1、它实现了ConcurrentMap接口,该接口定义了一些原子操作约定
2、线程安全
- 完全的并发读和高并发写
- 读操作完全无锁,牺牲了一致性;写操作部分有锁
- 它与
HashTable、Collections.synchronizedMap HashMap支持null,ConcurrentHashMap、HashTable不支持null
3、java7
- 分段锁
- 哈希表/链表
4、java8
CAS+Unsafe- 哈希表/链表 + 红黑树
java7的实现
一、相关概念
1、分段锁
ConcurrentHashMap底层采用多个分段Segment,每段下面都是一个哈希表,这就是分段。每当需要对每段数据上锁操作时,只需要对Segment上锁即可,这就是分段锁。通常称Segment的数量叫做并发度concurrency。
优点:
- 在未上锁的情况下,提高了并发度;
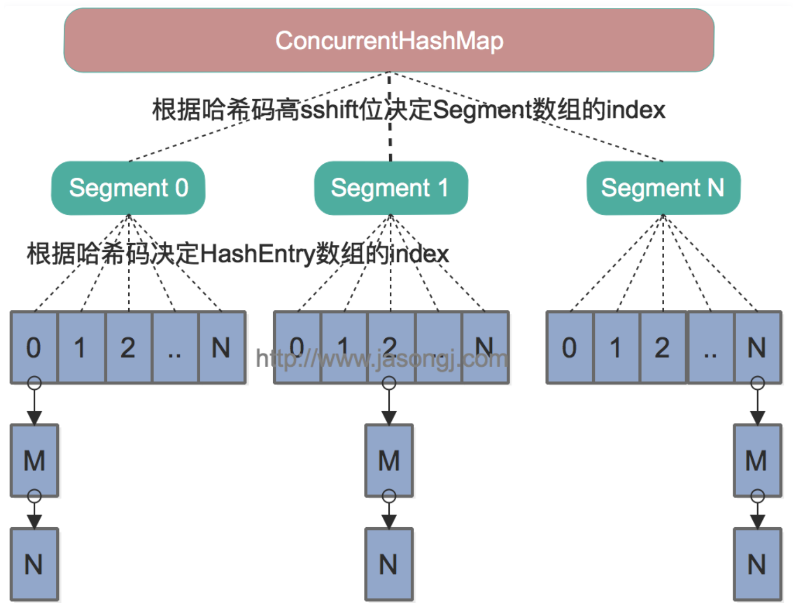
2、并发度concurrency
/**
* The default concurrency level for this table, used when not
* otherwise specified in a constructor.
*/
static final int DEFAULT_CONCURRENCY_LEVEL = 16;
这表示默认情况下,会有16个段
Segment
3、每个Segment的哈希表长度都是2的幂次方
在ConcurrentHashMap构造方法中
二、源码分析
1、get方法
- 计算
segment的位置 - 找到这个段下面的哈希表
- 遍历链表,看是否存在
public V get(Object key) {
Segment<K,V> s; // manually integrate access methods to reduce overhead
HashEntry<K,V>[] tab;
int h = hash(key);
// 获取到key所在Segment数组的下标
long u = (((h >>> segmentShift) & segmentMask) << SSHIFT) + SBASE;
// 判断这个下标是否存在,以及Segment下面的哈希表是否存在
if ((s = (Segment<K,V>)UNSAFE.getObjectVolatile(segments, u)) != null &&
(tab = s.table) != null) {
// 熟悉的:(tab.length - 1) & h操作
for (HashEntry<K,V> e = (HashEntry<K,V>) UNSAFE.getObjectVolatile
(tab, ((long)(((tab.length - 1) & h)) << TSHIFT) + TBASE);
e != null; e = e.next) {
K k;
if ((k = e.key) == key || (e.hash == h && key.equals(k)))
return e.value;
}
}
return null;
}
(1)为什么要使用UNSAFE.getObjectVolatile(segments, u)这种方式来读取数组下标的某个元素?
提高性能。使用常用segments[i]这种语法,在编译字节码的时候,是会检查数组是否越界;而使用上面的代码,会节省这一步。
(2)如何保证线程安全性?
即如何保证在多线程环境下,当线程在做更新操作时,如果其他线程在同步读的话,是可能出现脏数据、空指针情况。那么ConcurrentHashMap是如何保证的?
ConcurrentHashMap为了提高高并发,而牺牲了一致性,但这种一致性是弱一致性,不会对程序造成大的过错。所以脏数据是无法避免的,因此在java8的类注释写到不建议使用size、isEmpty、containsValue来进行判断语句。
* Bear in mind that the results of aggregate status methods including
* {@code size}, {@code isEmpty}, and {@code containsValue} are typically
* useful only when a map is not undergoing concurrent updates in other threads.
* Otherwise the results of these methods reflect transient states
* that may be adequate for monitoring or estimation purposes, but not
* for program control.
2、put方法
- 找到
Segment,必要时新建; Segment执行put操作,必要时扩容;
public V put(K key, V value) {
Segment<K,V> s;
if (value == null)
throw new NullPointerException();
int hash = hash(key);
int j = (hash >>> segmentShift) & segmentMask;
if ((s = (Segment<K,V>)UNSAFE.getObject // nonvolatile; recheck
(segments, (j << SSHIFT) + SBASE)) == null) // in ensureSegment
s = ensureSegment(j);
return s.put(key, hash, value, false);
}
(1)扩容时如何保证线程安全性?
- 在创建
Segment时,采用CAS保证线程安全性; - 在创建
Entry时,因为Segment本身就是ReentrantLock,在其Segment.put()方法是一定保证在获取到锁的情况下才执行操作的;
(2)Unsafe.getObject()的作用?
java8的实现
一、与java7的改进
使用哈希表 + 链表/红黑树 的数据结构
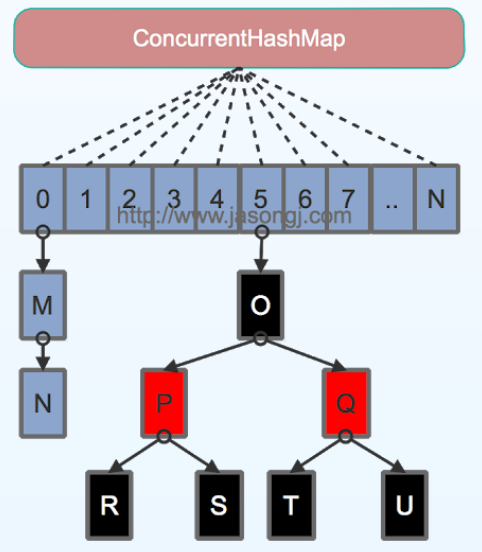
放弃使用分段锁,改用CAS、volatile、Unsafe
java7的分段锁很好,但锁毕竟还是很慢的,所以java8实现了尽可能地无锁环境。
这里所说地无锁也仅仅大多数情况下,在某些特殊场景还是需要锁地。
锁的粒度更细
java7锁地粒度是Segment,而在java8中锁地粒度是每个Entry
二、源码分析
1、get方法
public V get(Object key) {
Node<K,V>[] tab; Node<K,V> e, p; int n, eh; K ek;
// 重新hash
int h = spread(key.hashCode());
if ((tab = table) != null && (n = tab.length) > 0 &&
(e = tabAt(tab, (n - 1) & h)) != null) {
// 如果第一个就找到,直接返回
if ((eh = e.hash) == h) {
if ((ek = e.key) == key || (ek != null && key.equals(ek)))
return e.val;
}
// 如果元素地hash值小于0,就往红黑树查找
else if (eh < 0)
return (p = e.find(h, key)) != null ? p.val : null;
// 链表下地查找
while ((e = e.next) != null) {
if (e.hash == h &&
((ek = e.key) == key || (ek != null && key.equals(ek))))
return e.val;
}
}
return null;
}
(1)查找没有锁,如何有人在写入怎么办?
- 在红黑树状态下,查找是有读写锁;
- 在链表状态下,跟
java7相似,牺牲了弱一致性;
2、put方法
final V putVal(K key, V value, boolean onlyIfAbsent) {
if (key == null || value == null) throw new NullPointerException();
// 重新hash
int hash = spread(key.hashCode());
int binCount = 0;
// 自旋操作:乐观锁
for (Node<K,V>[] tab = table;;) {
Node<K,V> f; int n, i, fh;
// 如果哈希表为空,就新建
if (tab == null || (n = tab.length) == 0)
tab = initTable();
// 找到对应下标Entry,如果为空,就新建
else if ((f = tabAt(tab, i = (n - 1) & hash)) == null) {
if (casTabAt(tab, i, null,
new Node<K,V>(hash, key, value, null)))
break; // no lock when adding to empty bin
}
// 如果当前节点处于转发节点,即正处于扩容转移状态,就帮忙一起转移
else if ((fh = f.hash) == MOVED)
tab = helpTransfer(tab, f);
// 在对应Entry下,进行put操作
else {
V oldVal = null;
// synchronized锁定entry,进行put
synchronized (f) {
if (tabAt(tab, i) == f) {
// 链表地put操作
if (fh >= 0) {
binCount = 1;
for (Node<K,V> e = f;; ++binCount) {
K ek;
if (e.hash == hash &&
((ek = e.key) == key ||
(ek != null && key.equals(ek)))) {
oldVal = e.val;
if (!onlyIfAbsent)
e.val = value;
break;
}
Node<K,V> pred = e;
if ((e = e.next) == null) {
pred.next = new Node<K,V>(hash, key,
value, null);
break;
}
}
}
// 红黑树地put操作
else if (f instanceof TreeBin) {
Node<K,V> p;
binCount = 2;
if ((p = ((TreeBin<K,V>)f).putTreeVal(hash, key,
value)) != null) {
oldVal = p.val;
if (!onlyIfAbsent)
p.val = value;
}
}
}
}
// 检查是否需要将链表转换成红黑树
if (binCount != 0) {
if (binCount >= TREEIFY_THRESHOLD)
treeifyBin(tab, i);
if (oldVal != null)
return oldVal;
break;
}
}
}
// 记录数量,必要地时候进行扩容
addCount(1L, binCount);
return null;
}