内容提要
- DIV标记的基本用法、常用属性。
- DIV嵌套与层叠的含义。
- SPAN标记的语法,灵活使用SPAN标记。
- DIV与SPAN标记在使用上的差异。DIV用于多行的、大片区的;SPAN用于行内标记。
- 使用DIV+CSS进行和简易页面布局。
HTML块级元素
- 块级元素(block level element)在浏览器显示时通常会以新行开始。
- 例如:<h1>、<p>、<ul>、<table>
HTML内联元素
- 内联元素(inline element)在浏览器显示时通常不以新行开始。
- 例如:<b>、<tb>、<a>、<img>
HTML<div>元素
- HTML<div>元素是块级元素,它是用于组合其他HTML元素的容器。
- <div>元素没有特定的含义。由于它属于块级元素,浏览器会在其前后显示换行。
- 如果与CSS一同使用,<div>元素可用于对大的内容块设置样式属性。
- <div>元素的另一个常见的用途是文档布局。它取代了使用表格定义布局的老式方法。
案例1:
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<title>div元素是块级元素 </title>
<style>
.cities {
background-color: black;
color: white;
margin: 20px; /* 容器外边距 */
padding: 20px; /* 容器内边距 */
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<div class="cities">
<h2>London</h2>
<p>
London is the capital city of England.
It is the most populous city in the United Kingdom,
with a metropolitan area of over 13 million inhabitants.
</p>
<!-- 默认的,我们知道,div是占满一行的 -->
<!-- 把两个div显示在一行,就需要float,设置第一个div的float为left -->
<div style="100px; float: left">11111</div>
<div style="150px">2222</div>
<!-- css的定义是后面的可以覆盖前面的 -->
<!-- clear是清除的意思,它有三个值,left,right,both,
如果设置了clear:left,就不让它的左边有float,
同理clear:right,clear:both, -->
<div style="100px;float:left;">test</div>
<div style="150px;clear:left;">hello</div>
</div>
</body>
</html>
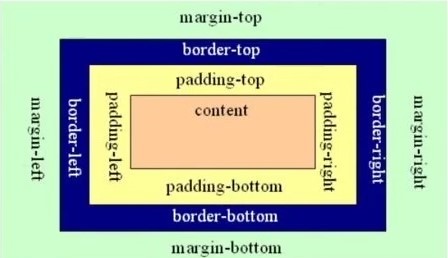
注意:搞清楚margin、padding、border这三个概念,不能混淆。
margin:容器自身与其他容器之间的距离
padding:容器内部的内容(content)与容器边框的距离。
border:容器的边框。
