http://www.cnblogs.com/yangecnu/p/3627386.html
前面一篇文章介绍了2-3查找树,可以看到,2-3查找树能保证在插入元素之后能保持树的平衡状态,最坏情况下即所有的子节点都是2-node,树的高度为lgN,从而保证了最坏情况下的时间复杂度。但是2-3树实现起来比较复杂,本文介绍一种简单实现2-3树的数据结构,即红黑树(Red-Black Tree)
定义
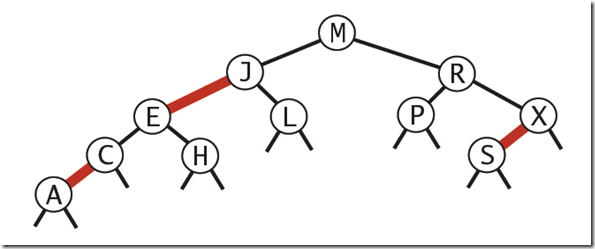
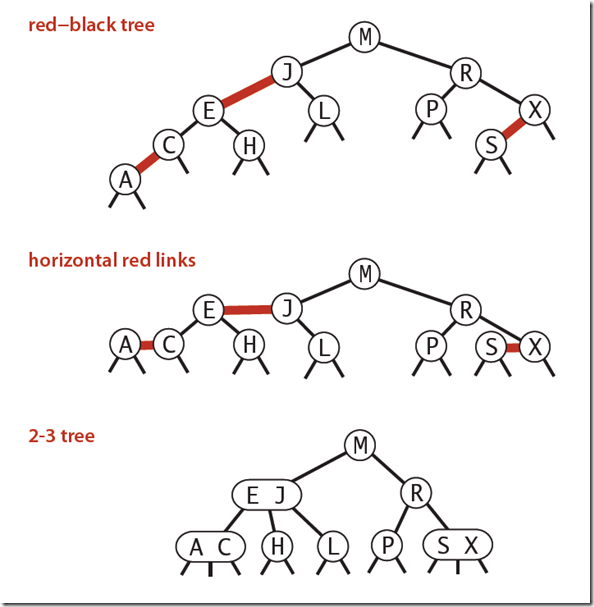
红黑树的主要是像是对2-3查找树进行编码,尤其是对2-3查找树中的3-nodes节点添加额外的信息。红黑树中将节点之间的链接分为两种不同类型,红色链接,他用来链接两个2-nodes节点来表示一个3-nodes节点。黑色链接用来链接普通的2-3节点。特别的,使用红色链接的两个2-nodes来表示一个3-nodes节点,并且向左倾斜,即一个2-node是另一个2-node的左子节点。这种做法的好处是查找的时候不用做任何修改,和普通的二叉查找树相同。
根据以上描述,红黑树定义如下:
红黑树是一种具有红色和黑色链接的平衡查找树,同时满足:
- 红色节点向左倾斜
- 一个节点不可能有两个红色链接
- 整个书完全黑色平衡,即从根节点到所以叶子结点的路径上,黑色链接的个数都相同。
下图可以看到红黑树其实是2-3树的另外一种表现形式:如果我们将红色的连线水平绘制,那么他链接的两个2-node节点就是2-3树中的一个3-node节点了。
表示
我们可以在二叉查找树的每一个节点上增加一个新的表示颜色的标记。该标记指示该节点指向其父节点的颜色。
private const bool RED = true;
private const bool BLACK = false;
private Node root;
class Node
{
public Node Left { get; set; }
public Node Right { get; set; }
public TKey Key { get; set; }
public TValue Value { get; set; }
public int Number { get; set; }
public bool Color { get; set; }
public Node(TKey key, TValue value,int number, bool color)
{
this.Key = key;
this.Value = value;
this.Number = number;
this.Color = color;
}
}
private bool IsRed(Node node)
{
if (node == null) return false;
return node.Color == RED;
}
实现
查找
红黑树是一种特殊的二叉查找树,他的查找方法也和二叉查找树一样,不需要做太多更改。
但是由于红黑树比一般的二叉查找树具有更好的平衡,所以查找起来更快。
//查找获取指定的值
public override TValue Get(TKey key)
{
return GetValue(root, key);
}
private TValue GetValue(Node node, TKey key)
{
if (node == null) return default(TValue);
int cmp = key.CompareTo(node.Key);
if (cmp == 0) return node.Value;
else if (cmp > 0) return GetValue(node.Right, key);
else return GetValue(node.Left, key);
}
平衡化
在介绍插入之前,我们先介绍如何让红黑树保持平衡,因为一般的,我们插入完成之后,需要对树进行平衡化操作以使其满足平衡化。
旋转
旋转又分为左旋和右旋。通常左旋操作用于将一个向右倾斜的红色链接旋转为向左链接。对比操作前后,可以看出,该操作实际上是将红线链接的两个节点中的一个较大的节点移动到根节点上。
左旋操作如下图:
//左旋转
private Node RotateLeft(Node h)
{
Node x = h.Right;
//将x的左节点复制给h右节点
h.Right = x.Left;
//将h复制给x右节点
x.Left = h;
x.Color = h.Color;
h.Color = RED;
return x;
}
左旋的动画效果如下:
右旋是左旋的逆操作,过程如下:
代码如下:
//右旋转
private Node RotateRight(Node h)
{
Node x = h.Left;
h.Left = x.Right;
x.Right = h;
x.Color = h.Color;
h.Color = RED;
return x;
}
右旋的动画效果如下:
颜色反转
当出现一个临时的4-node的时候,即一个节点的两个子节点均为红色,如下图:
