本文转自:http://www.cnblogs.com/qqzy168/archive/2013/08/03/3219201.html
本文由网络资料整理转载而来,如有问题,欢迎指正!
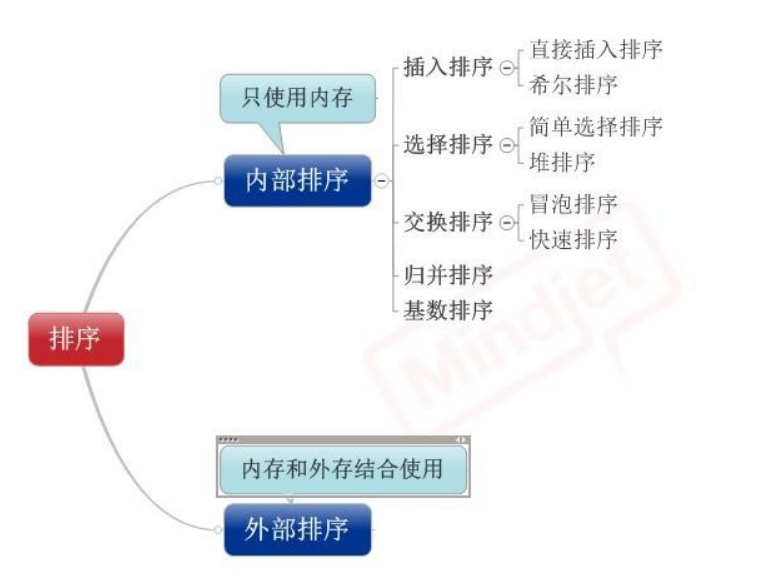
分类:
1)插入排序(直接插入排序、希尔排序)
2)交换排序(冒泡排序、快速排序)
3)选择排序(直接选择排序、堆排序)
4)归并排序
5)分配排序(基数排序)
所需辅助空间最多:归并排序
所需辅助空间最少:堆排序
平均速度最快:快速排序
不稳定:快速排序,希尔排序,堆排序。
先来看看 8种排序之间的关系:
1.直接插入排序
(1)基本思想:在要排序的一组数中,假设前面(n-1)[n>=2] 个数已经是排
好顺序的,现在要把第n 个数插到前面的有序数中,使得这 n个数
也是排好顺序的。如此反复循环,直到全部排好顺序。
(2)实例
(3)用java实现
[java] view plaincopy
1. package com.njue;
2.
3. publicclass insertSort {
4.
5. public insertSort(){
6. inta[]={49,38,65,97,76,13,27,49,78,34,12,64,5,4,62,99,98,54,56,17,18,23,
34,15,35,25,53,51};
7. int temp=0;
8. for(int i=1;i<a.length;i++){
9. int j=i-1;
10. temp=a[i];
11. for(;j>=0&&temp<a[j];j--){
12. a[j+1]=a[j]; //将大于temp 的值整体后移一个单位
13. }
14. a[j+1]=temp;
15. }
16.
17. for(int i=0;i<a.length;i++){
18. System.out.println(a[i]);
19. }
20. }
2. 希尔排序(最小增量排序)
(1)基本思想:算法先将要排序的一组数按某个增量 d(n/2,n为要排序数的个数)分成若
干组,每组中记录的下标相差 d.对每组中全部元素进行直接插入排序,然后再用一个较小
的增量(d/2)对它进行分组,在每组中再进行直接插入排序。当增量减到 1 时,进行直接
插入排序后,排序完成。
(2)实例:
(3)用java实现
[java] view plaincopy
1. publicclass shellSort {
2.
3. publicshellSort(){
4.
5. int a[]={1,54,6,3,78,34,12,45,56,100};
6. double d1=a.length;
7. int temp=0;
8.
9. while(true){
10. d1= Math.ceil(d1/2);
11. int d=(int) d1;
12. for(int x=0;x<d;x++){
13.
