散列表
概念
散列表,又称杂凑表,是一种十分实用的查找技术,具有极高的查找效率。其基本思想是根据 关键码值(查找码)与表项存储位置的映射关系,进行高效、精确的查找。查找效率与散列函数的 计算复杂度、冲突解决方案的使用有直接的关系。散列查找是根据关键码(查找码)与表项存储位 置的映射关系,进行高效、精确的查找,因此也需要采用顺序结构存储。 当关键码比较多时,很可能出现散列函数值相同的情况,即出现冲突。我们通常也称为冲突的 两个关键是该散列函数的同义词。
要点
p=H(key), p是地址,key是关键字,H称为散列函数。散列函数的构造方法有:数字分析法,平方取中法,折叠法,除留余数法。(代码中采用除留余数法)。冲突处理的方法采用开放地址法的二次探测法。
代码实现
1 #include<iostream> 2 using namespace std; 3 #define Length 50 4 typedef int keyType; 5 typedef struct 6 { 7 keyType data; 8 char other; 9 }SList,*List; 10 int H(keyType m); 11 void createList(List &l) 12 { 13 l = new SList[Length]; 14 for(int i=0;i<Length;i++) 15 l[i].data = 0; 16 cout<<"请输入初始化存入的个数:"; 17 int counts; 18 cin>>counts; 19 if(counts>50) 20 { 21 cout<<"散列表空间不足"; 22 return ; 23 } 24 for(int i=0;i<counts;i++) 25 { 26 cout<<"请输入第"<<i+1<<"个数:"; 27 keyType tmp; 28 cin>>tmp; 29 if(!l[H(tmp)].data) 30 l[H(tmp)].data = tmp; 31 else 32 { 33 int next = H(tmp); 34 while(l[next].data) 35 { 36 next = (next+1)%47; 37 } 38 l[next].data = tmp; 39 } 40 } 41 } 42 int H(keyType m) 43 { 44 return m%47; 45 } 46 47 int searchList(List l,keyType key) 48 { 49 int h = H(key); 50 if(l[h].data == 0) 51 { 52 return -1; 53 }else if(l[h].data==key){ 54 return h; 55 }else{ 56 for(int i=0;i<Length;i++) 57 { 58 int next = (h+1)%47; 59 if(l[next].data ==0) 60 return -1; 61 else if(l[next].data == key) 62 return next; 63 } 64 return -1; 65 } 66 } 67 68 int main() 69 { 70 List l; 71 createList(l); 72 cout<<endl; 73 while(true){ 74 cout<<"请输入要查询的关键字:"; 75 int key; 76 cin>>key; 77 int mysearch = searchList(l,key); 78 if(mysearch==-1) 79 cout<<"没有找到"<<endl; 80 else 81 cout<<"位置:"<<mysearch<<endl; 82 int k; 83 cin>>k; 84 if(!k) 85 break; 86 } 87 88 return 0; 89 }
快速排序
思想概念
快速排序采用了一种分治的策略,通常称其为分治法。其基本思想是将原问题分解为若干个规 模更小但结构与原问题相似的子问题。递归地解这些子问题,然后将这些子问题的解组合为原问题 的解。
具体排序过程
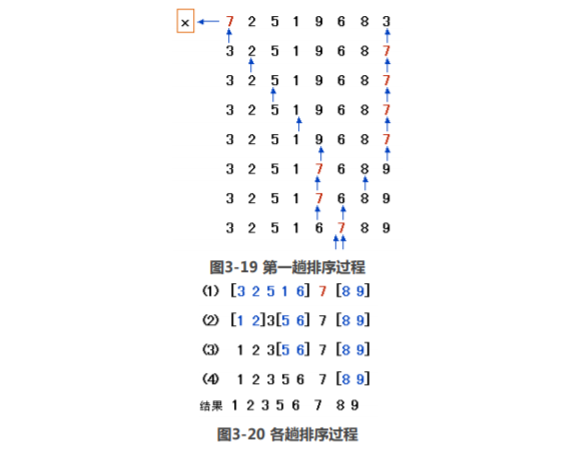
第一步,在待排序的n个记录中任取一个记录,以该记录的排序码为准,将所有记录分成两组, 第1组各记录的排序码都小于等于该排序码,第2组各记录的排序码都大于该排序码,并把该记录排 在这两组中间。
第二步,采用同样的方法,对左边的组和右边的组进行排序,直到所有记录都排到相应的位置 为止。(递归思想)
要点
在快速排序中,选定了以第一个元素为基准,接着就拿最后一个元素和第一个元素 比较,如果大于第一个元素,则保持不变,再拿倒数第二个元素和基准比较,如果小于基准,则进 行交换。交换之后,再从前面的元素开始与基准比较,如果小于基准,则保持不变;如果大于基 准,则交换。交换之后,再从后面开始比较,依次类推,前后交叉进行。
代码实现
1 #include<iostream> 2 using namespace std; 3 typedef char other; 4 #define maxl 5000 5 typedef struct 6 { 7 int data; 8 other info; 9 }elem,*elemptr; 10 11 typedef struct 12 { 13 elemptr p; 14 int length; 15 }SList; 16 17 void InitList(SList &t) 18 { 19 t.p = new elem[maxl]; 20 t.length = 0; 21 } 22 void createList(SList &t) 23 { 24 cout<<"请输入赋值的个数:"; 25 int counts; 26 cin>>counts; 27 for(int i=1;i<=counts;i++) 28 { 29 cout<<"请输入第"<<i<<"个数:"; 30 int tmp; 31 cin>>tmp; 32 t.p[i].data = tmp; 33 t.length++; 34 } 35 } 36 //根据low 和high 进行一轮快速排序 37 int partition(SList &t,int low,int high) 38 { 39 t.p[0].data = t.p[low].data; 40 int pivotkey = t.p[low].data; 41 while(low<high) 42 { 43 while(low<high&&(t.p[high].data>=pivotkey)) high--; 44 t.p[low].data = t.p[high].data; 45 while(low<high&&(t.p[low].data<=pivotkey)) low++; 46 t.p[high].data = t.p[low].data; 47 } 48 t.p[low].data = pivotkey; 49 50 return low; 51 } 52 //递归进行快排 53 void Qsort(SList &t,int low,int high) 54 { 55 if(low<high) 56 { 57 int mid = partition(t,low,high); 58 Qsort(t,low,mid-1); 59 Qsort(t,mid+1,high); 60 } 61 } 62 63 void show(SList t) 64 { 65 int len =t.length; 66 for(int i=1;i<len;i++) 67 cout<<t.p[i].data<<" "; 68 69 cout<<endl; 70 } 71 int main() 72 { 73 SList t; 74 InitList(t); 75 createList(t); 76 cout<<"排序前:"; 77 show(t); 78 int low = 1; 79 int high = t.length; 80 Qsort(t,low,high); 81 cout<<"排序后:"; 82 show(t); 83 84 return 0; 85 }