这其实是个A,E,S 4-node连接,我们需要将E提升至父节点,操作方法很简单,就是把E对子节点的连线设置为黑色,自己的颜色设置为红色。
有了以上基本操作方法之后,我们现在对应之前对2-3树的平衡操作来对红黑树进行平衡操作,这两者是可以一一对应的,如下图:
现在来讨论各种情况:
Case 1 往一个2-node节点底部插入新的节点
先热身一下,首先我们看对于只有一个节点的红黑树,插入一个新的节点的操作:
这种情况很简单,只需要:
- 标准的二叉查找树遍历即可。新插入的节点标记为红色
- 如果新插入的节点在父节点的右子节点,则需要进行左旋操作
Case 2往一个3-node节点底部插入新的节点
先热身一下,假设我们往一个只有两个节点的树中插入元素,如下图,根据待插入元素与已有元素的大小,又可以分为如下三种情况:
- 如果带插入的节点比现有的两个节点都大,这种情况最简单。我们只需要将新插入的节点连接到右边子树上即可,然后将中间的元素提升至根节点。这样根节点的左右子树都是红色的节点了,我们只需要调研FlipColor方法即可。其他情况经过反转操作后都会和这一样。
- 如果插入的节点比最小的元素要小,那么将新节点添加到最左侧,这样就有两个连接红色的节点了,这是对中间节点进行右旋操作,使中间结点成为根节点。这是就转换到了第一种情况,这时候只需要再进行一次FlipColor操作即可。
- 如果插入的节点的值位于两个节点之间,那么将新节点插入到左侧节点的右子节点。因为该节点的右子节点是红色的,所以需要进行左旋操作。操作完之后就变成第二种情况了,再进行一次右旋,然后再调用FlipColor操作即可完成平衡操作。
有了以上基础,我们现在来总结一下往一个3-node节点底部插入新的节点的操作步骤,下面是一个典型的操作过程图:
可以看出,操作步骤如下:
- 执行标准的二叉查找树插入操作,新插入的节点元素用红色标识。
- 如果需要对4-node节点进行旋转操作
- 如果需要,调用FlipColor方法将红色节点提升
- 如果需要,左旋操作使红色节点左倾。
- 在有些情况下,需要递归调用Case1 Case2,来进行递归操作。如下:
代码实现
经过上面的平衡化讨论,现在就来实现插入操作,一般地插入操作就是先执行标准的二叉查找树插入,然后再进行平衡化。对照2-3树,我们可以通过前面讨论的,左旋,右旋,FlipColor这三种操作来完成平衡化。
具体操作方式如下:
- 如果节点的右子节点为红色,且左子节点位黑色,则进行左旋操作
- 如果节点的左子节点为红色,并且左子节点的左子节点也为红色,则进行右旋操作
- 如果节点的左右子节点均为红色,则执行FlipColor操作,提升中间结点。
根据这一逻辑,我们就可以实现插入的Put方法了。
public override void Put(TKey key, TValue value)
{
root = Put(root, key, value);
root.Color = BLACK;
}
private Node Put(Node h, TKey key, TValue value)
{
if (h == null) return new Node(key, value, 1, RED);
int cmp = key.CompareTo(h.Key);
if (cmp < 0) h.Left = Put(h.Left, key, value);
else if (cmp > 0) h.Right = Put(h.Right, key, value);
else h.Value = value;
//平衡化操作
if (IsRed(h.Right) && !IsRed(h.Left)) h = RotateLeft(h);
if (IsRed(h.Right) && IsRed(h.Left.Left)) h = RotateRight(h);
if (IsRed(h.Left) && IsRed(h.Right)) h = FlipColor(h);
h.Number = Size(h.Left) + Size(h.Right) + 1;
return h;
}
private int Size(Node node)
{
if (node == null) return 0;
return node.Number;
}
分析
对红黑树的分析其实就是对2-3查找树的分析,红黑树能够保证符号表的所有操作即使在最坏的情况下都能保证对数的时间复杂度,也就是树的高度。
在分析之前,为了更加直观,下面是以升序,降序和随机构建一颗红黑树的动画:
- 以升序插入构建红黑树:
- 以降序插入构建红黑树:
- 随机插入构建红黑树
从上面三张动画效果中,可以很直观的看出,红黑树在各种情况下都能维护良好的平衡性,从而能够保证最差情况下的查找,插入效率。
下面来详细分析下红黑树的效率:
1. 在最坏的情况下,红黑树的高度不超过2lgN
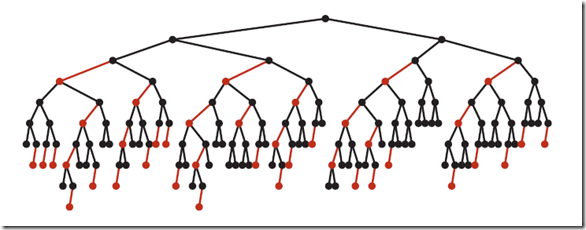
最坏的情况就是,红黑树中除了最左侧路径全部是由3-node节点组成,即红黑相间的路径长度是全黑路径长度的2倍。
