipconfig查看 self.conn = pymysql.Connect(host='127.0.0.1',port=3306,user='root',password='123',db='qiubai',charset='utf8') # 该方法可以接受爬虫文件中提交过来的item对象,并且对item对象的页面数据进行持久化处理 # 参数:item表示的就是接受到的item对象 def process_item(self, item, spider): # 1.链接数据库 # 执行sql语句 # 插入数据 sql = 'insert into qiubai(author,content) values("%s","%s")'%(item['author'], item['content']) # 获取游标 self.cursor = self.conn.cursor() try: self.cursor.execute(sql) self.conn.commit() except Exception as e: print(e) self.conn.rollback() # 提交事务 return item # 该方法只会在爬虫结束的时候被调用一次 def close_spider(self,spider): print('爬虫结束') self.cursor.close() self.conn.close()
开启数据库并创建表格
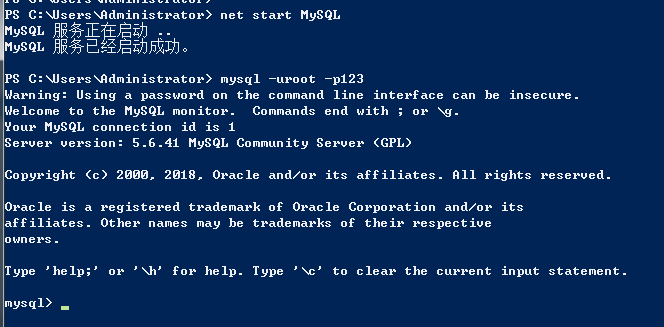
创建qiubai数据库

在qiubai数据库下创建表
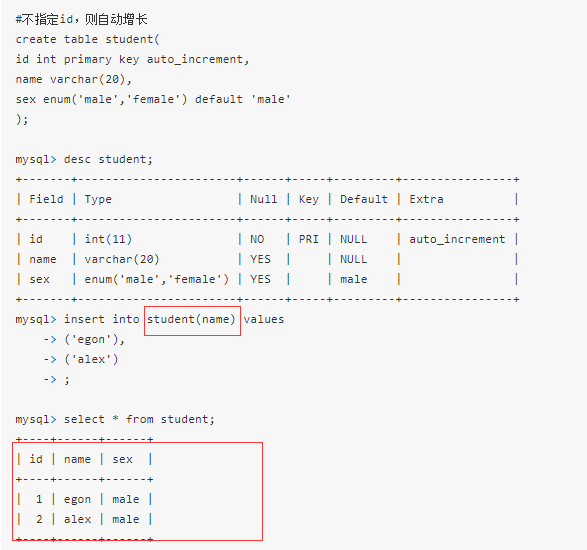
create table t1(
id int primary key auto_increment,
author varchar(20),
content varchar(255));
insert into qiubai(author content) values()

auto_increment
-----------------------------------------------

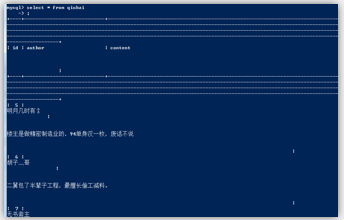
基于mysql的测试成功
Python3使用pip工具安装模块、Anaconda的安装、Anaconda中的python.exe与Python3中的python.exe的冲突解决、Cannot uninstall X错误
Anaconda介绍:
我们还可以直接安装Anaconda,这是一个基于Python的数据处理和科学计算平台,里面内置了数十个非常有用的第三方库。Anaconda会把系统Path中的python指向自己自带的Python,并且,Anaconda安装的第三方模块会安装在Anaconda自己的路径下,不影响系统已安装的Python目录。
安装了Anaconda后,我们再在cmd中输入python后,会发现python的路径变成了Anaconda下的python.exe。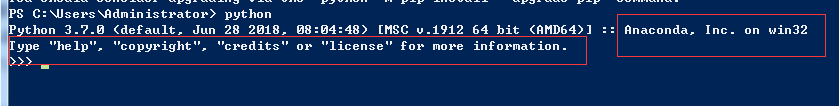
这种情况下有时会导致一些编译问题(即有些模块安装在Anaconda的文件夹里,有些则安装在Python3的文件夹里)
为了区分使用这几个python.exe,我们可以把Anaconda文件夹中的ptyhon.exe重命名为pythona.exe。
把python2.7文件夹中的python.exe重命名为python2.exe,把ptyhon3.6文件夹中的python.exe重命名为python3.exe。并将这三个文件所在的目录都添加到环境变量path中。