另外:top表示上、bottom表示下、left表示左、right表示右。
案例2:
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<title>div元素没有特定的含义</title>
<style>
.cities {
background-color: rgb(7, 6, 6);
color: white;
margin: 20px;
padding: 20px;
}
span.red {
color: red;
}
h1{
text-align: center;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
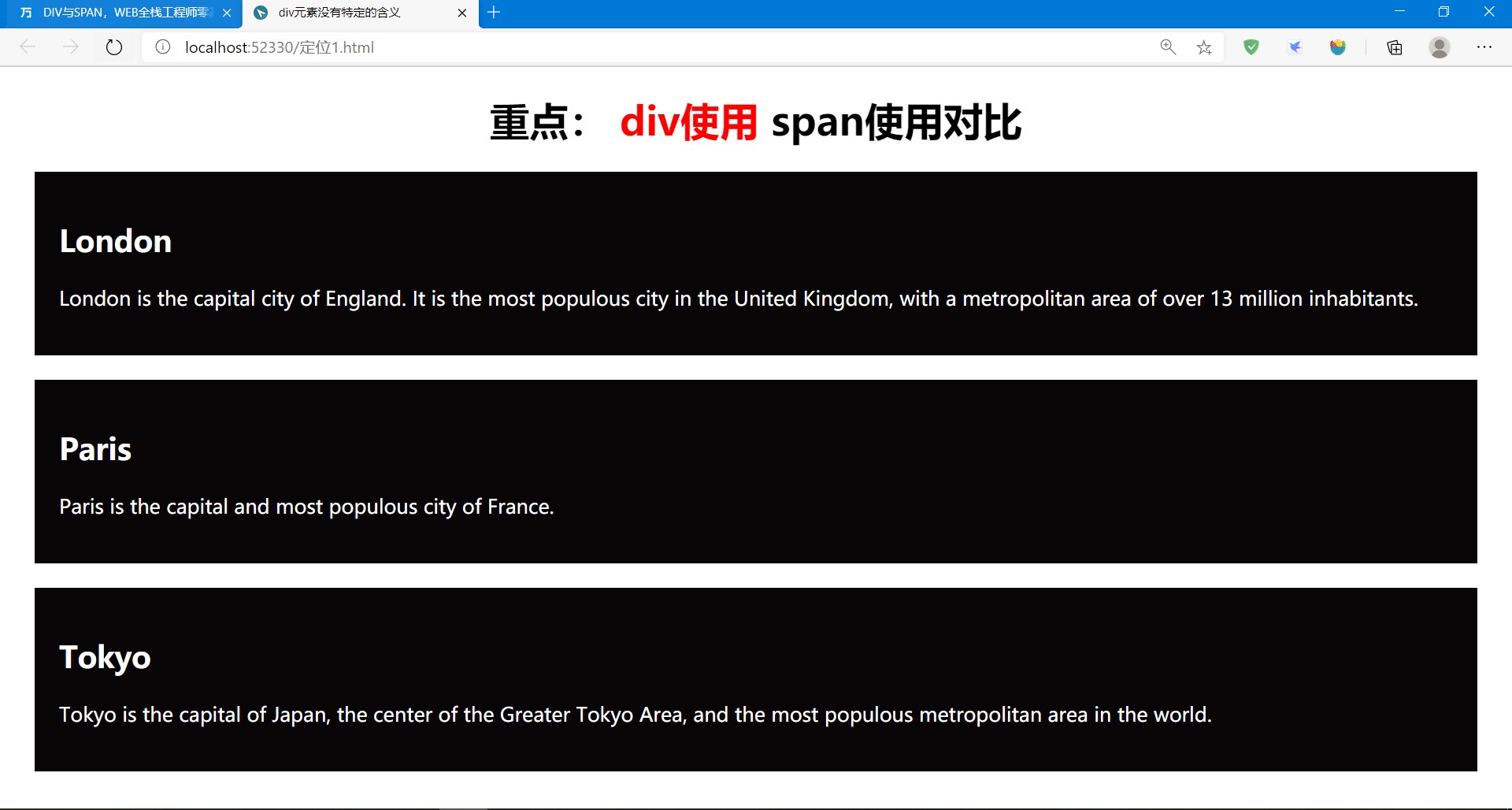
<h1>重点: <span class="red">div使用</span> span使用对比</h1>
<div class="cities">
<h2>London</h2>
<p>London is the capital city of England.
It is the most populous city in the United Kingdom,
with a metropolitan area of over 13 million inhabitants.</p>
</div>
<div class="cities">
<h2>Paris</h2>
<p>Paris is the capital and most populous city of France.</p>
</div>
<div class="cities">
<h2>Tokyo</h2>
<p>Tokyo is the capital of Japan, the center of the Greater Tokyo Area,
and the most populous metropolitan area in the world.</p>
</div>
</body>
</html>
讲解:
- 在这个案例中通过合理设置margin和padding,使得不同的div之间有合理的间距,div内部文本也有恰当的间距。
- 注意span标记的用法,它是对指定内容做特殊处理用的。在上述案例中对"div使用"改变了字体颜色。
案例3:
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>DIV嵌套与层叠</title>
<style>
.div1 {
padding: 50px;
background: red;
400px;
height: 400px;
position: relative;
left: 10px;
top: 10px;
}
.div2 {
padding: 60px;
background: green;
position: absolute;
left: 0px;
top: 0px;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<div class="div1">
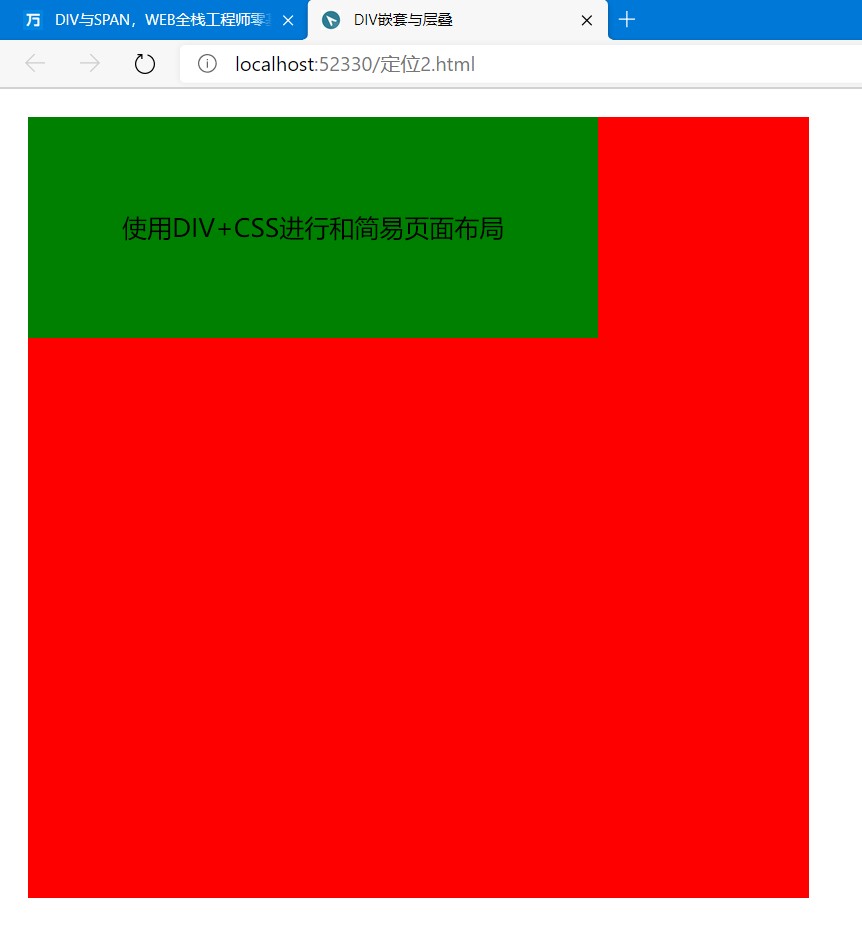
<div class="div2">使用DIV+CSS进行和简易页面布局</div>
