Asyncio进行异步IO请求操作:
1. @asyncio.coroutine 装饰任务函数
2. 函数内配合yield from 和装饰器@asyncio.coroutine 配合使用【固定格式】
3. loop = asyncio.get_event_loop()
loop.run_until_complete(asyncio.gather(*tasks)) # 接受异步IO的任务并异步执行任务
实例一:
异步IO: 协程机制 + 回调函数
import asyncio
@asyncio.coroutine # 装饰任务函数
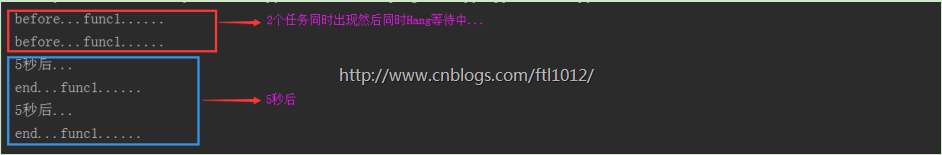
def func1():
print('before...func1......')
# yield from 和装饰器@asyncio.coroutine 配合使用【固定格式】
yield from asyncio.sleep(5) # 必须写asyncio才表示异步IO执行5秒,time.sleep(5)不生效
print('5秒后...')
print('end...func1......')
tasks = [func1(), func1()]
# 事件循环: 对涉及异步,协成,阻塞等IO操作时进行事件的循环操作
loop = asyncio.get_event_loop()
loop.run_until_complete(asyncio.gather(*tasks)) # 接受异步IO的任务并异步执行任务
loop.close()
AsyncIO缺点:
不支持HTTP请求,也就是说不能直接发送URL过去进行访问
支持TCP请求,也就是说可以发送【IP+端】进行访问
注:HTTP在TCP之上
基于asyncio实现利用TCP模拟HTTP请求
import asyncio
# 基于asyncio实现利用TCP模拟HTTP请求[asyncio实际上不支持HTTP请求]
@asyncio.coroutine
def fetch_async(host, url='/'):
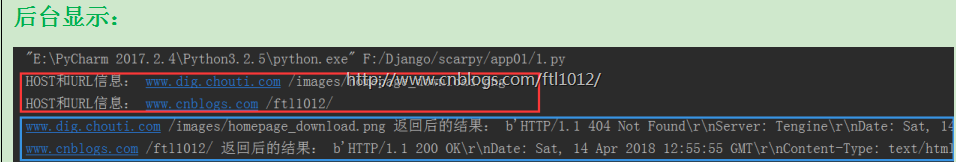
print('HOST和URL信息:', host, url)
# reader: 用于读取连接的信息
# writer: 用于给服务器写信息
reader, writer = yield from asyncio.open_connection(host, 80)
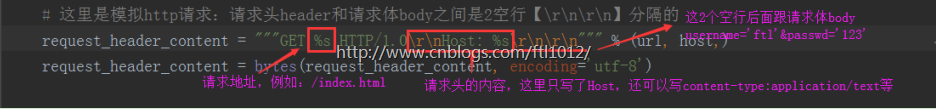
# 基于TCP模拟的HTTP请求:请求头header和请求体body之间是2空行【
】分隔的
request_header_content = """GET %s HTTP/1.0
Host: %s
""" % (url, host,)
request_header_content = bytes(request_header_content, encoding='utf-8') # 字符串转换字节
writer.write(request_header_content) # 准备发送数据给服务器
# drain: 英文翻译为喝光,这里作发送完成理解
yield from writer.drain() # 发送数据给服务器,此时可能会阻塞执行个请求,考虑数据量大等原因
text = yield from reader.read() # 等待返回的数据,text就是先收到回复的请求完成后等待其他返回
print(host,url,'返回后的结果:', text)
writer.close() # 关闭流
tasks = [
fetch_async('www.cnblogs.com', '/ftl1012/'),
fetch_async('www.dig.chouti.com', '/images/homepage_download.png')
]
loop = asyncio.get_event_loop()
results = loop.run_until_complete(asyncio.gather(*tasks))
loop.close()
基于TCP模拟HTTP详解: