Prim 算法是一种解决最小生成树问题(Minimum Spanning Tree)的算法。和 Kruskal 算法类似,Prim 算法的设计也是基于贪心算法(Greedy algorithm)。
Prim 算法的思想很简单,一棵生成树必须连接所有的顶点,而要保持最小权重则每次选择邻接的边时要选择较小权重的边。Prim 算法看起来非常类似于单源最短路径 Dijkstra 算法,从源点出发,寻找当前的最短路径,每次比较当前可达邻接顶点中最小的一个边加入到生成树中。
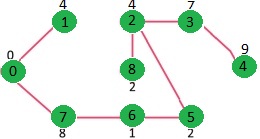
例如,下面这张连通的无向图 G,包含 9 个顶点和 14 条边,所以期待的最小生成树应包含 (9 - 1) = 8 条边。
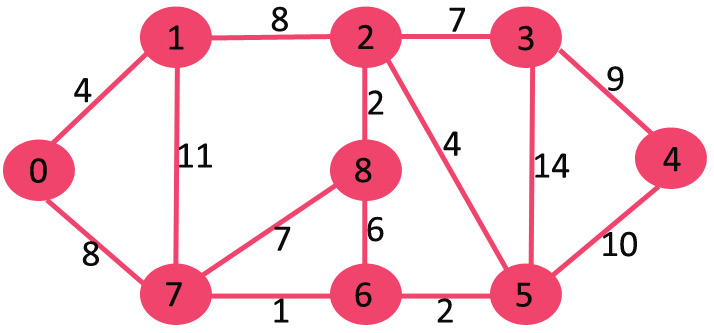
创建 mstSet 包含到所有顶点的距离,初始为 INF,源点 0 的距离为 0,{0, INF, INF, INF, INF, INF, INF, INF, INF}。
选择当前最短距离的顶点,即还是顶点 0,将 0 加入 MST,此时邻接顶点为 1 和 7。
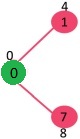
选择当前最小距离的顶点 1,将 1 加入 MST,此时邻接顶点为 2。

选择 2 和 7 中最小距离的顶点为 7,将 7 加入 MST,此时邻接顶点为 6 和 8。
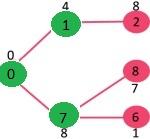
选择 2, 6, 8 中最小距离的顶点为 6,将 6 加入 MST,此时邻接顶点为 5。
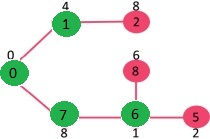
重复上面步骤直到遍历完所有顶点为止,会得到如下 MST。
C# 实现 Prim 算法如下。Prim 算法可以达到 O(ElogV) 的运行时间,如果采用斐波那契堆实现,运行时间可以减少到 O(E + VlogV),如果 V 远小于 E 的话,将是对算法较大的改进。
1 using System; 2 using System.Collections.Generic; 3 using System.Linq; 4 5 namespace GraphAlgorithmTesting 6 { 7 class Program 8 { 9 static void Main(string[] args) 10 { 11 Graph g = new Graph(9); 12 g.AddEdge(0, 1, 4); 13 g.AddEdge(0, 7, 8); 14 g.AddEdge(1, 2, 8); 15 g.AddEdge(1, 7, 11); 16 g.AddEdge(2, 3, 7); 17 g.AddEdge(2, 5, 4); 18 g.AddEdge(3, 4, 9); 19 g.AddEdge(3, 5, 14); 20 g.AddEdge(5, 4, 10); 21 g.AddEdge(6, 5, 2); 22 g.AddEdge(7, 6, 1); 23 g.AddEdge(7, 8, 7); 24 g.AddEdge(8, 2, 2); 25 g.AddEdge(8, 6, 6); 26 27 // sorry, this is an undirect graph, 28 // so, you know that this is not a good idea. 29 List<Edge> edges = g.Edges 30 .Select(e => new Edge(e.End, e.Begin, e.Weight)) 31 .ToList(); 32 foreach (var edge in edges) 33 { 34 g.AddEdge(edge.Begin, edge.End, edge.Weight); 35 } 36 37 Console.WriteLine(); 38 Console.WriteLine("Graph Vertex Count : {0}", g.VertexCount); 39 Console.WriteLine("Graph Edge Count : {0}", g.EdgeCount); 40 Console.WriteLine(); 41 42 List<Edge> mst = g.Prim(); 43 Console.WriteLine("MST Edges:"); 44 foreach (var edge in mst.OrderBy(e => e.Weight)) 45 { 46 Console.WriteLine(" {0}", edge); 47 } 48 49 Console.ReadKey(); 50 } 51 52 class Edge 53 { 54 public Edge(int begin, int end, int weight) 55 { 56 this.Begin = begin; 57 this.End = end; 58 this.Weight = weight; 59 } 60 61 public int Begin { get; private set; } 62 public int End { get; private set; } 63 public int Weight { get; private set; } 64 65 public override string ToString() 66 { 67 return string.Format( 68 "Begin[{0}], End[{1}], Weight[{2}]", 69 Begin, End, Weight); 70 } 71 } 72 73 class Graph 74 { 75 private Dictionary<int, List<Edge>> _adjacentEdges 76 = new Dictionary<int, List<Edge>>(); 77 78 public Graph(int vertexCount) 79 { 80 this.VertexCount = vertexCount; 81 } 82 83 public int VertexCount { get; private set; } 84 85 public IEnumerable<int> Vertices { get { return _adjacentEdges.Keys; } } 86 87 public IEnumerable<Edge> Edges 88 { 89 get { return _adjacentEdges.Values.SelectMany(e => e); } 90 } 91 92 public int EdgeCount { get { return this.Edges.Count(); } } 93 94 public void AddEdge(int begin, int end, int weight) 95 { 96 if (!