</div>
</body>
</html>
讲解:
-
在.div1中定义了padding内部边距为50像素、background背景色为红色、width容器宽度为400像素、height容器高度为400像素、position定位类型为relative相对定位(相对定位会按照元素的原始位置对该元素进行移动)、left为容器左边坐标是10像素、top为容器上边坐标是10像素。
-
在.div2中定义了padding内部边距位60像素、background背景色为绿色、position定位类型为absolute绝对定位(绝对定位会按照页面的绝对位置定位元素,通过绝对定位可以将指定元素放置在页面上指定位置),left为容器左边坐标是0像素、top为容器上边坐标是0像素。
-
postion定位类型有三种:
-
position:relative;相对定位:对某元素设置了相对定位,那么首先这个元素会出现在文档流中该出现的位置,然后再根据该位置按设定的偏移量进行移动。
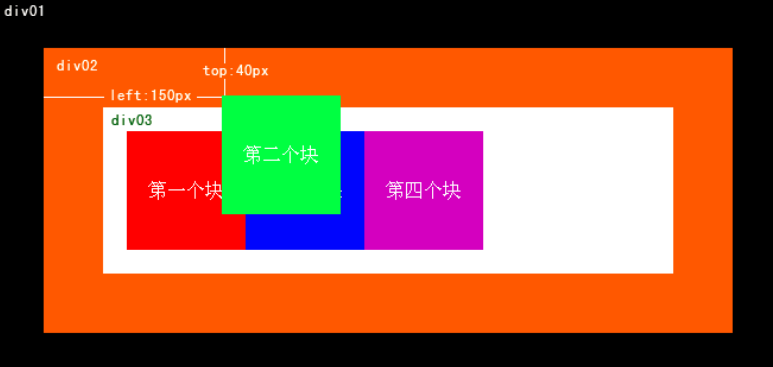
- 关注第二个块,这是正常状态或者说是相对定位水平及垂直偏移量为0时的初始位置:
-

+ 这是第二个块在使用相对定位左边偏移50像素和上边偏移30像素后的结果。请注意:它有部分内容与第三个块重叠了,但它位于文档流中的初始位置仍然还在占着(虚线框标示的地方),即使把偏移量设得再大它的初始位置也不会被第三个块填补。同时它的偏移位置也不会把别的块在文档流的位置挤开,如果有重叠它会和其他元素重叠。

-
position:absolute;绝对定位:相对于页面的绝对值来对元素进行定位。
- 要使用绝对定位时,必须要有2个条件(口诀:父相子绝):
- 必须给父元素(也可以是祖父级、曾祖父级)增加定位属性,一般建议使用position:relative。
- 给子元素加绝对定位position:absolute,同时指定left、right、top、bottom属性。
-
使用了绝对定位的元素会脱离文档流,即它原来的位置会被其他元素占用,而且它会和其他元素重叠。
-
案例:
- 下图中第二个块是未使用绝对定位时的样式。
+ 下图中的第二个块是使用了绝对定位时的样式。
-
position:fixed;固定定位:将元素放置在浏览器窗口的固定位置,即使窗口滚动它也不会移动。
- Fixed定位使元素的位置与文档流无关,因此不占据空间。
- Fixed定位的元素会和其他元素重叠。
-
position:fstatic;静态定位:HTML元素的默认值,即没有定位,遵循正常的文档流对象。另外静态定位的元素不会受到 top、bottom、left、right影响。
HTML<span>元素
- HTML<span>元素是内联元素,可用作文本的容器。
- <span>元素没有特定的含义。
- 当与CSS一同使用时,<span>元素可用于为指定文本设置样式属性。
<div>与<span>区别
- <div>用来定义文档中的division分区或section节。
- <span>用来指定文档中的行内元素。
div图层
-
div(division/section)定义
- <div> </div>是一个块级(block-level)元素,其前后均有换行符,可定义文档中的分区或节。
-
基本语法