下图是一个典型的红黑树,从中可以看到最长的路径(红黑相间的路径)是最短路径的2倍:
2. 红黑树的平均高度大约为lgN
下图是红黑树在各种情况下的时间复杂度,可以看出红黑树是2-3查找树的一种实现,他能保证最坏情况下仍然具有对数的时间复杂度。
下图是红黑树各种操作的时间复杂度。
应用
红黑树这种数据结构应用十分广泛,在多种编程语言中被用作符号表的实现,如:
- Java中的java.util.TreeMap,java.util.TreeSet
- C++ STL中的:map,multimap,multiset
- .NET中的:SortedDictionary,SortedSet 等
下面以.NET中为例,通过Reflector工具,我们可以看到SortedDictionary的Add方法如下:
public void Add(T item)
{
if (this.root == null)
{
this.root = new Node<T>(item, false);
this.count = 1;
}
else
{
Node<T> root = this.root;
Node<T> node = null;
Node<T> grandParent = null;
Node<T> greatGrandParent = null;
int num = 0;
while (root != null)
{
num = this.comparer.Compare(item, root.Item);
if (num == 0)
{
this.root.IsRed = false;
ThrowHelper.ThrowArgumentException(ExceptionResource.Argument_AddingDuplicate);
}
if (TreeSet<T>.Is4Node(root))
{
TreeSet<T>.Split4Node(root);
if (TreeSet<T>.IsRed(node))
{
this.InsertionBalance(root, ref node, grandParent, greatGrandParent);
}
}
greatGrandParent = grandParent;
grandParent = node;
node = root;
root = (num < 0) ? root.Left : root.Right;
}
Node<T> current = new Node<T>(item);
if (num > 0)
{
node.Right = current;
}
else
{
node.Left = current;
}
if (node.IsRed)
{
this.InsertionBalance(current, ref node, grandParent, greatGrandParent);
}
this.root.IsRed = false;
this.count++;
this.version++;
}
}
可以看到,内部实现也是一个红黑树,其操作方法和本文将的大同小异,感兴趣的话,您可以使用Reflector工具跟进去查看源代码。
总结
前文讲解了自平衡查找树中的2-3查找树,这种数据结构在插入之后能够进行自平衡操作,从而保证了树的高度在一定的范围内进而能够保证最坏情况下的时间复杂度。但是2-3查找树实现起来比较困难,红黑树是2-3树的一种简单高效的实现,他巧妙地使用颜色标记来替代2-3树中比较难处理的3-node节点问题。红黑树是一种比较高效的平衡查找树,应用非常广泛,很多编程语言的内部实现都或多或少的采用了红黑树。
希望本文对您了解红黑树有所帮助,下文将介绍在文件系统以及数据库系统中应用非常广泛的另外一种平衡树结构:B树。
//http://algs4.cs.princeton.edu/33balanced/RedBlackBST.java.html
/*************************************************************************
* Compilation: javac RedBlackBST.java
* Execution: java RedBlackBST < input.txt
* Dependencies: StdIn.java StdOut.java
* Data files: http://algs4.cs.princeton.edu/33balanced/tinyST.txt
*
* A symbol table implemented using a left-leaning red-black BST.
* This is the 2-3 version.
*
* Note: commented out assertions because DrJava now enables assertions
* by default.
*
* % more tinyST.txt
* S E A R C H E X A M P L E
*
* % java RedBlackBST < tinyST.txt
* A 8
* C 4
* E 12