-----------------------------------

2、redis
redis的下载:

cd 到文件目录
启动服务端
redis-server.exe redis.windows.conf
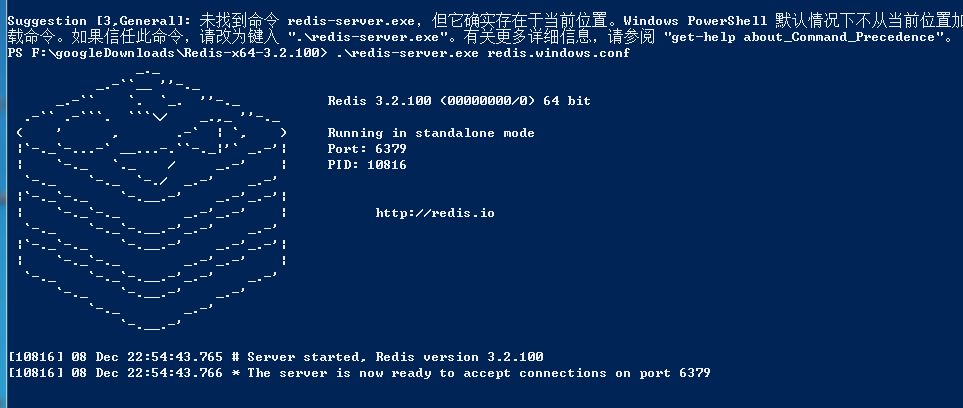
这时候另启一个 cmd 窗口,原来的不要关闭,不然就无法访问服务端了。
切换到 redis 目录下运行:
启动客户端

设置键值对:
set name 'aa'
取出健值对
get name

----------------------------------------------------------------------
qiubai.py和mysql一样
import scrapy from qiubaipro.items import QiubaiproItem class QiubaiSpider(scrapy.Spider): name = 'qiubai' #allowed_domains = ['www.qiushibaike.com/text'] start_urls = ['https://www.qiushibaike.com/text/'] def parse(self, response): # 建议大家使用xpath进行解析(框架集成了xpath解析的接口) div_list = response.xpath("//div[@id='content-left']/div") # 存储到的解析到的页面数据 data_list = [] for div in div_list: author = div.xpath('./div/a[2]/h2/text()').extract_first() content = div.xpath(".//div[@class='content']/span/text()").extract_first() # 1.将解析到数据值(author和content)储存到items对象 item = QiubaiproItem() item['author'] = author item['content'] = content # 2.将item对象提交给管道 yield item
pipelines.py
import redis class QiubaiproPipeline(object): conn = None def open_spider(self,spider): print('开始爬虫') # redis服务器port self.conn = redis.Redis(host='127.0.0.1',port=6379) # 该方法可以接受爬虫文件中提交过来的item对象,并且对item对象的页面数据进行持久化处理 # 参数:item表示的就是接受到的item对象 def process_item(self, item, spider): # 1.链接数据库 dict = {'author':item['author'], 'content':item['content']} self.conn.lpush('data',dict) return item # 该方法只会在爬虫结束的时候被调用一次 def close_spider(self,spider): print('爬虫结束')
执行将数据存在redis数据库中

在命令行下打开redis服务端
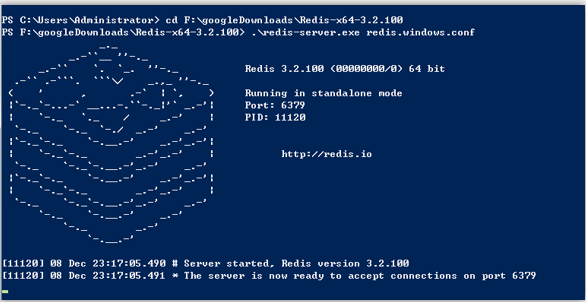
在命令行下打开redis客户端
取值出现错误-----是否是没有建立数据库和---表格导致?
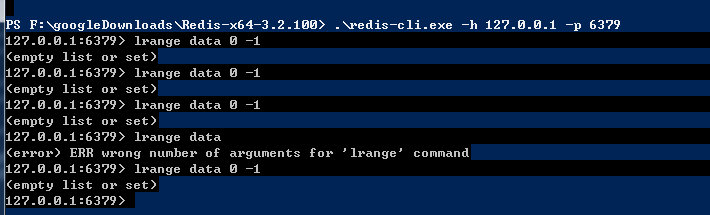
一一排查检查错误源

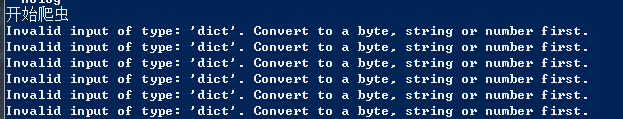
写入redis数据的格式不正确,必须是byte,string,number
更改后:
dict = json.dumps(dict)
写入redis数据库的步骤,先打开服务端
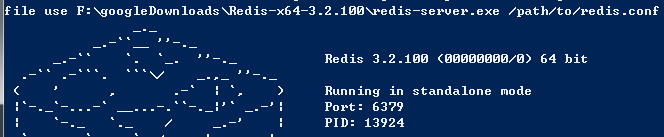
在执行scrapy命令写入数据到服务器

最后在客户端进行查看:

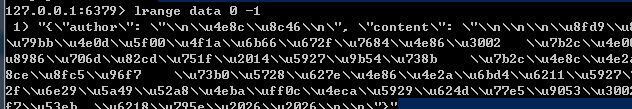
测试成功