<div id="layer1" class=" " style="position:absolute; left:29px;top;12px;135px;height:24px;background:#99cccc;border:2px dashed #ffff00;">块包含的内容</div>
图层CSS属性
- position:定位,static|absolute|relative|fixed,其中static是默认值
- width|height:图层的宽度|图层的高度
- left|top:左边距|上边距
- border:边框,“粗细 形状 颜色”
- z-index:图层重叠,子层永远在父层之上,值越大越在上层,前提条件是position属性值为“absolute”。
- clear
- clear:none,默认值,允许两边有浮动元素。
- clear:left,不许左边有浮动元素。
- clear:right,不行右边有浮动元素。
- clear:both,不许有浮动元素。
- fload
- fload:left,当前元素向左浮动。
- fload:right,当前元素向右浮动。
- fload:none,当前元素不浮动。
图层嵌套与重叠
-
图层包含其它图层,称为图层的嵌套。
-
图层嵌套经常需要与CSS样式一起使用,达到更加精确控制页面显示效果。
-
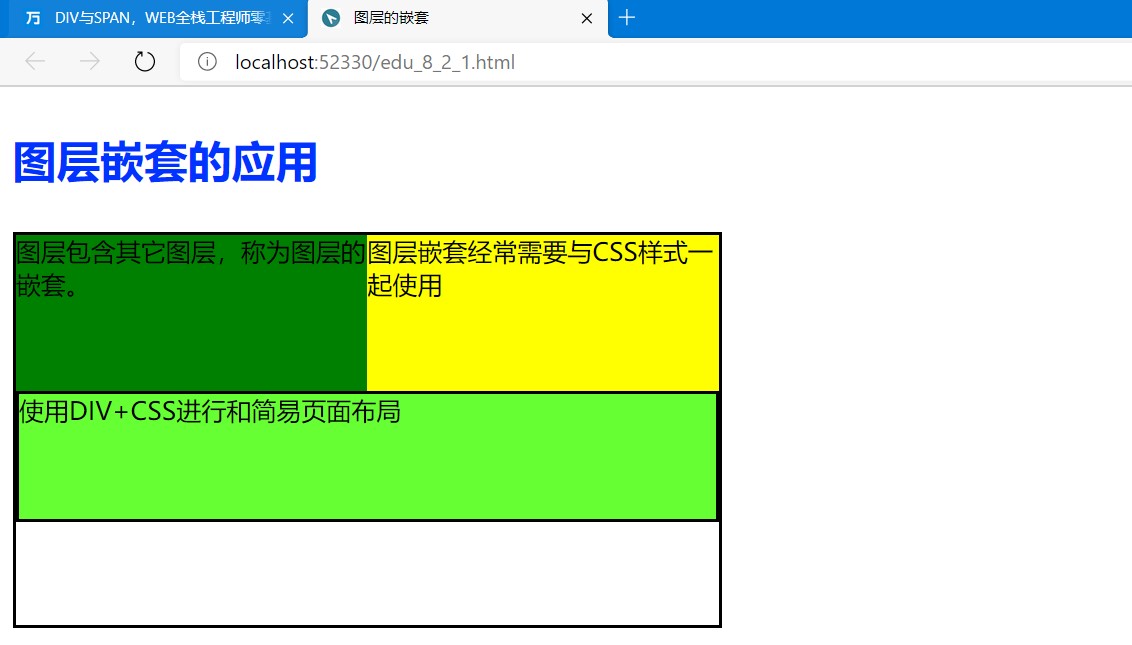
案例1,图层嵌套:
<!doctype html> <html lang="en"> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <title>图层的嵌套</title> <style type="text/css"> .inline_div { display: inline-block; /* 行内显示方式*/ } #wrap { 450px; height: 250px; border: 2px solid black; } #d1{ height: 100px; 225px; background-color: green; margin: 20px red; float: left; /*margin表示边距*/ } #d2 { height: 100px; 225px; background-color: green; margin: 20px red; float: left; /*margin表示边距*/ } #d2 { background-color: yellow; } #d3 { height: 80px; 400; border: 2px solid black; background-color: #66ff33; margin: 0 auto; clear: both; } h3 { font-size: 28px; color: #0033ff; } </style> </head> <body> <h3>图层嵌套的应用</h3> <div id="wrap"> <div id="d1" class="inline_div">图层包含其它图层,称为图层的嵌套。 </div> <div id="d2" class="inline_div">图层嵌套经常需要与CSS样式一起使用</div> <div id="d3">使用DIV+CSS进行和简易页面布局</div> </div> </body> </html>