* H 5
* L 11
* M 9
* P 10
* R 3
* S 0
* X 7
*
*************************************************************************/
import java.util.NoSuchElementException;
public class RedBlackBST<Key extends Comparable<Key>, Value> {
private static final boolean RED = true;
private static final boolean BLACK = false;
private Node root; // root of the BST
// BST helper node data type
private class Node {
private Key key; // key
private Value val; // associated data
private Node left, right; // links to left and right subtrees
private boolean color; // color of parent link
private int N; // subtree count
public Node(Key key, Value val, boolean color, int N) {
this.key = key;
this.val = val;
this.color = color;
this.N = N;
}
}
/*************************************************************************
* Node helper methods
*************************************************************************/
// is node x red; false if x is null ?
private boolean isRed(Node x) {
if (x == null) return false;
return (x.color == RED);
}
// number of node in subtree rooted at x; 0 if x is null
private int size(Node x) {
if (x == null) return 0;
return x.N;
}
/*************************************************************************
* Size methods
*************************************************************************/
// return number of key-value pairs in this symbol table
public int size() { return size(root); }
// is this symbol table empty?
public boolean isEmpty() {
return root == null;
}
/*************************************************************************
* Standard BST search
*************************************************************************/
// value associated with the given key; null if no such key
public Value get(Key key) { return get(root, key); }
// value associated with the given key in subtree rooted at x; null if no such key
private Value get(Node x, Key key) {
while (x != null) {
int cmp = key.compareTo(x.key);
if (cmp < 0) x = x.left;
else if (cmp > 0) x = x.right;
else return x.val;
}
return null;
}
// is there a key-value pair with the given key?
public boolean contains(Key key) {
return get(key) != null;
}
// is there a key-value pair with the given key in the subtree rooted at x?
