第十三章、用户自定义认证
13.1.用户自定义认证
- class Meta:
abstract = True (不会创建表,只把字段继承给子类)
- django加密方式:md5 + 盐
- account
LADP:轻量级目录账号管理协议(集中账号管理):通过网络到LDAP服务器上进行验证
- SSO:Single Sign on (单点登录)
(1)settings.py
AUTH_USER_MODEL = 'crm.UserProfile'
(2)crm/models.py
class UserProfileManager(BaseUserManager): def create_user(self, email, name, password=None): """ Creates and saves a User with the given email, date of birth and password. """ if not email: raise ValueError('Users must have an email address') user = self.model( email=self.normalize_email(email), name=name, ) user.set_password(password) user.save(using=self._db) return user def create_superuser(self, email, name, password): """ Creates and saves a superuser with the given email, date of birth and password. """ user = self.create_user( email, password=password, name=name, ) user.is_admin = True user.save(using=self._db) return user class UserProfile(AbstractBaseUser,PermissionsMixin): email = models.EmailField( verbose_name='email address', max_length=255, unique=True, ) name = models.CharField(max_length=64) role = models.ManyToManyField(Role, blank=True, null=True) is_active = models.BooleanField(default=True) is_admin = models.BooleanField(default=False) is_staff = models.BooleanField(default=False) #创建用户和超级用户,关联上面的 objects = UserProfileManager() USERNAME_FIELD = 'email' #必须要有的字段 REQUIRED_FIELDS = ['name'] def __str__(self): return self.email def has_perm(self, perm, obj=None): "Does the user have a specific permission?" # Simplest possible answer: Yes, always return True def has_module_perms(self, app_label): "Does the user have permissions to view the app `app_label`?" # Simplest possible answer: Yes, always return True def get_full_name(self): # The user is identified by their email address return self.email def get_short_name(self): # The user is identified by their email address return self.email @property def is_staff(self): "Is the user a member of staff?" # Simplest possible answer: All admins are staff return self.is_admin
(3)crm/admin.py
from django import forms from django.contrib import admin from django.contrib.auth.models import Group from django.contrib.auth.admin import UserAdmin as BaseUserAdmin from django.contrib.auth.forms import ReadOnlyPasswordHashField from crm.models import UserProfile class UserCreationForm(forms.ModelForm): """A form for creating new users. Includes all the required fields, plus a repeated password.""" password1 = forms.CharField(label='Password', widget=forms.PasswordInput) password2 = forms.CharField(label='Password confirmation', widget=forms.PasswordInput) class Meta: model = UserProfile fields = ('email', 'name') #进行验证 def clean_password2(self): # Check that the two password entries match password1 = self.cleaned_data.get("password1") password2 = self.cleaned_data.get("password2") if