今天要爬取的网页是虎嗅网
我们将完成如下几个步骤:
- 创建一个新的Scrapy工程
- 定义你所需要要抽取的Item对象
- 编写一个spider来爬取某个网站并提取出所有的Item对象
- 编写一个Item Pipline来存储提取出来的Item对象
创建Scrapy工程
在任何目录下执行如下命令
scrapy startproject coolscrapy
cd coolscrapy
scrapy genspider huxiu huxiu.com
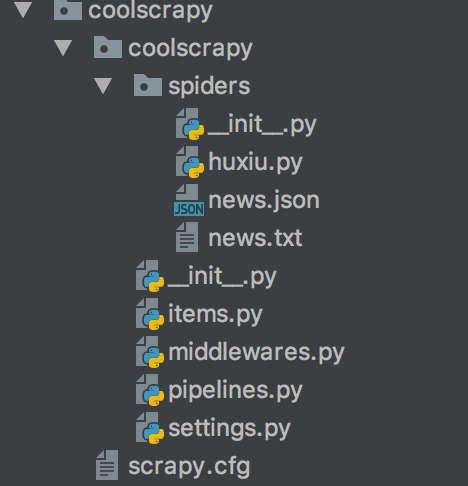
我们看看创建的工程目录结构:(news.json,news.txt是最后结果保存的)
定义Item
我们通过创建一个scrapy.Item类,并定义它的类型为scrapy.Field的属性, 我们准备将虎嗅网新闻列表的名称、链接地址和摘要爬取下来。
1 import scrapy 2 3 4 class CoolscrapyItem(scrapy.Item): 5 # define the fields for your item here like: 6 # name = scrapy.Field() 7 title = scrapy.Field() #标题 8 link = scrapy.Field() #链接 9 desc = scrapy.Field() #简述 10 posttime = scrapy.Field() #发布时间
编写Spider
蜘蛛就是你定义的一些类,Scrapy使用它们来从一个domain(或domain组)爬取信息。 在蜘蛛类中定义了一个初始化的URL下载列表,以及怎样跟踪链接,如何解析页面内容来提取Item。
定义一个Spider,只需继承scrapy.Spider类并定于一些属性:
- name: Spider名称,必须是唯一的
- start_urls: 初始化下载链接URL
- parse(): 用来解析下载后的Response对象,该对象也是这个方法的唯一参数。 它负责解析返回页面数据并提取出相应的Item(返回Item对象),还有其他合法的链接URL(返回Request对象)。
我们打开在coolscrapy/spiders文件夹下面的huxiu.py,内容如下:
1 # -*- coding: utf-8 -*- 2 import scrapy 3 from coolscrapy.items import CoolscrapyItem 4 5 class HuxiuSpider(scrapy.Spider): 6 name = "huxiu" 7 allowed_domains = ["huxiu.com"] 8 start_urls = ['http://huxiu.com/index.php'] 9 10 def parse(self, response): 11 items = [] 12 data = response.xpath('//div[@class="mod-info-flow"]/div/div[@class="mob-ctt"]') 13 for sel in data: 14 item = CoolscrapyItem() 15 if len(sel.xpath('./h2/a/text()').extract()) <= 0: 16 item['title'] = 'No title' 17 else: 18 item['title'] = sel.xpath('./h2/a/text()').extract()[0] 19 if len(sel.xpath('./h2/a/@href').extract()) <= 0: 20 item['link'] = 'link在哪里!!!!!!!!' 21 else: 22 item['link'] = sel.xpath('./h2/a/@href').extract()[0] 23 url = response.urljoin(item['link']) 24 if len(sel.xpath('div[@class="mob-sub"]/text()').extract()) <= 0: 25 item['desc'] = '啥也没有哦...' 26 else: 27 item['desc'] = sel.xpath('div[@class="mob-sub"]/text()').extract()[0] 28 #item['posttime'] = sel.xpath('./div[@class="mob-author"]/span/@text()').extract()[0] 29 print(item['title'], item['link'], item['desc']) 30 items.append(item) 31 return items
现在可以在终端运行了,是可以打印每个新闻信息的。
scrapy crawl huxiu
如果一切正常,应该可以打印出每一个新闻
处理链接
如果想继续跟踪每个新闻链接进去,看看它的详细内容的话,那么可以在parse()方法中返回一个Request对象, 然后注册一个回调函数来解析新闻详情。
下面继续编写huxiu.py
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*- import scrapy from coolscrapy.items import CoolscrapyItem class HuxiuSpider(scrapy.Spider): name = "huxiu" allowed_domains = ["huxiu.com"] start_urls = ['http://huxiu.com/index.php'] def parse(self, response): #items = [] data = response.xpath('//div[@class="mod-info-flow"]/div/div[@class="mob-ctt"]') for