14. for(int i=x+d;i<a.length;i+=d){
15. int j=i-d;
16. temp=a[i];
17. for(;j>=0&&temp<a[j];j-=d){
18. a[j+d]=a[j];
19. }
20. a[j+d]=temp;
21. }
22. }
23.
24. if(d==1){
25. break;
26. }
27.
28. for(int i=0;i<a.length;i++){
29. System.out.println(a[i]);
30. }
31. }
3.简单选择排序
(1)基本思想:在要排序的一组数中,选出最小的一个数与第一个位置的数交换;
然后在剩下的数当中再找最小的与第二个位置的数交换,如此循环到倒数第二个数和最后一
个数比较为止。
(2)实例:
(3)用java实现
[java] view plaincopy
1. publicclass selectSort {
2.
3. public selectSort(){
4. int a[]={1,54,6,3,78,34,12,45};
5. int position=0;
6. for(int i=0;i<a.length;i++){
7. int j=i+1;
8. position=i;
9. int temp=a[i];
10. for(;j<a.length;j++){
11. if(a[j]<temp){
12. temp=a[j];
13. position=j;
14. }
15. }
16. a[position]=a[i];
17. a[i]=temp;
18. }
19.
20. for(int i=0;i<a.length;i++)
21. System.out.println(a[i]);
22. }
23. }
4, 堆排序
(1)基本思想:堆排序是一种树形选择排序,是对直接选择排序的有效改进。
堆的定义如下:具有n个元素的序列(h1,h2,...,hn),当且仅当满足(hi>=h2i,hi>=2i+1)或
(hi<=h2i,hi<=2i+1)(i=1,2,...,n/2)时称之为堆。在这里只讨论满足前者条件的堆。由堆的
定义可以看出,堆顶元素(即第一个元素)必为最大项(大顶堆)。完全二叉树可以很直观
地表示堆的结构。堆顶为根,其它为左子树、右子树。初始时把要排序的数的序列看作是一
棵顺序存储的二叉树,调整它们的存储序,使之成为一个堆,这时堆的根节点的数最大。然
后将根节点与堆的最后一个节点交换。然后对前面(n-1)个数重新调整使之成为堆。依此类
推,直到只有两个节点的堆,并对它们作交换,最后得到有 n个节点的有序序列。从算法
描述来看,堆排序需要两个过程,一是建立堆,二是堆顶与堆的最后一个元素交换位置。所
以堆排序有两个函数组成。一是建堆的渗透函数,二是反复调用渗透函数实现排序的函数。
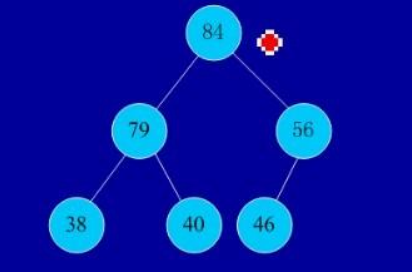
(2)实例:
初始序列:46,79,56,38,40,84
建堆:
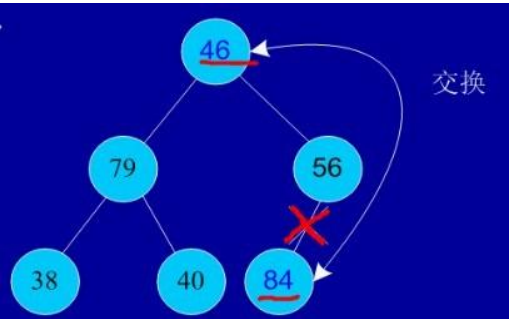
交换,从堆中踢出最大数
剩余结点再建堆,再交换踢出最大数
依次类推:最后堆中剩余的最后两个结点交换,踢出一个,排序完成。
(3)用java实现
[java] view plaincopy
1. import java.util.Arrays;
2.
3. publicclass HeapSort {
4. inta[]={49,38,65,97,76,13,27,49,78,34,12,64,5,4,62,99,98,54,56,17,18,23,
34,15,35,25,53,51};
5. public HeapSort(){
6. heapSort(a);
7. }
8.