-
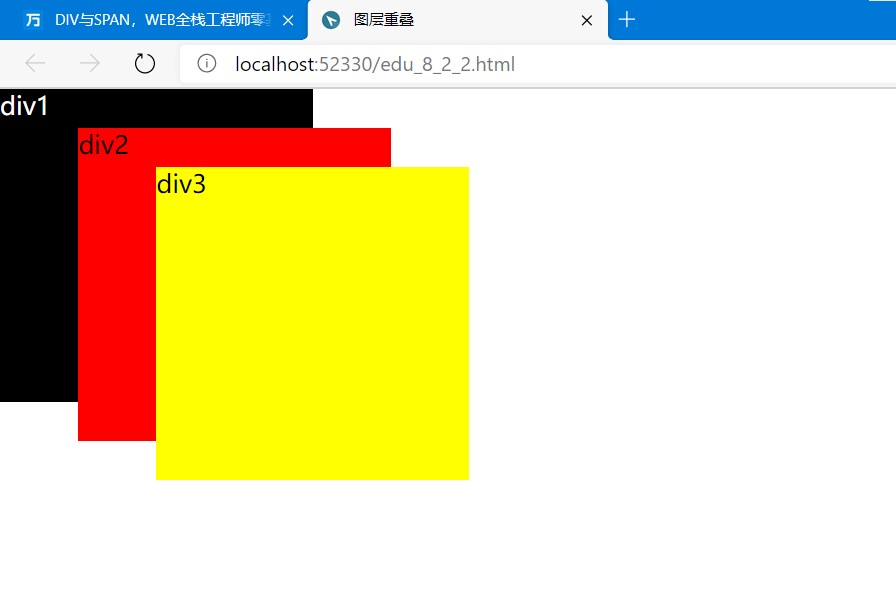
案例2,图层重叠:
<!doctype html> <html lang="en"> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <title>图层重叠</title> <style type="text/css"> body { margin: 0; /*margin表示边距*/ } div { position: absolute; /* 定位方式为绝对定位 */ 200px; height: 200px; } #d1 { background-color: black; color: white; /* z-index:图层层叠,子层永远在父层之上,值越大越在上层,前提条件是position属性值为“absolute”。 */ z-index: 0; /* 该图层在最下面 */ } #d2 { background-color: red; top: 25px; left: 50px; z-index: 1; /* 该图层在中间 */ } #d3 { background-color: yellow; top: 50px; left: 100px; z-index: 2; /* 该图层在最上面 */ } </style> </head> <body> <div id="d1">div1</div> <div id="d2">div2</div> <div id="d3">div3</div> </body> </html>
div标记与span标记使用区别
-
div标记和span标记默认情况下都没有对标记内的内容进行格式化或渲染,只有使用CSS来定义相应的样式才会显示出不同。
-
div标记是块标记,一般包含较大范围,在区域的前后会自动换行;span标记是行内标记,一般包含范围较窄,通常在一行内,在此区域的范围外不会自动换行。
-
一般来说,div标记可以包含span标记,但span标记不能包含div标记。
-
但是块标记和行标记不是绝对的,可以通过定义CSS的display属性来相互转换。
-
display:inline;指定元素显示在行内。
-
display:block;指定元素显示在块内。
案例:
<!doctype html> <html lang="en"> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <title>div的使用</title> <style type="text/css"> div { background-color: #f6f6f6; color: #000000; height: 2em; margin: 2px; /*margin表示边距*/ } .inline_disp { display: inline; /*改变div显示方式*/ } .block_disp { display: block; /*改变span显示方式*/ height: 4em; background-color: rgb(200, 200, 200); margin: 