0 Reference
NoSQL论文
在 Stuttgart Media 大学的 Christof Strauch 历时8个月(2010年6月-2011年2月)完成了一篇150页长的NoSQL相关的论文, 对NoSQL的各个方面做了探讨
http://www.christof-strauch.de/nosqldbs.pdf
分布式系统领域经典论文翻译集
http://duanple.blog.163.com/blog/static/709717672011330101333271/
2010 NoSQL Summer Reading List
http://blog.nosqlfan.com/html/1647.html
http://www.empiricalreality.com/2010/09/22/2010-nosql-summer-reading-list/
NoSQL技术综述
Distributed Algorithms in NoSQL Databases
http://highlyscalable.wordpress.com/2012/09/18/distributed-algorithms-in-nosql-databases/
NOSQL Patterns
http://horicky.blogspot.com/2009/11/nosql-patterns.html
---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 起源和历史
1.1 Goolge为一切的开始
Google created a full mechanism that included a distributed filesystem, a column-family-oriented data store, a distributed coordination system, and a MapReduce-based parallel algorithm execution environment. Graciously enough, Google published and presented a series of papers explaining some of the key pieces of its infrastructure. The most important of these publications are as follows:
Sanjay Ghemawat, Howard Gobioff, and Shun-Tak Leung. “The Google File System”; pub. 19th ACM Symposium on Operating Systems Principles, Lake George, NY, October 2003.URL: http://labs.google.com/papers/gfs.html
Jeffrey Dean and Sanjay Ghemawat. “MapReduce: Simplifi ed Data Processing on Large Clusters”; pub. OSDI’04: Sixth Symposium on Operating System Design and Implementation, San Francisco, CA, December 2004. URL: http://labs.google.com/papers/mapreduce.html
Fay Chang, Jeffrey Dean, Sanjay Ghemawat, Wilson C. Hsieh, Deborah A. Wallach, Mike Burrows, Tushar Chandra, Andrew Fikes, and Robert E. Gruber. “Bigtable: A Distributed Storage System for Structured Data”; pub. OSDI’06: Seventh Symposium on Operating System Design and Implementation, Seattle, WA, November 2006. URL: http://labs.google.com/papers/bigtable.htmlMike Burrows. “The Chubby Lock Service for Loosely-Coupled Distributed Systems”; pub.OSDI’06: Seventh Symposium on Operating System Design and Implementation, Seattle,WA, November 2006. URL: http://labs.google.com/papers/chubby.html
1.2 Open-source和Yahoo
The creators of the open-source search engine, Lucene, were the first to develop an open-source version that replicated some of the features of Google’s infrastructure. Subsequently, the core Lucene developers joined Yahoo, where with the help of a host of other contributors, they created a parallel universe that mimicked all the pieces of the Google distributed computing stack.
This open-source alternative is Hadoop.
1.3 Amazon的Dynamo
A year after the Google papers had catalyzed interest in parallel scalable processing and nonrelational distributed data stores, Amazon decided to share some of its own success story. In 2007, Amazon presented its ideas of a distributed highly available and eventually consistent data store named Dynamo.
You can read more about Amazon Dynamo in a research paper, the details of which are as follows:
Giuseppe DeCandia, Deniz Hastorun, Madan Jampani, Gunavardhan Kakulapati, Avinash Lakshman, Alex Pilchin, Swami Sivasubramanian, Peter Vosshall, and Werner Vogels, “Dynamo: Amazon’s Highly Available Key/value Store,” in the Proceedings of the 21st ACM Symposium on Operating Systems Principles, Stevenson, WA, October 2007. Werner Vogels, the Amazon CTO, explained the key ideas behind Amazon Dynamo in a blog post accessible online at www.allthingsdistributed.com/2007/10/amazons_dynamo.html.