9. public void heapSort(int[] a){
10. System.out.println("开始排序");
11. int arrayLength=a.length;
12. //循环建堆
13. for(int i=0;i<arrayLength-1;i++){
14. //建堆
15. buildMaxHeap(a,arrayLength-1-i);
16. //交换堆顶和最后一个元素
17. swap(a,0,arrayLength-1-i);
18. System.out.println(Arrays.toString(a));
19. }
20. }
21.
22.
23.
24. private void swap(int[] data, int i, int j) {
25. // TODO Auto-generated method stub
26. int tmp=data[i];
27. data[i]=data[j];
28. data[j]=tmp;
29. }
30.
31. //对data 数组从0到lastIndex 建大顶堆
32. privatevoid buildMaxHeap(int[] data, int lastIndex) {
33. // TODO Auto-generated method stub
34. //从lastIndex 处节点(最后一个节点)的父节点开始
35.
36. for(int i=(lastIndex-1)/2;i>=0;i--){
37. //k 保存正在判断的节点
38. int k=i;
39. //如果当前k节点的子节点存在
40. while(k*2+1<=lastIndex){
41. //k 节点的左子节点的索引
42. int biggerIndex=2*k+1;
43. //如果biggerIndex 小于lastIndex,即biggerIndex+1 代表的k 节点的
右子节点存在
44. if(biggerIndex<lastIndex){
45. //若果右子节点的值较大
46. if(data[biggerIndex]<data[biggerIndex+1]){
47. //biggerIndex 总是记录较大子节点的索引
48. biggerIndex++;
49. }
50. }
51.
52. //如果k节点的值小于其较大的子节点的值
53. if(data[k]<data[biggerIndex]){
54. //交换他们
55. swap(data,k,biggerIndex);
56. //将biggerIndex 赋予k,开始while 循环的下一次循环,重新保证k
节点的值大于其左右子节点的值
57. k=biggerIndex;
58. }else{
59. break;
60. }
61. }
62. }
63. }
64. }
5.冒泡排序
(1)基本思想:在要排序的一组数中,对当前还未排好序的范围内的全部数,自上而下对
相邻的两个数依次进行比较和调整,让较大的数往下沉,较小的往上冒。即:每当两相邻的
数比较后发现它们的排序与排序要求相反时,就将它们互换。
(2)实例:
(3)用java实现
[java] view plaincopy
1. publicclass bubbleSort {
2.
3. publicbubbleSort(){
4. inta[]={49,38,65,97,76,13,27,49,78,34,12,64,5,4,62,99,98,54,56,17,18,23
,34,15,35,25,53,51};
5. int temp=0;
6. for(int i=0;i<a.length-1;i++){
7. for(int j=0;j<a.length-1-i;j++){
8. if(a[j]>a[j+1]){
9. temp=a[j];
10. a[j]=a[j+1];
11. a[j+1]=temp;
12. }
13. }
14. }
15.
16. for(int i=0;i<a.length;i++){
17. System.out.println(a[i]);
18. }
19. }
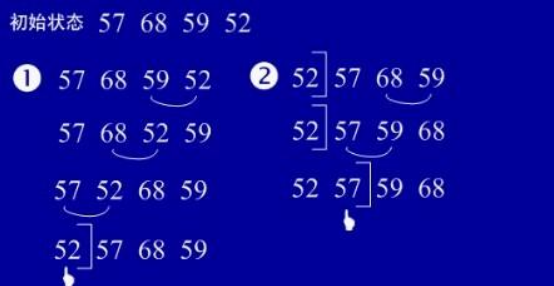
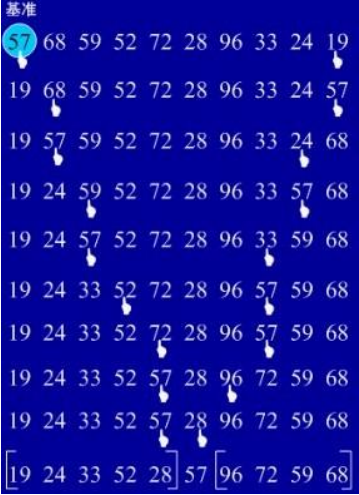
6.快速排序
(1)基本思想:选择一个基准元素,通常选择第一个元素或者最后一个元素,通过一趟扫描,
将待排序列分成两部分,一部分比基准元素小,一部分大于等于基准元素,此时基准元素在其
排好序后的正确位置,然后再用同样的方法递归地排序划分的两部分。
(2)实例:
(3)用java实现
[java] view plaincopy
1. publicclass quickSort {
2.
