一. 多项目开发:
1. 建立项目:
两种方式:
(1) 项目和解决方案一起建立

(2) 先建立解决方案,然后添加项目

2. 有需要用到的公用类,建立类库,其他项目引用时,先添加引用,在命名控件引用:
(1) 添加类库

(2) 添加引用:
(3) 引用类方法:

3. 配置文件读取:
只有读取主项目(当前运行项目)的config才起作用
4. 调用第三方类,直接添加引用即可,如需查询具体的代码,可反编译;
二、 索引器:
索引器没有名字,索引器的内部本质 this[参数] {get; set;}
索引器不仅能根据数字索引还能根据字符串索引;
允许多个索引器参数;
三、 密封类和静态类:
1、 密封类无法创建子类:sealed
2、 静态类: static 无法创建子类,只能声明static成员;
3. static 成员: 可以在静态类中,也可以被非静态类创建,使用时:类名.方法()
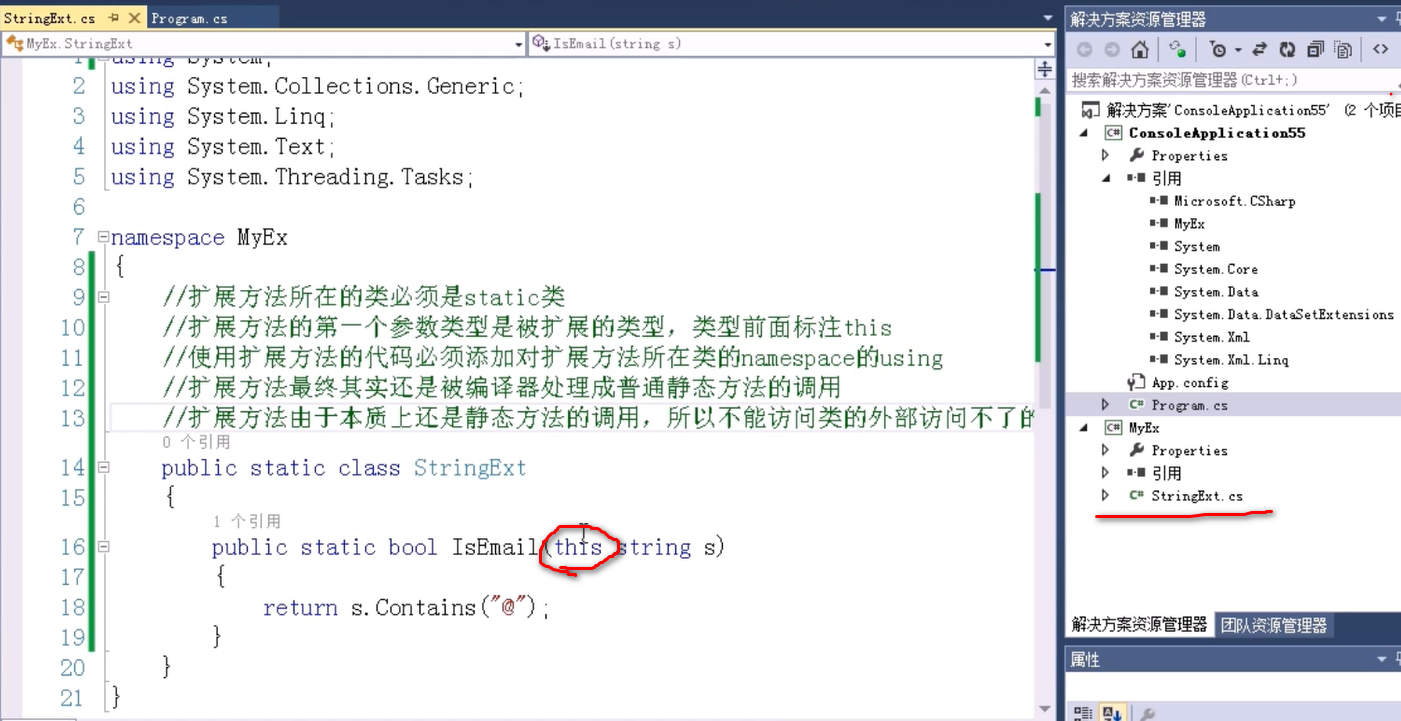
4. string 类扩展方法:



四、 委托:
1、 delegate 类型 名称() 使用时先实例化,然后传入参数;
namespace ConsoleApp12
{
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
MyDel myDel = new MyDel(GetName);
// 或者 MyDel myDel =GetName;
myDel("chen", 1);
}
static string GetName(string name,int num)
{
return name + num;
}
}
delegate string MyDel(string name, int num);
}
2、 一般平时开发时,不需要自定义委托;
.NET内置泛型委托: func 和action : 对于没有返回值的委托用Action ,所有有返回值的委托用Func ,返回值在最后一个
static void Main(string[] args) { Action a1 = F1; Action<string> a2 = F2; Func<string,int> f1 = F3; } static void F1() { Console.WriteLine("F1"); } static void F2(string s1) { Console.WriteLine("F2"); } static int F3(string name) { return 1; }
3、 匿名方法:
匿名方法就是没有名字的方法 MyDelegate p=delegate(int s) {s=10}
五、 ref 和out