// private boolean contains(Node x, Key key) {
// return (get(x, key) != null);
// }
/*************************************************************************
* Red-black insertion
*************************************************************************/
// insert the key-value pair; overwrite the old value with the new value
// if the key is already present
public void put(Key key, Value val) {
root = put(root, key, val);
root.color = BLACK;
// assert check();
}
// insert the key-value pair in the subtree rooted at h
private Node put(Node h, Key key, Value val) {
if (h == null) return new Node(key, val, RED, 1);
int cmp = key.compareTo(h.key);
if (cmp < 0) h.left = put(h.left, key, val);
else if (cmp > 0) h.right = put(h.right, key, val);
else h.val = val;
// fix-up any right-leaning links
if (isRed(h.right) && !isRed(h.left)) h = rotateLeft(h);
if (isRed(h.left) && isRed(h.left.left)) h = rotateRight(h);
if (isRed(h.left) && isRed(h.right)) flipColors(h);
h.N = size(h.left) + size(h.right) + 1;
return h;
}
/*************************************************************************
* Red-black deletion
*************************************************************************/
// delete the key-value pair with the minimum key
public void deleteMin() {
if (isEmpty()) throw new NoSuchElementException("BST underflow");
// if both children of root are black, set root to red
if (!isRed(root.left) && !isRed(root.right))
root.color = RED;
root = deleteMin(root);
if (!isEmpty()) root.color = BLACK;
// assert check();
}
// delete the key-value pair with the minimum key rooted at h
private Node deleteMin(Node h) {
if (h.left == null)
return null;
if (!isRed(h.left) && !isRed(h.left.left))
h = moveRedLeft(h);
h.left = deleteMin(h.left);
return balance(h);
}
// delete the key-value pair with the maximum key
public void deleteMax() {
if (isEmpty()) throw new NoSuchElementException("BST underflow");
// if both children of root are black, set root to red
if (!isRed(root.left) && !isRed(root.right))
root.color = RED;
root = deleteMax(root);
if (!isEmpty()) root.color = BLACK;
// assert check();
}
// delete the key-value pair with the maximum key rooted at h
private Node deleteMax(Node h) {
if (isRed(h.left))
h = rotateRight(h);
if (h.right == null)
return null;
if (!isRed(h.right) && !isRed(h.right.left))
h = moveRedRight(h);
h.right = deleteMax(h.right);
return balance(h);
}
// delete the key-value pair with the given key
public void delete(Key key) {
if (!contains(key)) {
System.err.println("symbol table does not contain " + key);
return;
}
// if both children of root are black, set root to red
if (!isRed(root.left) && !isRed(root.right))
root.color = RED;
root = delete(root, key);
if (!isEmpty()) root.color = BLACK;
// assert check();
}
// delete the key-value pair with the given key rooted at h
private Node delete(Node h, Key key) {
// assert get(h, key) != null;
if (key.compareTo(h.key) < 0) {
if (!isRed(h.left) && !isRed(h.left.left))
h = moveRedLeft(h);
h.left = delete(h.left, key);
}
else {
if (isRed(h.left))
h = rotateRight(h);
if (key.compareTo(h.key) == 0 && (h.right == null))
return null;
if (!isRed(h.right) && !isRed(h.right.left))
h = moveRedRight(h);
if (key.compareTo(h.key) == 0) {
Node x = min(h.right);
h.key = x.key;
h.val = x.val;
// h.val = get(h.right, min(h.right).key);
// h.key = min(h.right).key;
h.right = deleteMin(h.right);
}
else h.right = delete(h.right, key);
}
return balance(h);
}
/*************************************************************************
* red-black tree helper functions
*************************************************************************/
// make a left-leaning link lean to the right
private Node rotateRight(Node h) {
// assert (h != null) && isRed(h.left);
Node x = h.left;
h.left = x.right;
x.right = h;
x.color = x.right.color;
x.right.color = RED;
x.N = h.N;
h.N = size(h.left) + size(h.right) + 1;
return x;
}
// make a right-leaning link lean to the left
private Node rotateLeft(Node h) {
// assert (h != null) && isRed(h.right);
Node x = h.right;
h.right = x.left;
x.left = h;
x.color = x.left.color;
x.left.color = RED;
x.N = h.N;
h.N = size(h.left) + size(h.right) + 1;
return x;
}
// flip the colors of a node and its two children
private void flipColors(Node h) {
// h must have opposite color of its two children
// assert (h != null) && (h.left != null) && (h.right != null);
// assert (!isRed(h) && isRed(h.left) && isRed(h.right))
// || (isRed(h) && !isRed(h.left) && !isRed(h.right));
h.color = !h.color;
h.left.color = !h.left.color;
h.right.color = !h.right.color;
}
// Assuming that h is red and both h.left and h.left.left
// are black, make h.left or one of its children red.