3. inta[]={49,38,65,97,76,13,27,49,78,34,12,64,5,4,62,99,98,54,56,17,18,23,34
,15,35,25,53,51};
4. publicquickSort(){
5. quick(a);
6. for(int i=0;i<a.length;i++){
7. System.out.println(a[i]);
8. }
9. }
10. publicint getMiddle(int[] list, int low, int high) {
11. int tmp =list[low]; //数组的第一个作为中轴
12. while (low < high){
13. while (low < high&& list[high] >= tmp) {
14. high--;
15. }
16.
17. list[low] =list[high]; //比中轴小的记录移到低端
18. while (low < high&& list[low] <= tmp) {
19. low++;
20. }
21.
22. list[high] =list[low]; //比中轴大的记录移到高端
23. }
24. list[low] = tmp; //中轴记录到尾
25. return low; //返回中轴的位置
26. }
27.
28. publicvoid _quickSort(int[] list, int low, int high) {
29. if (low < high){
30. int middle =getMiddle(list, low, high); //将list 数组进行一分
为二
31. _quickSort(list, low, middle - 1); //对低字表进行递归排
序
32. _quickSort(list,middle + 1, high); //对高字表进行递归排
序
33. }
34. }
35.
36. publicvoid quick(int[] a2) {
37. if (a2.length > 0) { //查看数组是否为空
38. _quickSort(a2,0, a2.length - 1);
39. }
40. }
41. }
7、归并排序
(1)基本排序:归并(Merge)排序法是将两个(或两个以上)有序表合并成一个新的有
序表,即把待排序序列分为若干个子序列,每个子序列是有序的。然后再把有序子序列合并
为整体有序序列。
(2)实例:
(3)用java实现
[java] view plaincopy
1. import java.util.Arrays;
2.
3. publicclass mergingSort {
4.
5. inta[]={49,38,65,97,76,13,27,49,78,34,12,64,5,4,62,99,98,54,56,17,18,23,34,1
5,35,25,53,51};
6.
7. publicmergingSort(){
8. sort(a,0,a.length-1);
9. for(int i=0;i<a.length;i++)
10. System.out.println(a[i]);
11. }
12.
13. publicvoid sort(int[] data, int left, int right) {
14. // TODO Auto-generatedmethod stub
15. if(left<right){
16. //找出中间索引
17. int center=(left+right)/2;
18. //对左边数组进行递归
19. sort(data,left,center);
20. //对右边数组进行递归
21. sort(data,center+1,right);
22. //合并
23. merge(data,left,center,right);
24. }
25.
26. }
27.
28. publicvoid merge(int[] data, int left, int center, int right) {
29. // TODO Auto-generatedmethod stub
30. int [] tmpArr=newint[data.length];
31. int mid=center+1;
32. //third 记录中间数组的索引
33. int third=left;
34. int tmp=left;
35. while(left<=center&&mid<=right){
36. //从两个数组中取出最小的放入中间数组
37. if(data[left]<=data[mid]){
38. tmpArr[third++]=data[left++];
39. }else{
40. tmpArr[third++]=data[mid++];
41. }
42.
43. }
44.
45. //剩余部分依次放入中间数组
46. while(mid<=right){
47. tmpArr[third++]=data[mid++];
48. }
49.