password1 and password2 and password1 != password2: raise forms.ValidationError("Passwords don't match") return password2 def save(self, commit=True): # Save the provided password in hashed format #继承基类的save() user = super(UserCreationForm, self).save(commit=False) #把明文密码改成密文 user.set_password(self.cleaned_data["password1"]) if commit: user.save() return user class UserChangeForm(forms.ModelForm): """A form for updating users. Includes all the fields on the user, but replaces the password field with admin's password hash display field. """ #把密码改成哈希的了 password = ReadOnlyPasswordHashField() class Meta: model = UserProfile fields = ('email', 'password', 'name', 'is_active', 'is_superuser') def clean_password(self): # Regardless of what the user provides, return the initial value. # This is done here, rather than on the field, because the # field does not have access to the initial value return self.initial["password"] class UserProfileAdmin(BaseUserAdmin): # The forms to add and change user instances form = UserChangeForm add_form = UserCreationForm # The fields to be used in displaying the User model. # These override the definitions on the base UserAdmin # that reference specific fields on auth.User. list_display = ('email', 'name','is_superuser') list_filter = ('is_superuser',) fieldsets = ( (None, {'fields': ('email', 'password')}), ('Personal info', {'fields': ('name',)}), ('Permissions', {'fields': ('is_staff','is_active','role','user_permissions','groups','is_superuser')}), ) # add_fieldsets is not a standard ModelAdmin attribute. UserAdmin # overrides get_fieldsets to use this attribute when creating a user. add_fieldsets = ( (None, { 'classes': ('wide',), 'fields': ('email', 'name', 'password1', 'password2')} ), ) search_fields = ('email',) ordering = ('email',) filter_horizontal = ('role','user_permissions','groups') # Now register the new UserProfileAdmin... admin.site.register(UserProfile, UserProfileAdmin) # ... and, since we're not using Django's built-in permissions, # unregister the Group model from admin. # admin.site.unregister(Group)
第十四章、万能通用权限框架设计
14.1.万能通用权限框架设计
(1)kingadmin/permission_list.py
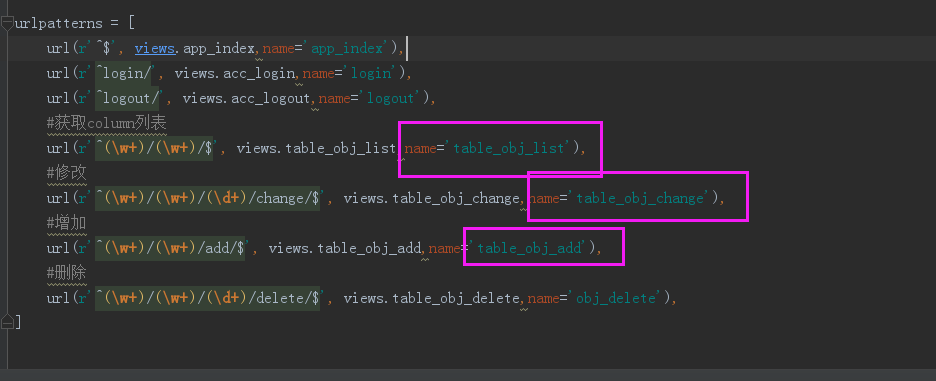
所有权限列表
# kingamdin/permission.py perm_dic = { # 'crm_table_index': ['table_index', 'GET', [], {}, ], # 可以查看CRM APP里所有数据库表 'crm_table_list': ['table_obj_list', 'GET', [], {}], # 可以查看每张表里所有的数据 # 'crm_table_list': ['table_obj_list', 'GET', [], {'source':0,'status':0}], # 添加参数:只能访问来源是qq和未报名的客户 'crm_table_list_view': ['table_obj_change', 'GET', [], {}], # 可以访问表里每条数据的修改页 'crm_table_list_change': ['table_obj_change', 'POST', [], {}], # 可以对表里的每条数据进行修改 'crm_table_list_add_view': ['table_obj_add ', 'GET', [], {}], # 可以访问数据增加页 'crm_table_list_add': ['table_obj_add ', 'POST', [], {}], # 可以添加表数据 }
value[0]跟kingadmin/url.py里面的url_name一致
