numpy创建ndarray对象的三种方法
1.1.list转化
In [8]: import numpy as np In [9]: a = [1,2,3,4] In [10]: x1 = np.array(a) In [11]: x1 Out[11]: array([1, 2, 3, 4]) In [12]: type(x1) Out[12]: numpy.ndarray
1.2.numpy内的函数生存
In [13]: x2 = np.arange(11) In [14]: x2 Out[14]: array([ 0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10])
1.3.文件生存
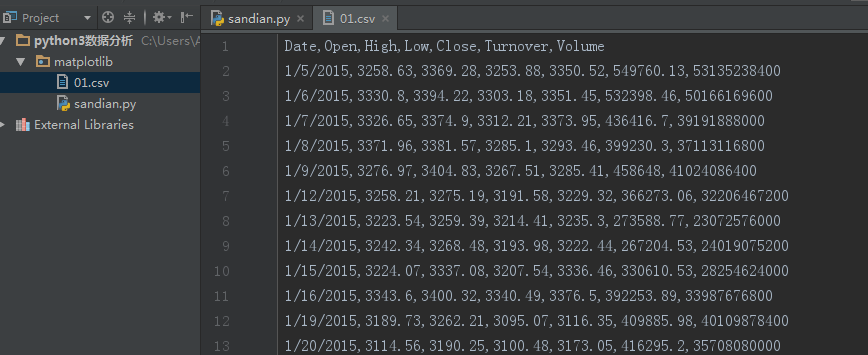
01.csv文件如下
使用numpy的loadtxt方法打开
- 第一个参数:文件名
- delimiter:以什么分隔
- skiprows:跳过的行
- usecols:使用哪几列
- unpack:默认False,表示是否把列分开
x = np.loadtxt('01.csv',delimiter=',',skiprows=1,usecols=(1,4,6),unpack=False)
显示结果
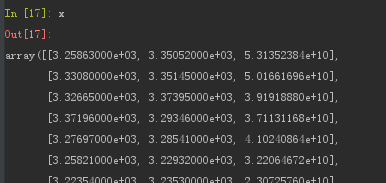
In [18]: x.shape
Out[18]: (242, 3)
把每列分开保存
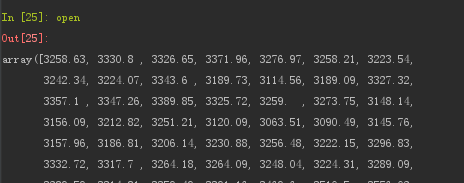
In [24]: open,close,volume = np.loadtxt('01.csv',delimiter=',',skiprows=1,usecols=(1,4,6),unpack=True)
结果:
In [26]: open.shape
Out[26]: (242,)
1.4.numpy的常用函数
In [36]: c = np.random.randint(1,100,10) In [37]: c Out[37]: array([44, 26, 40, 87, 32, 82, 20, 70, 62, 14]) In [38]: c.min() Out[38]: 14 In [39]: c.max() Out[39]: 87 In [40]: c.mean() Out[40]: 47.7 In [43]: y = np.sort(c) In [44]: y Out[44]: array([14, 20, 26, 32, 40, 44, 62, 70, 82, 87])