50. while(left<=center){
51. tmpArr[third++]=data[left++];
52. }
53.
54. //将中间数组中的内容复制回原数组
55. while(tmp<=right){
56. data[tmp]=tmpArr[tmp++];
57. }
58. System.out.println(Arrays.toString(data));
59. }
60. }
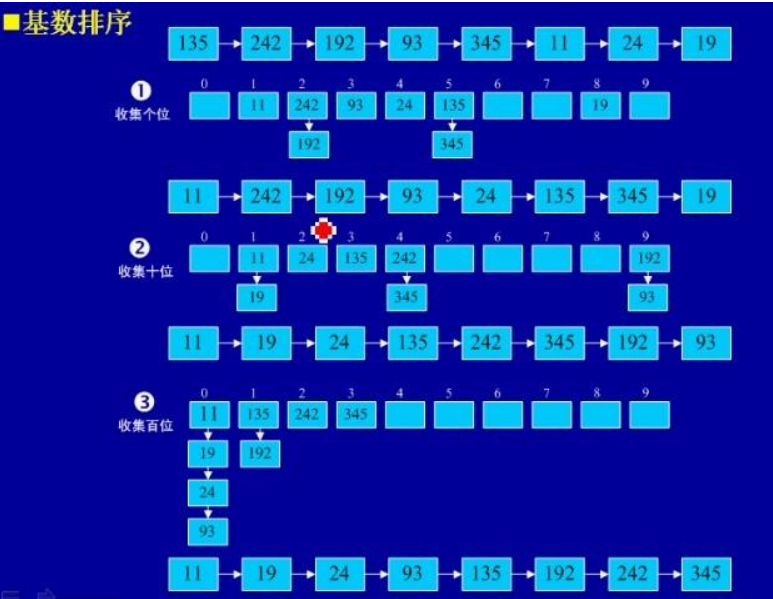
8、基数排序
(1)基本思想:将所有待比较数值(正整数)统一为同样的数位长度,数位较短的数前面
补零。然后,从最低位开始,依次进行一次排序。这样从最低位排序一直到最高位排序完成
以后,数列就变成一个有序序列。
(2)实例:
(3)用java实现
[java] view plaincopy
1. import java.util.ArrayList;
2. import java.util.List;
3.
4. public class radixSort {
5. inta[]={49,38,65,97,76,13,27,49,78,34,12,64,5,4,62,99,98,54,101,56,17,18
,23,34,15,35,25,53,51};
6. public radixSort(){
7. sort(a);
8. for(inti=0;i<a.length;i++){
9. System.out.println(a[i]);
10. }
11. }
12. public void sort(int[] array){
13. //首先确定排序的趟数;
14. int max=array[0];
15. for(inti=1;i<array.length;i++){
16. if(array[i]>max){
17. max=array[i];
18. }
19. }
20. int time=0;
21. //判断位数;
22. while(max>0){
23. max/=10;
24. time++;
25. }
26.
27. //建立10个队列;
28. List<ArrayList> queue=newArrayList<ArrayList>();
29. for(int i=0;i<10;i++){
30. ArrayList<Integer>queue1=new ArrayList<Integer>();
31. queue.add(queue1);
32. }
33.