(2)kingadmin/permissions
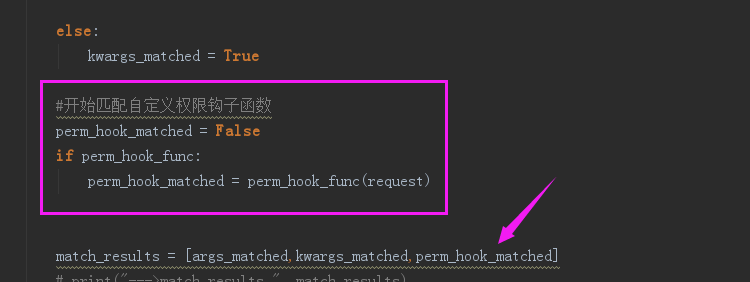
# kingadmin/permissions.py # from django.core.urlresolvers import resolve from django.urls import resolve from django.shortcuts import render,redirect,HttpResponse from kingadmin.permission_list import perm_dic from django.conf import settings def perm_check(*args,**kwargs): #1.获取当前请求的url #2.把url解析成url_name(通过resolve) #3.判断用户是否已登录(user.is_authenticated()) #3.拿url_name到permission_dict去匹配,匹配时要包括请求方法和参数 #4.拿匹配到可权限key,调用user.has_perm(key) match_results = [None,] request = args[0] resolve_url_obj = resolve(request.path) #通过resolve解析出当前访问的url_name current_url_name = resolve_url_obj.url_name print('---perm:',request.user,request.user.is_authenticated(),current_url_name) #match_flag = False match_key = None #判断用户是否登录 if request.user.is_authenticated() is False: return redirect(settings.LOGIN_URL) for permission_key,permission_val in perm_dic.items(): #key和value(值有四个参数): 比如 'crm_table_index': ['table_index', 'GET', [], {}, ] per_url_name = permission_val[0] per_method = permission_val[1] perm_args = permission_val[2] perm_kwargs = permission_val[3] #如果当前访问的url_name匹配上了权限里面定义的url_name if per_url_name == current_url_name: #url_name匹配上,接着匹配方法(post,get....) if per_method == request.method: # if not perm_args: #if no args defined in perm dic, then set this request to passed perm #逐个匹配参数,看每个参数是否都能对应的上。 args_matched = False #for args only for item in perm_args: #通过反射获取到request.xxx函数 这里request_methon_func = request.GET/request.POST request_method_func = getattr(request,per_method) if request_method_func.get(item,None): # request字典中有此参数 args_matched = True else: print("arg not match......") args_matched = False break # 有一个参数不能匹配成功,则判定为假,退出该循环。因为可能有很多参数,必须所有参数都一样才匹配成功 else: # perm_dic里面的参数可能定义的就是空的,就走这里 args_matched = True #匹配有特定值的参数 kwargs_matched = False for k,v in perm_kwargs.items(): request_method_func = getattr(request, per_method) arg_val = request_method_func.get(k, None) # request字典中有此参数 print("perm kwargs check:",arg_val,type(arg_val),v,type(v)) if arg_val == str(v): #匹配上了特定的参数 及对应的 参数值, 比如,需要request 对象里必须有一个叫 user_id=3的参数 kwargs_matched = True else: kwargs_matched = False break # 有一个参数不能匹配成功,则判定为假,退出该循环。 else: kwargs_matched = True match_results = [args_matched,kwargs_matched] print("--->match_results ", match_results) #列表里面的元素都为真 if all(match_results): #都匹配上了 match_key = permission_key break if all(match_results): #主要是获取到app_name app_name, *per_name = match_key.split('_') print("--->matched ",match_results,match_key) print(app_name, *per_name) #per_obj = 例如:crm.crm_obj_list perm_obj = '%s.%s' % (app_name,match_key) print("perm str:",perm_obj) if request.user.has_perm(perm_obj): print('当前用户有此权限') return True else: print('当前用户没有该权限') return False else: print("未匹配到权限项,当前用户无权限") def check_permission(func): def inner(*args,**kwargs): if not perm_check(*args,**kwargs): request = args[0] return render(request,'kingadmin/page_403.html') return func(*args,**kwargs) return inner
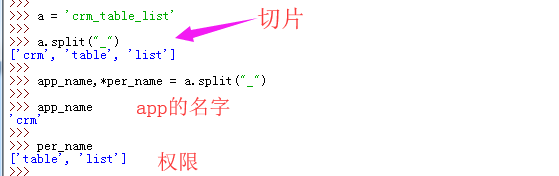
