find命令把匹配到的文件传递给xargs命令,而xargs命令每次只获取一部分文件而不是全部
xargs要处理的文件如果不是在结尾,需要加上 -i这个参数
xargs常见命令参数
args:xargs的默认命令是echo,空格是默认定界符。 默认替换符号是{}
-I {}批定了替换字符串,表示文件内容,能循环按要求替换相应的参数 使用-I指定一个替换字符串{},这个字符串在xargs扩展时会被替换掉,
当-I与xargs结合使用,每一个参数命令都会被执行一次:
-n num 后面加次数,表示命令在执行的时候一次用的argument的个数,默认是用所有的
-d 自定义定界符
常用的命令展示
多行内容的单输出且每行3个
[root@localhost ftl]# cat /home/omc/ftl/logs.txt |xargs -n3
查找系统中的每一个普通文件,然后使用xargs命令来测试它们分别属于哪类文件
[root@localhost log]# find /home/omc/ -maxdepth 1 -user root -type f | xargs file {}
在/var/log/下查找log文件,复制文件到/home/omc/ftl且把结果保存到/home/omc/ftl/logs.txt文件中
[root@localhost log]# find /var/log/*.log -type f | xargs -i cp {} /home/omc/ftl
[root@localhost log]# ll -ltr /home/omc/ftl
[root@localhost log]# find /var/log/*.log -type f > /home/omc/ftl/logs.txt
[root@localhost log]# ll /home/omc/ftl/logs.txt
删除 /home/omc/ftl/下的log文件
[root@localhost ftl]# ll *.log |xargs rm -rf {} 【错误】
[root@localhost ftl]# ls *.log |xargs rm -rf {} 【正确】
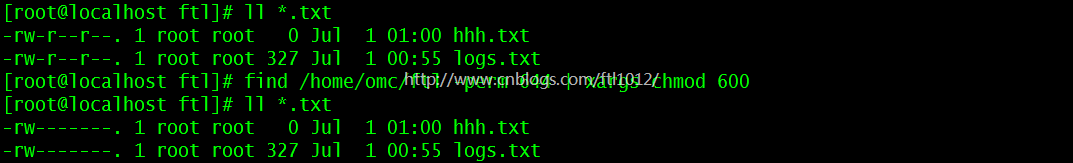
在当前目录下查找所有用户权限644的文件,并更改权限600
[root@localhost ftl]# ll *.txt [root@localhost ftl]# find /home/omc/ftl -perm 644 | xargs chmod 600 [root@localhost ftl]# ll *.txt
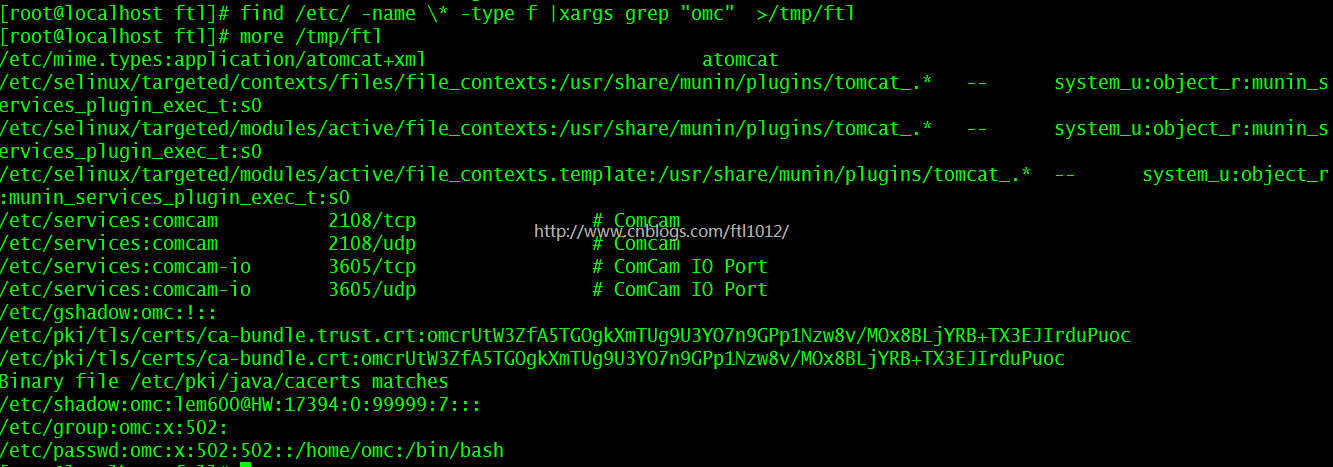
用grep命令在当前目录下的所有普通文件中搜索omc这个词
find /etc/ -name * -type f |xargs grep "omc" >/tmp/ftl
==>find /etc/ -name "*" -type f |xargs grep "omc" >/tmp/ftl
使用-i参数默认的前面输出用{}代替,-I参数可以指定其他代替字符,如例子中的[]
find /var/ -name "*.log" |xargs -I [] cp [] /tmp/ 【xargs 默认用是i表示{},用I可以替换符号】
ll -ltr /tmp/ | more 5
xargs的-p参数的使用
find . -name "*.log" |xargs -p -i cp {} ../ltesig/
【-p参数会提示让你确认是否执行后面的命令,y执行,n不执行】
利用for循环实现和xargs同样的效果
find /home/omc/ -name *.txt | xargs -i cp {} /home/omc/h
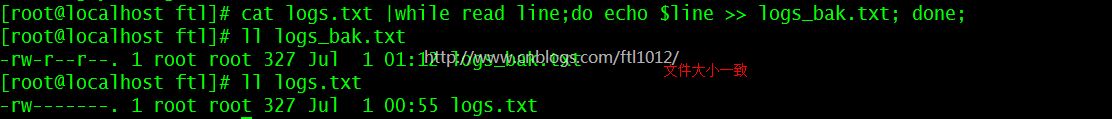
cat logs.txt |while read line;do echo $line >> logs_bak.txt; done;
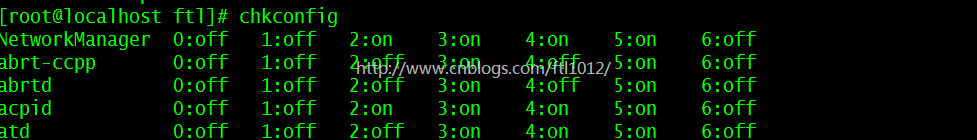
利用xargs关闭不常用的系统启动软件
chkconfig | awk '{print $1}' | grep -Ev "sshd|network|crond|sysstat|rsyslog" | xargs -I{} chkconfig {} off
xargs总结示范:
find . -name "*.log" |xargs -p -i cp {} ../ltesig/ 【正确】
find . -name "*.log" |xargs -p cp {} ../ltesig/ 【错误】
find . -type f -print | xargs file 【正确】
find . -type f -print | xargs rm {} 【错误】
总结一下:如果命令后面可以跟内容,且没有目的路径的时候,可以省略-i,否则得加上