sel in data: item = CoolscrapyItem() if len(sel.xpath('./h2/a/text()').extract()) <= 0: item['title'] = 'No title' else: item['title'] = sel.xpath('./h2/a/text()').extract()[0] if len(sel.xpath('./h2/a/@href').extract()) <= 0: item['link'] = 'link在哪里!!!!!!!!' else: item['link'] = sel.xpath('./h2/a/@href').extract()[0] url = response.urljoin(item['link']) if len(sel.xpath('div[@class="mob-sub"]/text()').extract()) <= 0: item['desc'] = '啥也没有哦...' else: item['desc'] = sel.xpath('div[@class="mob-sub"]/text()').extract()[0] #item['posttime'] = sel.xpath('./div[@class="mob-author"]/span/@text()').extract()[0] print(item['title'], item['link'], item['desc']) #items.append(item) #return items yield scrapy.Request(url,callback=self.parse_article) def parse_article(self,response): detail = response.xpath('//div[@class="article-wrap"]') item = CoolscrapyItem() item['title'] = detail.xpath('./h1/text()')[0].extract().strip() item['link'] = response.url item['posttime'] = detail.xpath('./div/div[@class="column-link-box"]/span[1]/text()')[0].extract() print(item['title'],item['link'],item['posttime']) yield item
现在parse只提取感兴趣的链接,然后将链接内容解析交给另外的方法去处理了。 你可以基于这个构建更加复杂的爬虫程序了。
导出抓取数据
最简单的保存抓取数据的方式是使用json格式的文件保存在本地,像下面这样运行:
scrapey crawl huxiu -o items.json