获取到表的名字的时候用到了 *per_name和split,具体用法解释:

(3)page_403.html
{#kingadmin/templates/kingamdin/page_403.html#} {% extends 'kingadmin/base.html' %} {% block body %} <div class="row col-lg-offset-2"> <h1 style="font-size: 200px;">403</h1> <h4>You have no permission to access this page</h4> </div> {% endblock %}
(4)crm/models.py
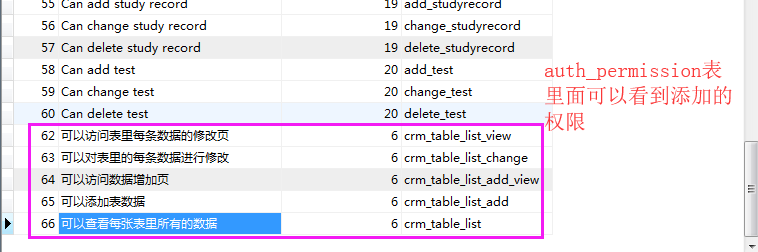
Meta里面加入权限
class UserProfile(AbstractBaseUser,PermissionsMixin): email = models.EmailField( verbose_name='email address', max_length=255, unique=True, ) name = models.CharField(max_length=64) role = models.ManyToManyField(Role, blank=True, null=True) is_active = models.BooleanField(default=True) is_admin = models.BooleanField(default=False) is_staff = models.BooleanField(default=True) #创建用户和超级用户,关联上面的 objects = UserProfileManager() USERNAME_FIELD = 'email' #必须要有的字段 REQUIRED_FIELDS = ['name'] def __str__(self): return self.email # def has_perm(self, perm, obj=None): # "Does the user have a specific permission?" # # Simplest possible answer: Yes, always # return True # # def has_module_perms(self, app_label): # "Does the user have permissions to view the app `app_label`?" # # Simplest possible answer: Yes, always # return True def get_full_name(self): # The user is identified by their email address return self.email def get_short_name(self): # The user is identified by their email address return self.email # @property # def is_staff(self): # "Is the user a member of staff?" # # Simplest possible answer: All admins are staff # return self.is_admin class Meta: permissions = ( ('crm_table_list','可以查看每张表里所有的数据'), ('crm_table_list_view','可以访问表里每条数据的修改页'), ('crm_table_list_change','可以对表里的每条数据进行修改'), ('crm_table_list_add_view','可以访问数据增加页'), ('crm_table_list_add','可以添加表数据'), )

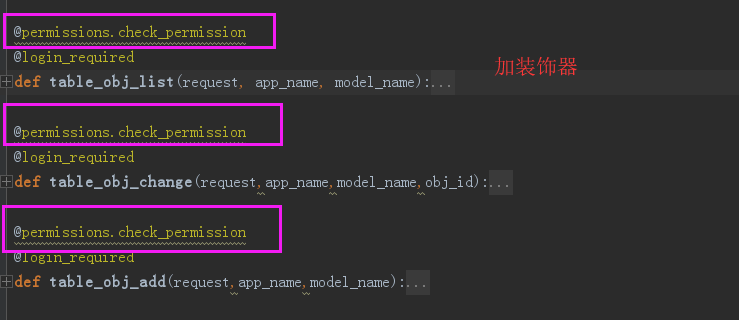
(5)kingadmin/views.py加装饰器
(6)admin后台管理权限
现在访问客户列表(还有增加修改页面)是没有权限的
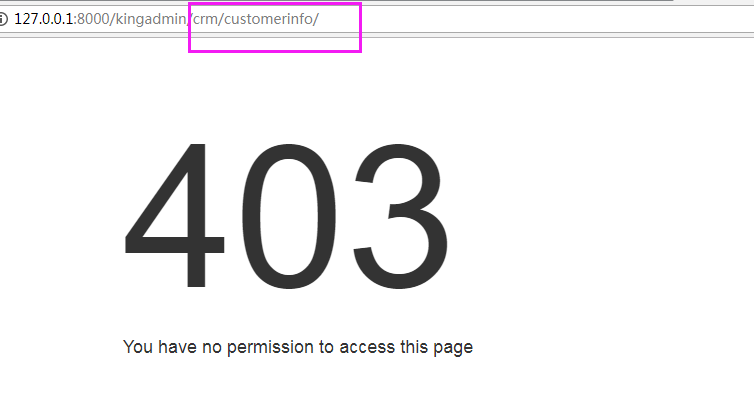
必须在后台赋予权限才可以

再访问就可以了

14.2.自定义权限钩子实现
只允许用户访问自己创建的数据,比如只允许销售访问自己创建的客户:
(1)kingadmin/permission_list.py
'crm_table_list': ['table_obj_list', 'GET', [], {},permission_hook.view_my_own_customers],
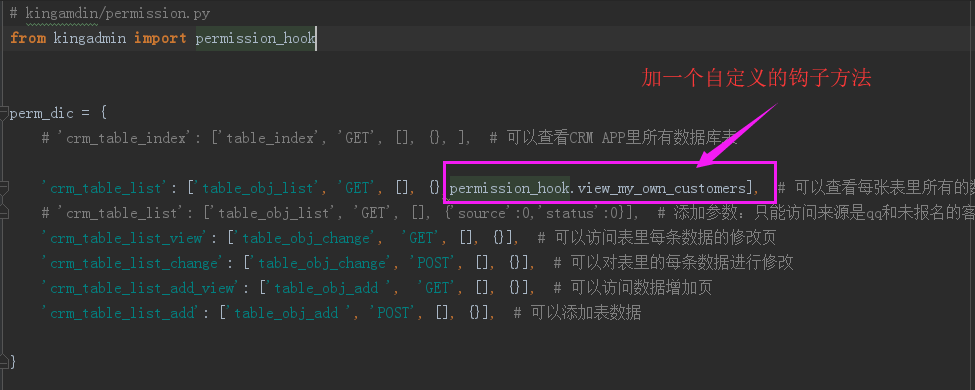
(2)kingadmin/permission_hook.py
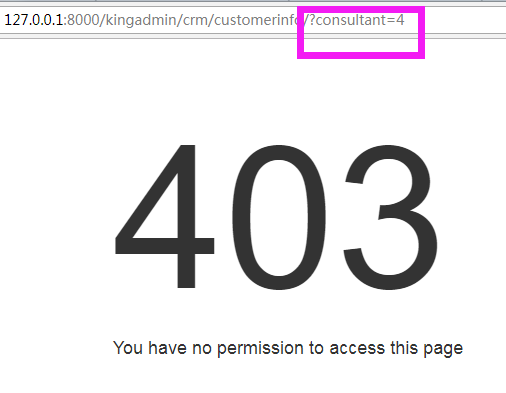
# kingadmin/permission_hook.py def view_my_own_customers(request): #当前登录的用户id 等于客户的顾问的id(销售创建客户的时候,顾问就是销售自己) #实现销售只能看自己的客户功能 if str(request.user.id) == request.GET.get('consultant'): return True else: return False
(3)kingadmin/permissions.py
现在销售就只能看到自己创建的客户了

这样,万通通用的权限框架就开发完毕了,权限的控制可大可小,而且想要移植到其它django项目时, 唯一需要改的,就是配置好perm_dic里的权限条目!