Then, Everyone…
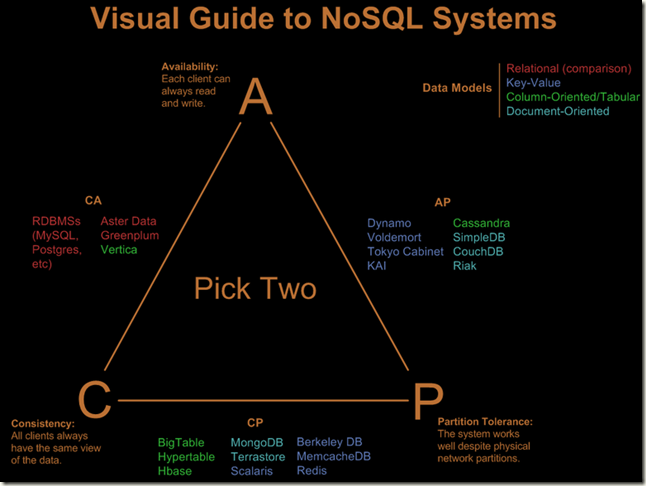
2 NoSQL分类
2.1 Taxonomies by Data Model (基于数据模型分类)
相关Blog:
NoSQL Data Modeling Techniques
Concerning the classification of NoSQL stores Highscalability author Todd Hoff cites a presentation by Stephen Yen in his blog post “A yes for a NoSQL taxonomy” (cf. [Hof09c]).
In the presentation “NoSQL is a Horseless Carriage” (cf. [Yen09]) Yen suggests a taxononmy that can be found in table 2.1.
| Key-Value-Cache | Memcached, Repcached, Coherence, Infinispan, EXtreme Scale, Jboss Cache, Velocity, Terracoqa |
| Key-Value-Store | keyspace, Flare, Schema Free, RAMCloud |
| Eventually-Consistent Key-Value-Store | Dynamo, Voldemort, Dynomite, SubRecord |
| Ordered-Key-Value-Store | Tokyo Tyrant, Lightcloud, NMDB, Luxio, MemcacheDB, Actord |
| Data-Structures Server | Redis |
| Tuple Store | Gigaspaces, Coord, Apache River |
| Object Database | ZopeDB, DB4O, Shoal |
| Document Store | CouchDB, MongoDB, Jackrabbit, XML Databases, ThruDB, CloudKit, Perservere, Riak Basho, Scalaris |
| Wide Columnar Store | Bigtable, Hbase, Cassandra, Hypertable, KAI, OpenNeptune, Qbase, KDI |
2.2 基于CAP理论分类
相关Blog:
CAP – Consistency, Availability, Partition Tolerance
3 NoSQL核心技术
3.1 Data Consistency, 数据一致性
3.1.1 一致性问题的理论基础
相关Blog:
在Lamport论文谈了那么多偏序和全序的问题, 全序到底有什么用? 论文里面给出互斥资源访问的例子, 如果觉得还是比较抽象
这里以分布式数据存储为例
对于并发写数据就存在一致性问题, 如何解决分布式数据库的一致性问题?
Lamport在上面那篇论文里面其实也给出了答案, 这就是他这篇paper里面第二个贡献, 也是常常为人忽略的
如果将分布式系统的所有节点看作有限状态机, 只要保证每个节点的执行命令序列一致, 就能保证所有节点的状态的一致性
对于分布式数据库, 其实就是在同样的初始状况下, 保证每个数据库节点的数据更新序列一致, 就能简单的保证所有数据库的数据的一致性
所以可以看出, 一致性问题已经转变为排序问题
所以这就是为什么上面的paper来讨论偏序和全序的原因, 因为其实你解决了这个问题就已经解决了数据一致性问题
于是上面的问题转变为, 如何在分布式的环境中, 给所有的写操作全序?
1. 基于master或固定参照系, 比如下面的利用时间戳, 悲观或乐观锁
这些方法确实可以保证全序, 但都存在单点或时钟同步问题
2. 使用Paxos算法来保证全序, 尤其在强一致性的场景下
但问题在于, 该算法耗费比较高, 如果对于海量并发写而言, 需要高可用性的方案
当然对于高可用性的方案, 必须要做出一些牺牲, 无法保证全序
那么Vector Clocks算法就是这样一种方案, 当然只能达到偏序, 因为他的原理就是基于paper中描述的偏序理论
3.1.2 Nosql中的一致性技术概要
相关Blog:
3.1.3 Quorum Read and Write
此概念成名于Dynamo的设计, 但是该设计不光可以用于最终一致性的方案, 而是一种保证一致性的通用思路
因为在分布式的环境中, 让w达到n是不现实的,在这种情况下怎样保证一致性...
