深度优先搜索(DFS:Depth-First Search)是一种图搜索策略,其将搜索限制到 2 种操作:
- (a) 访问图中的一个节点;
- (b) 访问该节点的子节点;
在深度优先搜索中,对于最新发现的顶点,如果它还有以此为起点而未探测到的边,就沿此边继续探测下去。当顶点 v 的所有边都已被探寻过后,搜索将回溯到发现顶点 v 有起始点的那些边。这一过程一直进行到已发现从源顶点可达的所有顶点为止。实际上深度优先搜索最初的探究也是为了解决迷宫问题。
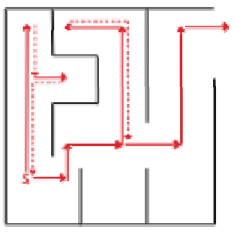
对图的深度优先搜索与对树(Tree)的深度优先遍历(Depth First Traversal)是类似的,区别在于图中可能存在环,所以可能会遍历到已经遍历的节点。
例如,下面的图中,从顶点 2 开始遍历,当遍历到顶点 0 时,子顶点为 1 和 2,而顶点 2 已经遍历过,如果不做标记,遍历过程将陷入死循环。所以,在 DFS 的算法实现中需要对顶点是否访问过做标记。
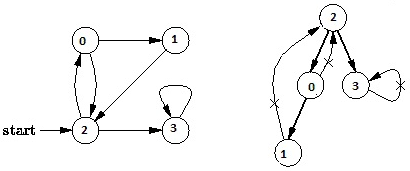
上图的 DFS 遍历结果为 2, 0, 1, 3。
DFS 算法可以通过不同方式来实现:
- 递归方式
- 非递归方式:使用栈(Stack)数据结构来存储遍历图中节点的中间状态;
DFS 算法的递归方式伪码如下:
1 procedure DFS(G,v): 2 label v as discovered 3 for all edges from v to w in G.adjacentEdges(v) do 4 if vertex w is not labeled as discovered then 5 recursively call DFS(G,w)
DFS 算法的非递归方式伪码如下:
1 procedure DFS-iterative(G,v): 2 let S be a stack 3 S.push(v) 4 while S is not empty 5 v ← S.pop() 6 if v is not labeled as discovered: 7 label v as discovered 8 for all edges from v to w in G.adjacentEdges(v) do 9 S.push(w)
深度优先搜索(DFS)的时间复杂度为 O(V+E),V 即 Vertex 顶点数量,E 即 Edge 边数量。
DFS 算法实现代码如下:
1 using System; 2 using System.Linq; 3 using System.Collections.Generic; 4 5 namespace GraphAlgorithmTesting 6 { 7 class Program 8 { 9 static void Main(string[] args) 10 { 11 Graph g = new Graph(4); 12 g.AddEdge(0, 1); 13 g.AddEdge(0, 2); 14 g.AddEdge(1, 2); 15 g.AddEdge(2, 0); 16 g.AddEdge(2, 3); 17 g.AddEdge(3, 3); 18 19 foreach (var vertex in g.DFS(2)) 20 { 21 Console.WriteLine(vertex); 22 } 23 foreach (var vertex in g.RecursiveDFS(2)) 24 { 25 Console.WriteLine(vertex); 26 } 27 28 Console.ReadKey(); 29 } 30 31 class Edge 32 { 33 public Edge(int begin, int end) 34 { 35 this.Begin = begin; 36 this.End = end; 37 } 38 39 public int Begin { get; private set; } 40 public int End { get; private set; } 41 } 42 43 class Graph 44 { 45 private Dictionary<int, List<Edge>> _adjacentEdges 46 = new Dictionary<int, List<Edge>>(); 47 48 public Graph(int vertexCount) 49 { 50 this.VertexCount = vertexCount; 51 } 52 53 public int VertexCount { get; private set; } 54 55 public void AddEdge(int begin, int end) 56 { 57 if (!_adjacentEdges.ContainsKey(begin)) 58 { 59 var edges = new List<Edge>(); 60 _adjacentEdges.Add(begin, edges); 61 } 62 63 _adjacentEdges[begin].Add(new Edge(begin, end)); 64 } 65 66 public List<int> DFS(int start) 67 { 68 List<int> traversal = new List<int>(); 69 int current = start; 70 71 // mark all the vertices as not visited 72 bool[] visited = new bool[VertexCount]; 73 for (int i = 0; i < VertexCount; i++) 74 { 75 visited[i] = false; 76 } 77 78 // create a stack for DFS 79 Stack<int> stack = new Stack<int>(); 80 81 // mark the current node as visited and push it 82 visited[current] = true; 83 stack.Push(current); 84 85 while (stack.Count > 0) 86 { 87 current = stack.Pop(); 88 89 // if this is what we are looking for 90 traversal.Add(current); 91 92 // get all child vertices of the popped vertex, 93 // if a child has not been visited, 94 // then mark it visited and push it 95 if (_adjacentEdges.ContainsKey(current)) 96 { 97 foreach (var edge in _adjacentEdges[current].OrderByDescending(e => e.End)) 98 { 99 if (!visited[edge.End]) 100 { 101 visited[edge.End] = true; 102 stack.Push(edge.End); 103 } 104 } 105 } 106 } 107 108 return traversal; 109 } 110 111 public List<int> RecursiveDFS(int start) 112 { 113 List<int> traversal = new List<int>(); 114 int current = start; 115 116 // mark all the vertices as not visited 117 bool[] visited = new bool[VertexCount]; 118 for (int i = 0; i < VertexCount; i++) 119 { 120 visited[i] = false; 121 } 122 123 // traversal 124 RecursiveDFSTraversal(current, visited, traversal); 125 126 return traversal; 127 } 128 129 private void RecursiveDFSTraversal(int current, bool[] visited, List<int> traversal) 130 { 131 visited[current] = true; 132 traversal.Add(current); 133 134 if (_adjacentEdges.ContainsKey(current)) 135 { 136 foreach (var edge in _adjacentEdges[current].OrderBy(e => e.End)) 137 { 138 if (!visited[edge.End]) 139 { 140 RecursiveDFSTraversal(edge.End, visited, traversal); 141 } 142 } 143 } 144 } 145 } 146 } 147 }
参考资料
- 广度优先搜索
- 深度优先搜索
- Breadth First Traversal for a Graph
- Depth First Traversal for a Graph
- 深度优先搜索 广度优先搜索类训练题
- Introduction to Algorithms 6.006 - Lecture 13
- 深度优先搜索 DFS
- 算法与数据结构
本篇文章《深度优先搜索》由 Dennis Gao 发表自博客园,未经作者本人同意禁止任何形式的转载,任何自动或人为的爬虫转载行为均为耍流氓。