private Node moveRedLeft(Node h) {
// assert (h != null);
// assert isRed(h) && !isRed(h.left) && !isRed(h.left.left);
flipColors(h);
if (isRed(h.right.left)) {
h.right = rotateRight(h.right);
h = rotateLeft(h);
flipColors(h);
}
return h;
}
// Assuming that h is red and both h.right and h.right.left
// are black, make h.right or one of its children red.
private Node moveRedRight(Node h) {
// assert (h != null);
// assert isRed(h) && !isRed(h.right) && !isRed(h.right.left);
flipColors(h);
if (isRed(h.left.left)) {
h = rotateRight(h);
flipColors(h);
}
return h;
}
// restore red-black tree invariant
private Node balance(Node h) {
// assert (h != null);
if (isRed(h.right)) h = rotateLeft(h);
if (isRed(h.left) && isRed(h.left.left)) h = rotateRight(h);
if (isRed(h.left) && isRed(h.right)) flipColors(h);
h.N = size(h.left) + size(h.right) + 1;
return h;
}
/*************************************************************************
* Utility functions
*************************************************************************/
// height of tree (1-node tree has height 0)
public int height() { return height(root); }
private int height(Node x) {
if (x == null) return -1;
return 1 + Math.max(height(x.left), height(x.right));
}
/*************************************************************************
* Ordered symbol table methods.
*************************************************************************/
// the smallest key; null if no such key
public Key min() {
if (isEmpty()) return null;
return min(root).key;
}
// the smallest key in subtree rooted at x; null if no such key
private Node min(Node x) {
// assert x != null;
if (x.left == null) return x;
else return min(x.left);
}
// the largest key; null if no such key
public Key max() {
if (isEmpty()) return null;
return max(root).key;
}
// the largest key in the subtree rooted at x; null if no such key
private Node max(Node x) {
// assert x != null;
if (x.right == null) return x;
else return max(x.right);
}
// the largest key less than or equal to the given key
public Key floor(Key key) {
Node x = floor(root, key);
if (x == null) return null;
else return x.key;
}
// the largest key in the subtree rooted at x less than or equal to the given key
private Node floor(Node x, Key key) {
if (x == null) return null;
int cmp = key.compareTo(x.key);
if (cmp == 0) return x;
if (cmp < 0) return floor(x.left, key);
Node t = floor(x.right, key);
if (t != null) return t;
else return x;
}
// the smallest key greater than or equal to the given key
public Key ceiling(Key key) {
Node x = ceiling(root, key);
if (x == null) return null;
else return x.key;
}
// the smallest key in the subtree rooted at x greater than or equal to the given key
private Node ceiling(Node x, Key key) {
if (x == null) return null;
int cmp = key.compareTo(x.key);
if (cmp == 0) return x;
if (cmp > 0) return ceiling(x.right, key);
Node t = ceiling(x.left, key);
if (t != null) return t;
else return x;
}
// the key of rank k
public Key select(int k) {
if (k < 0 || k >= size()) return null;
Node x = select(root, k);
return x.key;
}
// the key of rank k in the subtree rooted at x
private Node select(Node x, int k) {
// assert x != null;
// assert k >= 0 && k < size(x);
int t = size(x.left);
if (t > k) return select(x.left, k);
else if (t < k) return select(x.right, k-t-1);
else return x;
}
// number of keys less than key
public int rank(Key key) {
return rank(key, root);
}
// number of keys less than key in the subtree rooted at x
private int rank(Key key, Node x) {
if (x == null) return 0;
int cmp = key.compareTo(x.key);
if (cmp < 0) return rank(key, x.left);
else if (cmp > 0) return 1 + size(x.left) + rank(key, x.right);
else return size(x.left);
}
/***********************************************************************
* Range count and range search.