对于M/S架构, 如果master只会同步更新部分复本W, 如果read操作需要读到最新数据, 要不通过master, 要不就至少需要读R个复本, 并保证R+W>N
Paxos同样也可以基于这样的设计
N The number of replicas for the data or the piece of data to be read or written.
R The number of machines contacted in read operations.
W The number of machines that have to be blocked in write operations5.
In the interest to provide e. g. the read-your-own-writes consistency model the following relation between the above parameters becomes necessary:
R +W > N
几种特殊情况:
W = 1, R = N,对写操作要求高性能高可用
R = 1, W = N , 对读操作要求高性能高可用,比如类似cache之类业务
W = Q, R = Q where Q = N / 2 + 1 一般应用适用,读写性能之间取得平衡。如N=3,W=2,R=2
3.1.4 Eventual Consistency (BASE), 最终一致性技术
当然最典型的代表就是Amazon Dynamo
高可用性的solution, 任意节点都可以写入数据, 必然导致版本的不一致和冲突
所以必须需要一种技术来记录各个版本之间的因果关系或偏序关系, 这就需要vector clocks
并且对于任意节点的更新, 如何在各个复本间同步以达到最终的一致性, 这就需要反熵协议
相关Blog:
Why Vector Clock are Easy or Hard?
3.1.5 Strong Consistency, 强一致性技术
如上图右下角, M/S比较简单在上面的引用已经描述, 简单但很实用, Goolge早期在GFS和Bigtable都使用的这种设计
其中最重要的算法是Paxos, Google的Megastore中使用
相关Blog:
3.2 Data Partitioning(Sharding), 数据动态划分
相关Blog:
3.3 Data Replication, 数据复本技术
相关Blog:
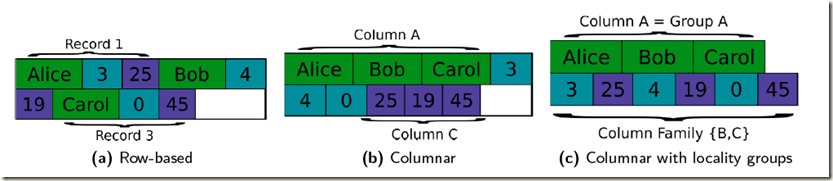
3.4 Data Storage Layout
Row-Based Storage Layout
A table of a relational model gets serialized as its lines are appended and flushed to disk.
Advantages
a. whole datasets can be read and written in a single IO operation
b. one has a “[g]ood locality of access (on disk and in cache) of different columns”.
Disadvantages
a. operating on columns is expensive as a considerable amount data has to be read.
Columnar Storage Layout
相关Blog:
Columnar Storage, 关于Row-based和Columnar的比较
Serializes tables by appending their columns and flushing them to disk.
Therefore operations on columns are fast and cheap while operations on rows are costly and can lead to seeks in a lot or all of the columns. A typical application field for this type
of storage layout is analytics where an efficient examination of columns for statistical purposes is important.
其实没有好坏, 只是不同的场景, 如果需要整行读当然row-based好, 如果只需要少量的column, 当然选columnar
做个balance, 就是下面的方案column-families
Columnar Storage Layout with Locality Groups
Similar to column-based storage but adds the feature of defining so called locality groups that are groups of columns expected to be accessed together by clients.
The columns of such a group may therefore be stored together and physically separated from other columns and column groups.
The idea of locality groups was introduced in Google’s Bigtable paper.
3.5 Storage Implementaton, 数据存储实现
Storage implementation pluggable. e.g. A local MySQL DB, Berkeley DB, Filesystem or even a in memory Hashtable can be used as a storage mechanism.