2px; /*margin表示边距*/ } </style> </head> <body> <div id="d1">这是div1</div> <div id="d2">这是div2</div> <span id="s1">这是span1</span> <span id="s2">这是span2</span> <div id="d3" class="inline_disp">这是div3</div> <div id="d4" class="inline_disp">这是div4</div> <span id="s3" class="block_disp">这是span3,在使用CSS排版的页面中,div标记和span标记是两个常用的标记。利用这两个标记,加上CSS对其样式的控制,可以很方便的实现各种效果。</span> <span id="s4" class="block_disp">这是span4,在使用CSS排版的页面中,div标记和span标记是两个常用的标记。利用这两个标记,加上CSS对其样式的控制,可以很方便的实现各种效果。</span> </body> </html> -

使用<div>元素的HTML布局
-
<div>元素常用作布局工具,因为能够轻松地通过CSS对其进行定位。
-
案例:
<!doctype html> <html lang="en"> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <title>图层重叠</title> <style type="text/css"> body { margin: 0; /*margin表示边距*/ } div { position: absolute; /* 定位方式为绝对定位 */ 200px; height: 200px; } #d1 { background-color: black; color: white; /* z-index:图层层叠,子层永远在父层之上,值越大越在上层,前提条件是position属性值为“absolute”。 */ z-index: 0; /* 该图层在最下面 */ } #d2 { background-color: red; top: 25px; left: 50px; z-index: 1; /* 该图层在中间 */ } #d3 { background-color: yellow; top: 50px; left: 100px; z-index: 2; /* 该图层在最上面 */ } </style> </head> <body> <div id="d1">div1</div> <div id="d2">div2</div> <div id="d3">div3</div> </body> </html>

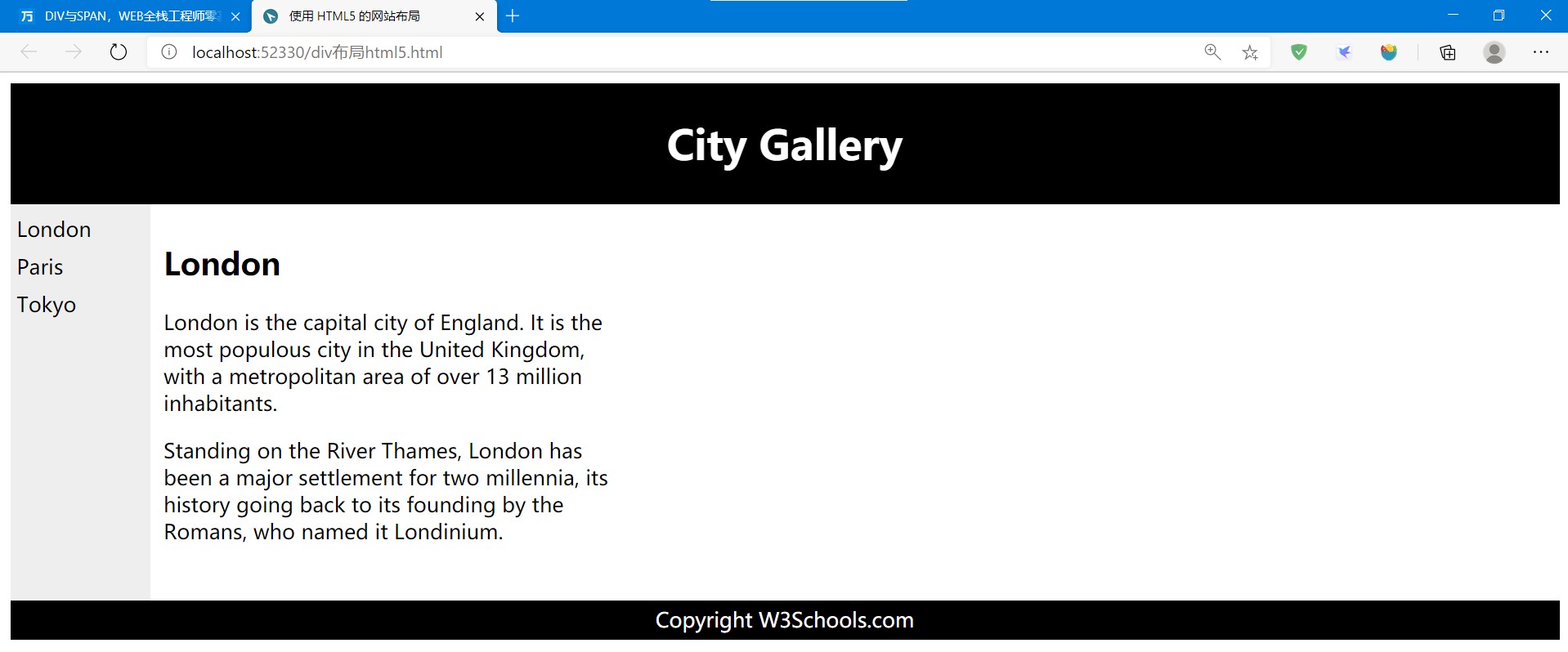
使用HTML5的网站布局
-
HTML5提供的新语义元素定义了网页的不同部分:
标签 用途 header 定义文档或节的页眉 nav 定义导航链接的容器 section 定义文档中的节 article 定义独立的自包含文章 aside 定义内容之外的内容(比如侧栏) footer 定义文档或节的页脚 details 定义额外的细节 summary 定义details元素的标题 -