34. //进行time 次分配和收集;
35. for(int i=0;i<time;i++){
36. //分配数组元素;
37. for(intj=0;j<array.length;j++){
38. //得到数字的第time+1 位数;
39. int x=array[j]%(int)Math.pow(10,i+1)/(int)Math.pow(10, i);
40. ArrayList<Integer>queue2=queue.get(x);
41. queue2.add(array[j]);
42. queue.set(x, queue2);
43. }
44. int count=0;//元素计数器;
45. //收集队列元素;
46. for(int k=0;k<10;k++){
47. while(queue.get(k).size()>0){
48. ArrayList<Integer>queue3=queue.get(k);
49. array[count]=queue3.get(0);
50. queue3.remove(0);
51. count++;
52. }
53. }
54. }
55. }
56. }
import java.io.*;
public class Paixu {
// 冒泡排序法
public void Maopao(int a[]) {
for (int i = 1; i < a.length; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < a.length - i; j++) {
if (a[j] > a[j + 1]) {
int temp = a[j + 1];
a[j + 1] = a[j];
a[j] = temp;
}
}
}
System.out.println(" " + "采用冒泡排序法:");
}
// 插入排序法:
public void Charu(int a[]) {
for (int i = 1; i < a.length; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < i; j++) {
if (a[j] > a[i]) {
int temp = a[i];
for (int k = i; k > j; k--) {
a[k] = a[k--];
}
a[j] = temp;
}
}
}
System.out.println(" " + "采用插入排序法:");
}
// 选择排序法:
public void Xuanze(int a[]) {
for (int i = 0; i < a.length; i++) {
int position = i;
for (int j = i + 1; j < a.length; j++) {
if (a[position] > a[j]) {
int temp = a[position];
a[position] = a[j];
a[j] = temp;
}
}
}
System.out.println(" " + "采用选择排序法:");
}
public void Print(int a[]) {
System.out.println("从小到大排序结果为:");
for (int i = 0; i < a.length; i++) {
System.out.print(a[i] + ",");
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
int a[] = new int[5];
Paixu px = new Paixu();
BufferedReader buf = new BufferedReader(
new InputStreamReader(System.in));
System.out.println("请输入五个整数:");
for (int i = 0; i < a.length; i++) {
try {
String s = buf.readLine();
int j = Integer.parseInt(s);
a[i] = j;
} catch (Exception e) {
System.out.println("出错了!必须输入整数,请重新输入!");
i--;
}
}
System.out.println("您输入的整数依次为:");
for (int i = 0; i < a.length; i++) {
System.out.print(a[i] + ",");
}
System.out.println(" " + "-------------");
px.Maopao(a); // 调用冒泡算法
px.Print(a);
System.out.println(" " + "-------------");
px.Charu(a); // 调用插入算法
px.Print(a);
System.out.println(" " + "-------------");
px.Xuanze(a); // 调用选择算法
px.Print(a);
}
}
Java实现二分查找
现在复习下
import java.util.*;
public class BinarySearch {
public static void main(String[] args) { ArrayList<Integer> a = new ArrayList<Integer>(); addIntegerInSequence(a,1,10); print(a); int pos = binarySearch(a,10); if ( pos != -1 ) { System.out.print("Element found: " + pos); } else { System.out.print("Element not found"); } }
/** * 二分查找法 * @param a * @param value 待查找元素 * @return */ public static int binarySearch(ArrayList<Integer> a, int value) { int size = a.size(); int low = 0 , high = size - 1; int mid; while (low <= high) { mid = (low + high) / 2; if ( a.get(mid) < value ) { low = low + 1; } else if ( a.get(mid) > value ) { high = high - 1; } else { return mid; } } return -1; }
/** * 填充顺序元素到数组 * @param a * @param begin 开始元素 * @param size 大小 */ public static void addIntegerInSequence(ArrayList<Integer> a, int begin, int size) { for (int i = begin; i < begin + size; i++) { a.add(i); } }
/** * 打印数组 * @param a */ public static void print(ArrayList<Integer> a) { Iterator<Integer> i = a.iterator(); while (i.hasNext()) { System.out.print(i.next() + " "); } System.out.println(""); }
}
/////
JAVA 库中的二分查找使用非递归方式实现,返回结果与前面写的有所不同:找不到时返回的是负数,但不一定是-1
private static int binarySearch0(int[] a, int fromIndex, int toIndex,
int key) {
int low = fromIndex;
int high = toIndex - 1;
while (low <= high) {
int mid = (low + high) >>> 1;
int midVal = a[mid];
if (midVal < key)
low = mid + 1;
else if (midVal > key)
high = mid - 1;
else
return mid; // key found
}
return -(low + 1); // key not found.
}