一般构建爬虫系统,建议自己编写Item Pipeline
数据保存为TXT/JSON/MySql
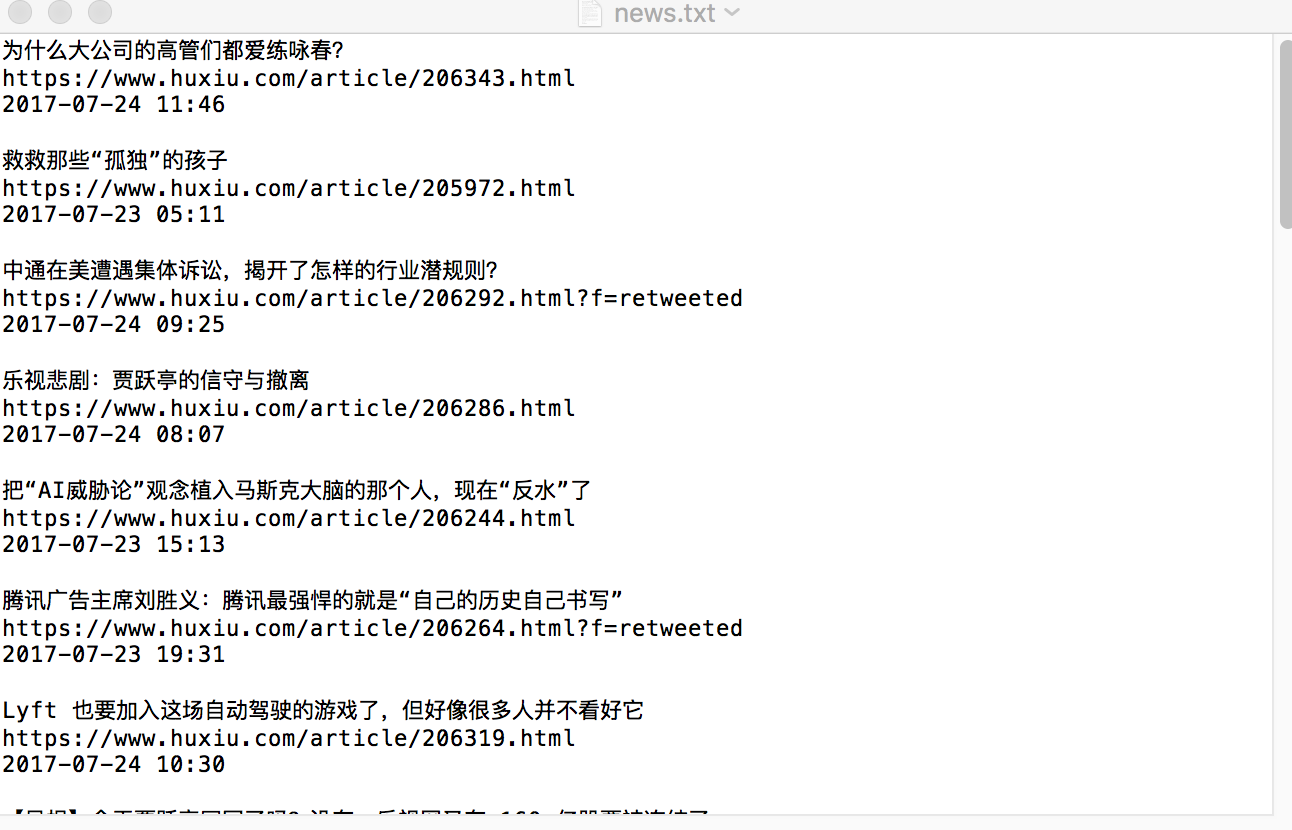
1.数据保存为TXT
打开Pipeline.py
1 import codecs 2 import os 3 import json 4 import pymysql 5 6 class CoolscrapyPipeline(object):#需要在setting.py里设置'coolscrapy.piplines.CoolscrapyPipeline':300 7 def process_item(self, item, spider): 8 # 获取当前工作目录 9 base_dir = os.getcwd() 10 fiename = base_dir + '/news.txt' 11 # 从内存以追加的方式打开文件,并写入对应的数据 12 with open(fiename, 'a') as f: 13 f.write(item['title'] + ' ') 14 f.write(item['link'] + ' ') 15 f.write(item['posttime'] + ' ') 16 return item
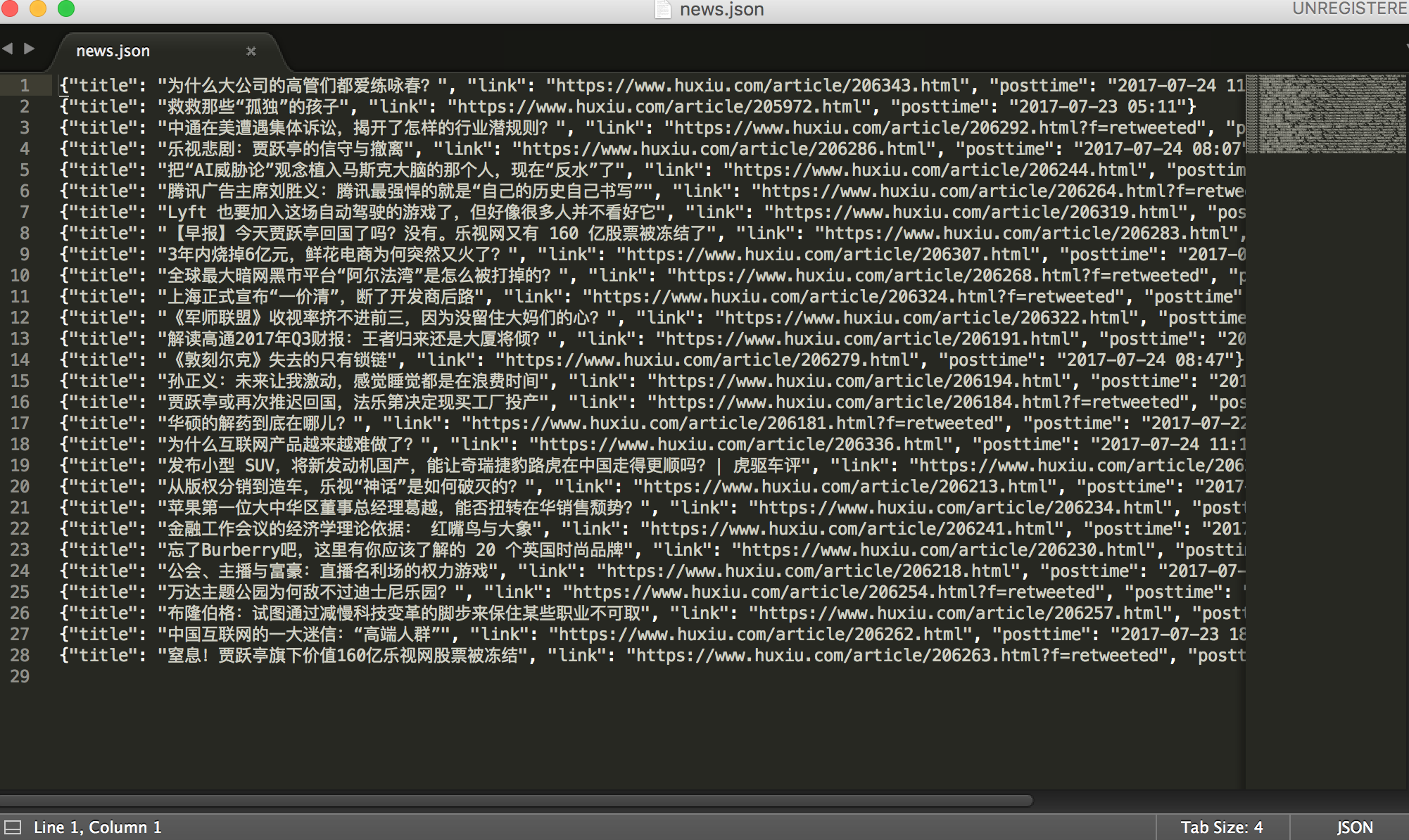
2.保存为json格式
在Pipeline.py里面新建一个类
1 #以下两种写法保存json格式,需要在settings里面设置'coolscrapy.pipelines.JsonPipeline': 200 2 3 class JsonPipeline(object): 4 def __init__(self): 5 self.file = codecs.open('logs.json', 'w', encoding='utf-8') 6 def process_item(self, item, spider): 7 line = json.dumps(dict(item), ensure_ascii=False) + " " 8 self.file.write(line) 9 return item 10 def spider_closed(self, spider): 11 self.file.close() 12 13 14 class JsonPipeline(object): 15 def process_item(self, item, spider): 16 base_dir = os.getcwd() 17 filename = base_dir + '/news.json' 18 # 打开json文件,向里面以dumps的方式吸入数据 19 # 注意需要有一个参数ensure_ascii=False ,不然数据会直接为utf编码的方式存入比如 20 # :“/xe15” 21 with codecs.open(filename, 'a') as f: 22 line = json.dumps(dict(item), ensure_ascii=False) + ' ' 23 f.write(line) 24 return item