***********************************************************************/
// all of the keys, as an Iterable
public Iterable<Key> keys() {
return keys(min(), max());
}
// the keys between lo and hi, as an Iterable
public Iterable<Key> keys(Key lo, Key hi) {
Queue<Key> queue = new Queue<Key>();
// if (isEmpty() || lo.compareTo(hi) > 0) return queue;
keys(root, queue, lo, hi);
return queue;
}
// add the keys between lo and hi in the subtree rooted at x
// to the queue
private void keys(Node x, Queue<Key> queue, Key lo, Key hi) {
if (x == null) return;
int cmplo = lo.compareTo(x.key);
int cmphi = hi.compareTo(x.key);
if (cmplo < 0) keys(x.left, queue, lo, hi);
if (cmplo <= 0 && cmphi >= 0) queue.enqueue(x.key);
if (cmphi > 0) keys(x.right, queue, lo, hi);
}
// number keys between lo and hi
public int size(Key lo, Key hi) {
if (lo.compareTo(hi) > 0) return 0;
if (contains(hi)) return rank(hi) - rank(lo) + 1;
else return rank(hi) - rank(lo);
}
/*************************************************************************
* Check integrity of red-black BST data structure
*************************************************************************/
private boolean check() {
if (!isBST()) StdOut.println("Not in symmetric order");
if (!isSizeConsistent()) StdOut.println("Subtree counts not consistent");
if (!isRankConsistent()) StdOut.println("Ranks not consistent");
if (!is23()) StdOut.println("Not a 2-3 tree");
if (!isBalanced()) StdOut.println("Not balanced");
return isBST() && isSizeConsistent() && isRankConsistent() && is23() && isBalanced();
}
// does this binary tree satisfy symmetric order?
// Note: this test also ensures that data structure is a binary tree since order is strict
private boolean isBST() {
return isBST(root, null, null);
}
// is the tree rooted at x a BST with all keys strictly between min and max
// (if min or max is null, treat as empty constraint)
// Credit: Bob Dondero's elegant solution
private boolean isBST(Node x, Key min, Key max) {
if (x == null) return true;
if (min != null && x.key.compareTo(min) <= 0) return false;
if (max != null && x.key.compareTo(max) >= 0) return false;
return isBST(x.left, min, x.key) && isBST(x.right, x.key, max);
}
// are the size fields correct?
private boolean isSizeConsistent() { return isSizeConsistent(root); }
private boolean isSizeConsistent(Node x) {
if (x == null) return true;
if (x.N != size(x.left) + size(x.right) + 1) return false;
return isSizeConsistent(x.left) && isSizeConsistent(x.right);
}
// check that ranks are consistent
private boolean isRankConsistent() {
for (int i = 0; i < size(); i++)
if (i != rank(select(i))) return false;
for (Key key : keys())
if (key.compareTo(select(rank(key))) != 0) return false;
return true;
}
// Does the tree have no red right links, and at most one (left)
// red links in a row on any path?
private boolean is23() { return is23(root); }
private boolean is23(Node x) {
if (x == null) return true;
if (isRed(x.right)) return false;
if (x != root && isRed(x) && isRed(x.left))
return false;
return is23(x.left) && is23(x.right);
}
// do all paths from root to leaf have same number of black edges?
private boolean isBalanced() {
int black = 0; // number of black links on path from root to min
Node x = root;
while (x != null) {
if (!isRed(x)) black++;
x = x.left;
}
return isBalanced(root, black);
}
// does every path from the root to a leaf have the given number of black links?
private boolean isBalanced(Node x, int black) {
if (x == null) return black == 0;
if (!isRed(x)) black--;
return isBalanced(x.left, black) && isBalanced(x.right, black);
}
/*****************************************************************************
* Test client
*****************************************************************************/
public static void main(String[] args) {
RedBlackBST<String, Integer> st = new RedBlackBST<String, Integer>();
for (int i = 0; !StdIn.isEmpty(); i++) {
String key = StdIn.readString();
st.put(key, i);
}
for (String s : st.keys())
StdOut.println(s + " " + st.get(s));
StdOut.println();
}
}