使用<header>、<nav>、<section>以及<footer>来创建多列布局。
-
案例:
<!DOCTYPE html> <html> <head> <title> 使用 HTML5 的网站布局</title> <style> header { background-color: black; color: white; text-align: center; padding: 5px; } nav { line-height: 30px; background-color: #eeeeee; height: 300px; 100px; float: left; padding: 5px; } section { 350px; float: left; padding: 10px; } footer { background-color: black; color: white; clear: both; text-align: center; padding: 5px; } </style> </head> <body> <header> <h1>City Gallery</h1> </header> <nav> London<br> Paris<br> Tokyo<br> </nav> <section> <h1>London</h1> <p> London is the capital city of England. It is the most populous city in the United Kingdom, with a metropolitan area of over 13 million inhabitants. </p> <p> Standing on the River Thames, London has been a major settlement for two millennia, its history going back to its founding by the Romans, who named it Londinium. </p> </section> <footer> Copyright W3Schools.com </footer> </body> </html>
CSS的display属性
-
display:规定元素应该生成的显示框类型。
-
对于HTML等文档类型,如果使用display不谨慎会很危险,因为可能违反HTML中已经定义的显示层次结构。
属性 用途 none 此元素不会被显示。 block 此元素将显示为块级元素,前后有换行。 inline 默认,此元素会被显示为内联元素,前后没有换行。 inherit 继承父元素的display属性值。
小结
- div及span标记的基本语法以及两个标记在使用时的区别:
- 一般而言,div标记是块标记,span标记是行内标记‘
- div标记可以自动换行,span标记不可以;
- div标记可以包含div子标记和span子标记,但span标记不能包含div子标记。
- 这两个标记可以通过设置display属性值为inline或block来实现转换。
- div、span标记必须配合CSS使用才能实现精确定位页面上的每一个元素。通过id、class来引用已经定义的CSS文件中类选择器、ID选择器及其它选择器。