上面是两种写法,都是一样的
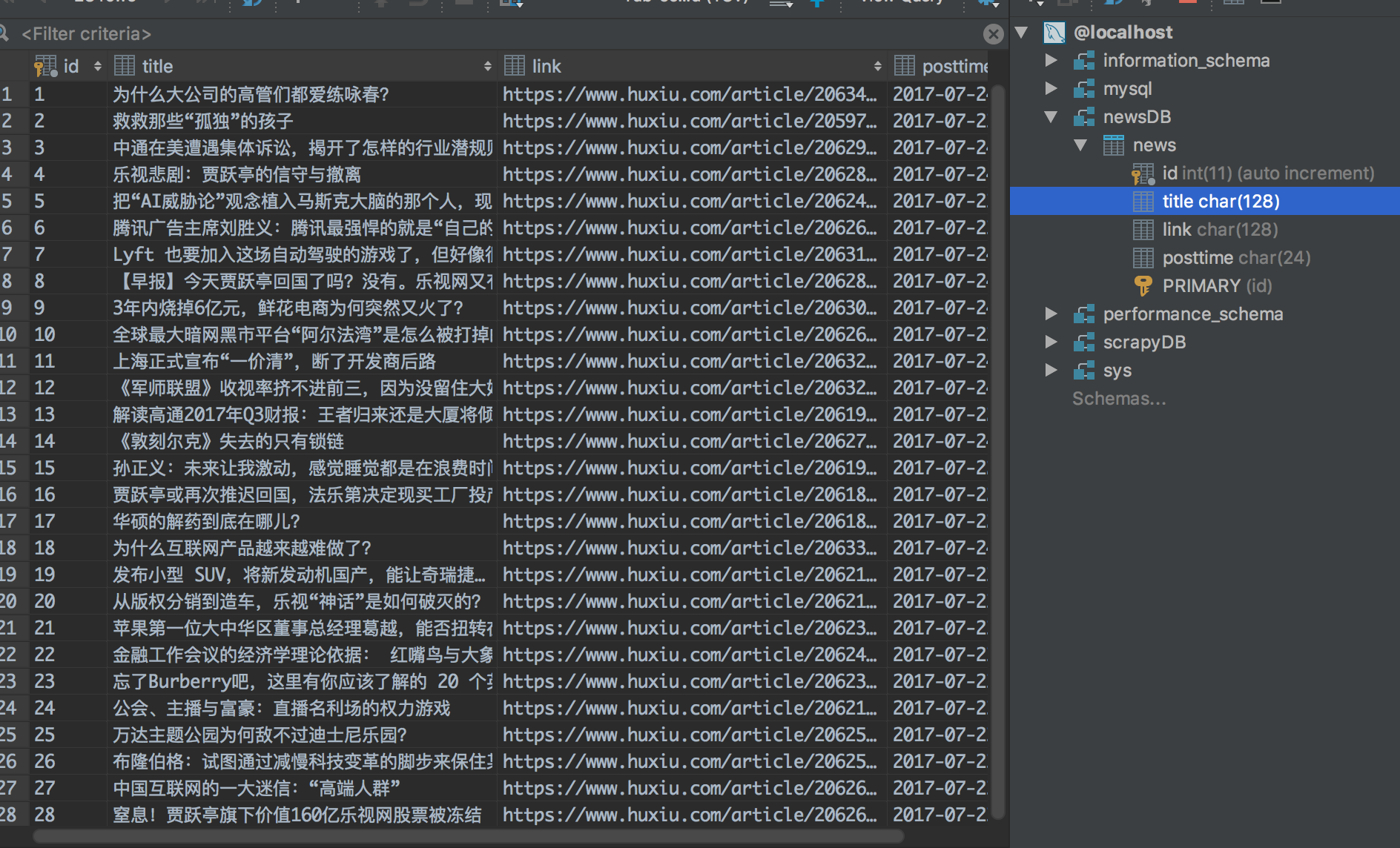
3.保存到mysql
保存到数据库需要建立表格newsDB,详情请参考http://www.cnblogs.com/freeman818/p/7223161.html
在Pipeline.py里面新建一个类
1 class mysqlPipeline(object): 2 def process_item(self,item,spider): 3 ''' 4 将爬取的信息保存到mysql 5 ''' 6 # 将item里的数据拿出来 7 title = item['title'] 8 link = item['link'] 9 posttime = item['posttime'] 10 11 # 和本地的newsDB数据库建立连接 12 db = pymysql.connect( 13 host='localhost', # 连接的是本地数据库 14 user='root', # 自己的mysql用户名 15 passwd='123456', # 自己的密码 16 db='newsDB', # 数据库的名字 17 charset='utf8mb4', # 默认的编码方式: 18 cursorclass=pymysql.cursors.DictCursor) 19 try: 20 # 使用cursor()方法获取操作游标 21 cursor = db.cursor() 22 # SQL 插入语句 23 sql = "INSERT INTO NEWS(title,link,posttime) 24 VALUES ('%s', '%s', '%s')" % (title,link,posttime) 25 # 执行SQL语句 26 cursor.execute(sql) 27 # 提交修改 28 db.commit() 29 finally: 30 # 关闭连接 31 db.close() 32 return item
编写Settings.py
我们需要在Settings.py将我们写好的PIPELINE添加进去,
scrapy才能够跑起来
这里只需要增加一个dict格式的ITEM_PIPELINES,
数字value可以自定义,数字越小的优先处理
1 ITEM_PIPELINES={'coolscrapy.pipelines.CoolscrapyPipeline':300, 2 'coolscrapy.pipelines.JsonPipeline': 200, 3 'coolscrapy.pipelines.mysqlPipeline': 100, 4 }
下面让程序跑起来
scrape crawl huxiu
看看结果:
好了,这次就到这里。代码要自己敲才会慢慢熟练。