特有的Storage implementation, HBase, Couchbase
3.5.1 SSTables(Sorted String Table)和Log Structured Merge Trees (LSM-trees)
相关Blog:
3.5.2 CouchDB Storage Implementation
相关Blog:
CouchDB has a MVCC model that uses a copy-on-modified approach. Any update will cause a private copy being made which in turn cause the index also need to be modified and causing the a private copy of the index as well, all the way up to the root pointer.
Notice that the update happens in an append-only mode where the modified data is appended to the file and the old data becomes garbage. Periodic garbage collection is done to compact the data. Here is how the model is implemented in memory and disks.
3.8 Query Models, 数据检索
Whereas key/value stores by design often only provide a lookup by primary key or some id field and lack capabilities to query any further fields, other datastores like the document databases CouchDB and MongoDB allow for complex queries—at least static ones predefined on the database nodes (as in CouchDB).
This is not surprising as in the design of many NoSQL databases rich dynamic querying features have been omitted in favor of performance and scalability.
On the other hand, also when using NoSQL databases, there are use-cases requiring at least some querying features for non-primary key attributes.
Nosql往往只支持基于主键query, 而无法支持复杂的查询, 比如范围查询, 非主键的查询, 当然也有象CouchDB和MangoDB可以支持这样的查询.
但大部分比较纯粹的NoSQL是不支持的, 因为基于key/value的query, 一般都是基于DHT(Distributed Hash Table)技术, 只支持exact match.
那么如果用nosql, 又想具有较复杂的querying features, 有如下思路,
Companion SQL-database is an approach in which searchable attributes are copied to a SQL or text database. The querying capabilities of this database are used to retrieve the primary keys of matching datasets by which the NoSQL database will subsequently be accessed.
如图, 这个想法就是用SQL当索引, 比较简单, 因为索引应该会小点, 所以扩展性问题不是那么突出, 但是还是有问题, 而且维护两个系统增加了复杂性
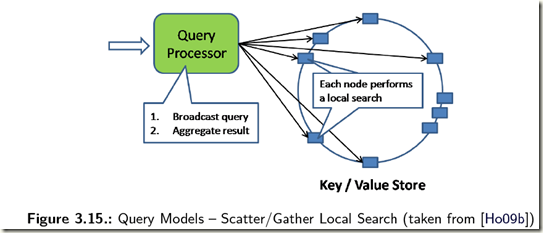
Scatter/Gather Local Search can be used if the NoSQL store allows querying and indexing within database server nodes. If this is the case a query processor can dispatch queries to the database
nodes where the query is executed locally. The results from all database servers are sent back to the query processor postprocessing them to e. g. do some aggregation and returning the results to a client that issued the query.
Distributed B+Trees are another alternative to implement querying features. The basic idea is to hash the searchable attribute to locate the root node of a distributed B+tree (further information on scalable, distributed B+Trees can be found in a paper by Microsoft, HP and the University of Toronto, cf. [AGS08]). The “value” of this root node then contains an id for a child node in the B+tree which can again be looked up. This process is repeated until a leaf node is reached which contains the primary-key or id of a NoSQL database entry matching search criteria.
Prefix Hash Table (aka Distributed Trie) is a tree-datastructure where every path from the root-node to the leafs contains the prefix of the key and every node in the trie contains all the data whose key is prefixed by it (for further information cf. a Berkley-paper on this datastructure [RRHS04]). Besides an illustration Ho provides some code-snippets in his blog post that describe how to operate on prefix hash tables / distributed tries and how to use them for querying purposes (cf.[Ho09b]).
前缀HT, effciently supporting 1-dimensional range queries over a DHT.
4 主流NoSQL
4.1 BigTable, HBase
bigtable: A Distributed Storage System for Structured Data
HBase-TDG ClientAPI The Basics
HBase-TDG ClientAPI Advanced Features
HBase-TDG Architecture, SSTable和LSMTree
4.2 KV
Dynamo: Amazon’s Highly Available Key-value Store
Cassandra - A Decentralized Structured Storage System