_adjacentEdges.ContainsKey(begin)) 97 { 98 var edges = new List<Edge>(); 99 _adjacentEdges.Add(begin, edges); 100 } 101 102 _adjacentEdges[begin].Add(new Edge(begin, end, weight)); 103 } 104 105 public List<Edge> Prim() 106 { 107 // Array to store constructed MST 108 int[] parent = new int[VertexCount]; 109 110 // Key values used to pick minimum weight edge in cut 111 int[] keySet = new int[VertexCount]; 112 113 // To represent set of vertices not yet included in MST 114 bool[] mstSet = new bool[VertexCount]; 115 116 // Initialize all keys as INFINITE 117 for (int i = 0; i < VertexCount; i++) 118 { 119 keySet[i] = int.MaxValue; 120 mstSet[i] = false; 121 } 122 123 // Always include first 1st vertex in MST. 124 // Make key 0 so that this vertex is picked as first vertex 125 keySet[0] = 0; 126 parent[0] = -1; // First node is always root of MST 127 128 // The MST will have V vertices 129 for (int i = 0; i < VertexCount - 1; i++) 130 { 131 // Pick thd minimum key vertex from the set of vertices 132 // not yet included in MST 133 int u = CalculateMinDistance(keySet, mstSet); 134 135 // Add the picked vertex to the MST Set 136 mstSet[u] = true; 137 138 // Update key value and parent index of the adjacent vertices of 139 // the picked vertex. Consider only those vertices which are not yet 140 // included in MST 141 for (int v = 0; v < VertexCount; v++) 142 { 143 // graph[u, v] is non zero only for adjacent vertices of m 144 // mstSet[v] is false for vertices not yet included in MST 145 // Update the key only if graph[u, v] is smaller than key[v] 146 if (!mstSet[v] 147 && _adjacentEdges.ContainsKey(u) 148 && _adjacentEdges[u].Exists(e => e.End == v)) 149 { 150 int d = _adjacentEdges[u].Single(e => e.End == v).Weight; 151 if (d < keySet[v]) 152 { 153 keySet[v] = d; 154 parent[v] = u; 155 } 156 } 157 } 158 } 159 160 // get all MST edges 161 List<Edge> mst = new List<Edge>(); 162 for (int i = 1; i < VertexCount; i++) 163 mst.Add(_adjacentEdges[parent[i]].Single(e => e.End == i)); 164 165 return mst; 166 } 167 168 private int CalculateMinDistance(int[] keySet, bool[] mstSet) 169 { 170 int minDistance = int.MaxValue; 171 int minDistanceIndex = -1; 172 173 for (int v = 0; v < VertexCount; v++) 174 { 175 if (!mstSet[v] && keySet[v] <= minDistance) 176 { 177 minDistance = keySet[v]; 178 minDistanceIndex = v; 179 } 180 } 181 182 return minDistanceIndex; 183 } 184 } 185 } 186 }
输出结果如下:

参考资料
- Connectivity in a directed graph
- Strongly Connected Components
- Tarjan's Algorithm to find Strongly Connected Components
本篇文章《Prim 最小生成树算法》由 Dennis Gao 发表自博客园,未经作者本人同意禁止任何形式的转载,任何自动或人为的爬虫转载行为均为耍流氓。