六、 lambda 表达式

练习1:
static void Main(string[] args) { //无返回值 Action<int> a1 = delegate (int i) { Console.WriteLine(i); }; Action<int> a2 = (int i)=>{ Console.WriteLine(i);}; Action<int> a3 = i => { Console.WriteLine(i); }; //只有一个参数 a1(3333); a2(4444); //有返回值 Func<int, string, bool> f1 = delegate (int i, string name) { return true; }; Func<int, string, bool> f2 = (int i, string name)=> { return true; }; Func<int, string, bool> f3 = (i, name) => { return true; }; Func<int, string, bool> f4 = (i, name) => true; //有返回值且只有一行代码,可以省略return 和大括号 f1(1, "chen"); f2(1, "chen"); Console.ReadKey(); }
练习2:
static void Main(string[] args) { int[] nums = new int[] { 3, 88, 6, 9 }; //1. // int m = GetMax(nums, compareInt); //2/ // Func<int, int, bool> f = delegate (int i1, int i2) { return i1 > i2; }; // int m=GetMax(nums,f) //3. int m = GetMax(nums, (i1, i2) => i1 > i2 ); Console.WriteLine(m); Console.ReadKey(); } static bool compareInt(int i1,int i2) { return i1 > i2; } static T GetMax<T>(T[] objs,Func<T,T,bool> compareFunc) { T max = objs[0]; for (int i = 0; i < objs.Length; i++) { if(compareFunc(objs[i],max)) max = objs[i]; } return max; }
练习3:
static class JiHeExt { public static IEnumerable<T> MyWhere<T>(this IEnumerable<T> data,Func<T,bool> func) { List<T> resultList = new List<T>(); foreach(T item in data) { if (func(item)) { resultList.Add(item); } } return resultList; } } class Program { static void Main(string[] args) { int[] nums = new int[] { 3, 88, 6, 9 }; IEnumerable<int> r1 = nums.MyWhere(i => i > 10); foreach (int item in r1) { Console.WriteLine(item); } Console.ReadKey(); } }
练习4:
static void Main(string[] args) { List<int> list1 = new List<int> { 1, 2,3,8,16,99 }; // IEnumerable<int> data= list1.Where(i => i > 10); //where 对数据按照lambda表达式进行过滤 IEnumerable<string> data = list1.Select(i => i +"你好"); //select 则对集合中的数据进行处理,生成一个新的集合 foreach (var item in data) { Console.WriteLine(item); } Console.ReadLine(); }
练习5:
class Program { static void Main(string[] args) { Person[] p = new Person[] { new Person{Name="chen",Age=12}, new Person{Name="chen2",Age=24}, new Person{Name="chen3",Age=12} }; int e = p.Sum(i => i.Age);
List<Person> ps = p.ToList();
Person[] ps4 = p.ToArray();
Console.WriteLine(e); Console.ReadKey(); } } class Person { public string Name { get; set; } public int Age { get; set; } }
六、扩展方法:

七、委托组合:
class Program { static void Main(string[] args) { Mydel d1 = F1; Mydel d2 = F2; Mydel d3 = F3; Mydel d4 = d1 + d2 + d3; d4(8); // Console.WriteLine(d4); Console.ReadKey(); } static void F1(int i) { Console.WriteLine("我是F1:"+i); } static void F2(int i) { Console.WriteLine("我是F2:" + i); } static void F3(int i) { Console.WriteLine("我是F3:" + i); } } delegate void Mydel(int i);
八、事件:
class Person { private int age; public int Age { get { return this.age; } set { this.age = value; if(value%12==0) { if(OnBenMingNian!=null) { OnBenMingNian(); //调用添加的组合的方法 } } } } public event Action OnBenMingNian; // event 委托类型 事件的名字 // public Action OnBenMingNian;//加上event就是事件,不加event就是委托; }
class Program { static void Main(string[] args) { Person p1 = new Person(); p1.OnBenMingNian += BMN;//方法的参数返回值要和事件的委托一致 p1.Age = 5; Console.WriteLine(p1.Age); p1.Age = 24; Console.WriteLine(p1.Age); p1.Age = 55; Console.WriteLine(p1.Age); // Console.WriteLine(d4); Console.ReadKey(); } static void BMN() { Console.WriteLine("本命年到了"); } }
事件和委托的关系:反编译看,事件是由一个私有的委托变量和add 和remove方法组成的
事件、索引器、属性本质上都是方法;面试题:接口中可以定义什么? 接口中可以定义方法,事件,属性和索引,因为他们本质上都是方法